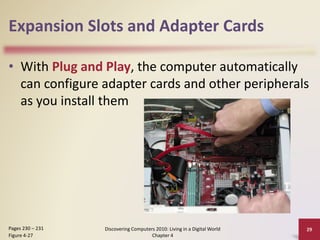
This document provides an overview and objectives for a lecture on computer hardware and components. It discusses the various parts inside a computer system unit including the motherboard, processor, memory, expansion slots, ports, buses, and power supply. The lecture describes how these components work together and interact to process data and run programs.