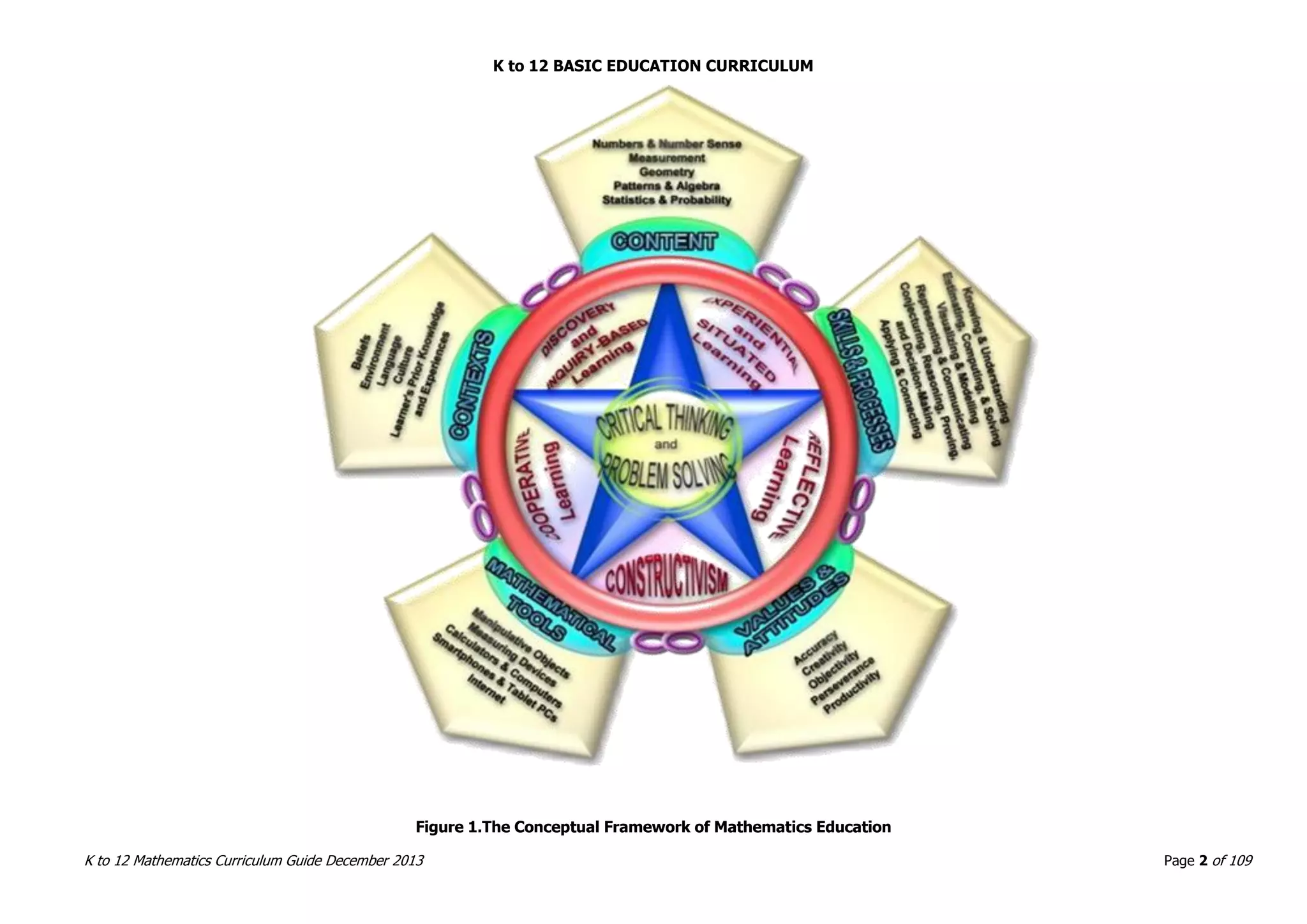
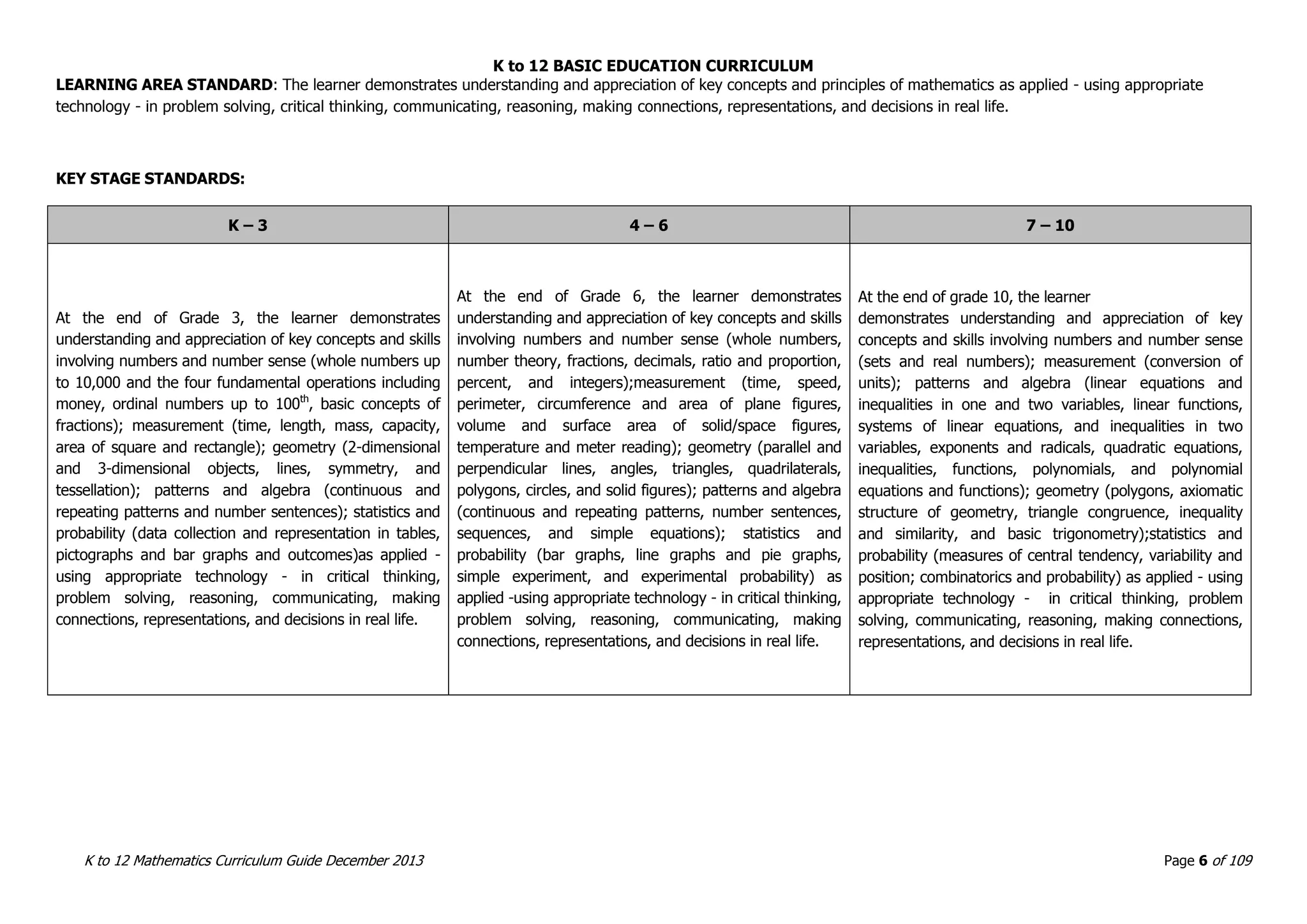
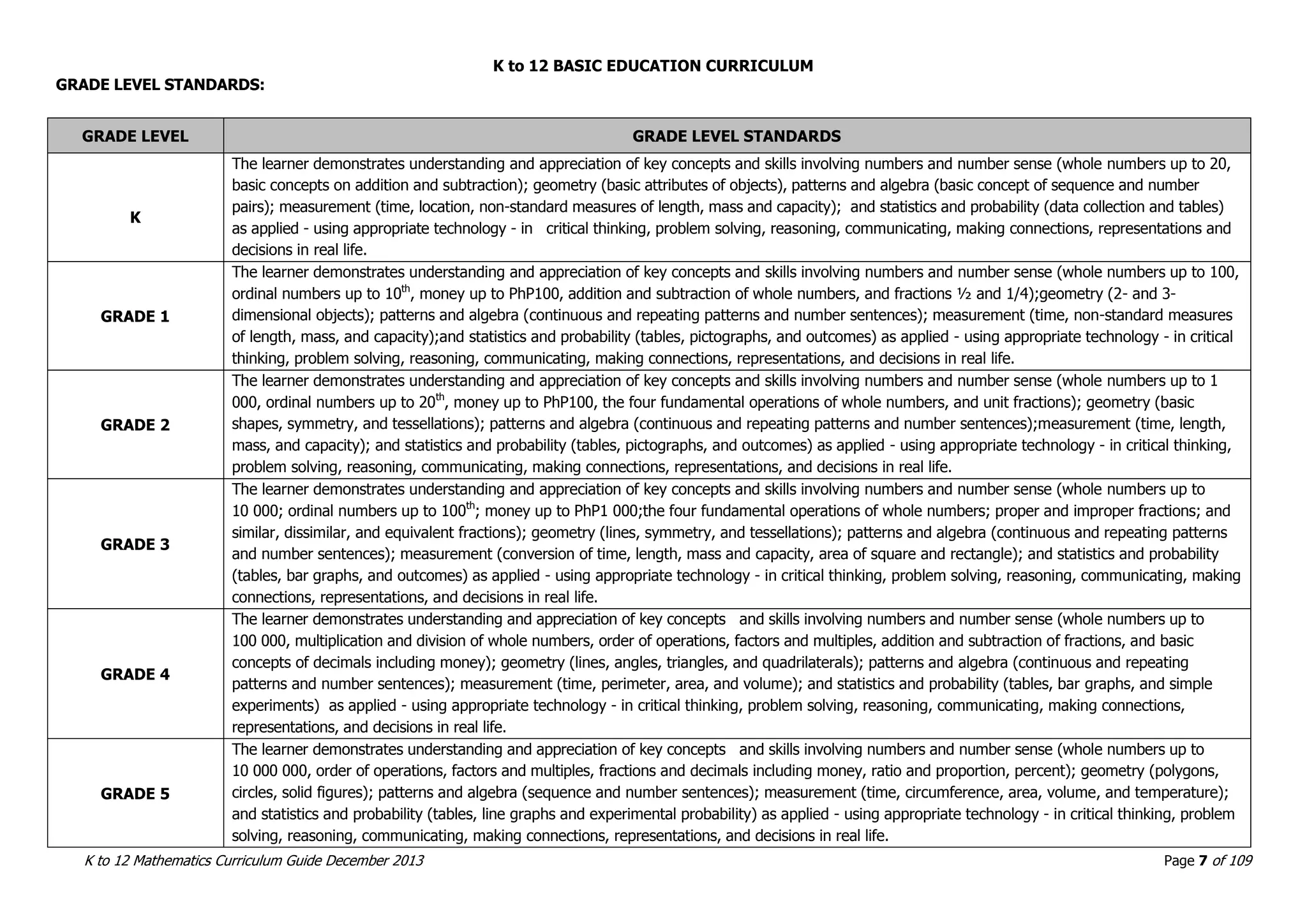
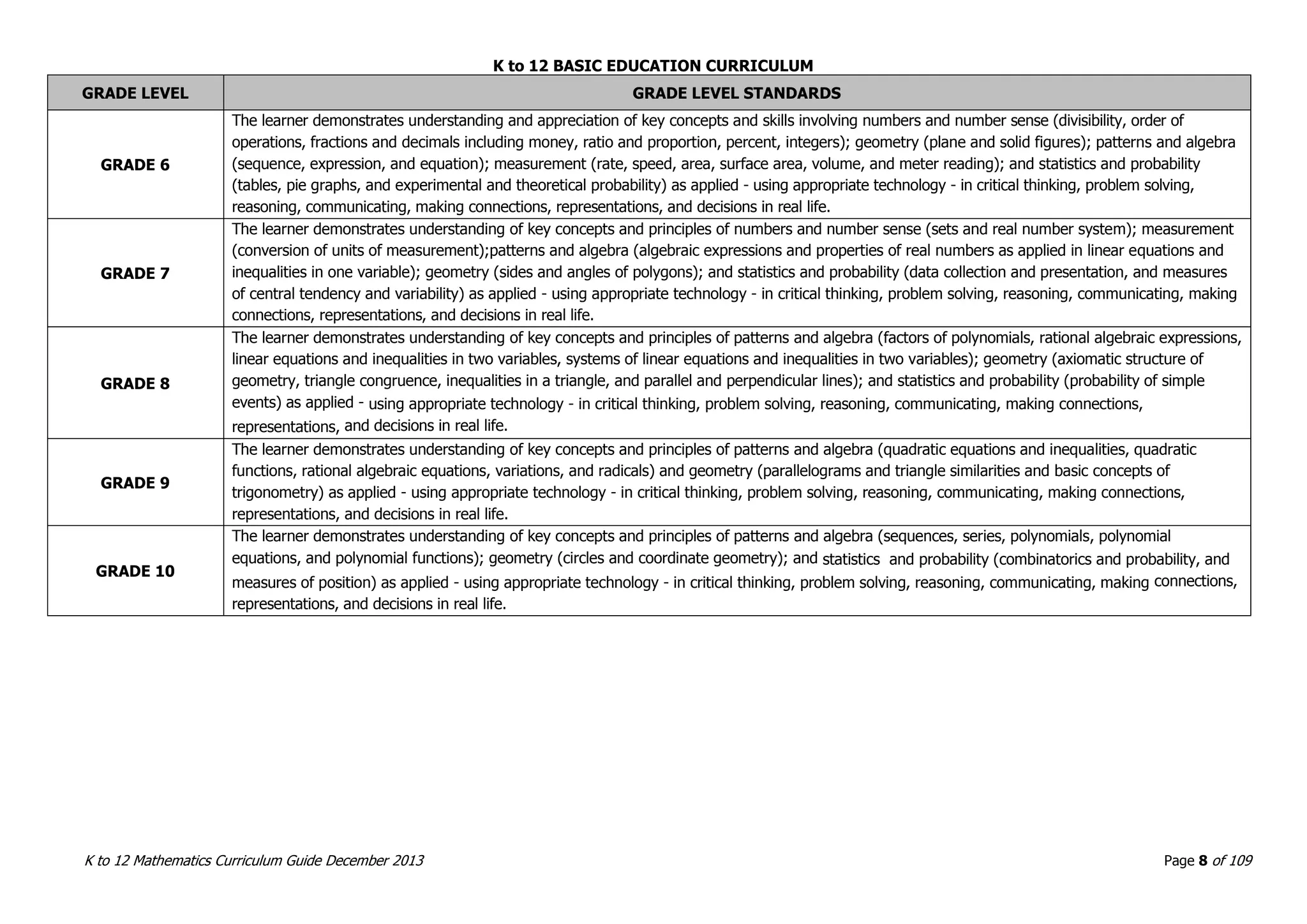
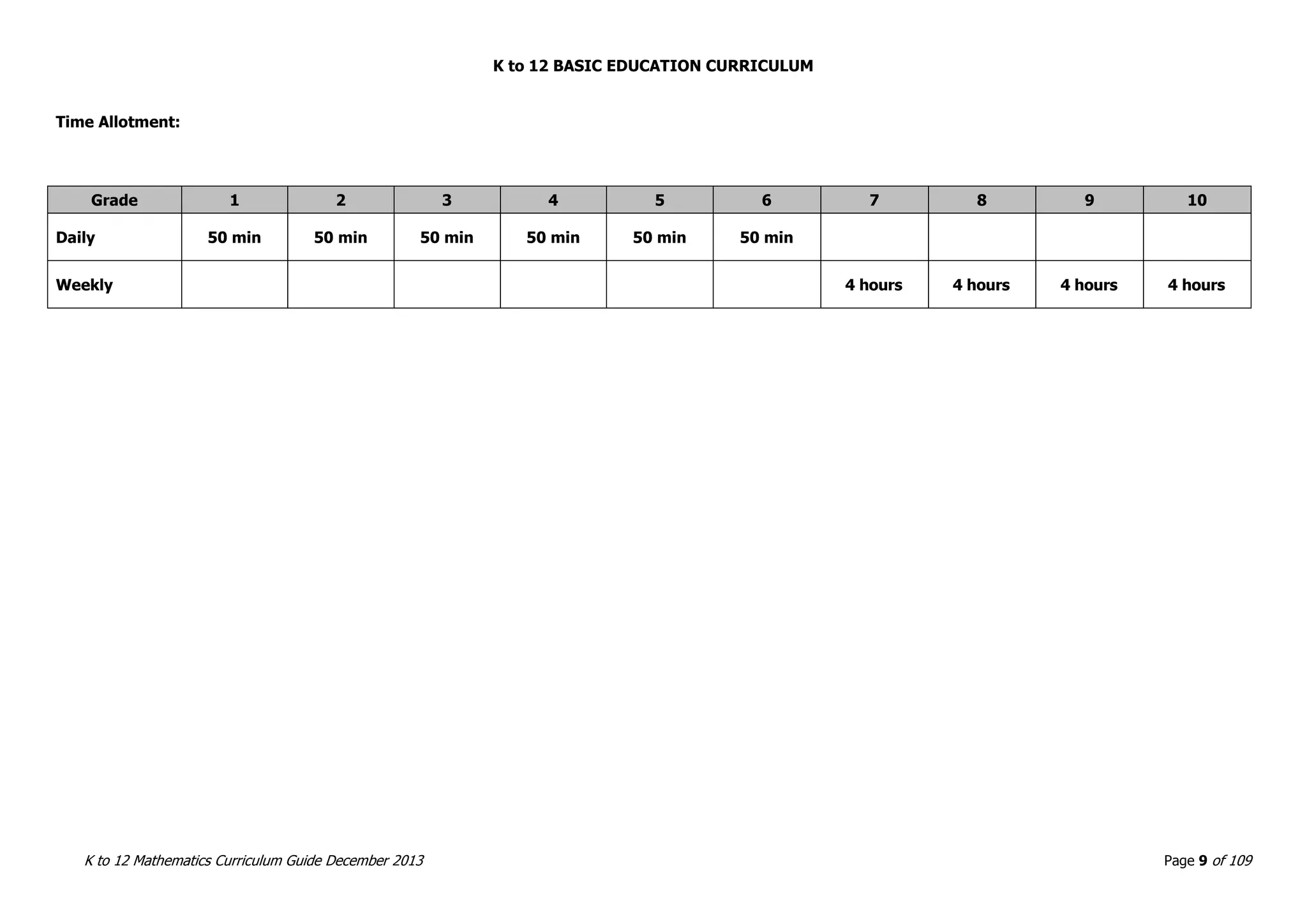
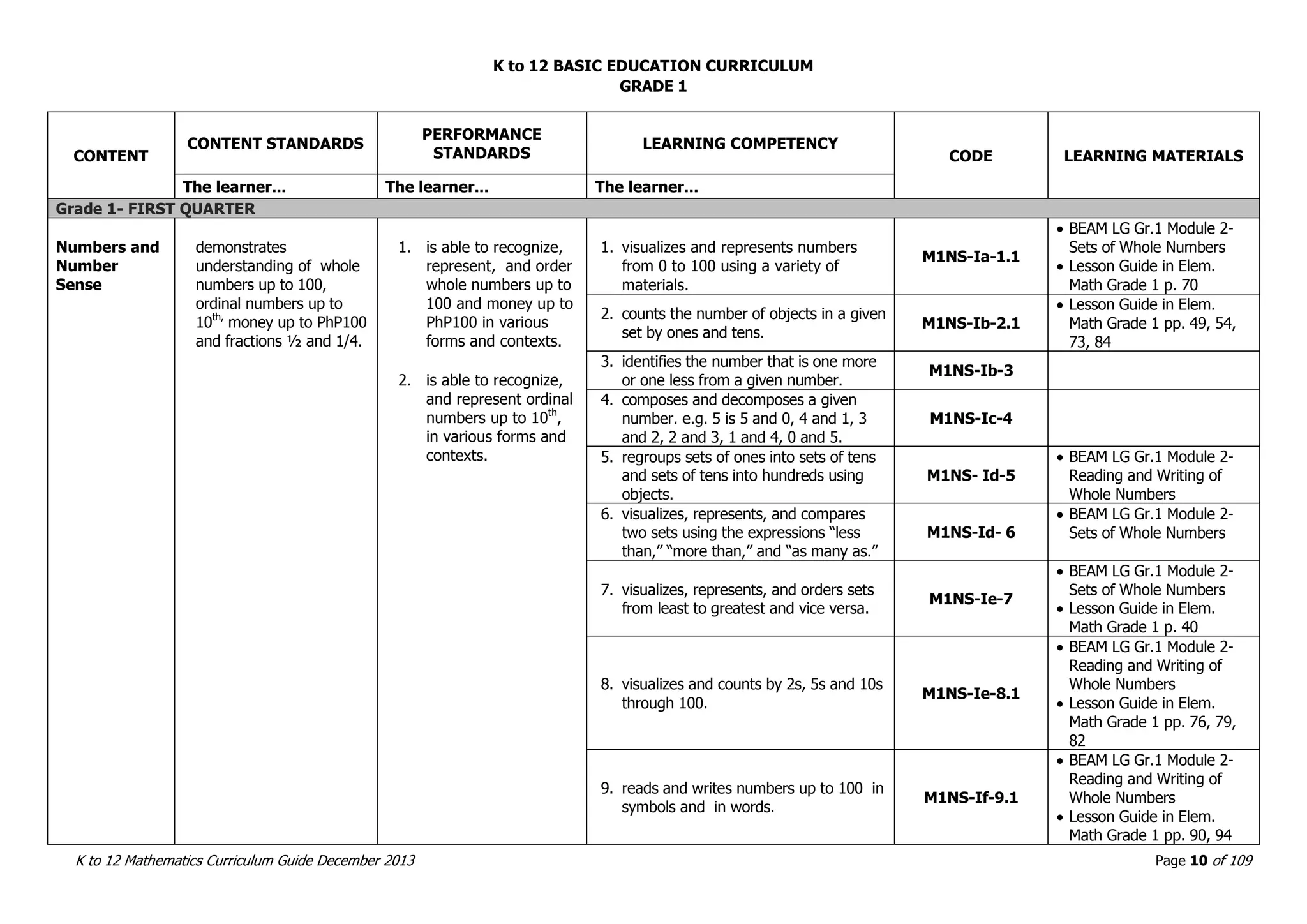
