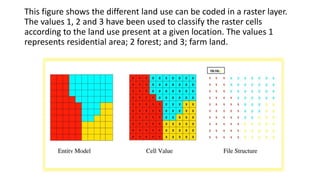
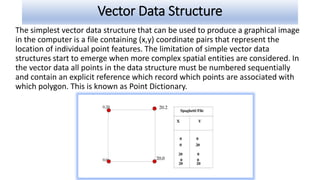
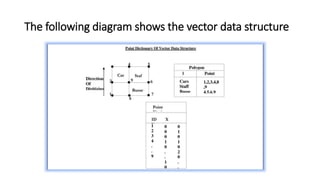
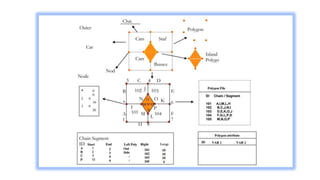
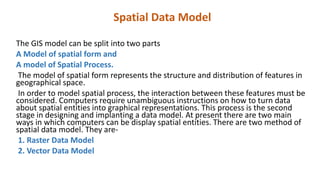
Spatial data can be represented using either a raster or vector data model. The raster model divides space into a grid of cells, with each cell storing an attribute value. The vector model represents features as points, lines, and polygons made up of x,y coordinates. Common spatial data structures include raster grids for storing raster data and point dictionaries and topological networks for vector data. The two models have different strengths, with raster better for overlays and modeling surfaces, and vector more accurate for features and cartography.




![The Vector Data Model:
A vector spatial data model uses two dimensional Cartesian [x, y] co-ordinates
to store the shape of spatial entity. In the vector spatial data can be
represented by using point. It is the basic building blocks from which all spatial
entities are constructed. The simplest spatial entity, the point is represented
by a single co-ordinate pair. Line and area entities are constructed by
connecting a series of points into chains and polygons. The more complex the
shape of a line or area feature the greater the number of points required
representing it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ashutoshjadhavgeoinformatics-231027132443-3c9e3e80/85/Geoinformatics-pptx-7-320.jpg)