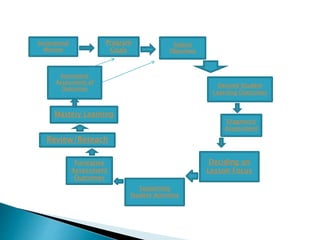
The document discusses various aspects of the research and writing process including: organizing information from secondary sources; developing logical arguments and integrating different perspectives; writing multi-page essays following standard formats; and assessing student learning through diagnostic, formative, and summative assessments. The goals are to help students improve their research, analytical, and writing skills through practicing various techniques.