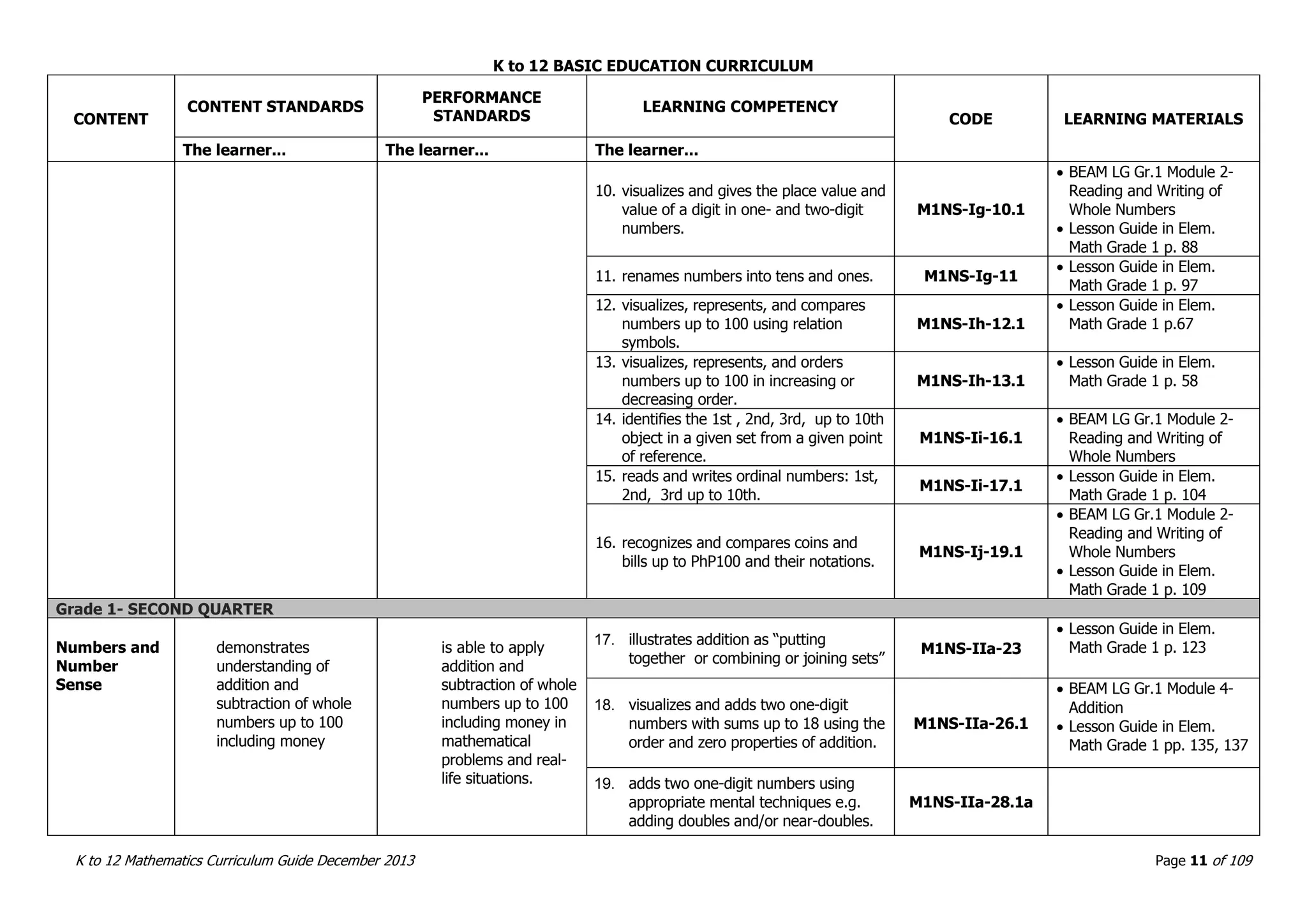
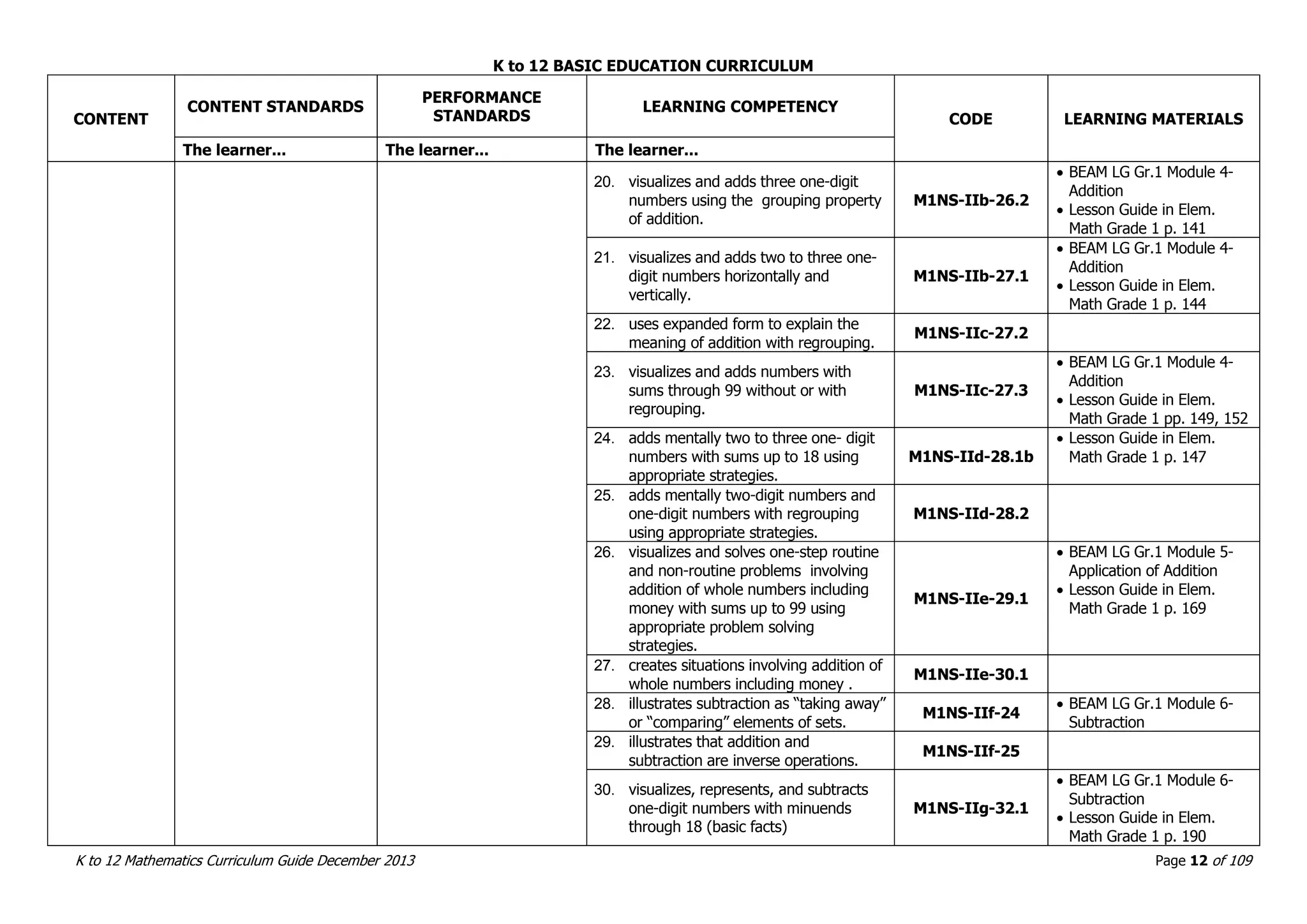
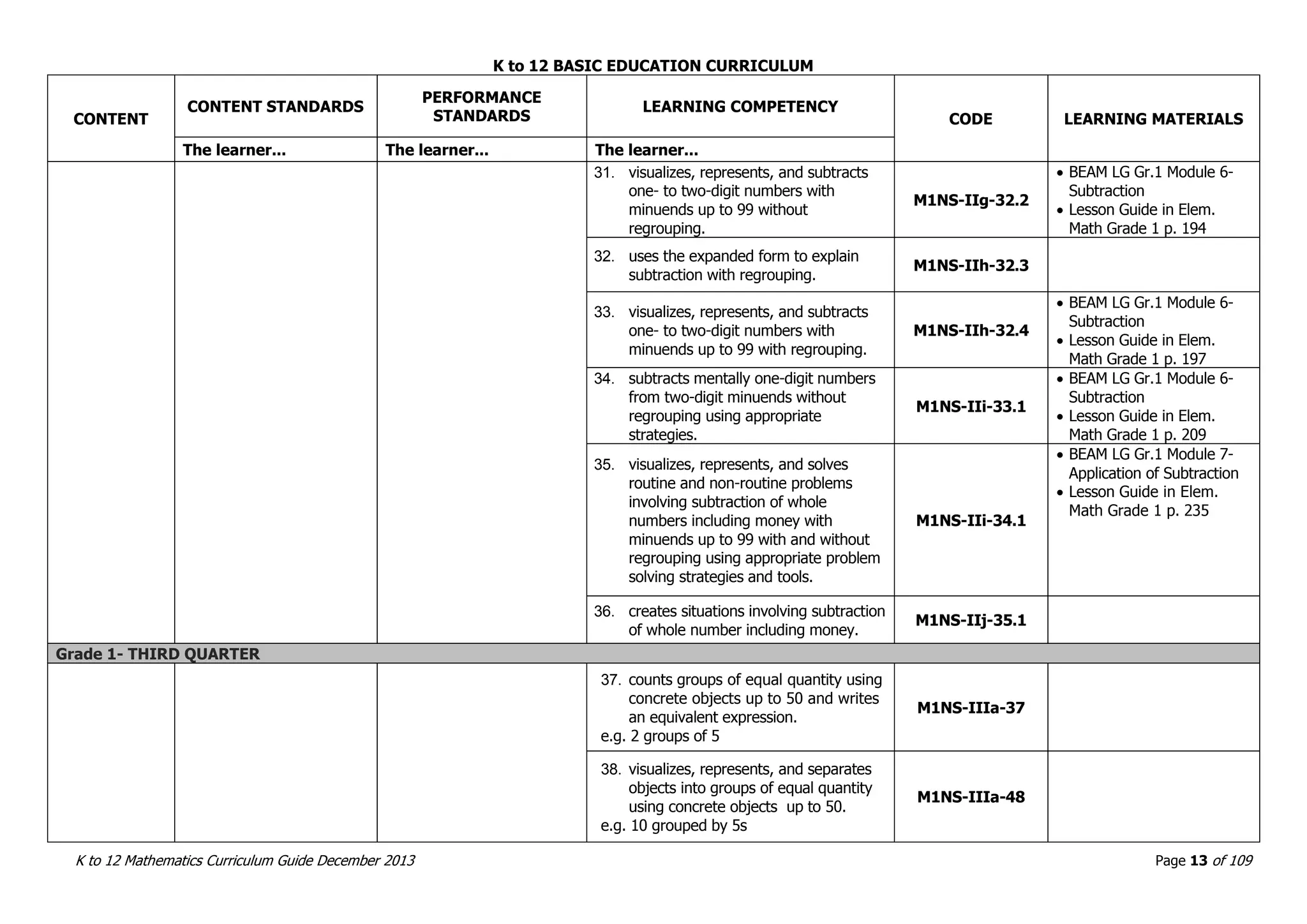
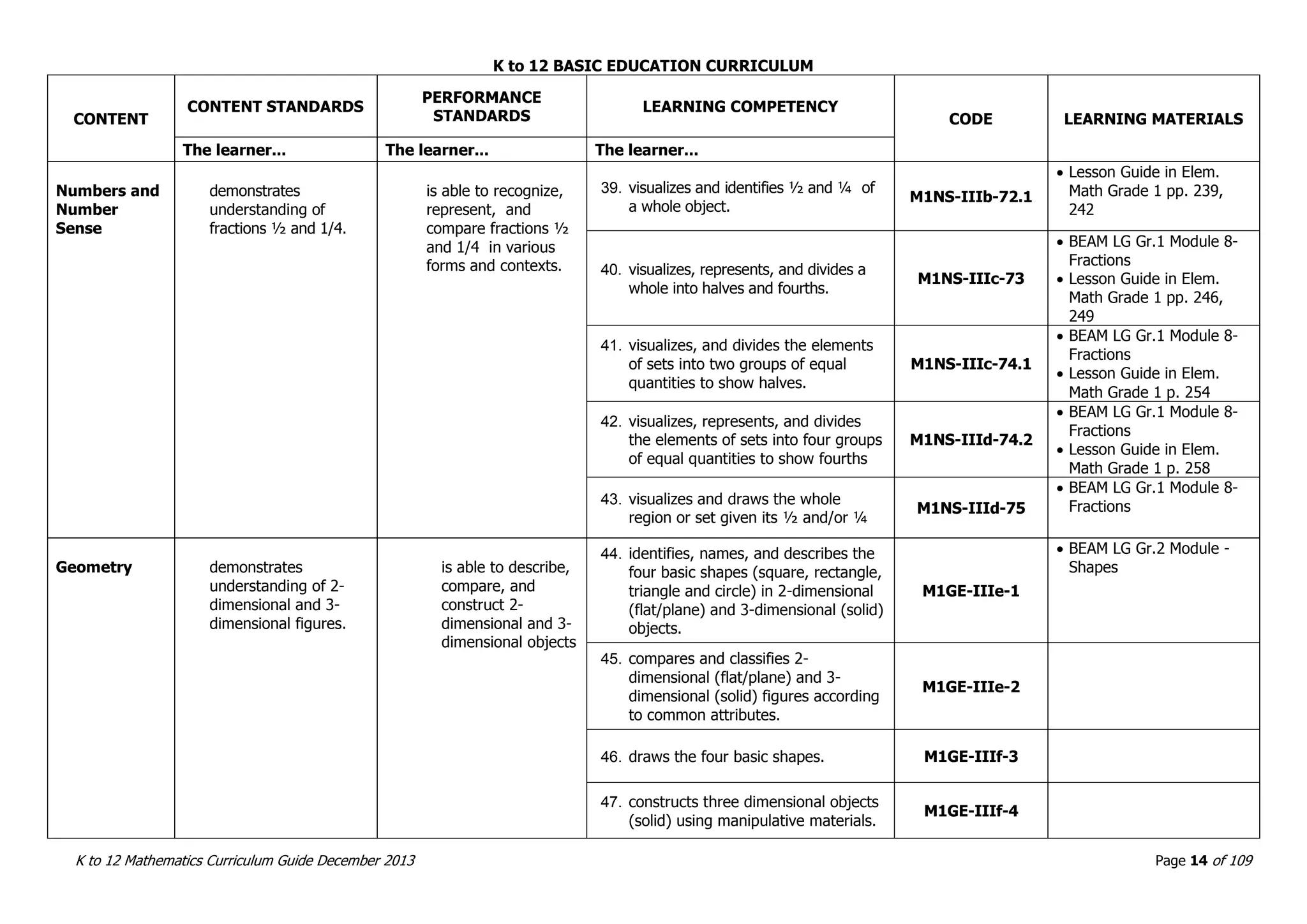
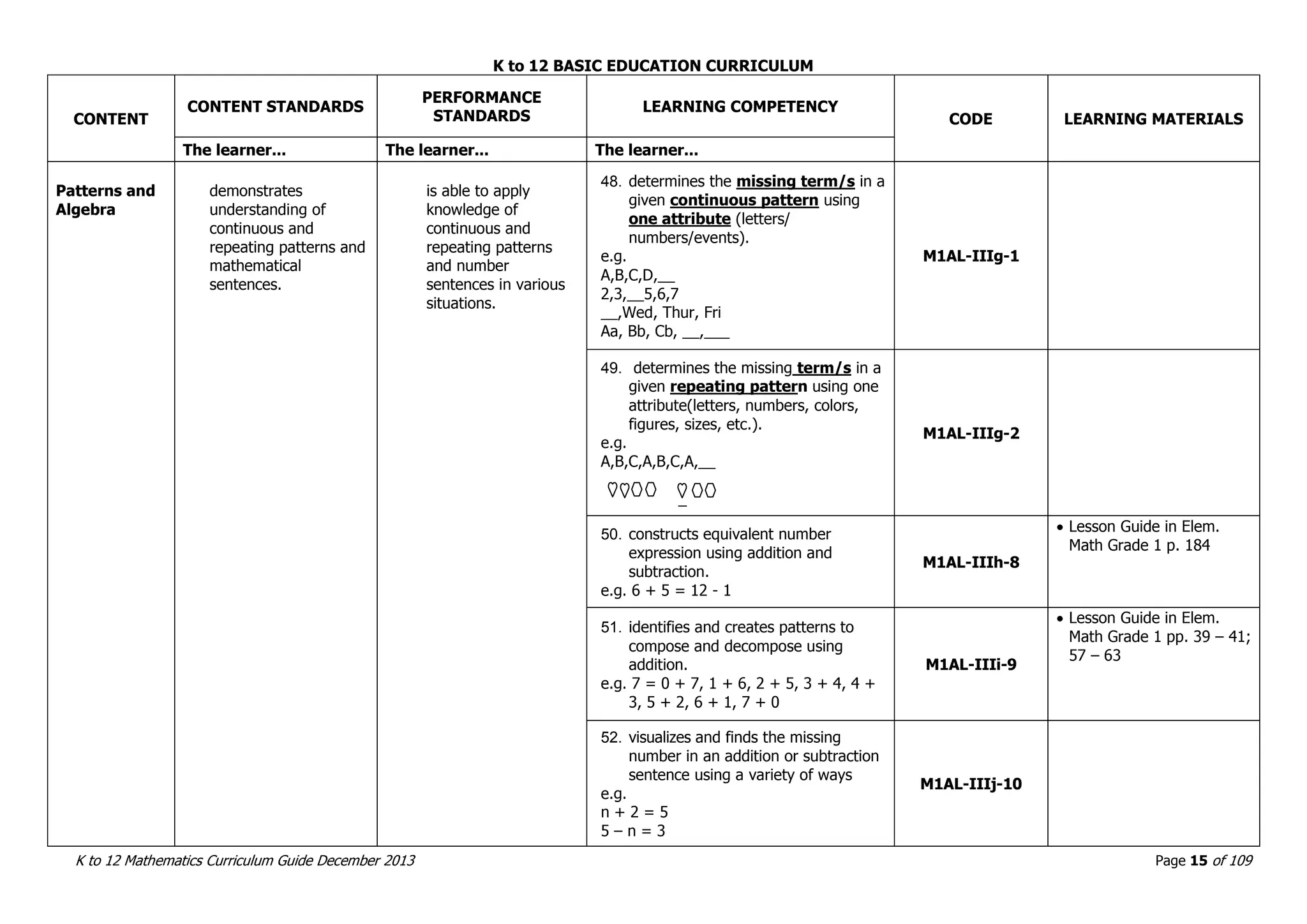
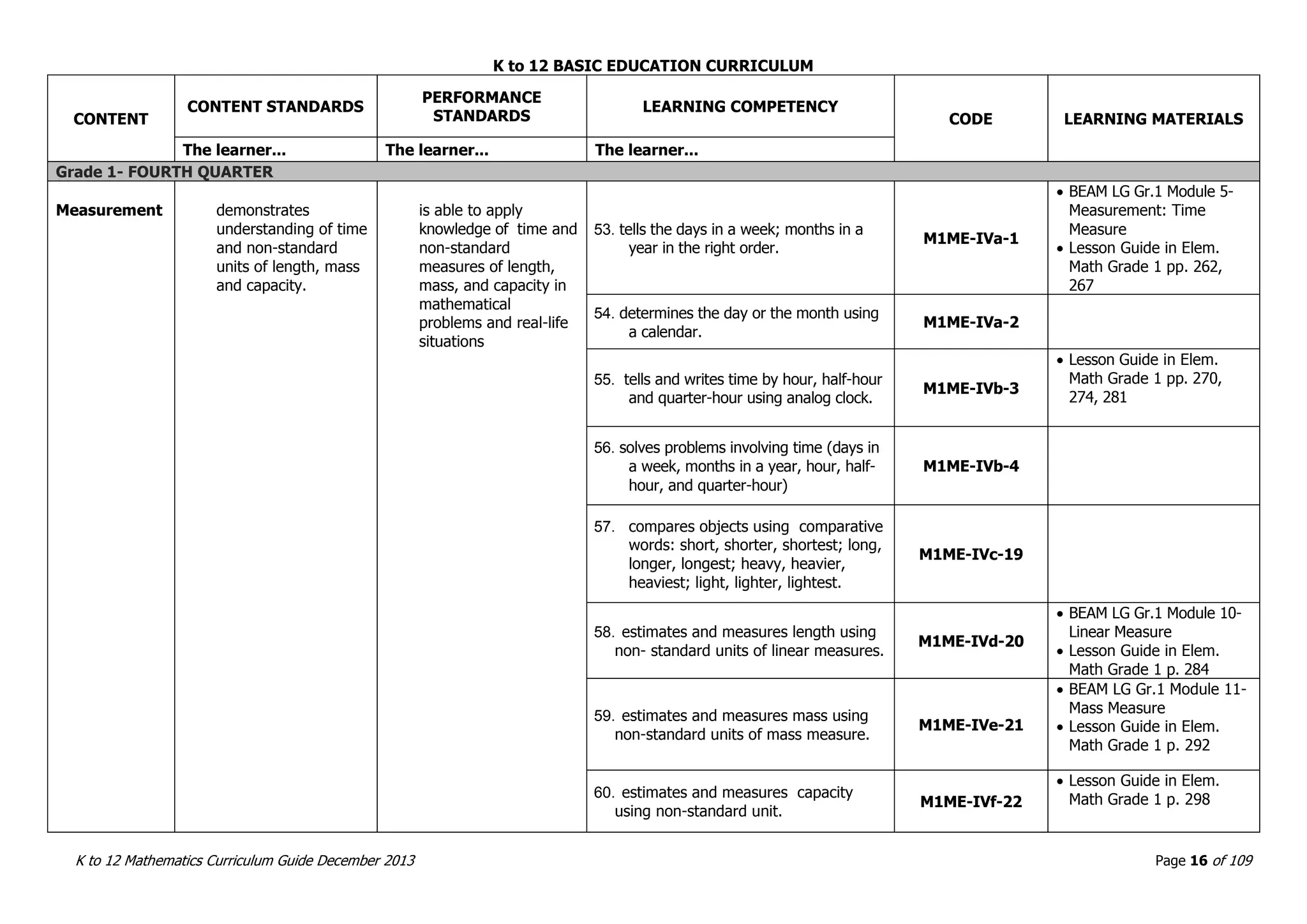
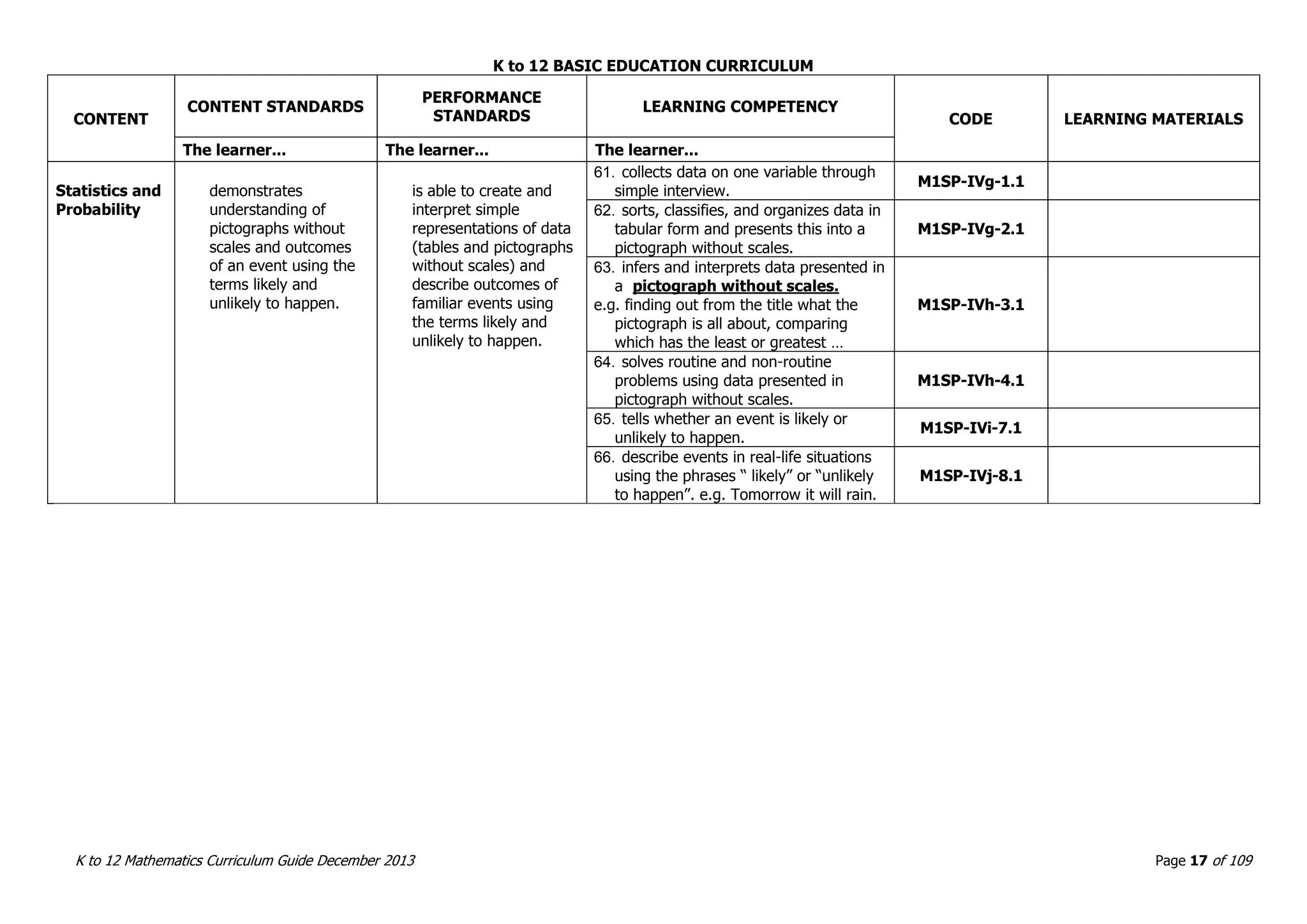
