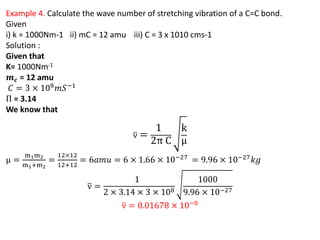
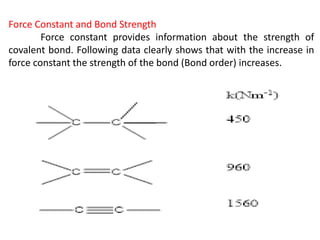
This document discusses the relationship between vibrational frequency and the force constant of a covalent bond. It states that for a diatomic molecule acting as a simple harmonic oscillator, the restoring force is proportional to displacement, as described by Hooke's Law. It then provides the equation relating vibrational frequency, force constant, and reduced mass. Several examples are given of calculating force constants from given vibrational frequencies and reduced masses. The document also notes that a higher force constant corresponds to a stronger covalent bond.