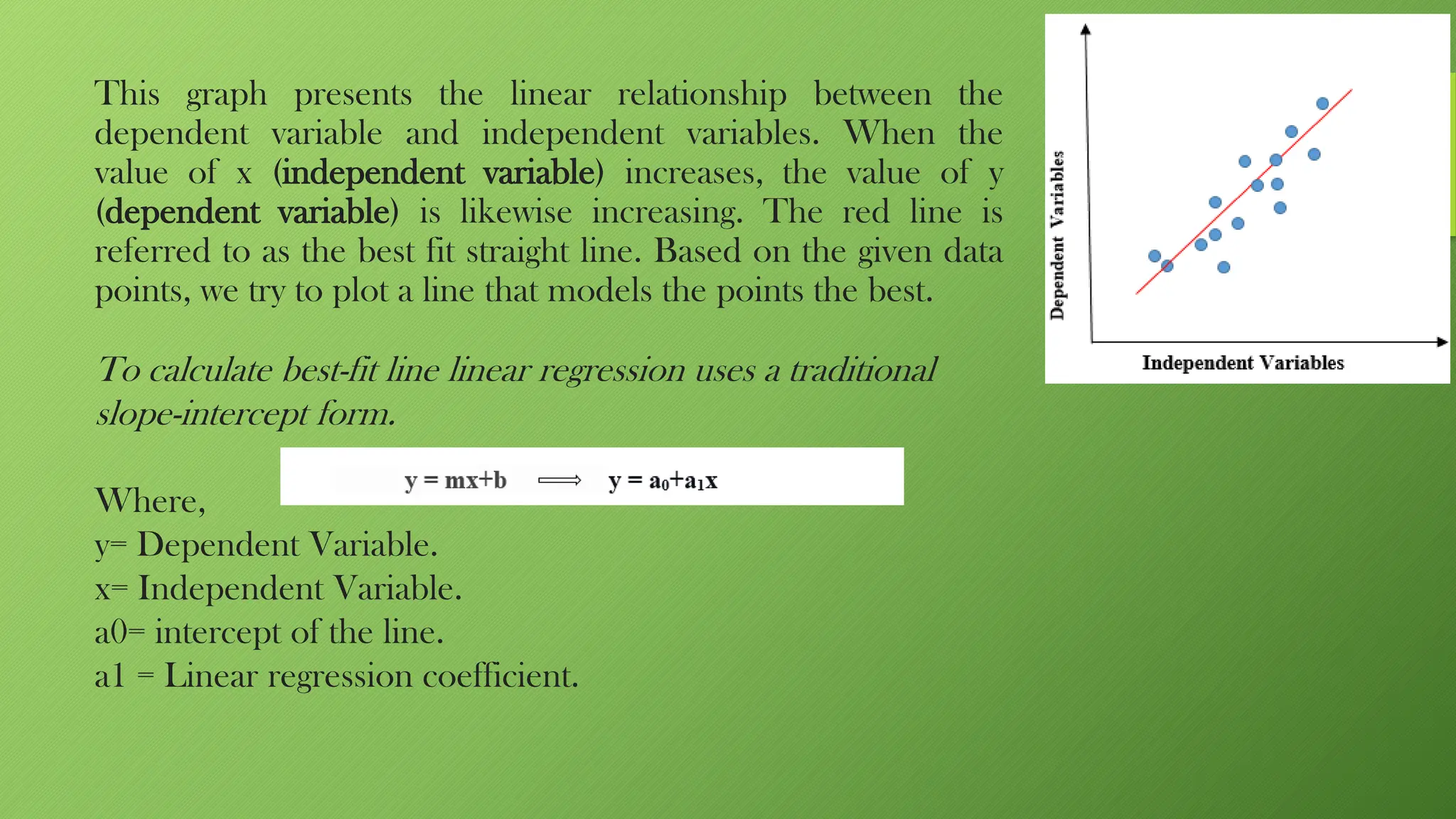
The document explains linear regression, a supervised machine learning algorithm used to predict continuous outcomes based on independent variables, such as predicting house prices from various factors. It covers key concepts, including types of regression (simple and multiple), the aim to minimize error between actual and predicted values, and essential assumptions for the model, such as linearity and independence. Additionally, it discusses optimization methods like gradient descent, evaluation metrics such as R-squared and root mean squared error, and the importance of achieving minimal error for accurate predictions.