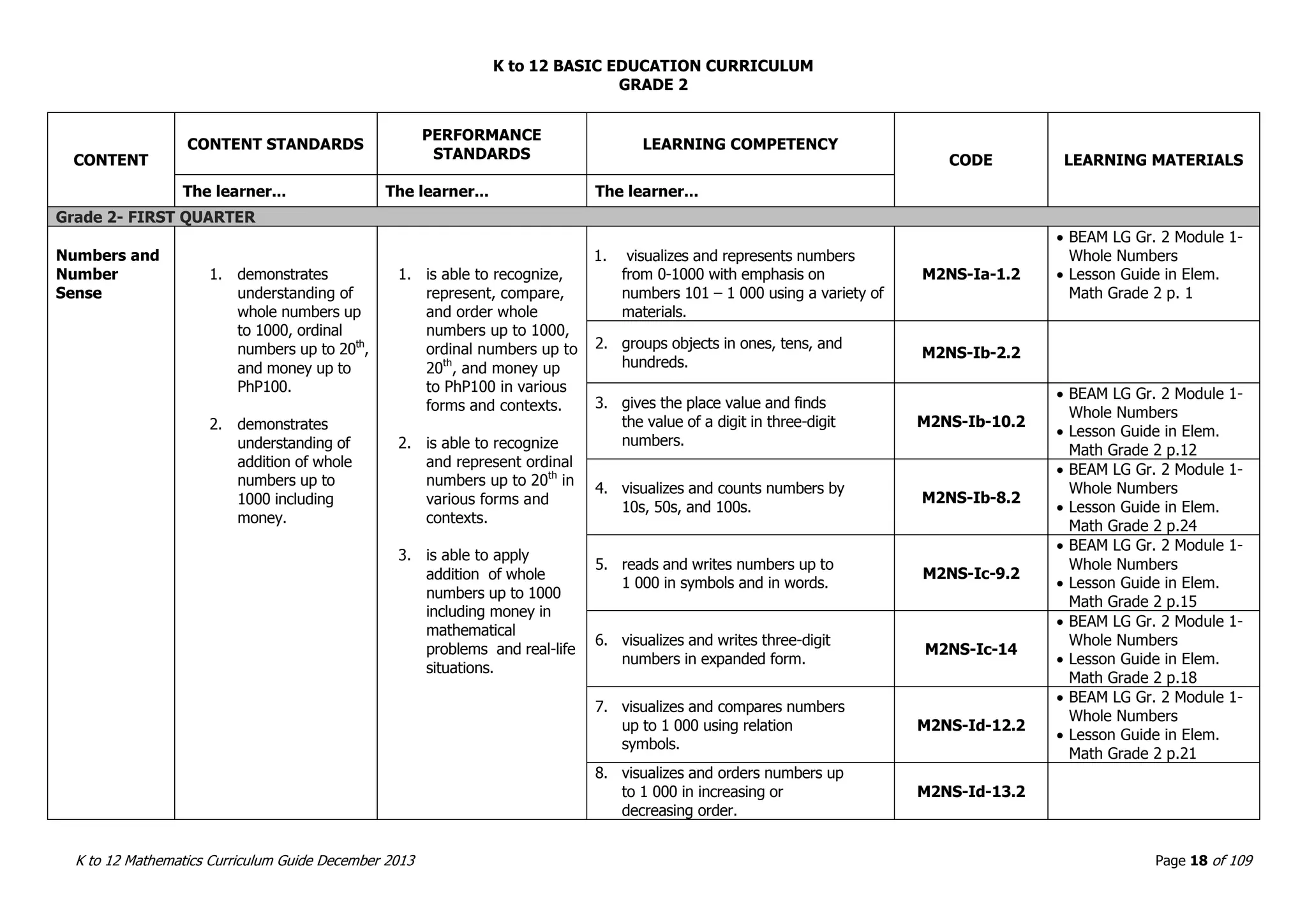
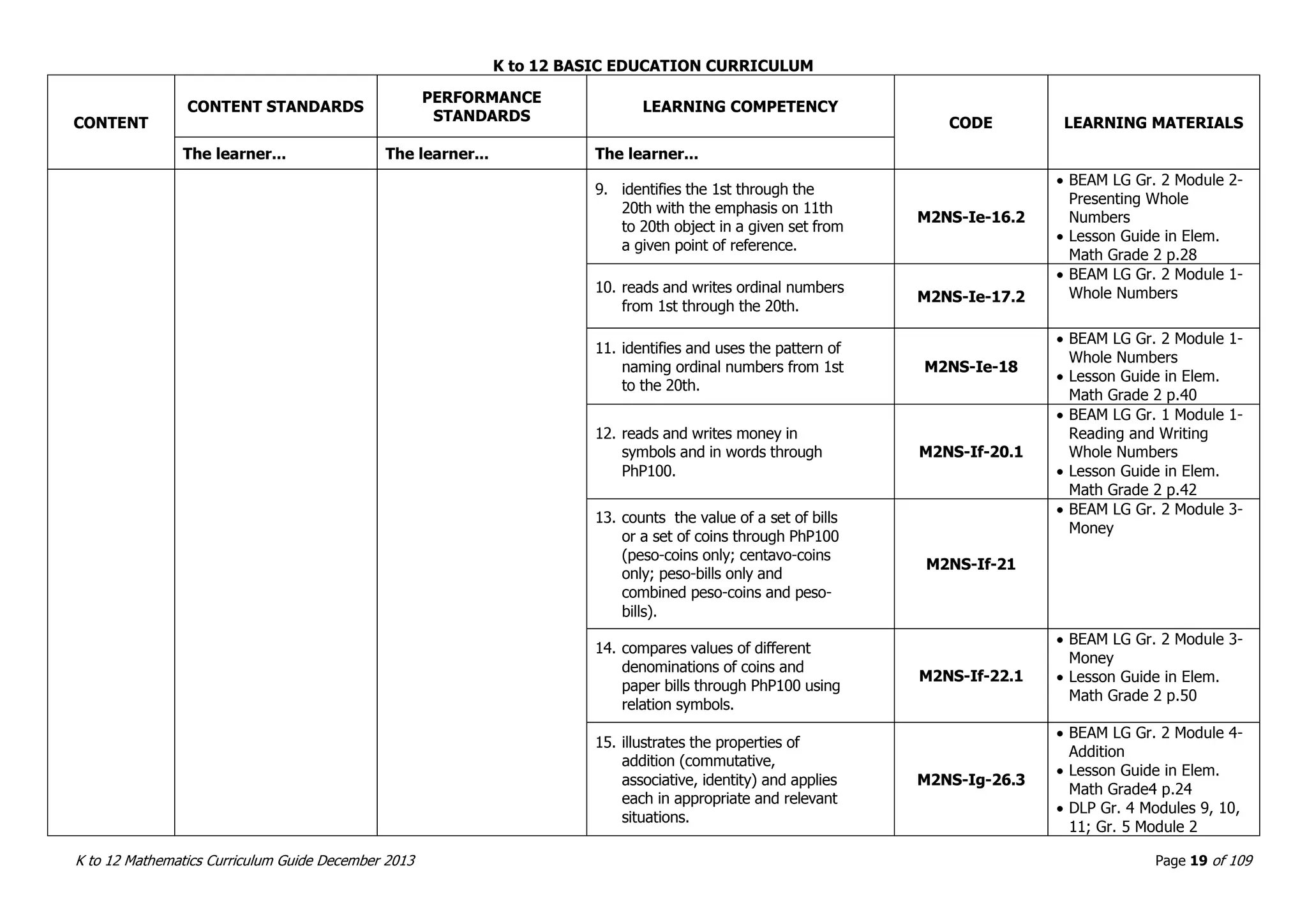
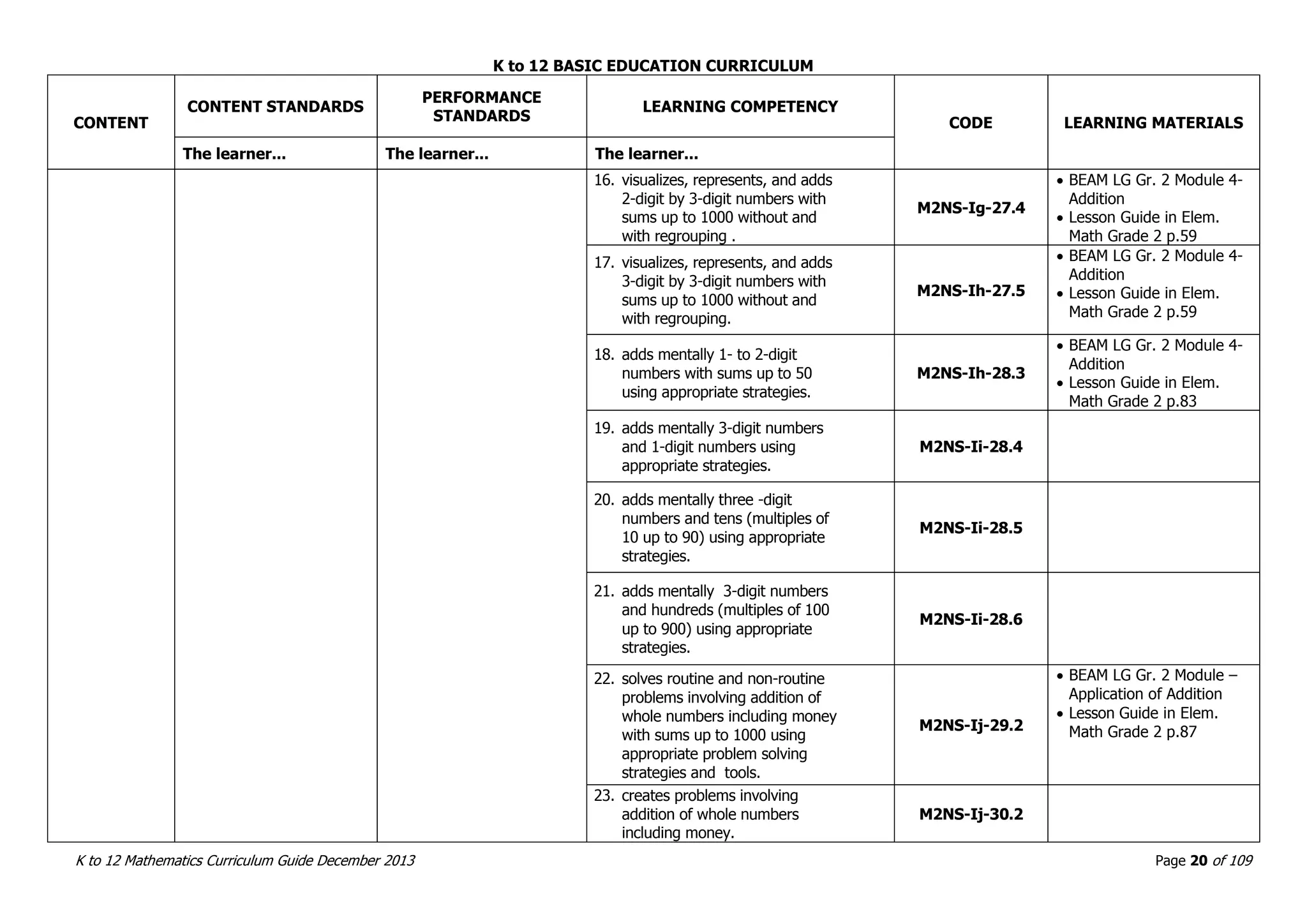
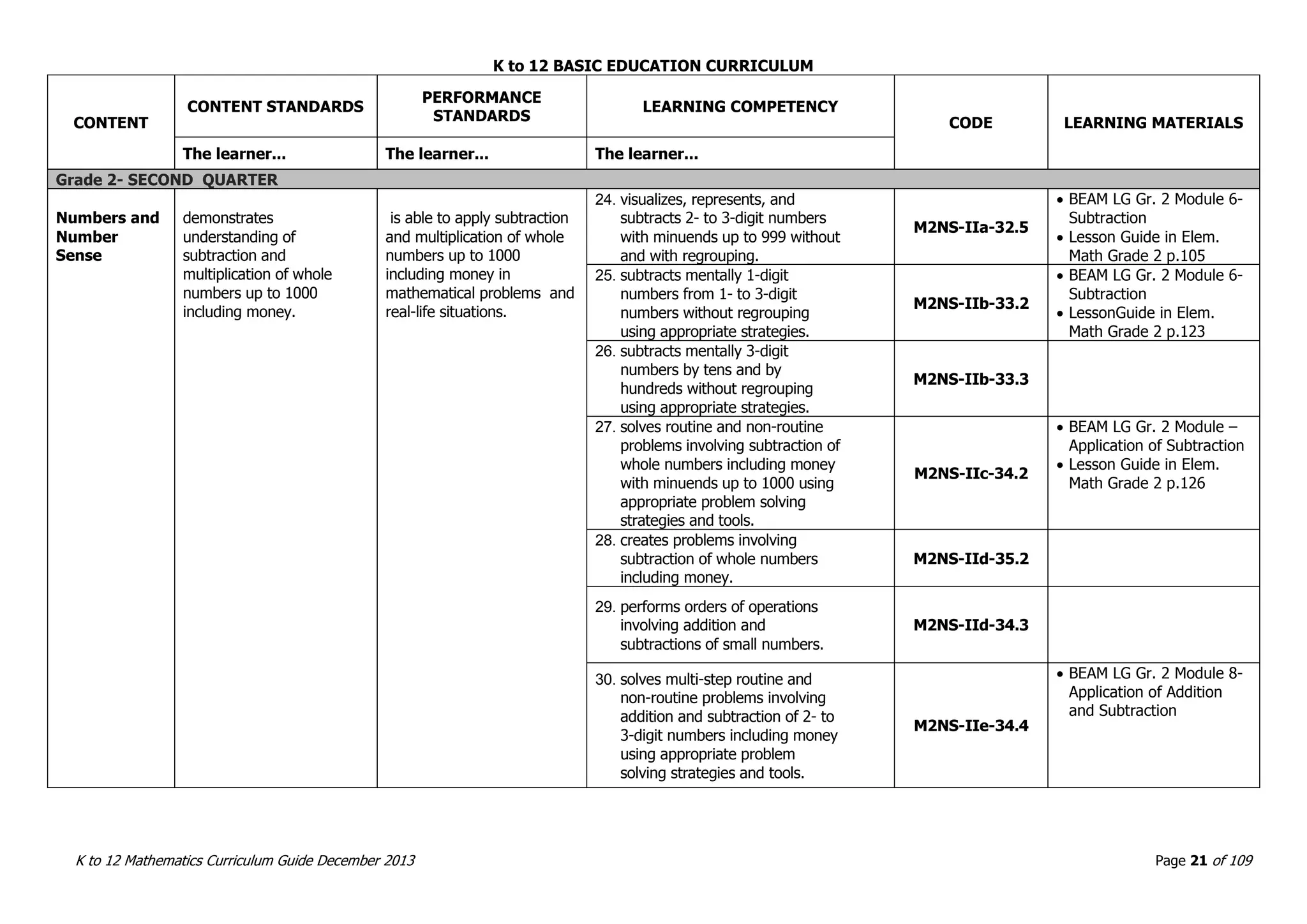
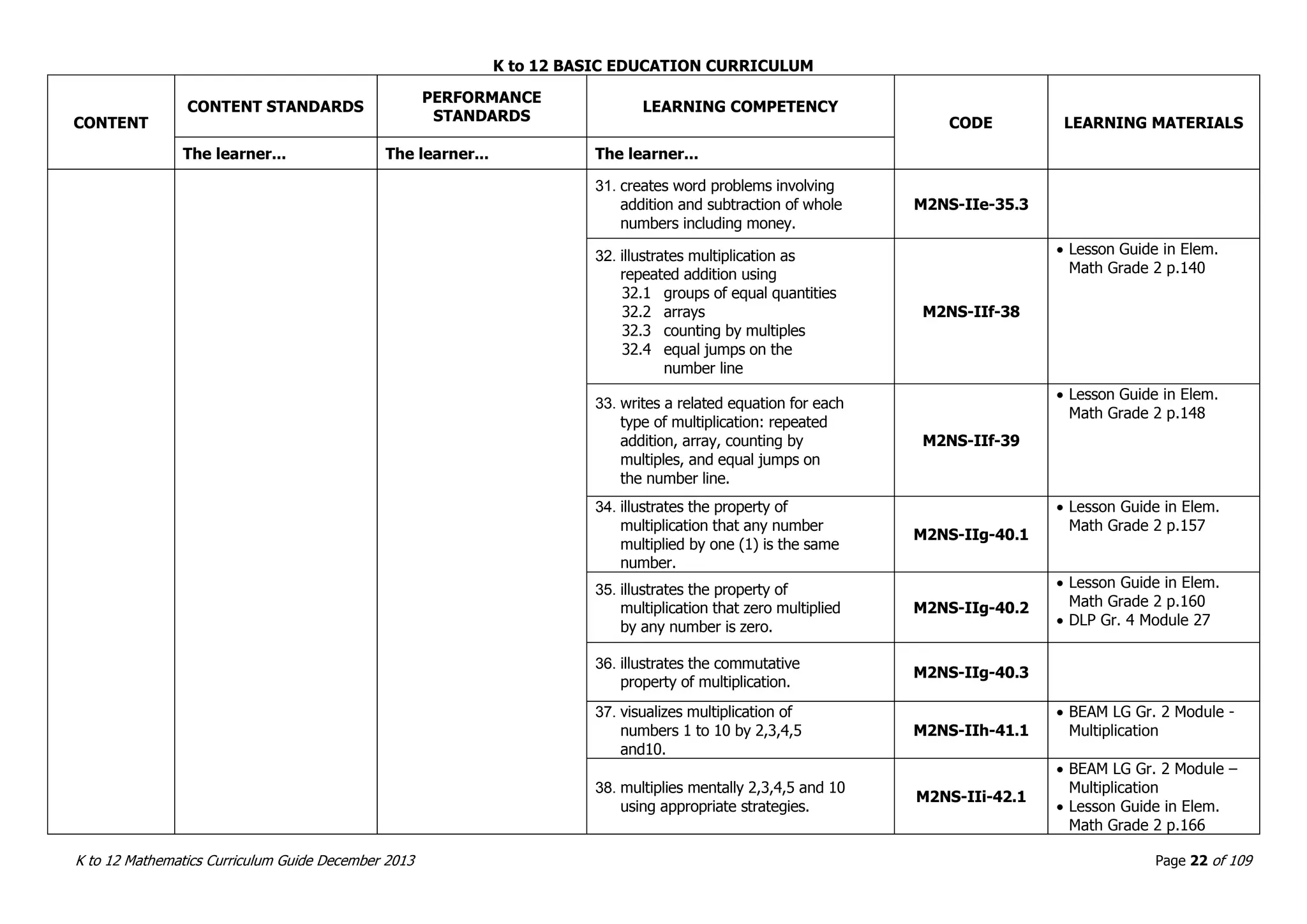
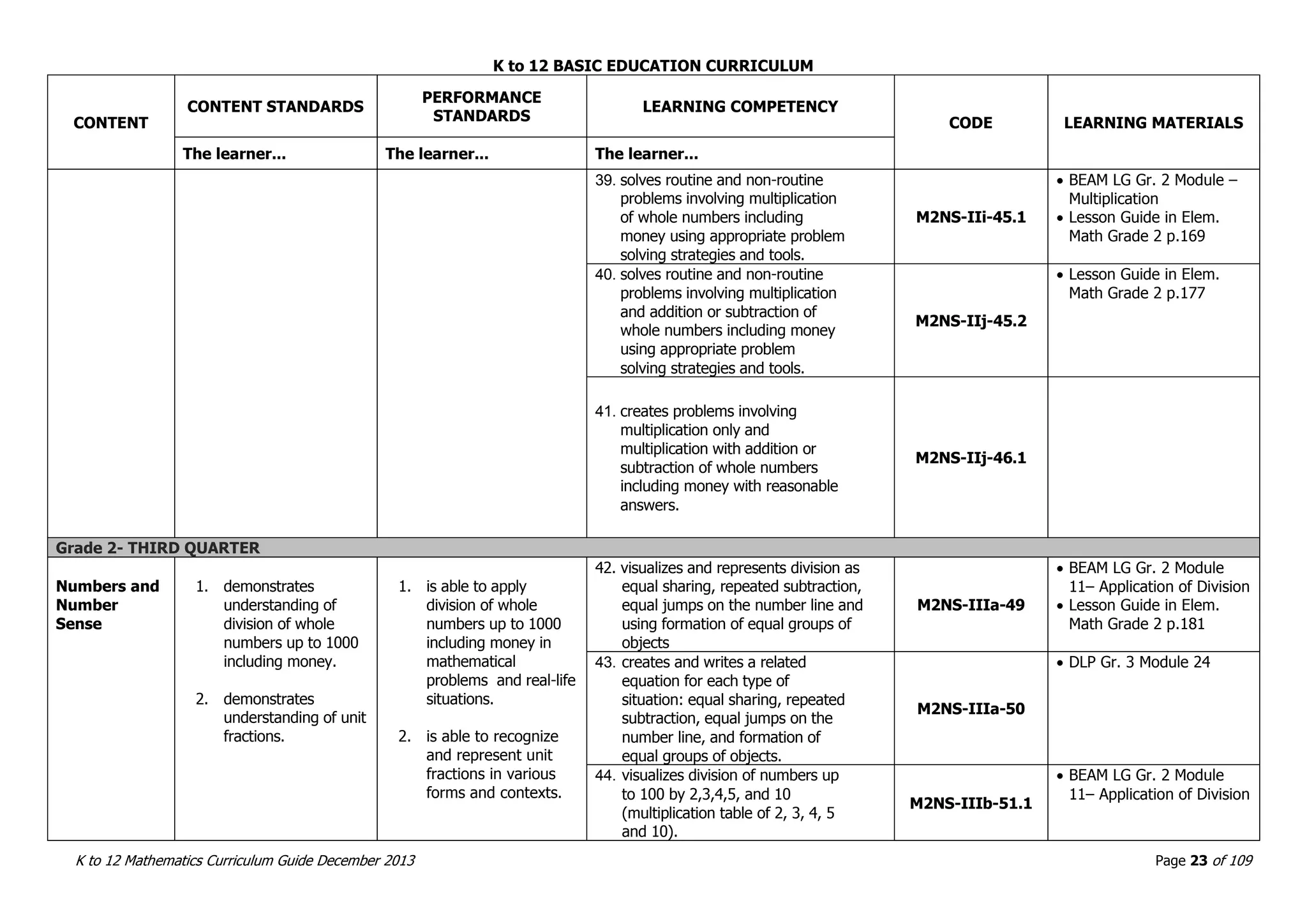
