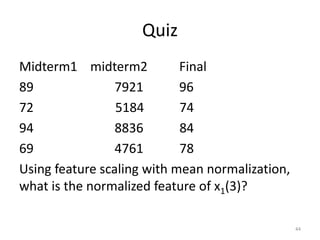
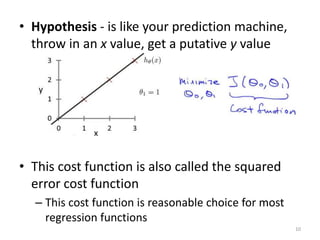
Linear regression is a supervised learning technique used to predict continuous valued outputs. It fits a linear equation to the training data to find the relationship between independent variables (x) and the dependent variable (y).
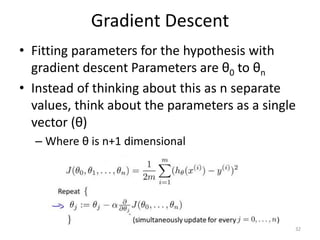
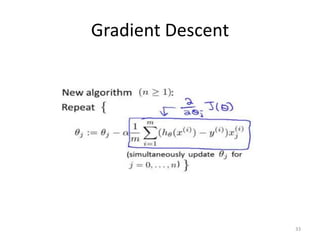
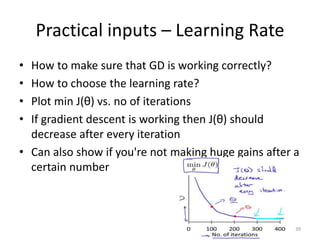
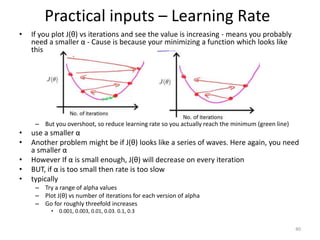
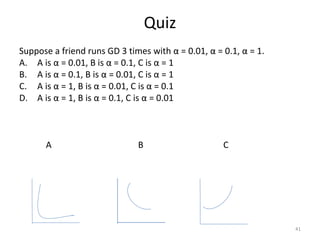
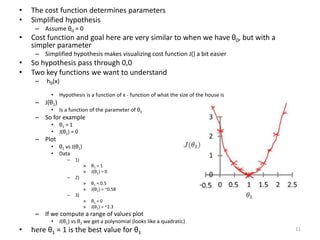
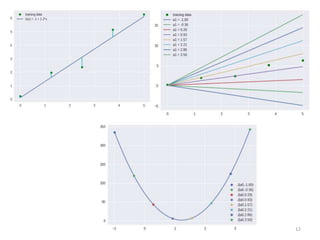
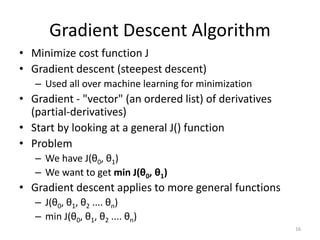
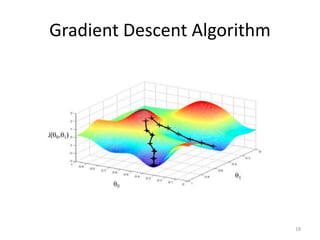
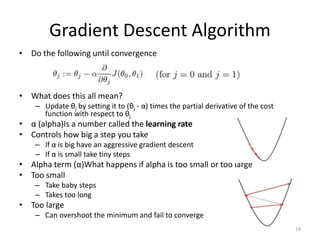
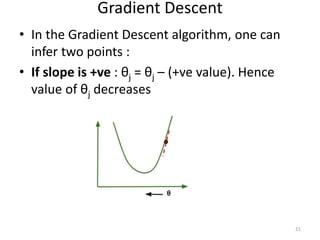
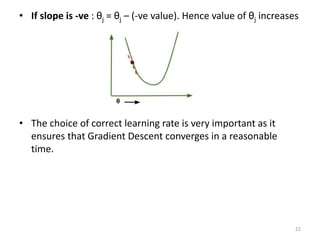
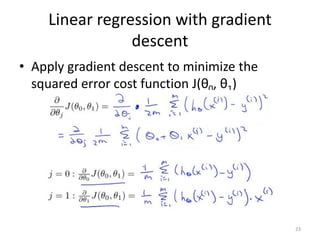
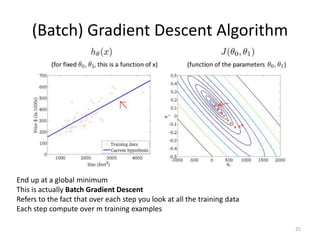
Gradient descent is an algorithm used to minimize the cost function in linear regression. It works by iteratively updating the parameters (θ values) in the direction of the steepest descent as calculated by the partial derivatives of the cost function with respect to each parameter. The learning rate (α) controls the step size in each iteration.
