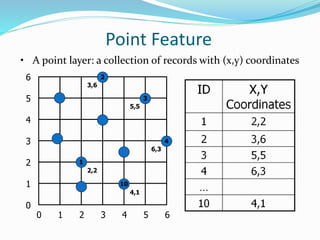
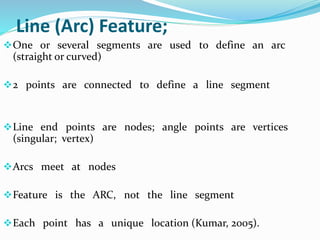
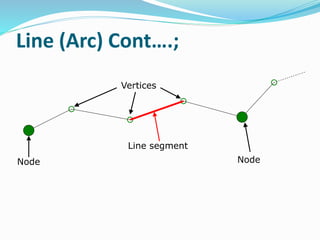
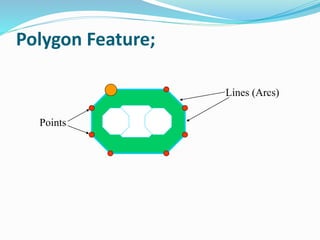
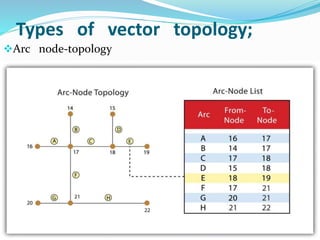
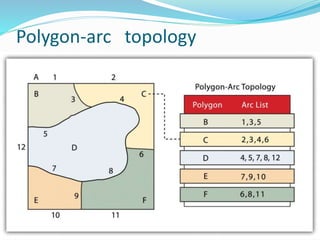
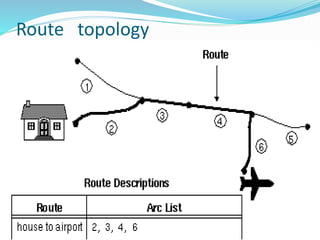
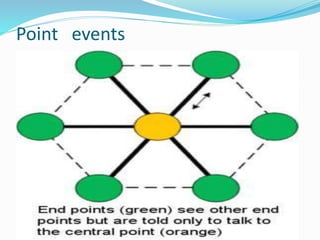
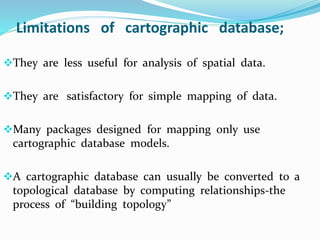
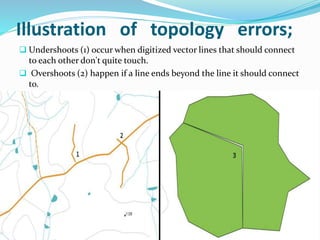
This document discusses vector GIS database structures. It explains that vector GIS represents the world using points, lines, and polygons. Vector models store discrete data like country borders and streets. Polygons are the basic unit and are created by connecting points with straight lines. Topology encodes spatial relationships between objects to accurately model real-world geometry. Topological rules govern connectivity and adjacency. Building topology involves calculating relationships between points, lines, and areas digitized in a GIS. Topological errors can occur if features do not perfectly connect. Vector databases are widely used in applications like transportation, utilities, and resource management.