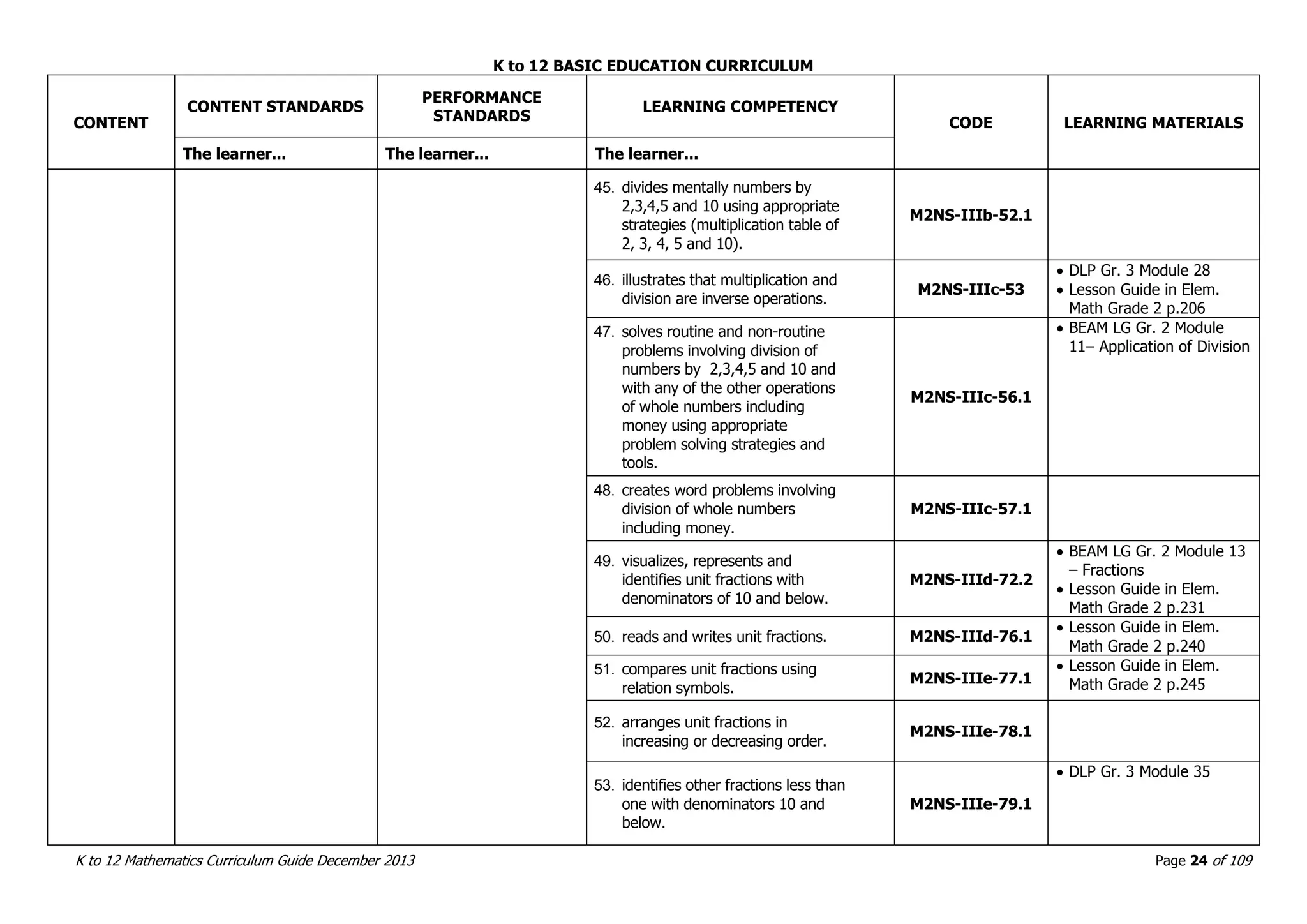
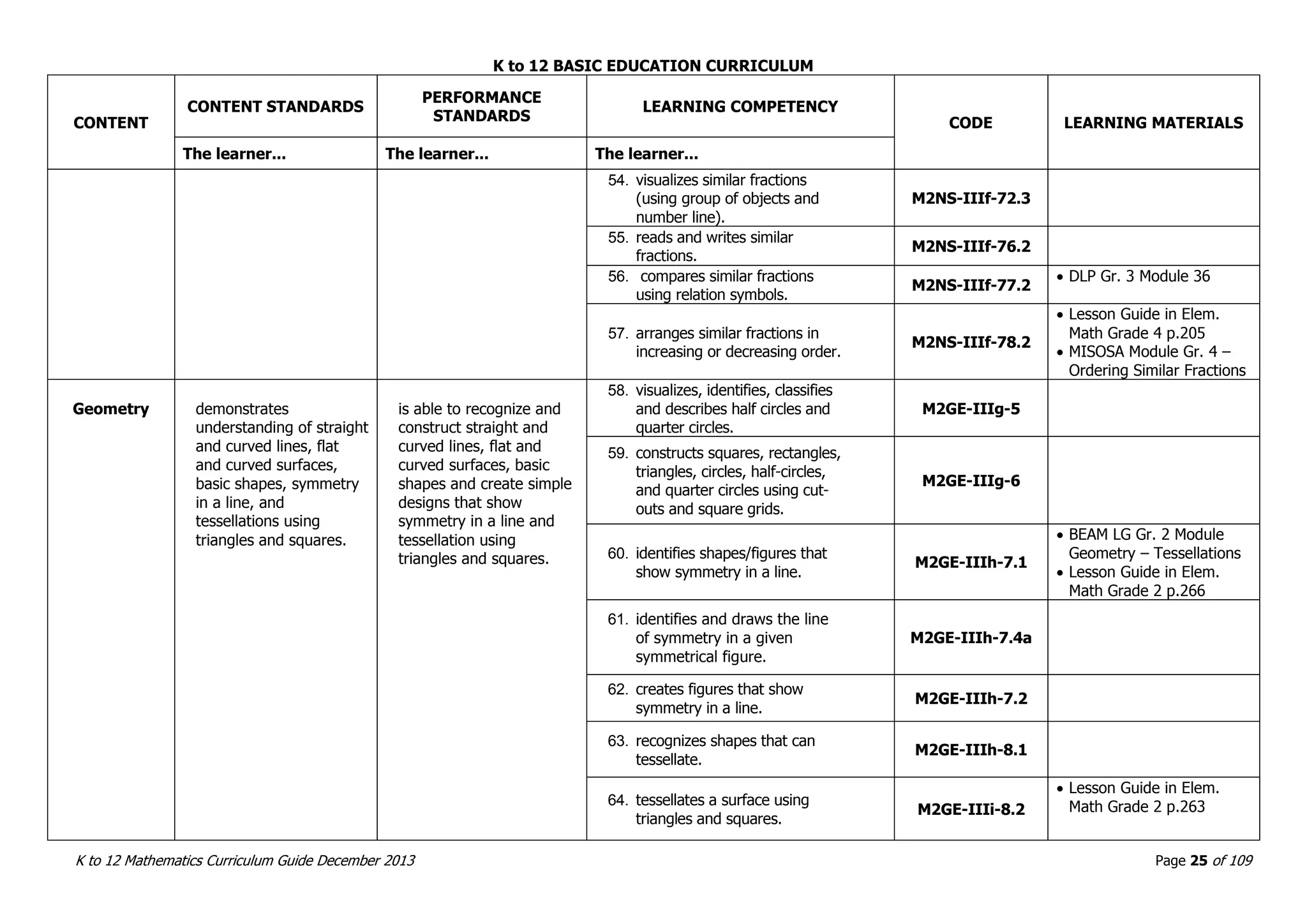
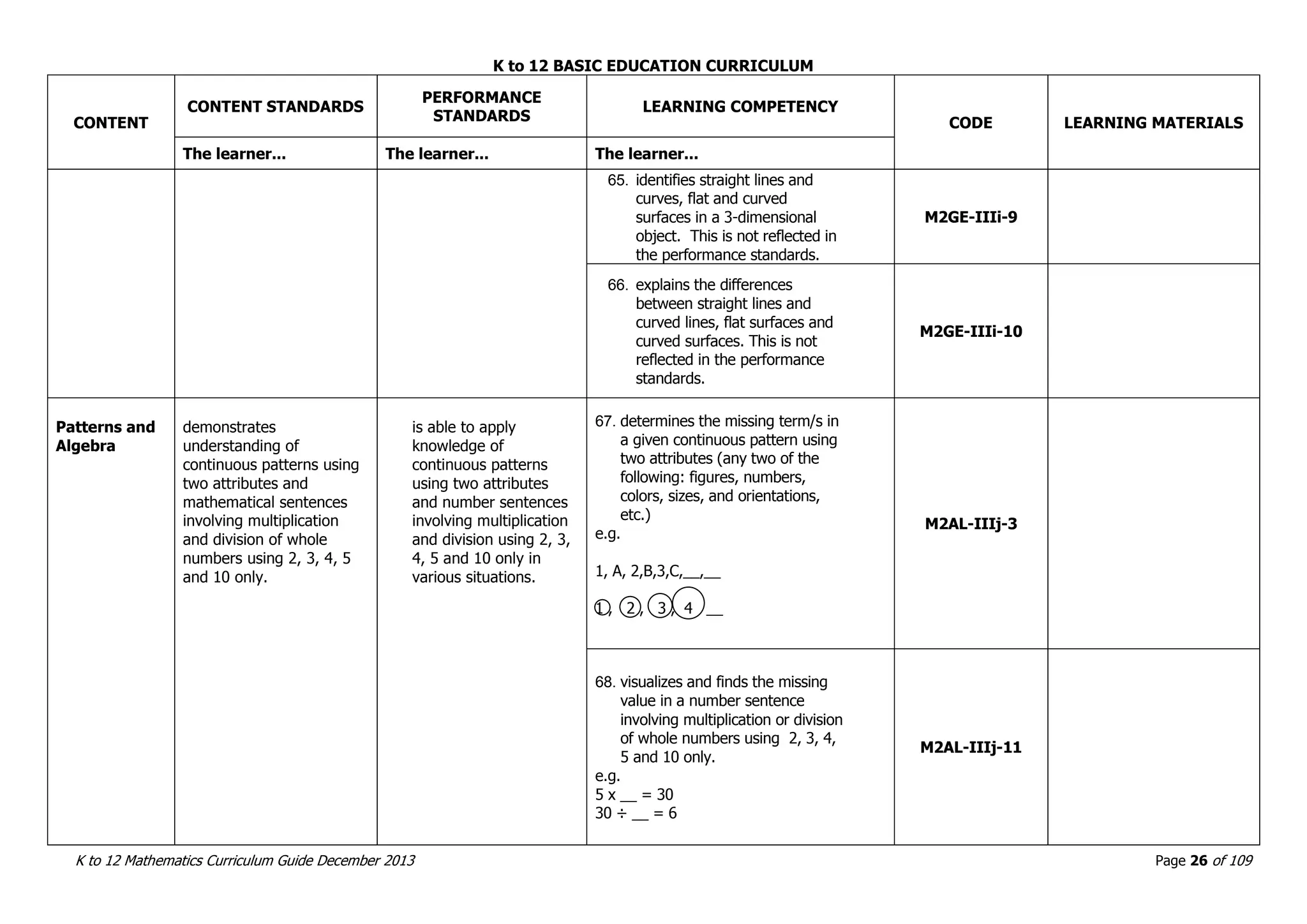
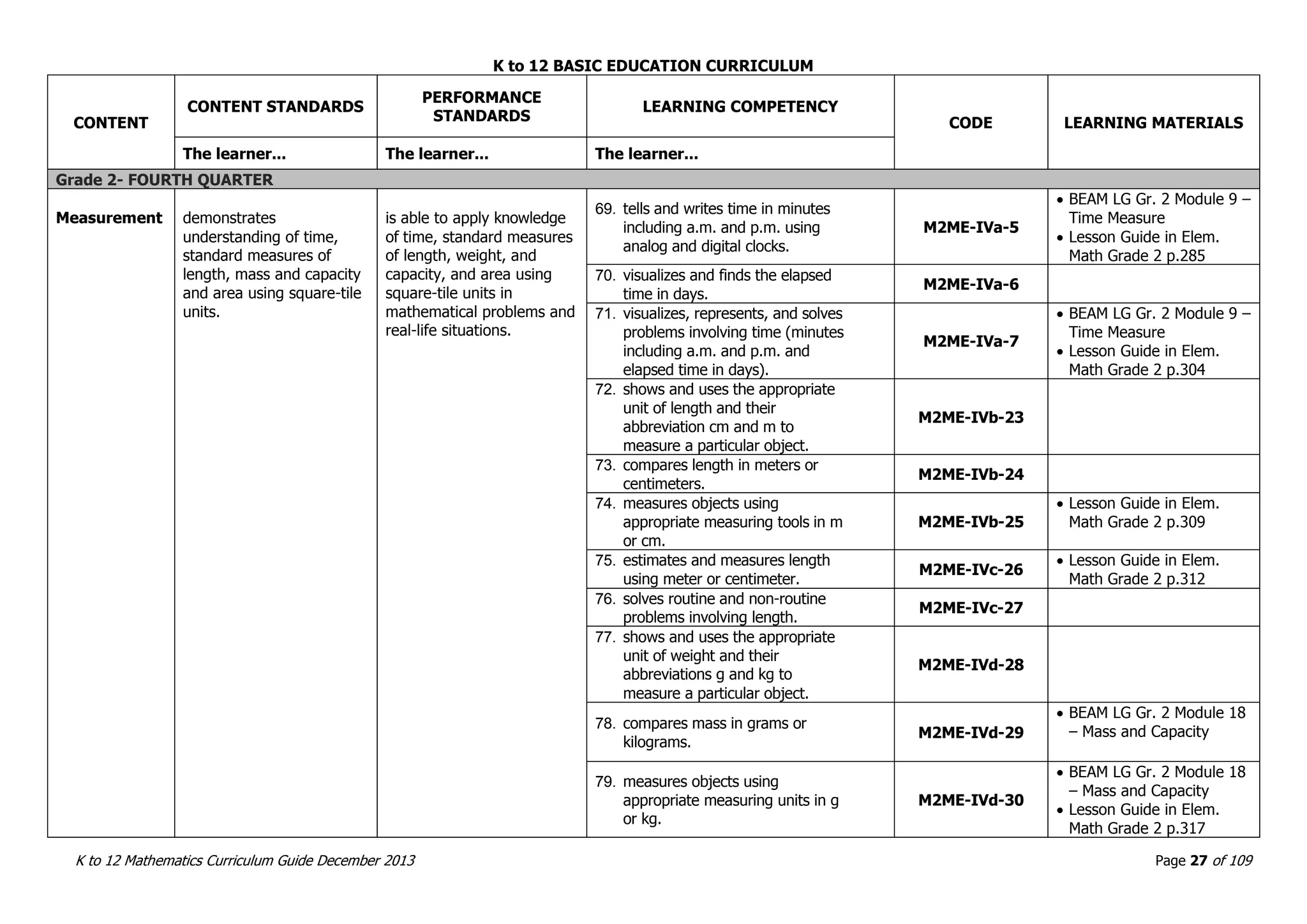
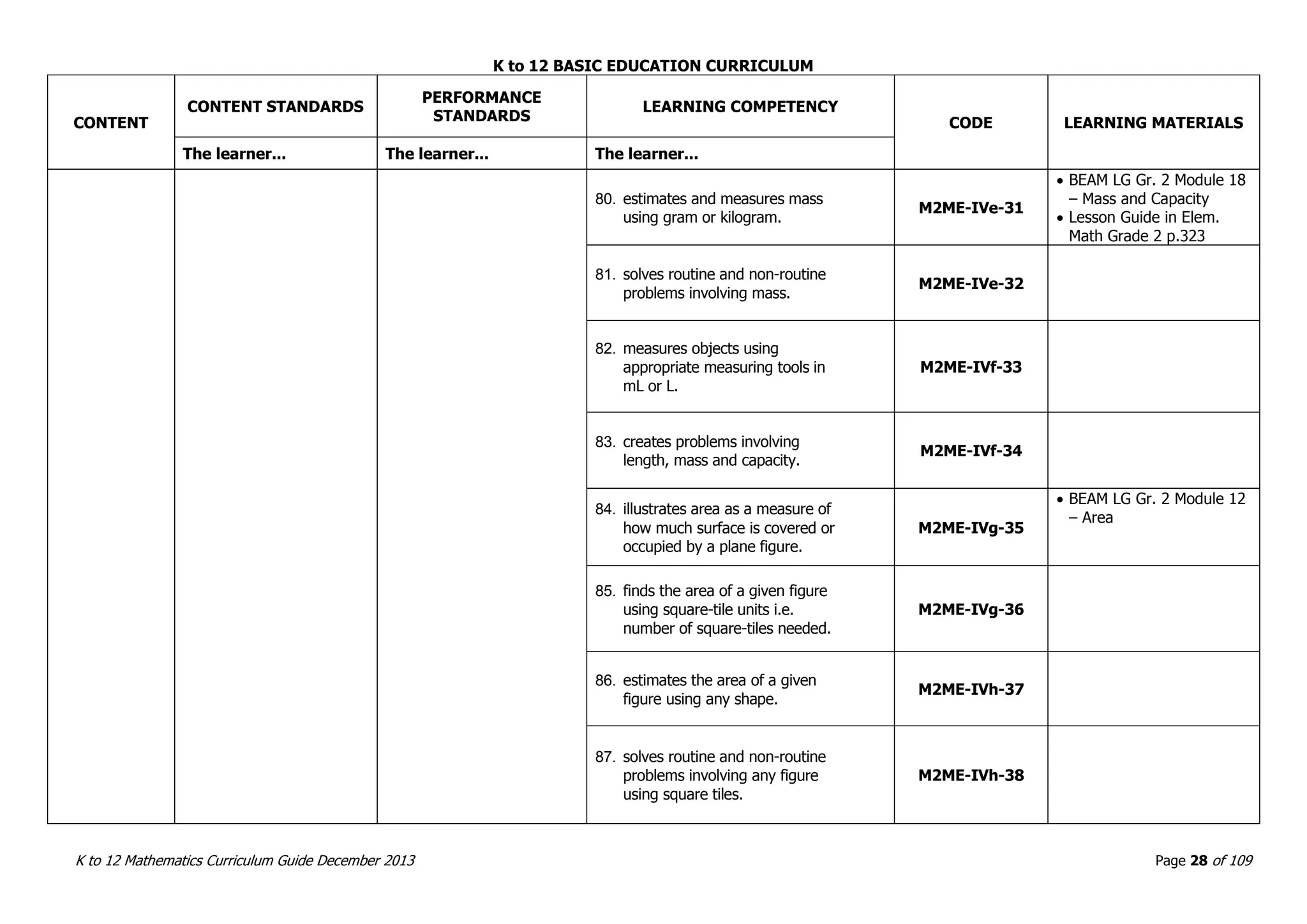
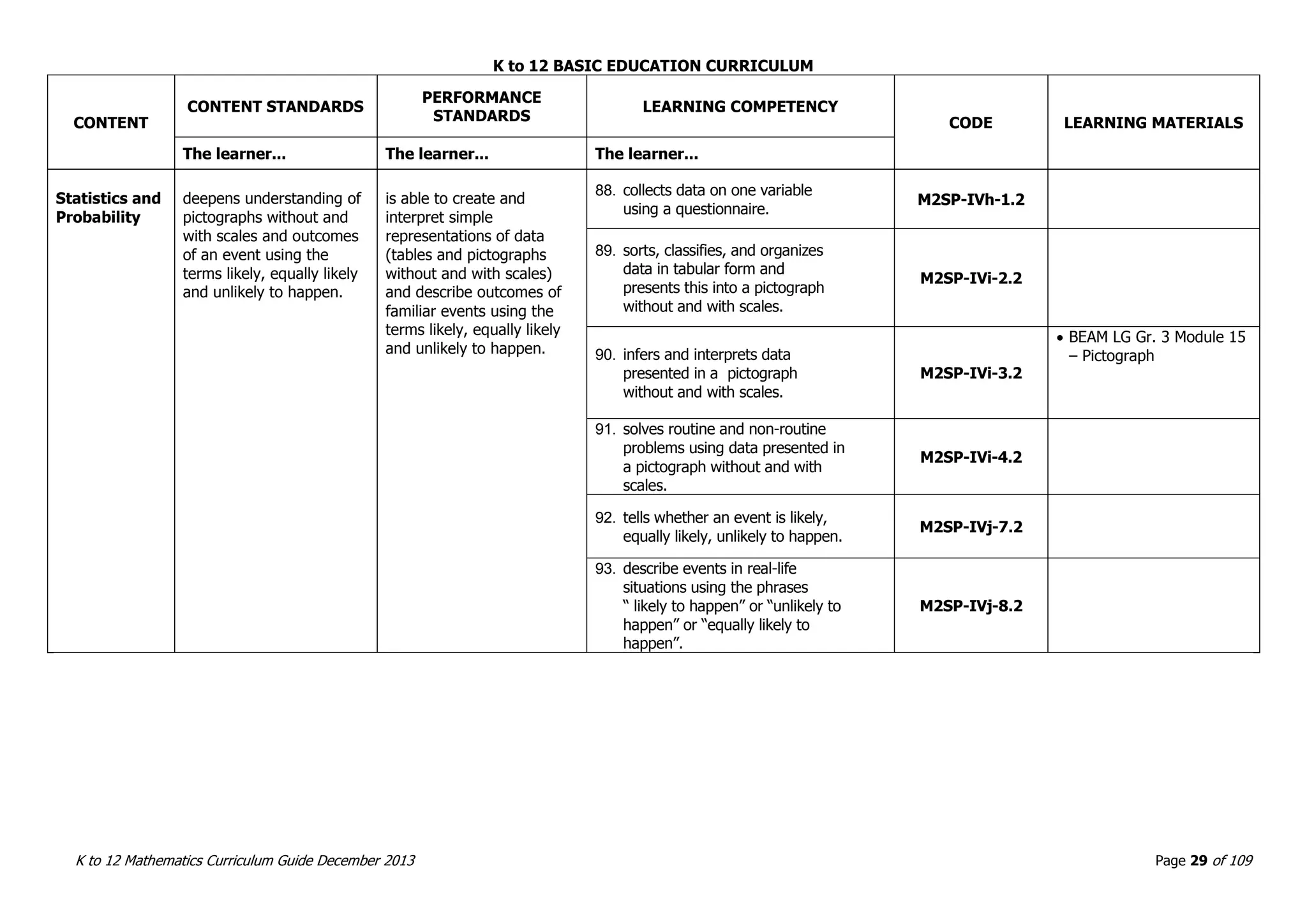
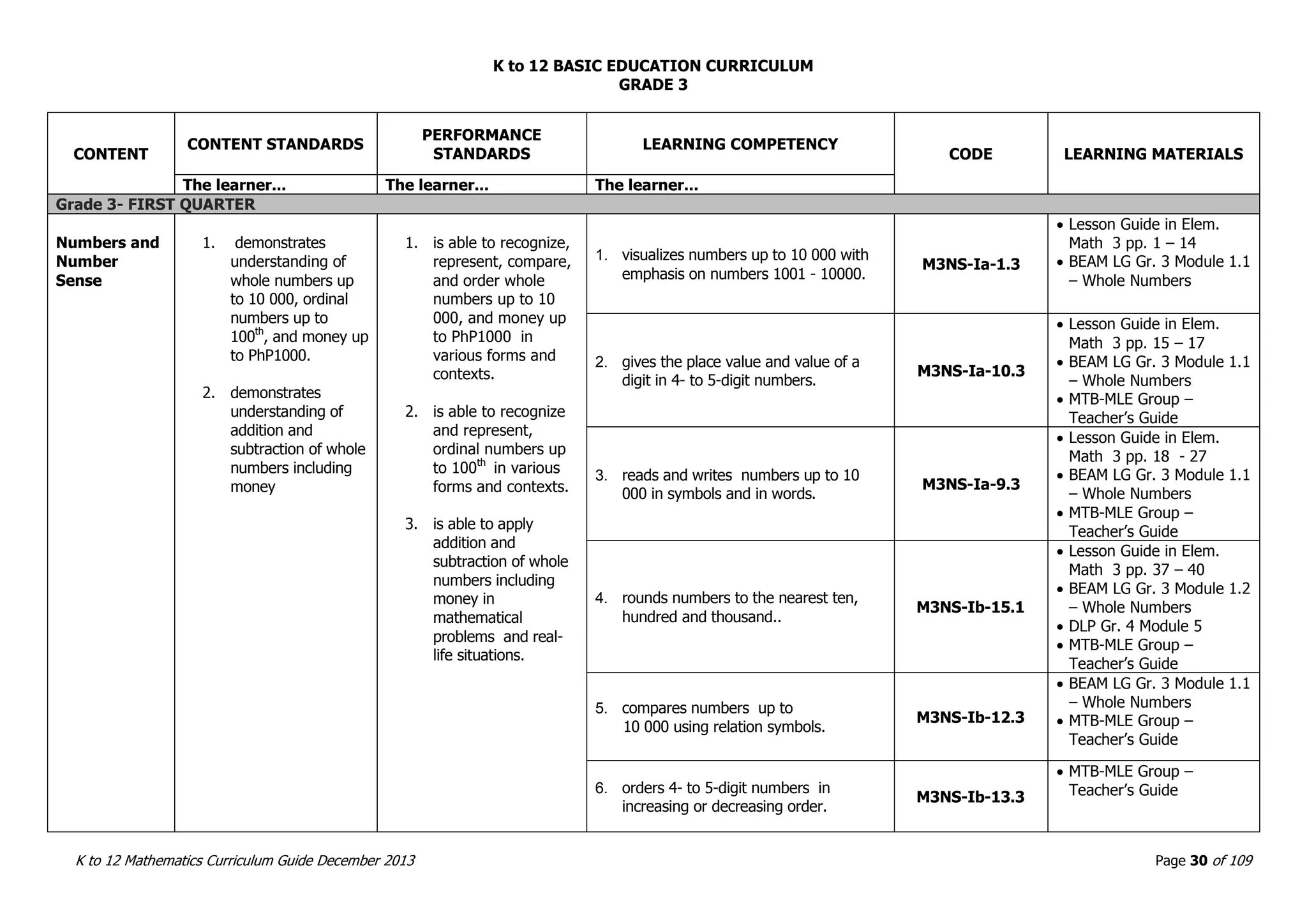
