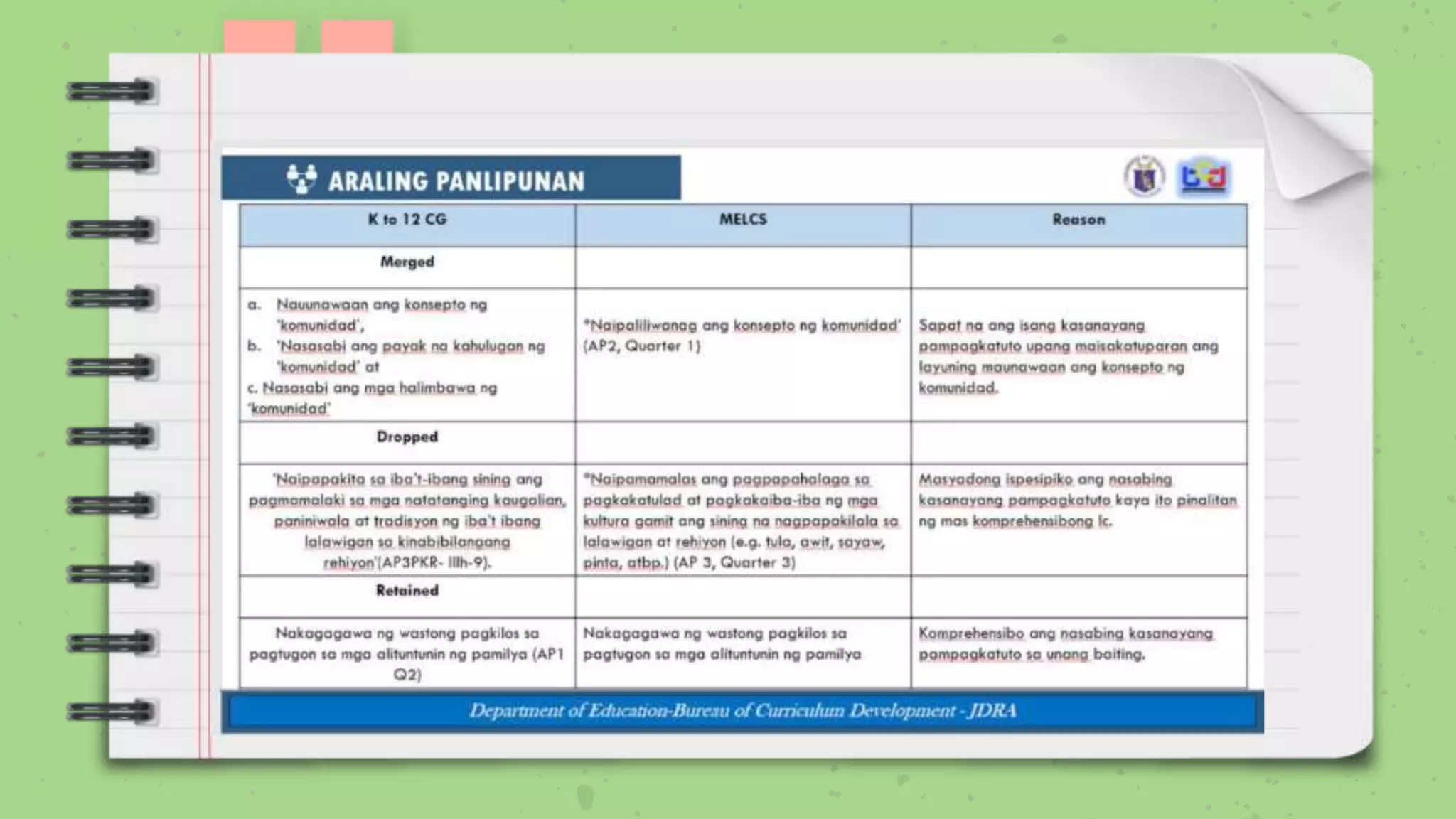
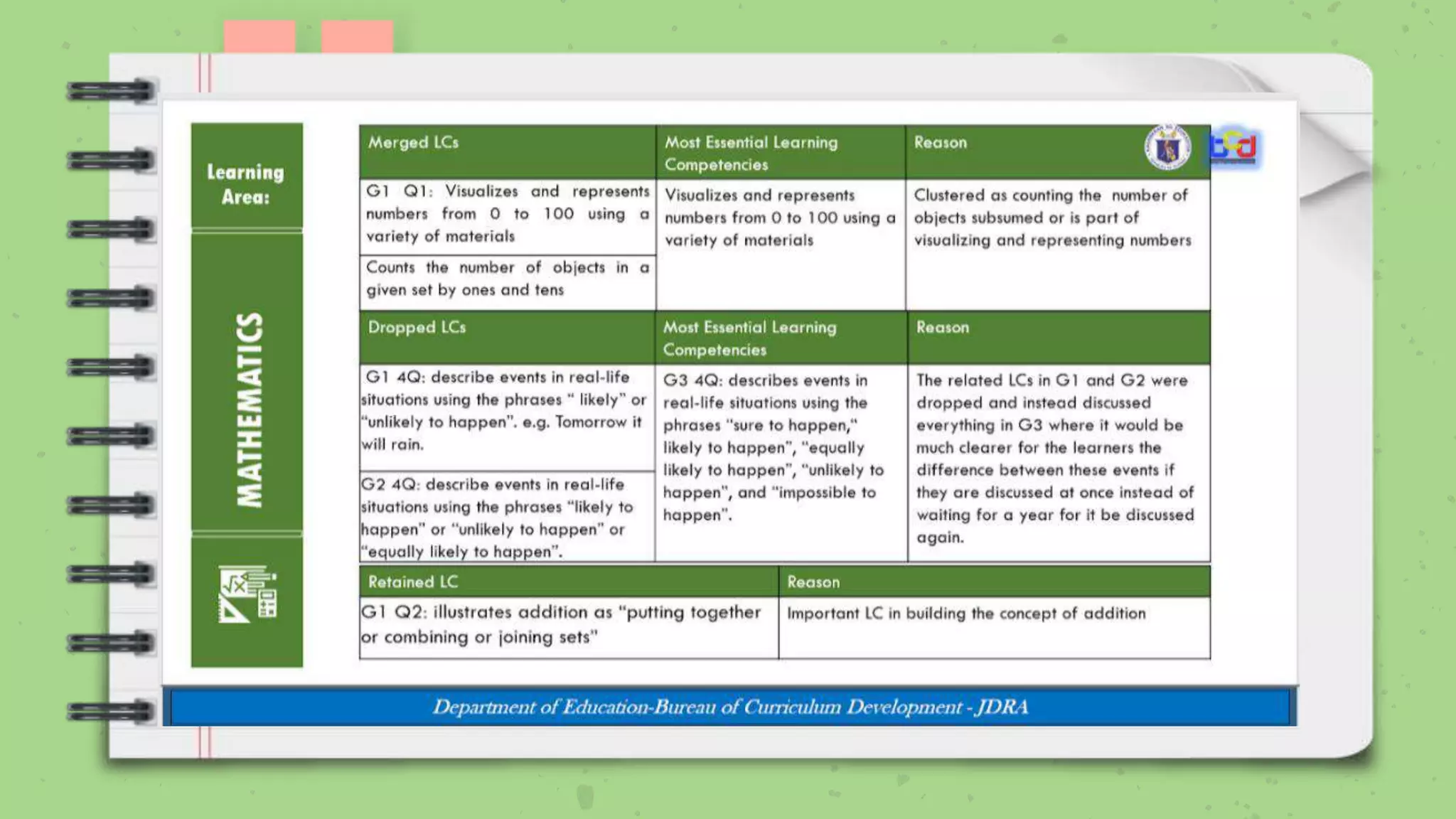
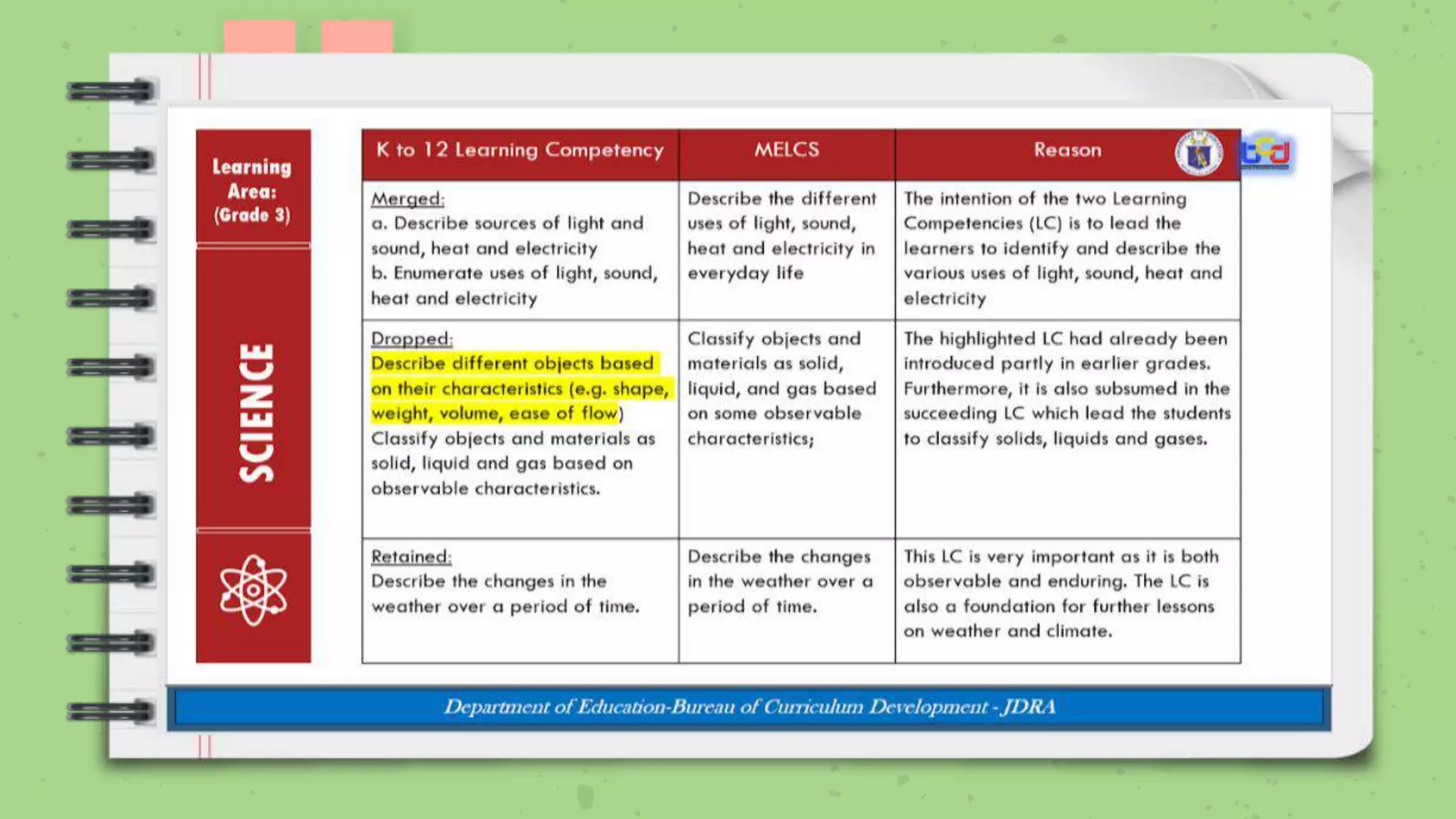
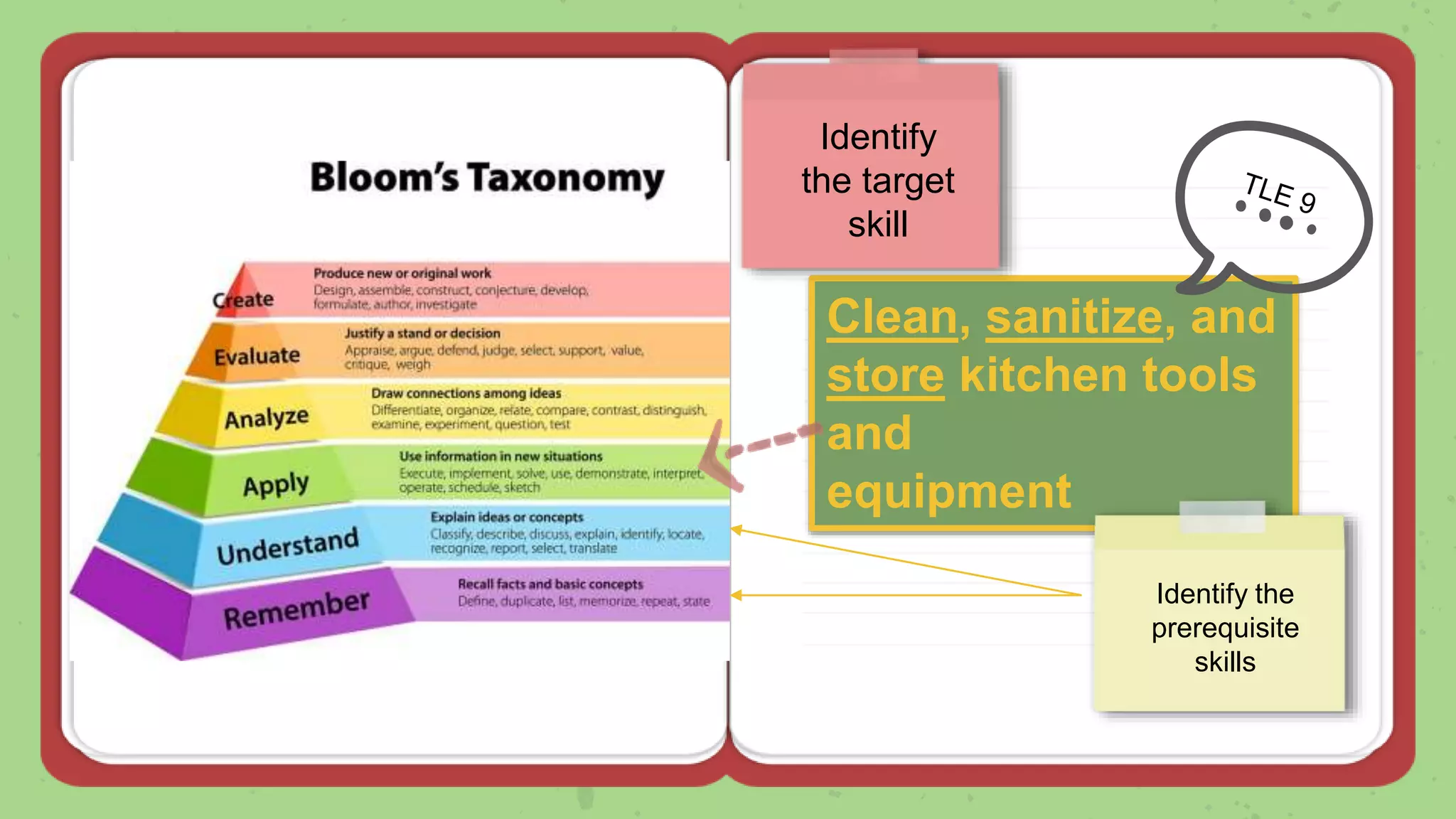
The document discusses the Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELCs) in the Philippines. It provides background on the development of the MELCs, including the rationale which was driven by the COVID-19 pandemic and the need to sustain education. Key aspects of the MELCs are that they identify essential and desirable competencies, and those that are enduring and help build lifelong learning skills. The document also provides guidance on unpacking and combining MELCs to develop clear learning objectives based on prerequisite skills and a logical sequence.