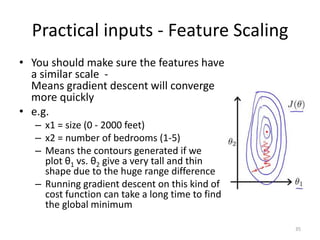
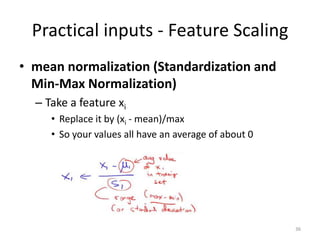
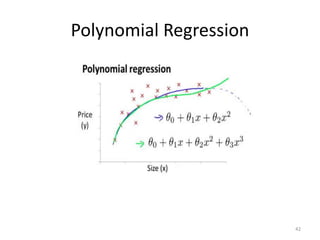
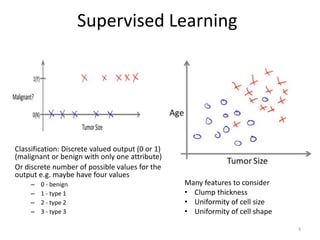
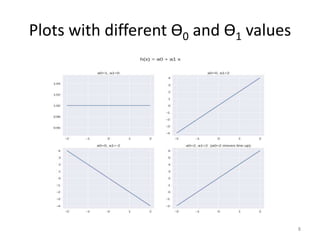
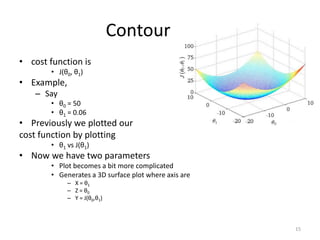
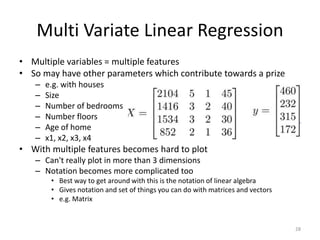
Multivariate linear regression extends the technique to problems with multiple independent variables by representing the hypothesis and parameters as vectors and matrices, allowing gradient descent to optimize the parameters to fit the linear model





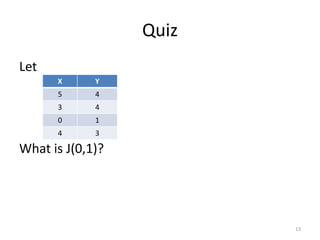







![Hypothesis
• If we do hθ(x) =θT X
– θT is an [1 x n+1] matrix
– In other words, because θ is a column vector, the transposition
operation transforms it into a row vector
– So before
• θ was a matrix [n + 1 x 1]
– Now
• θT is a matrix [1 x n+1]
– Which means the inner dimensions of θT and X match, so they
can be multiplied together as
• [1 x n+1] * [n+1 x 1]
• = hθ(x)
• So, in other words, the transpose of our parameter vector * an input
example X gives you a predicted hypothesis which is [1 x 1]
dimensions (i.e. a single value)
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearregression-240203090856-1ab2e64e/85/Linear-Regression-pptx-31-320.jpg)