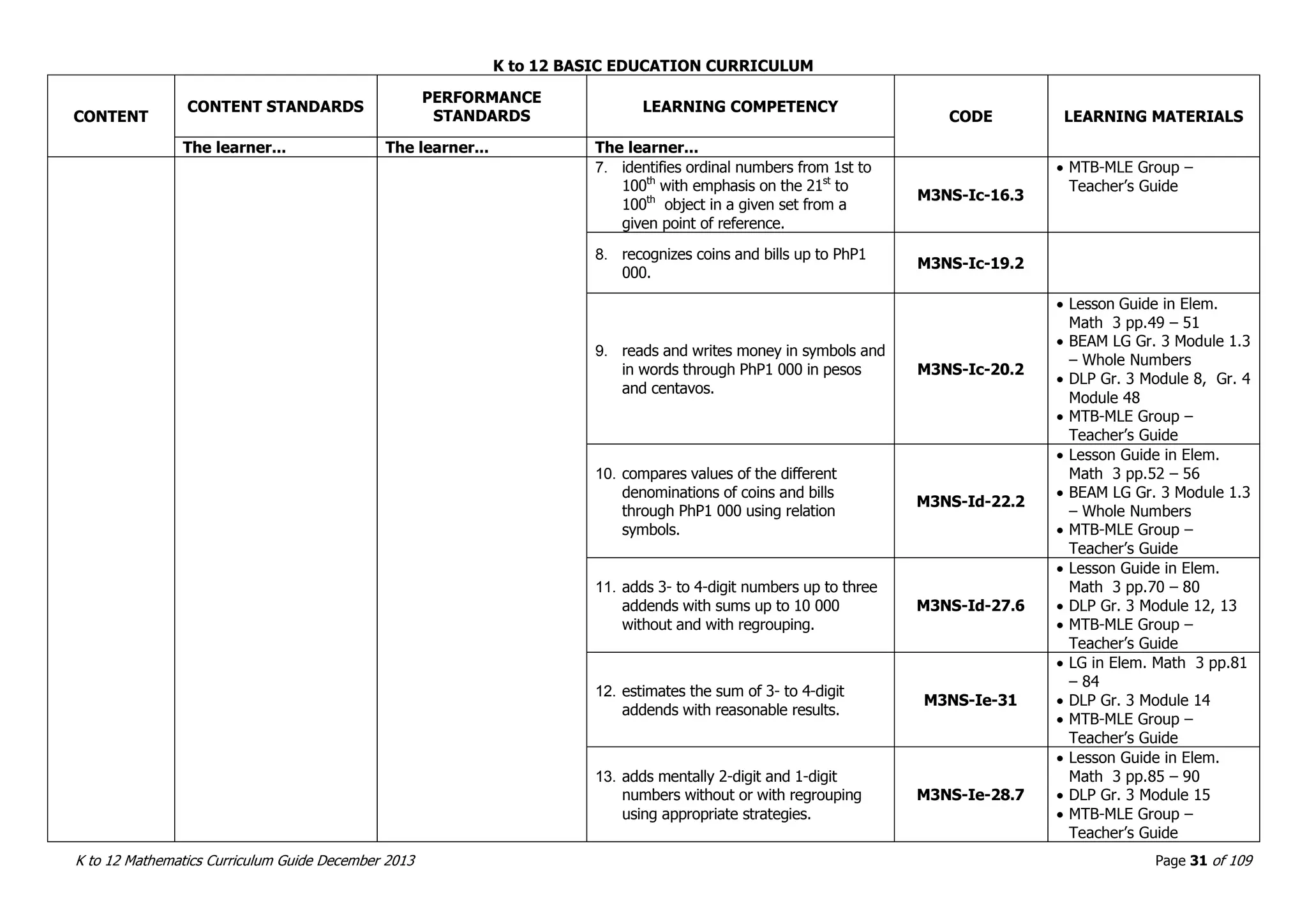
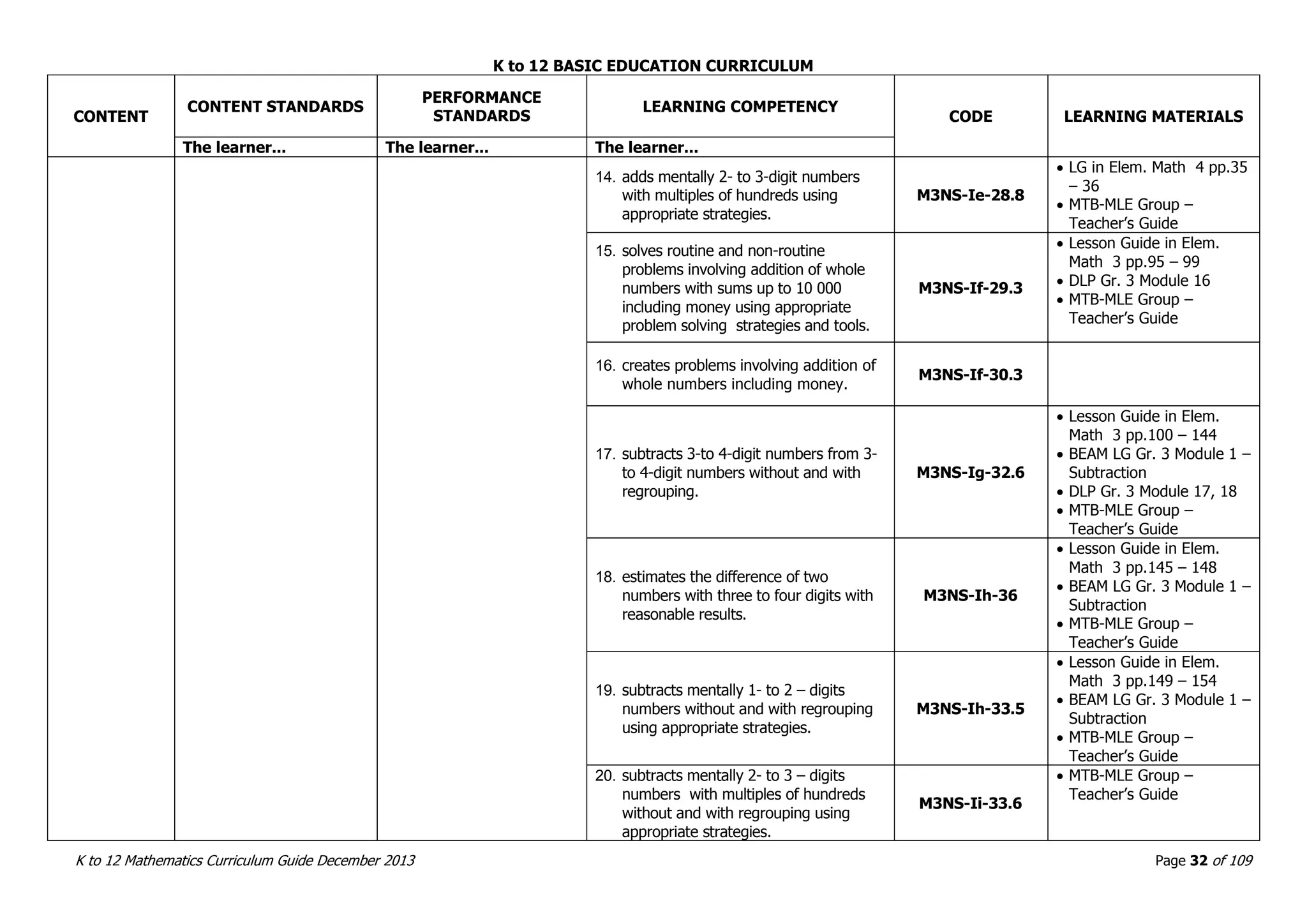
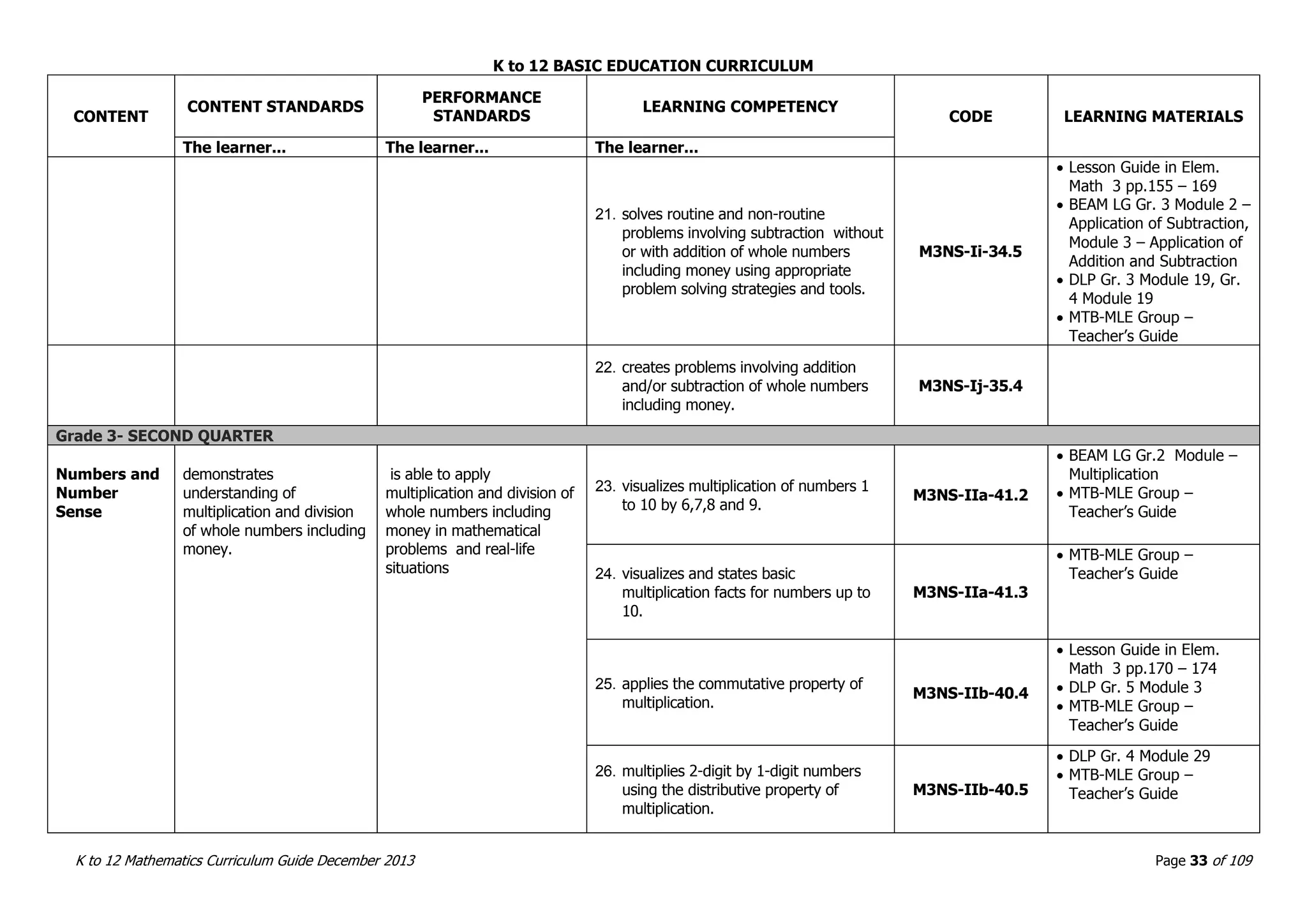
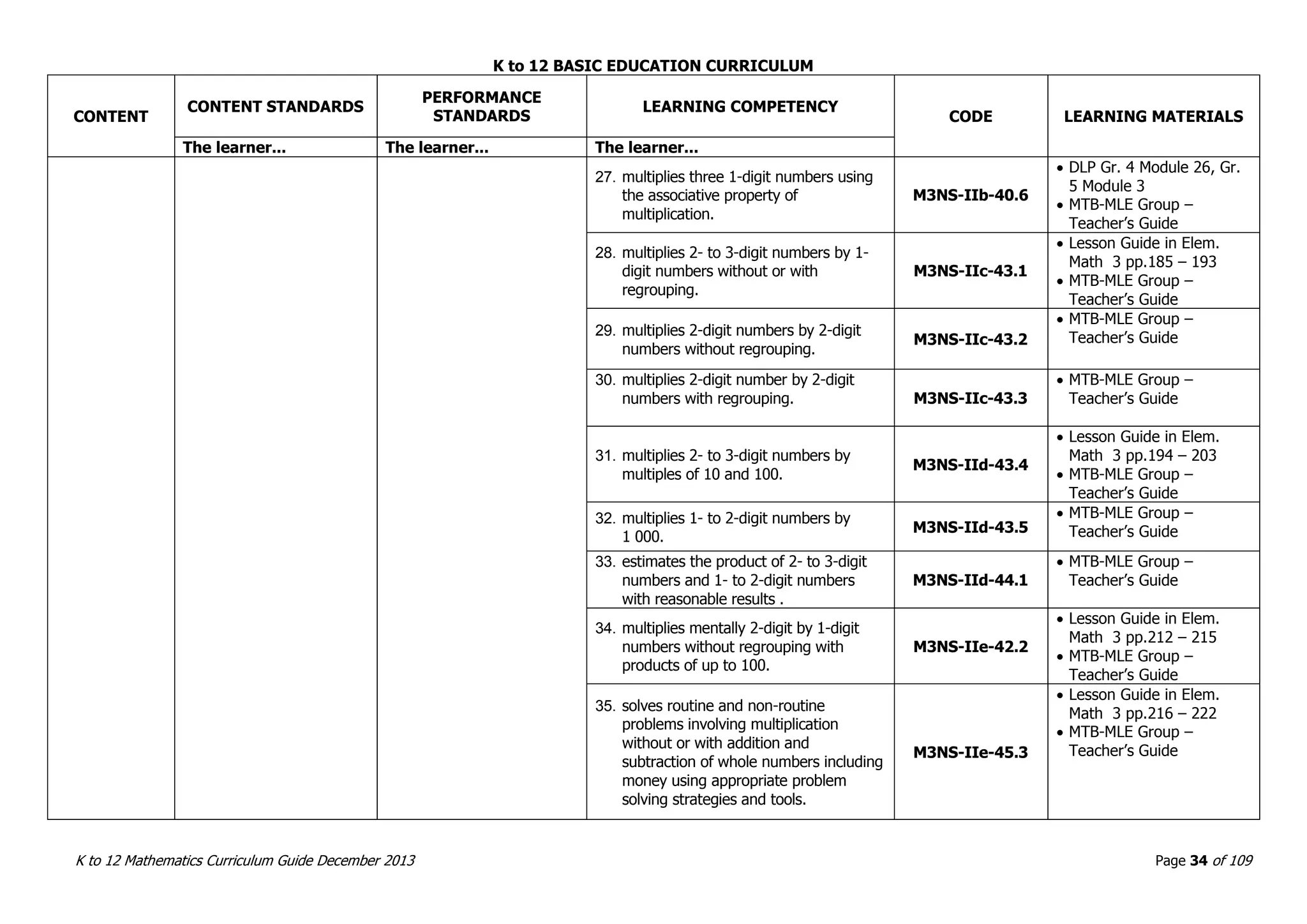
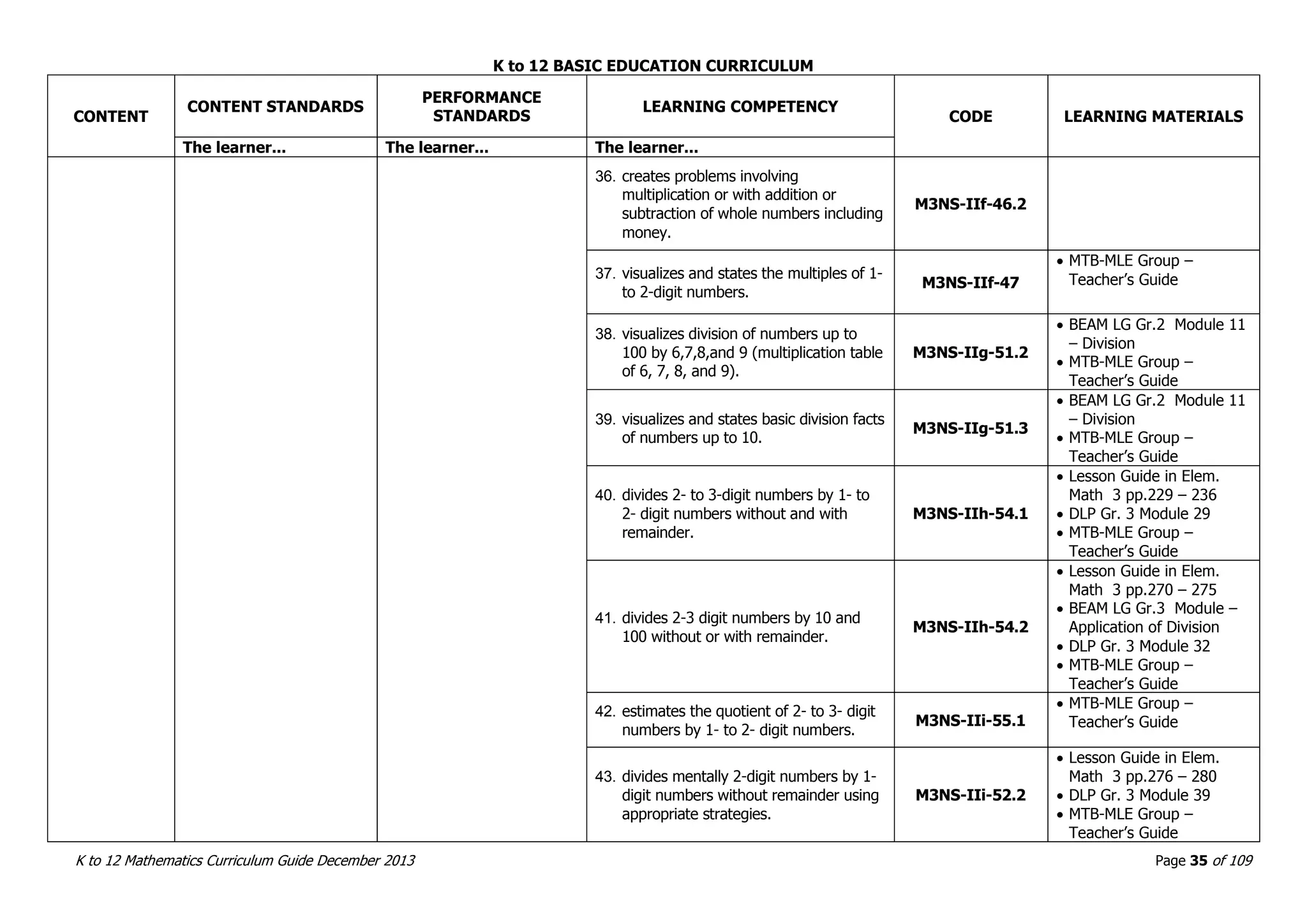
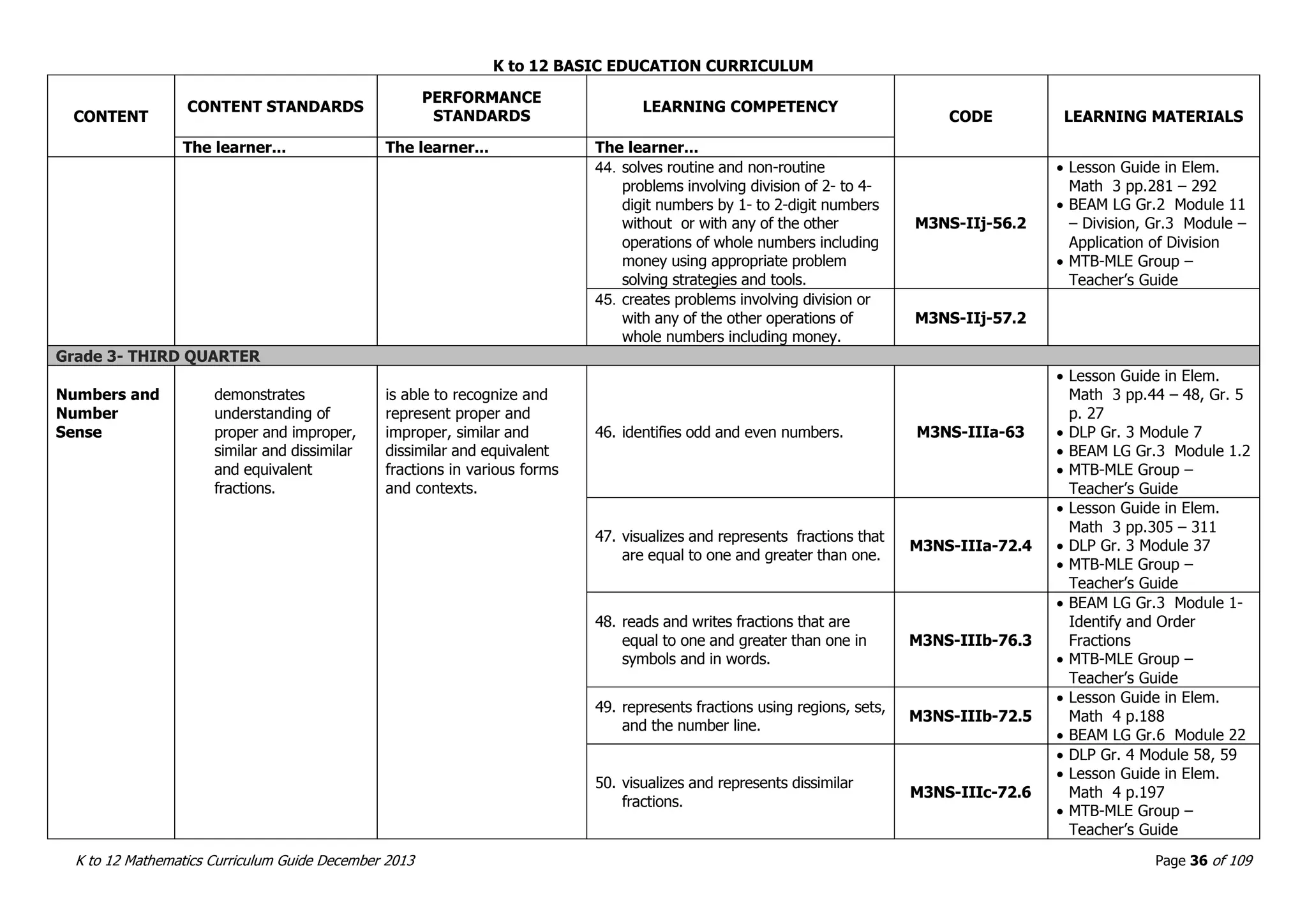
