The document discusses linear regression as a key statistical and machine learning method for predictive modeling, focusing on curve fitting and least squares. It outlines the process of fitting a line to a dataset, using a training set of house prices and sizes, and minimizes errors through a cost function. Additionally, it addresses advanced topics like multiple linear regression and optimization methods such as gradient descent.





![Understanding the model and cost function
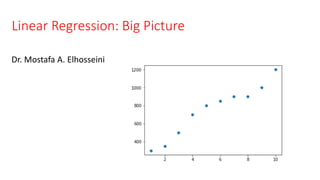
Ꚛ [Data] -- dataset that include house price and house size
Ꚛ [Training Set] -- After looking at and evaluating the data we extracted a
training set that gives us house sale prices vs house size in 𝑓𝑡2
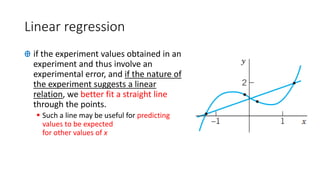
▪ Univariate linear regression
Ꚛ [Model function] -- Our model ("hypothesis" or "estimator" or
"predictor") will be a straight line "fit" to the training set".
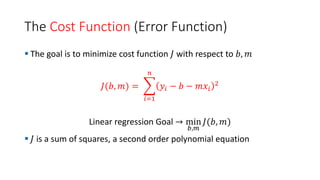
Ꚛ [Cost Function] -- Sum of squared errors that we will minimize with
respect to the model parameters.
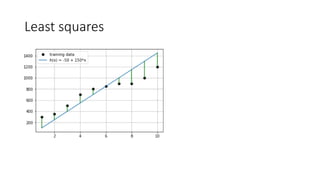
▪ The distance between the points and line are taken and each of them is squared to
get rid of negative values and then the values are summed which gives the error
which needs to be minimized – how to minimize error?
Ꚛ [Learning Algorithm] -- Linear "least squares" Regression](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6fqjirxzrc5qg1muscbw-signature-76fc122d20f6cfc2b2c81a71d8898f1eb9f4b751b18b68a890e47c810d98f207-poli-200304235202/85/Lecture-11-linear-regression-9-320.jpg)