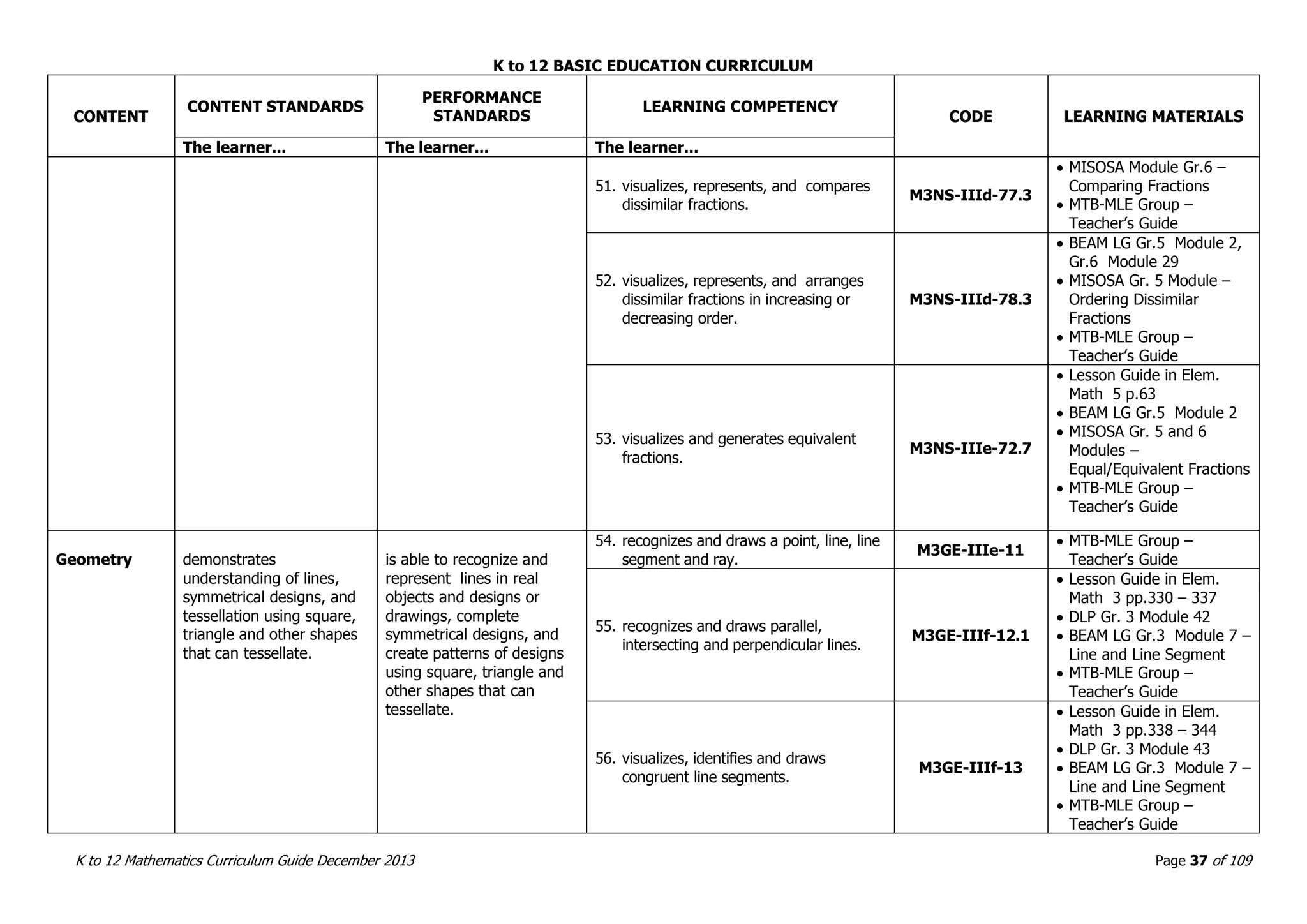
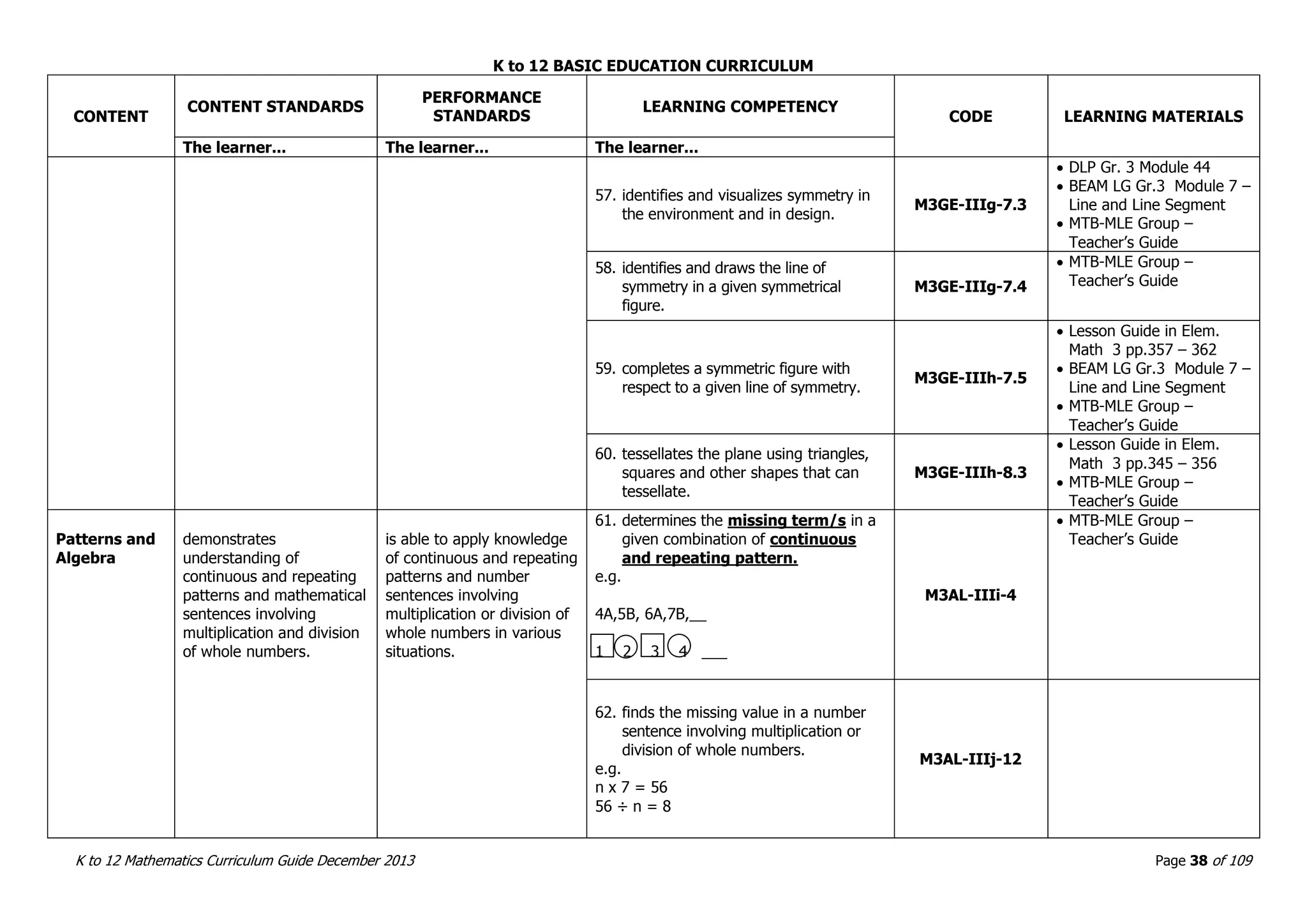
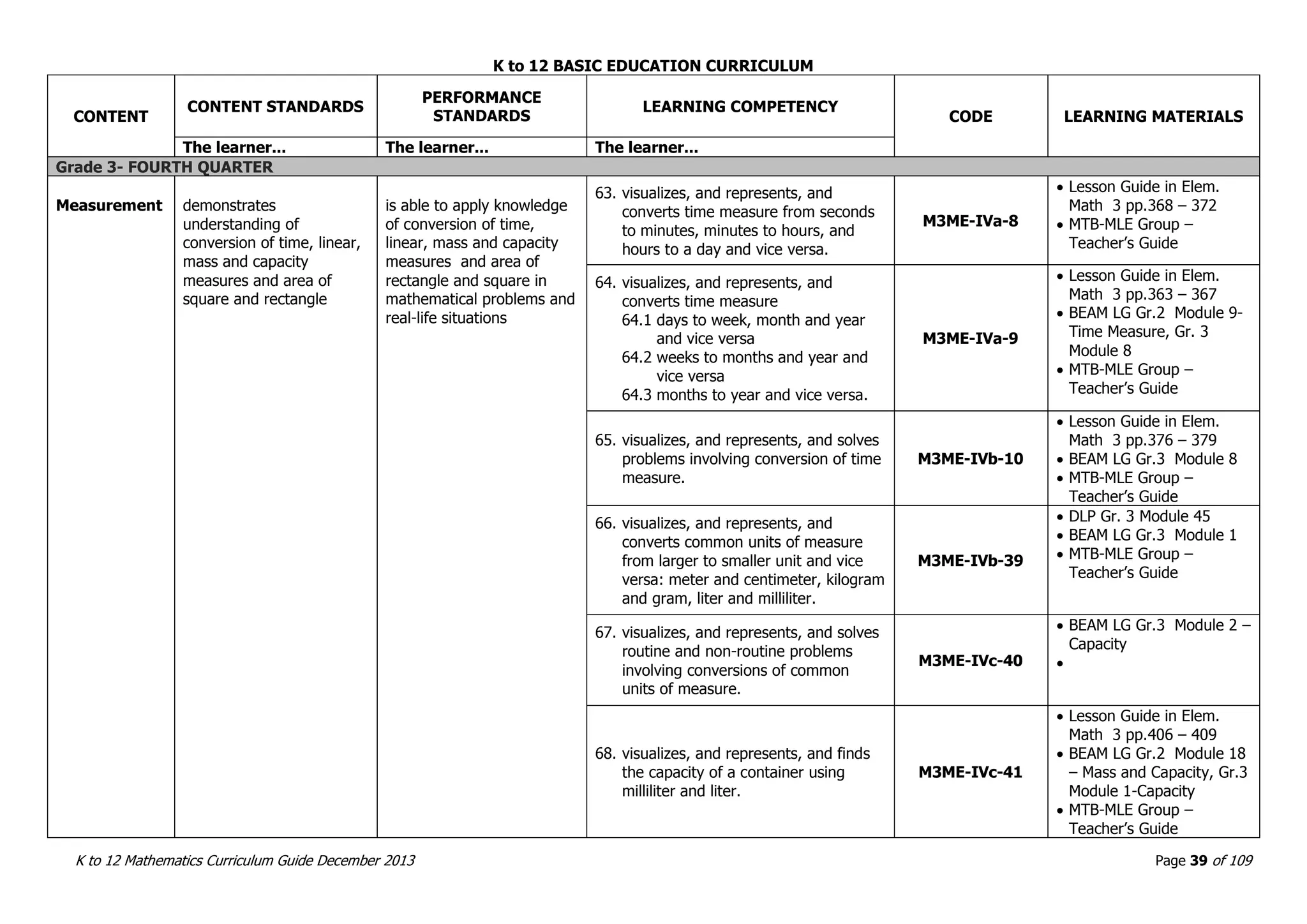
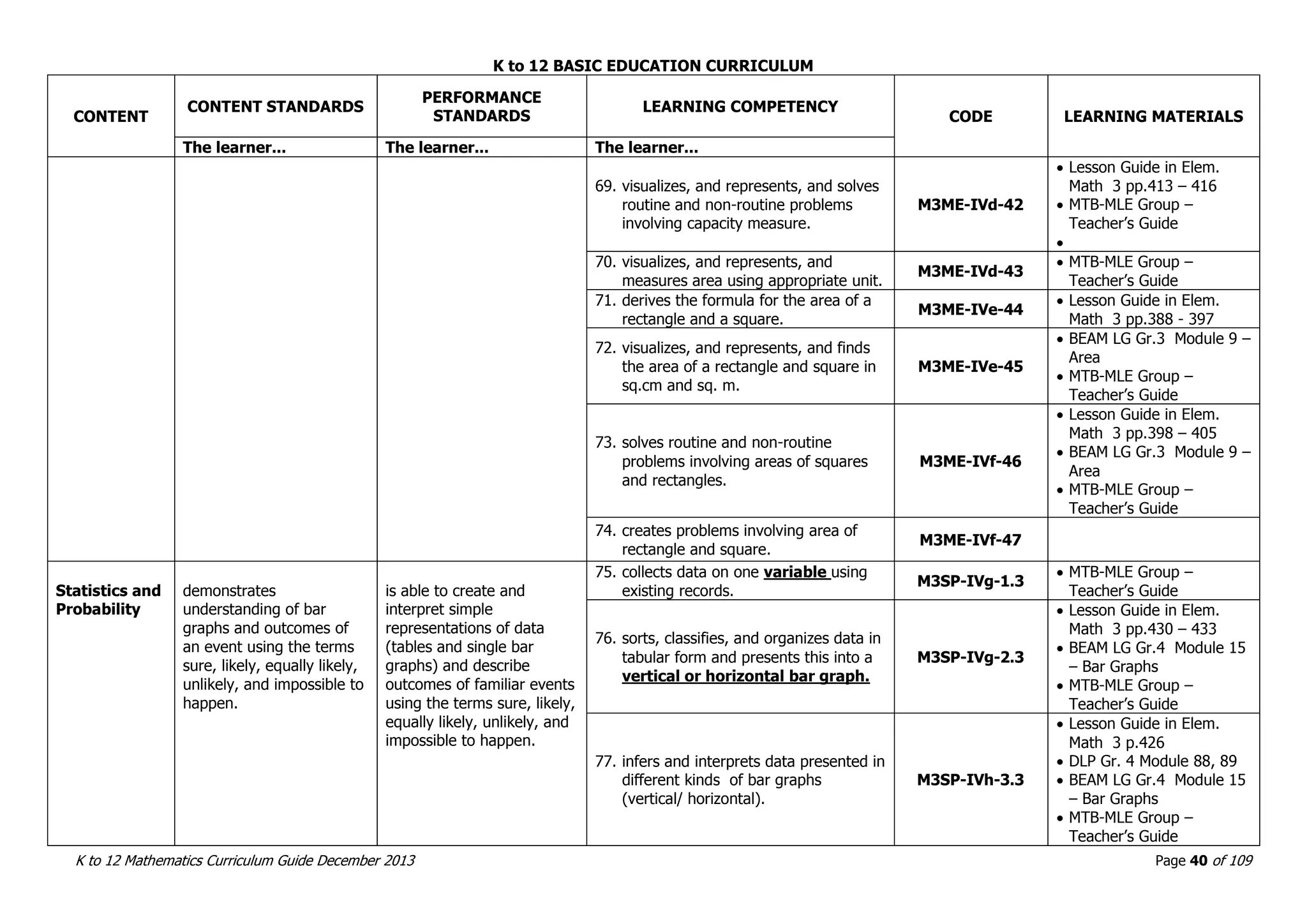
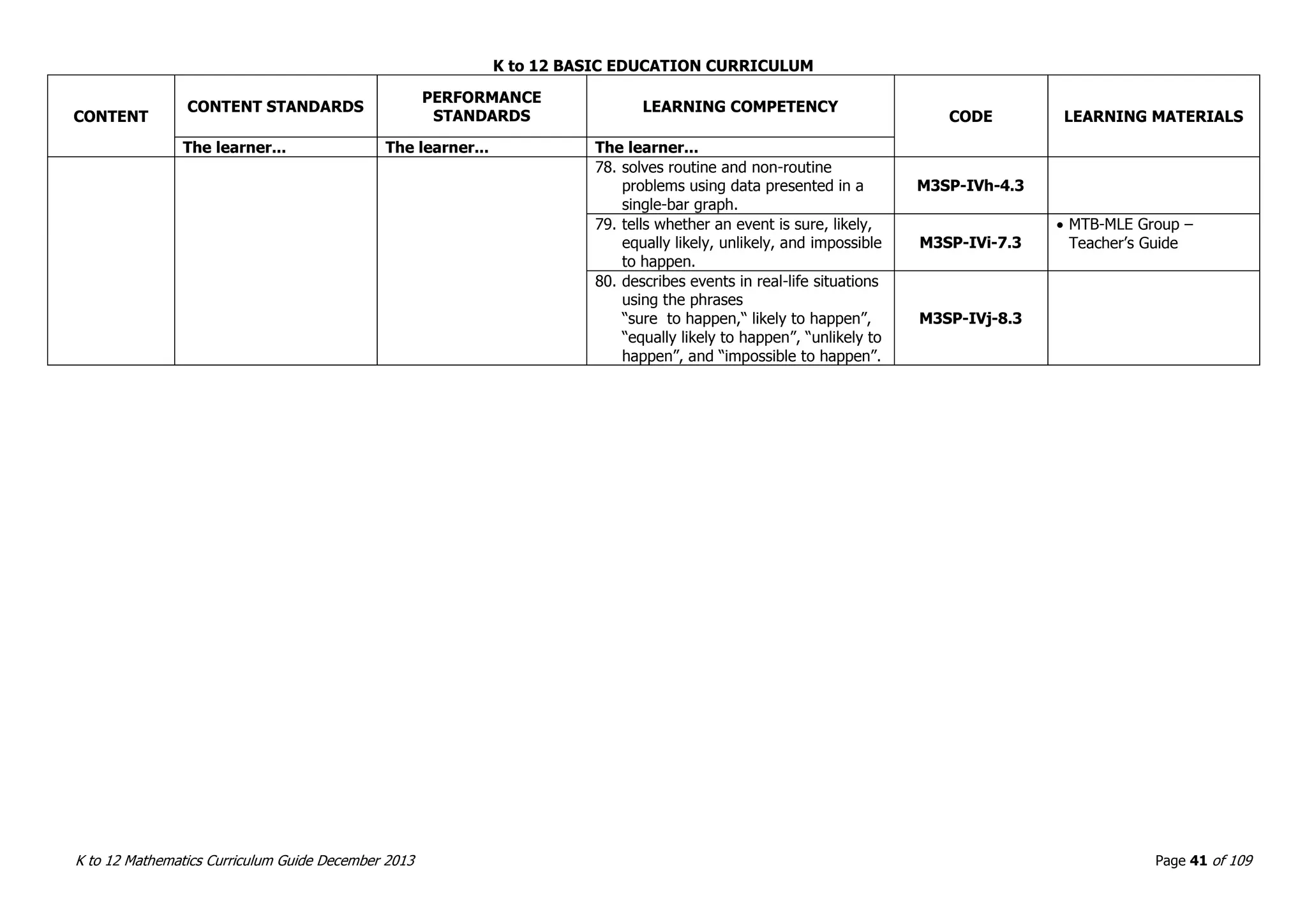
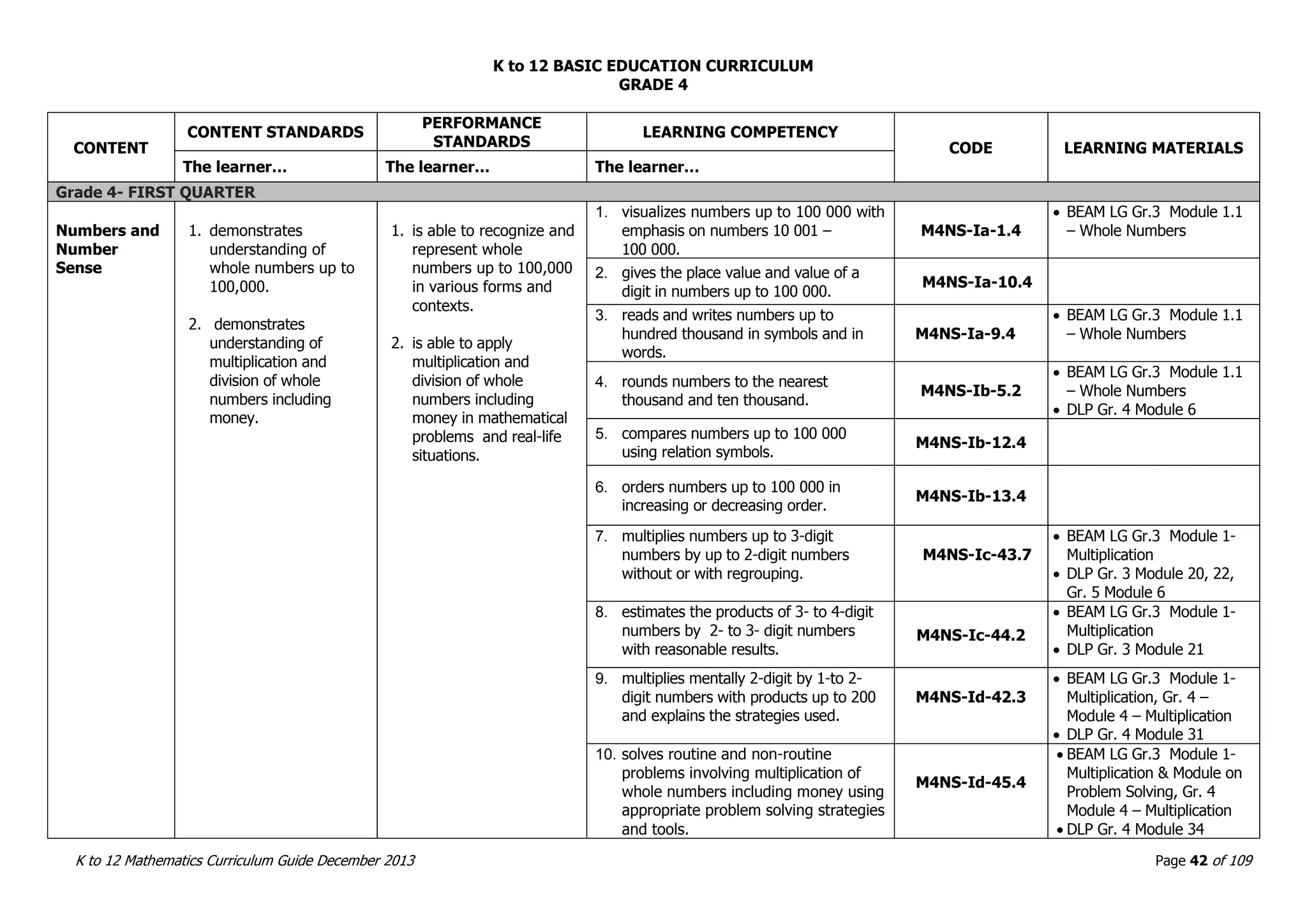
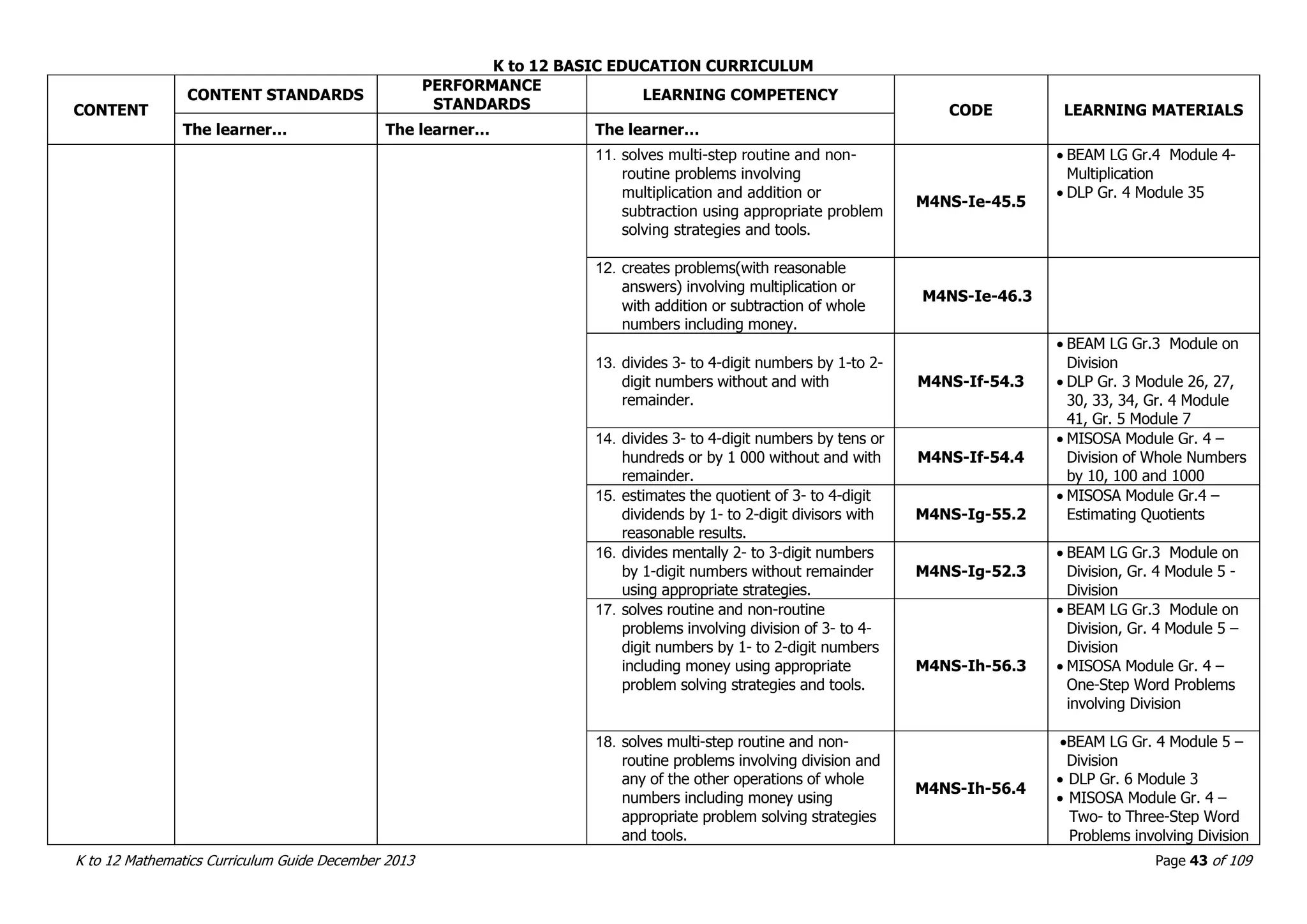
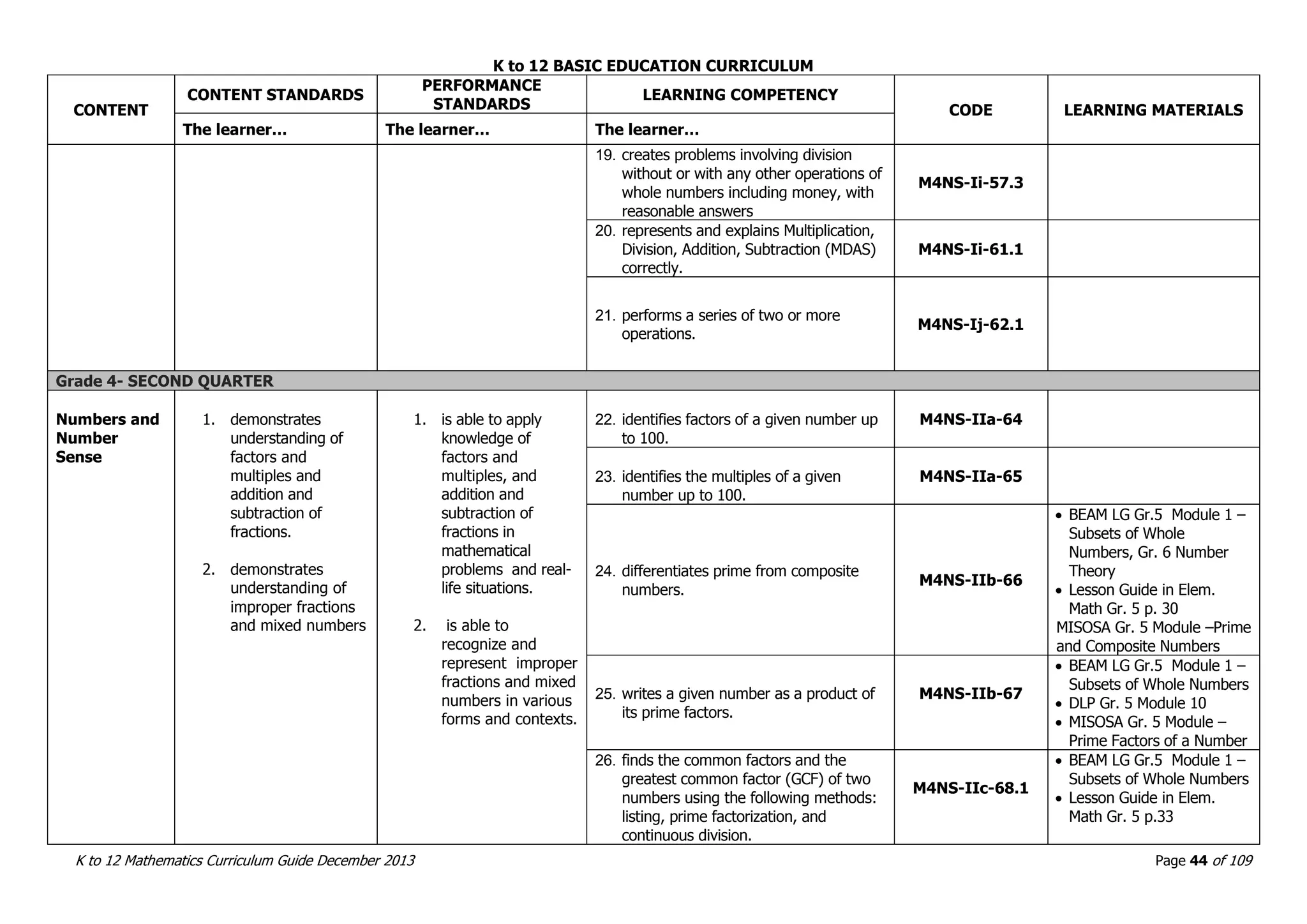
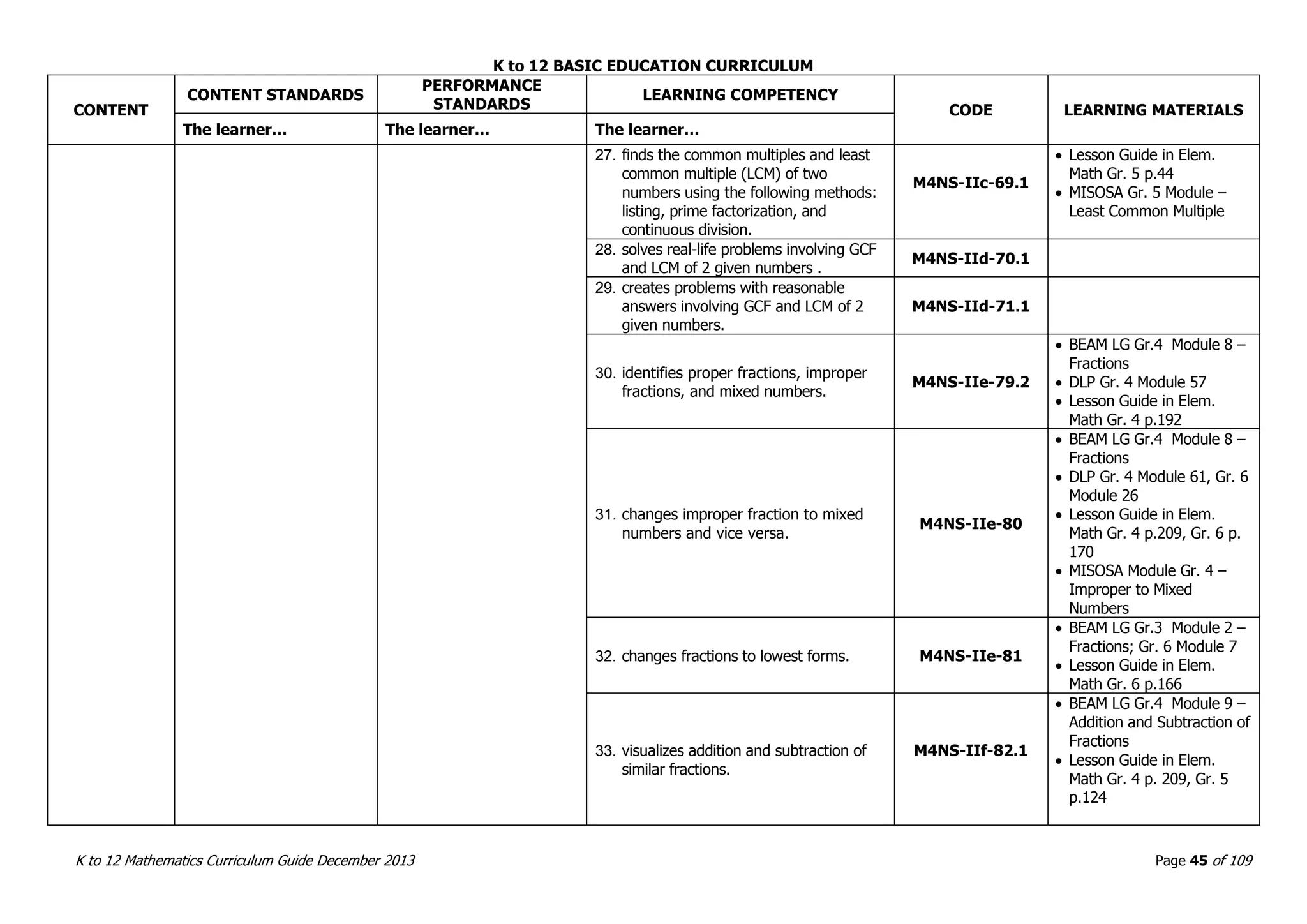
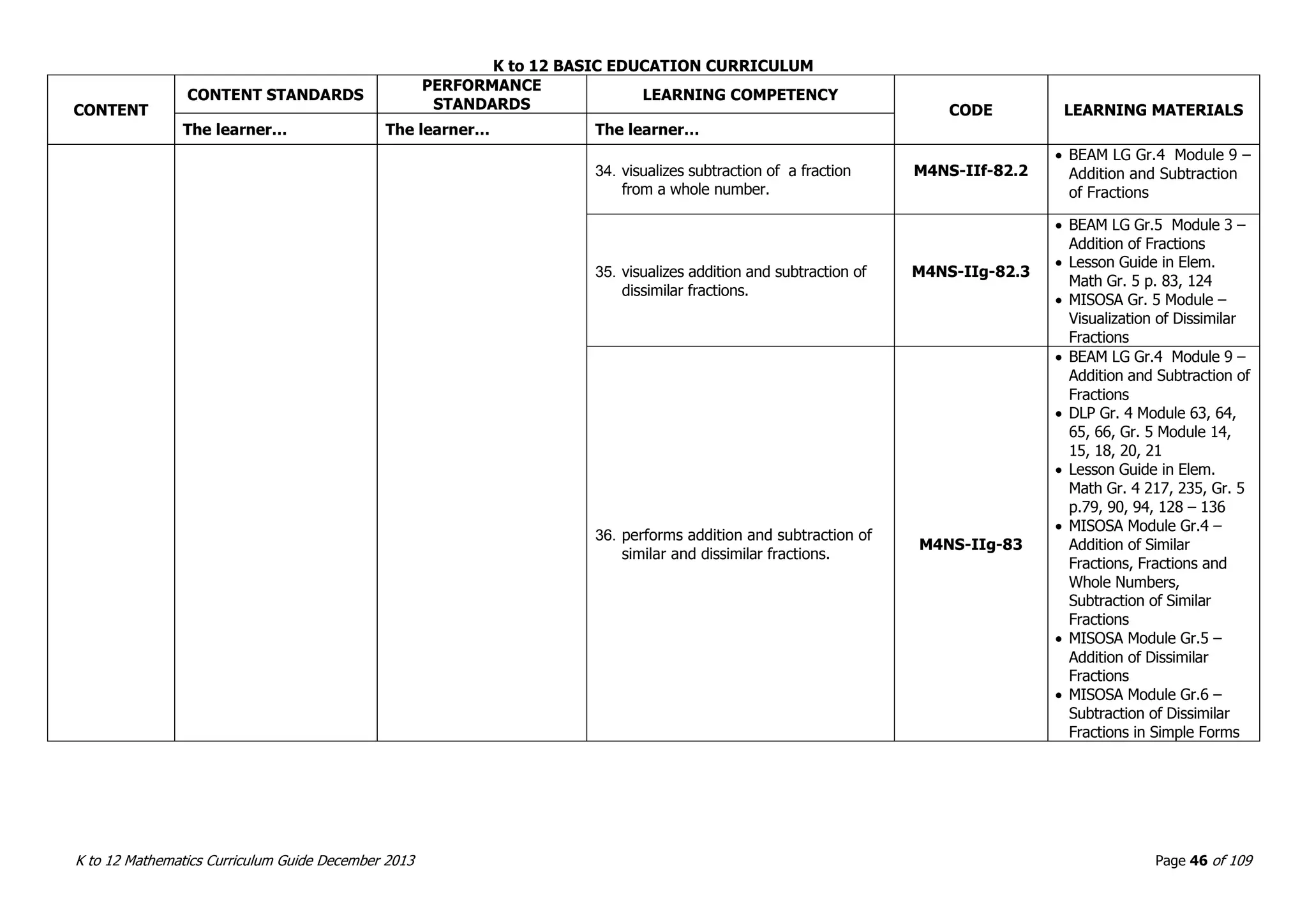
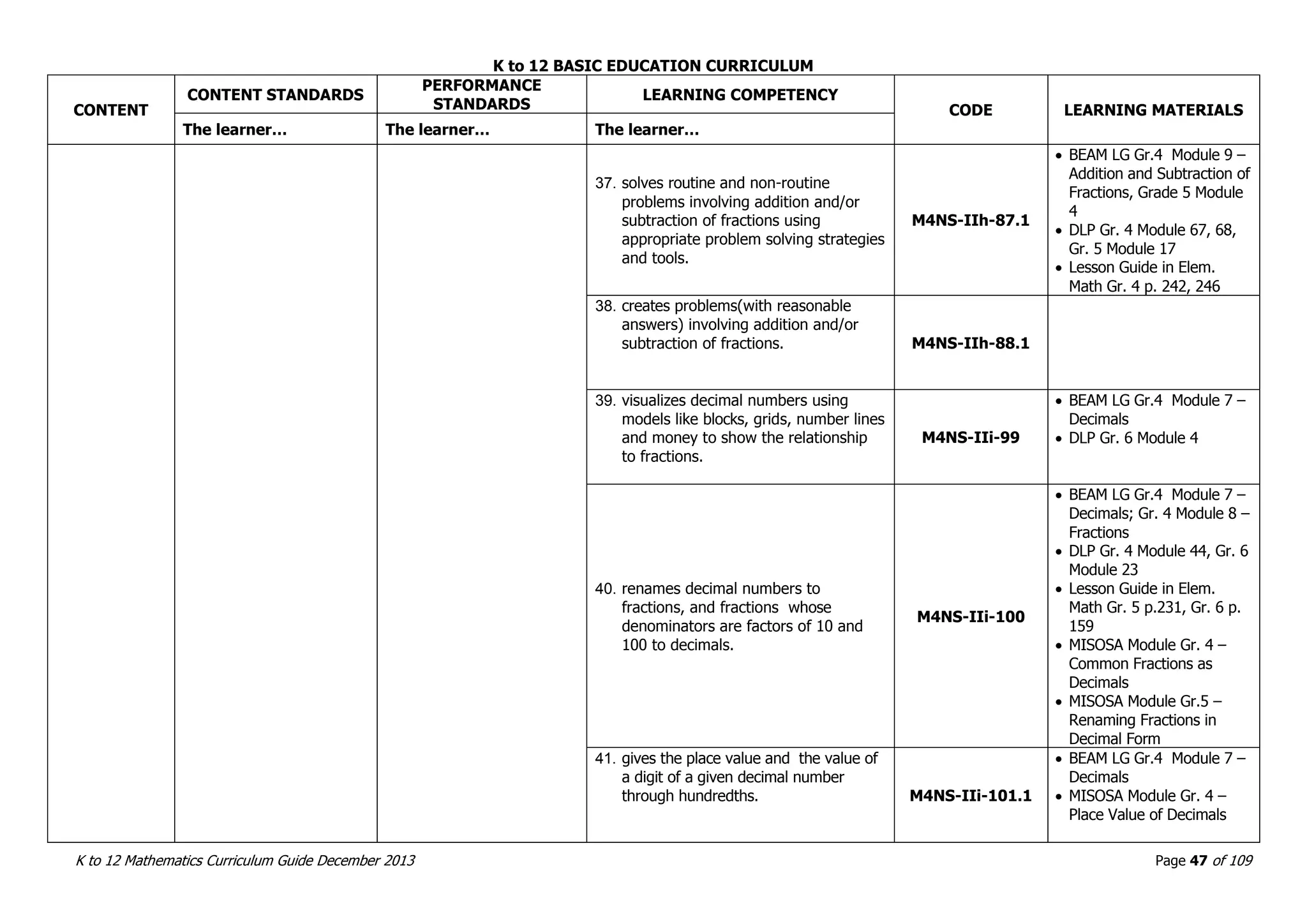
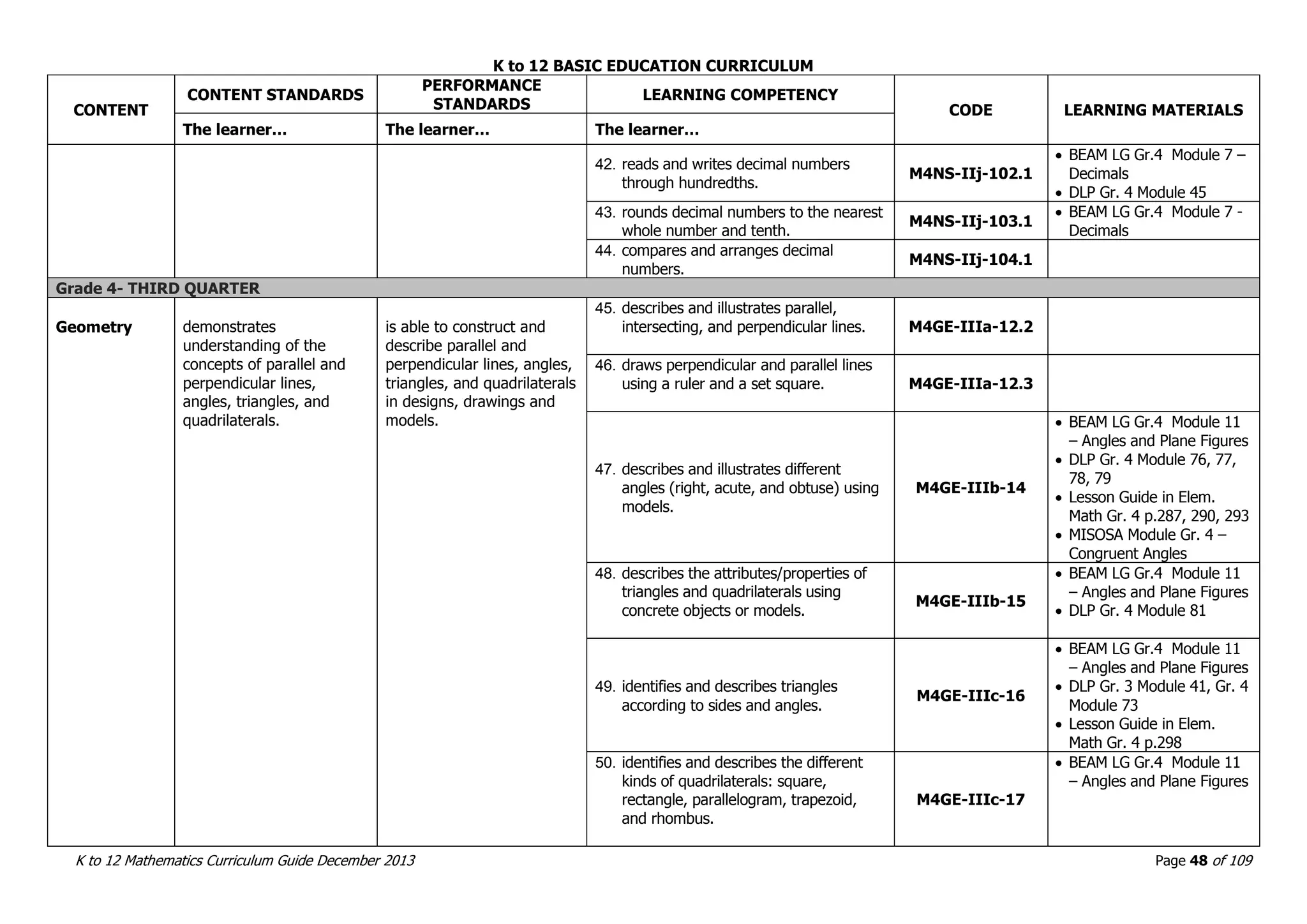
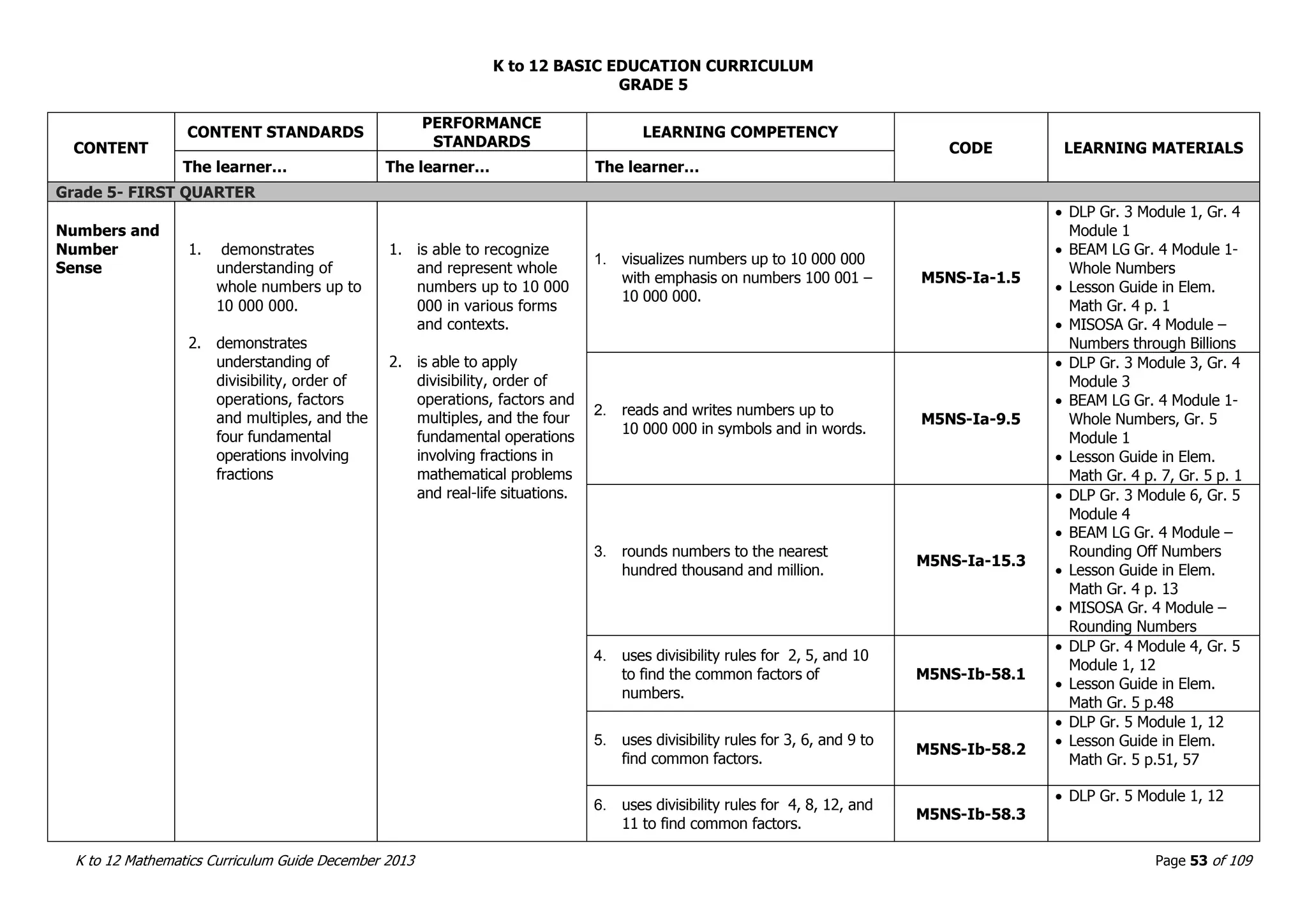
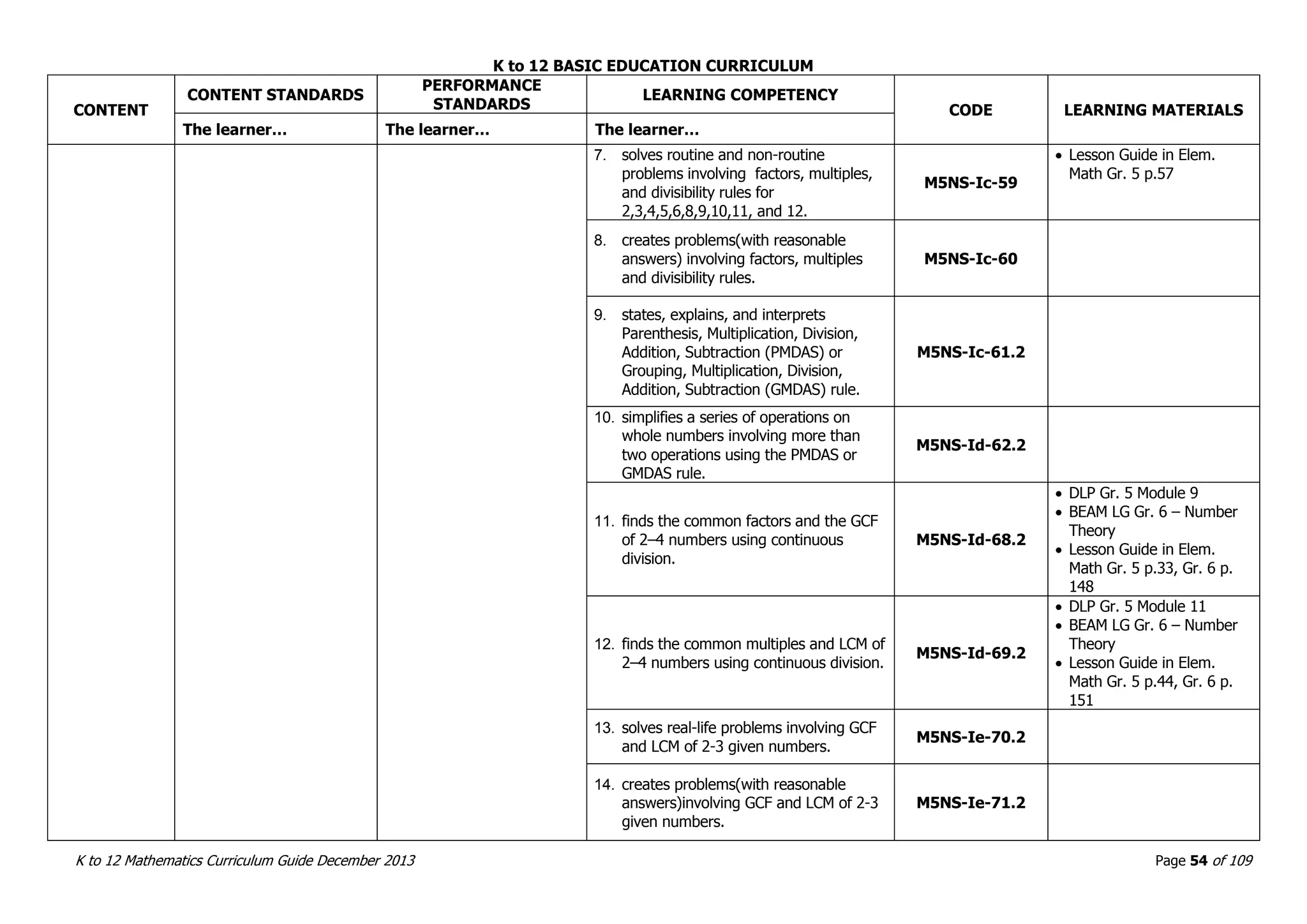
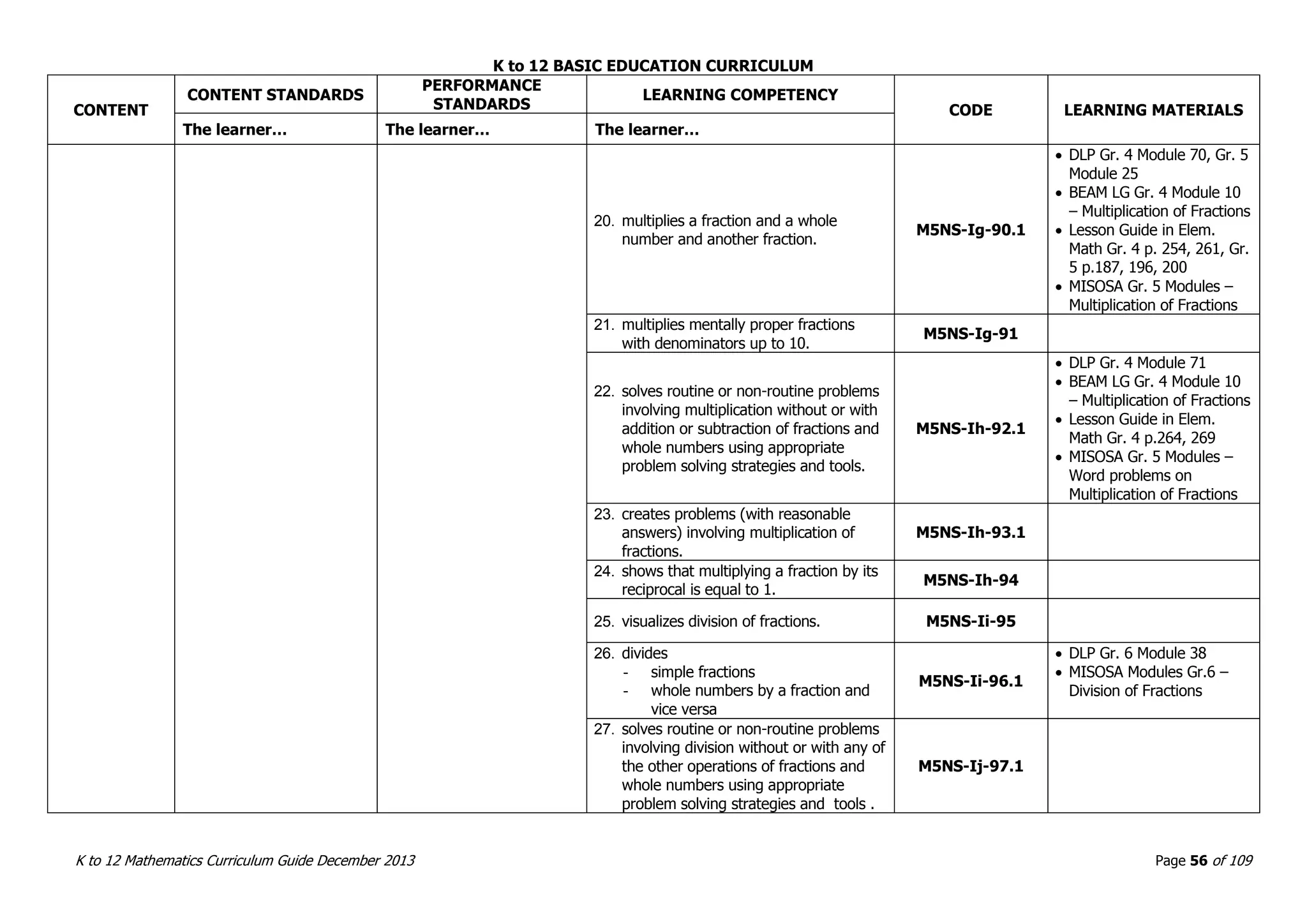
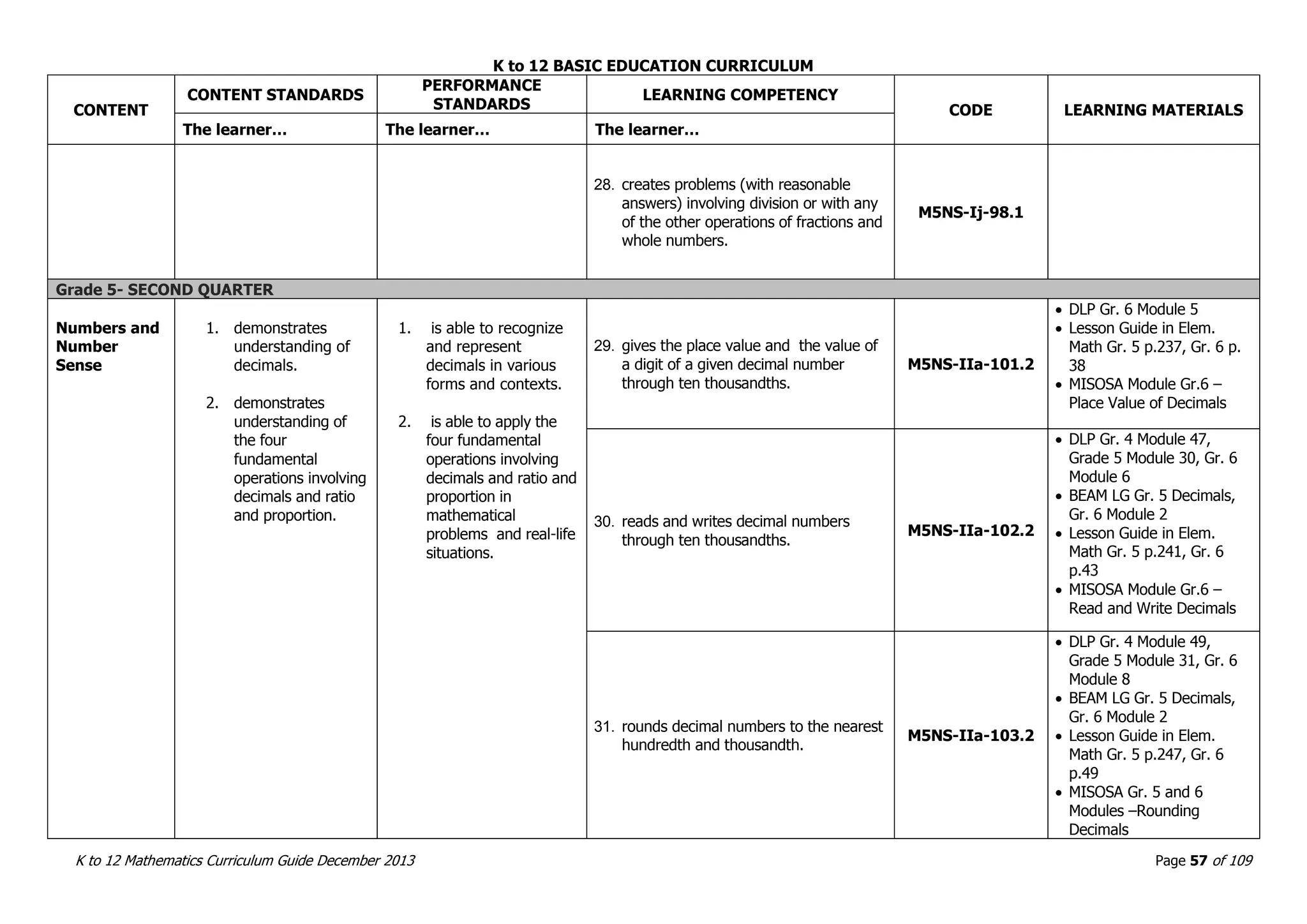
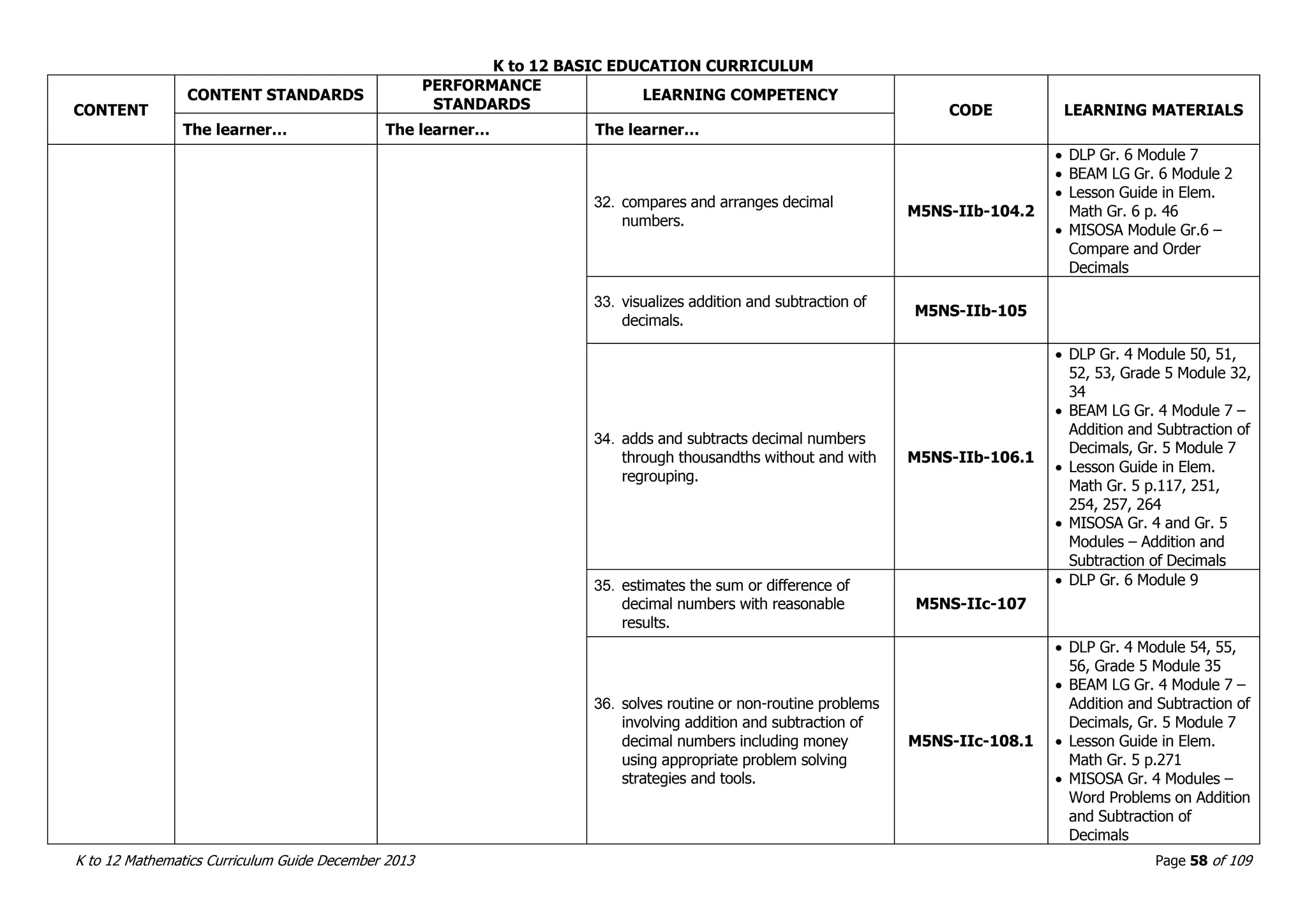
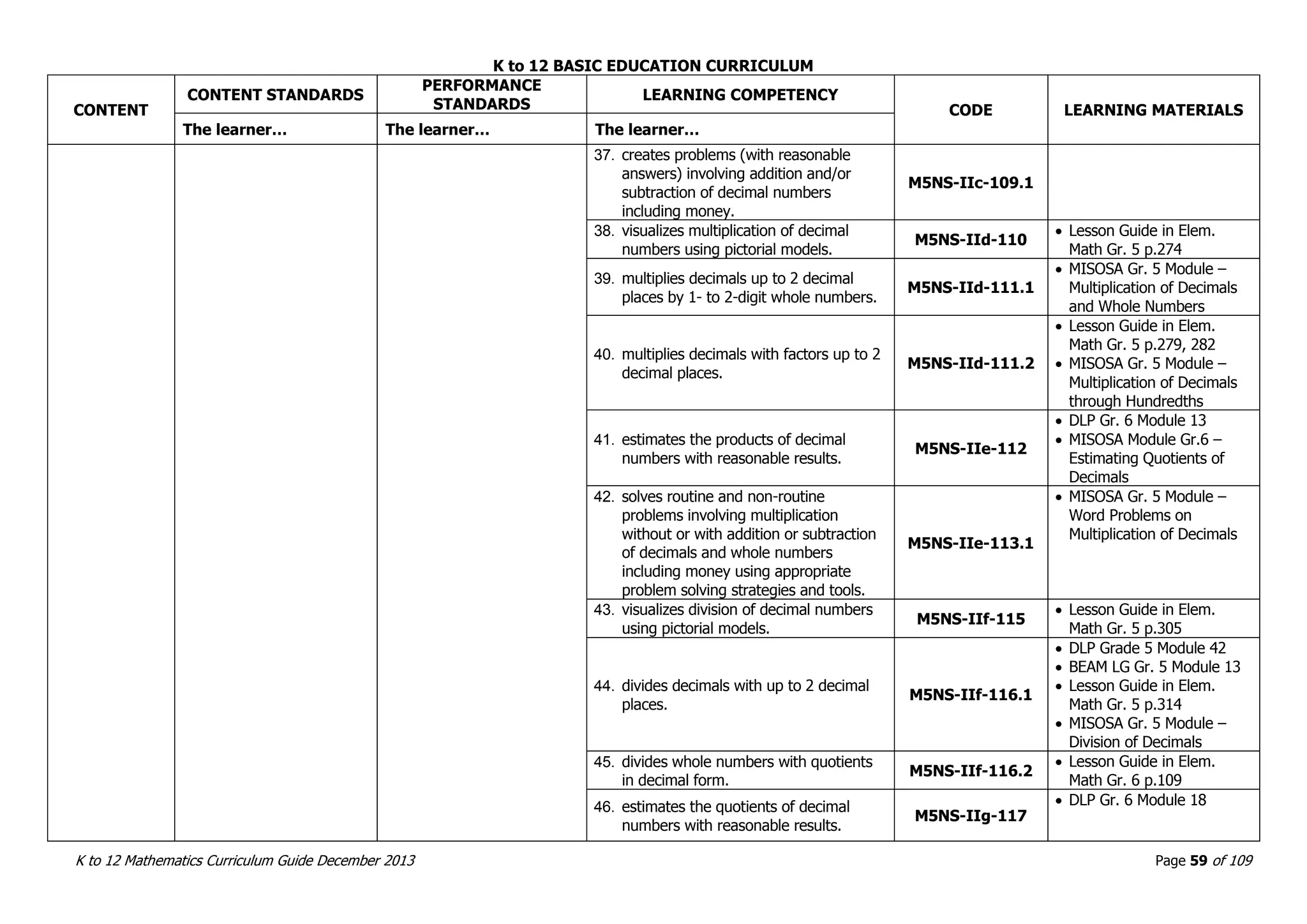
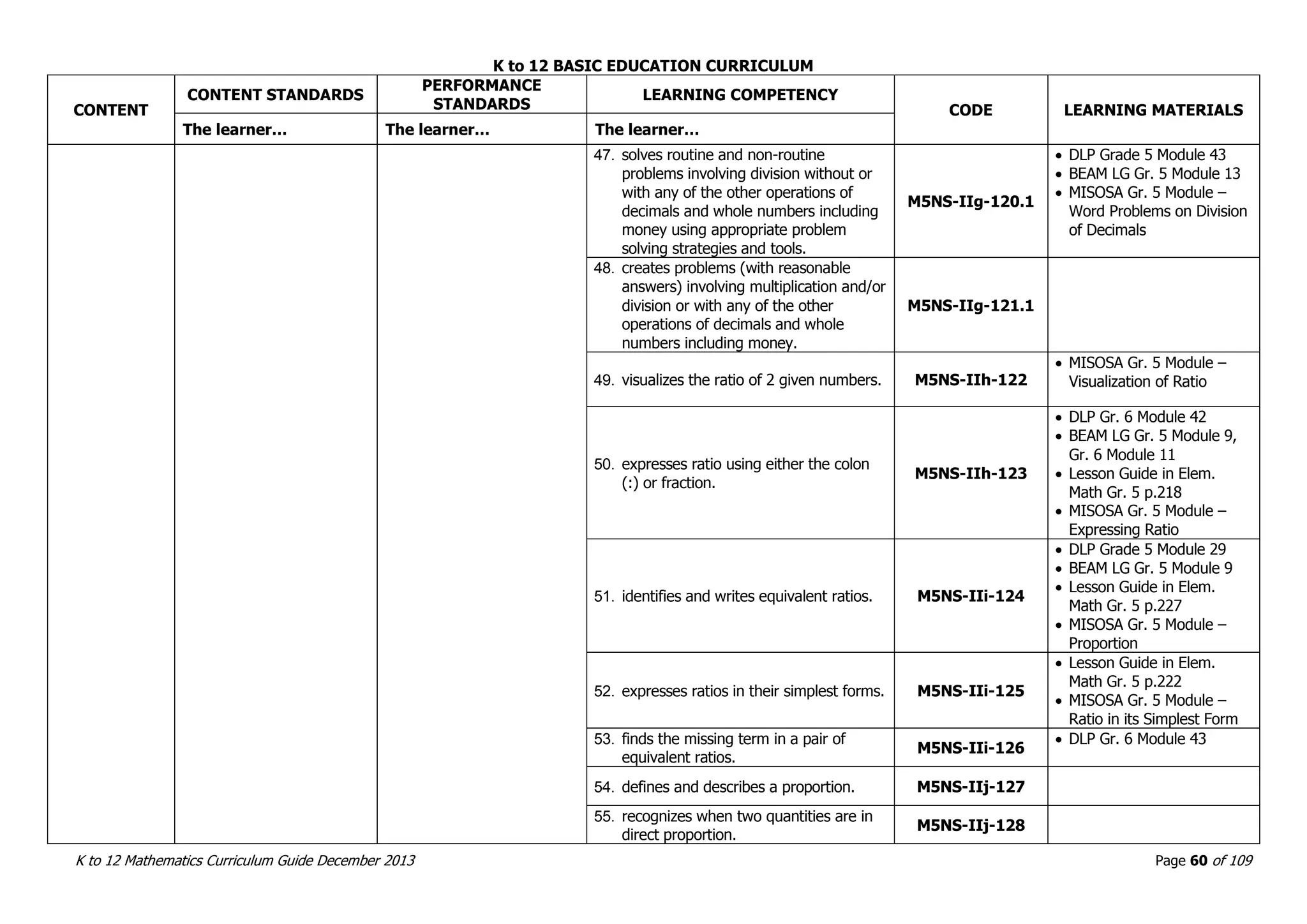
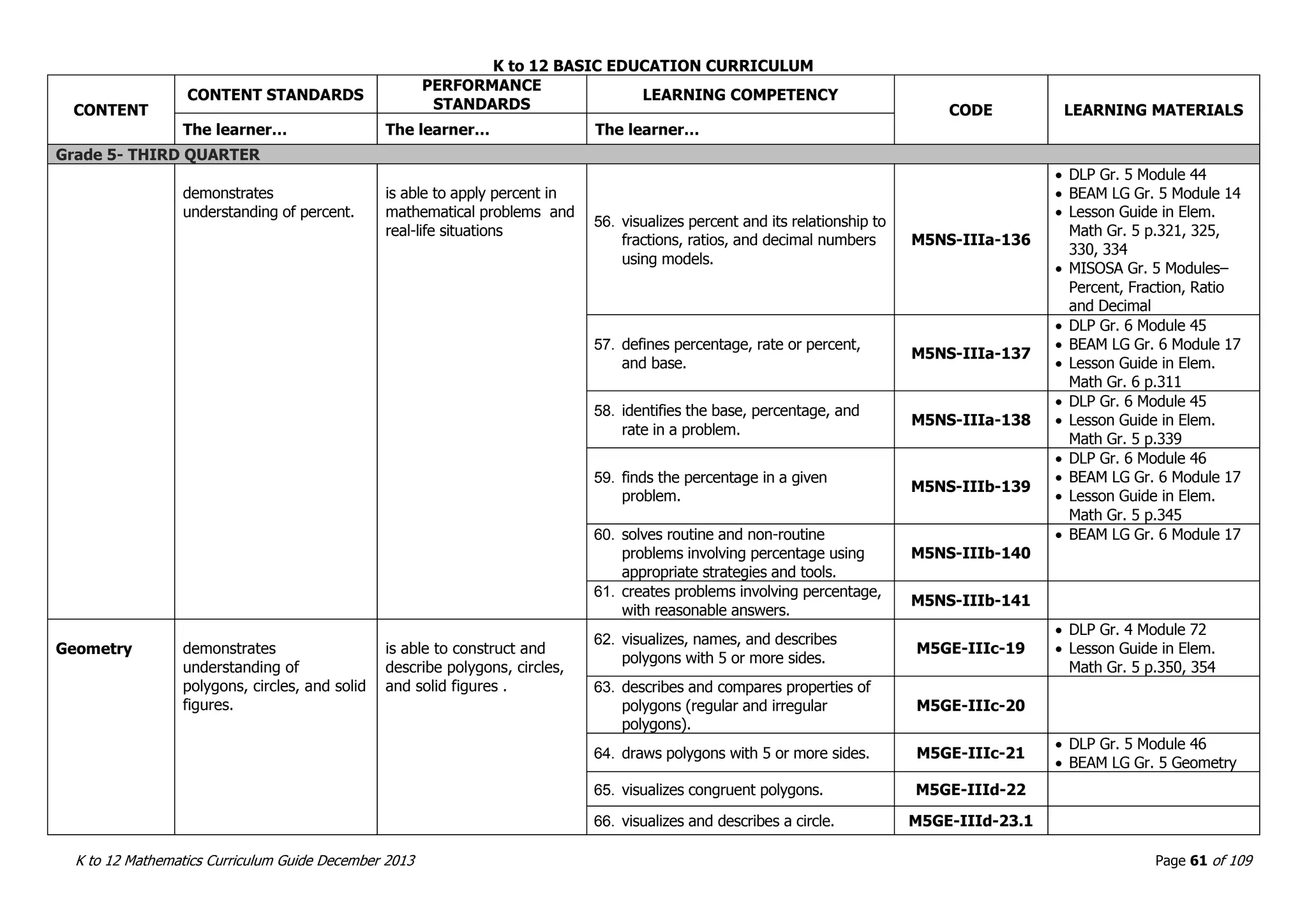
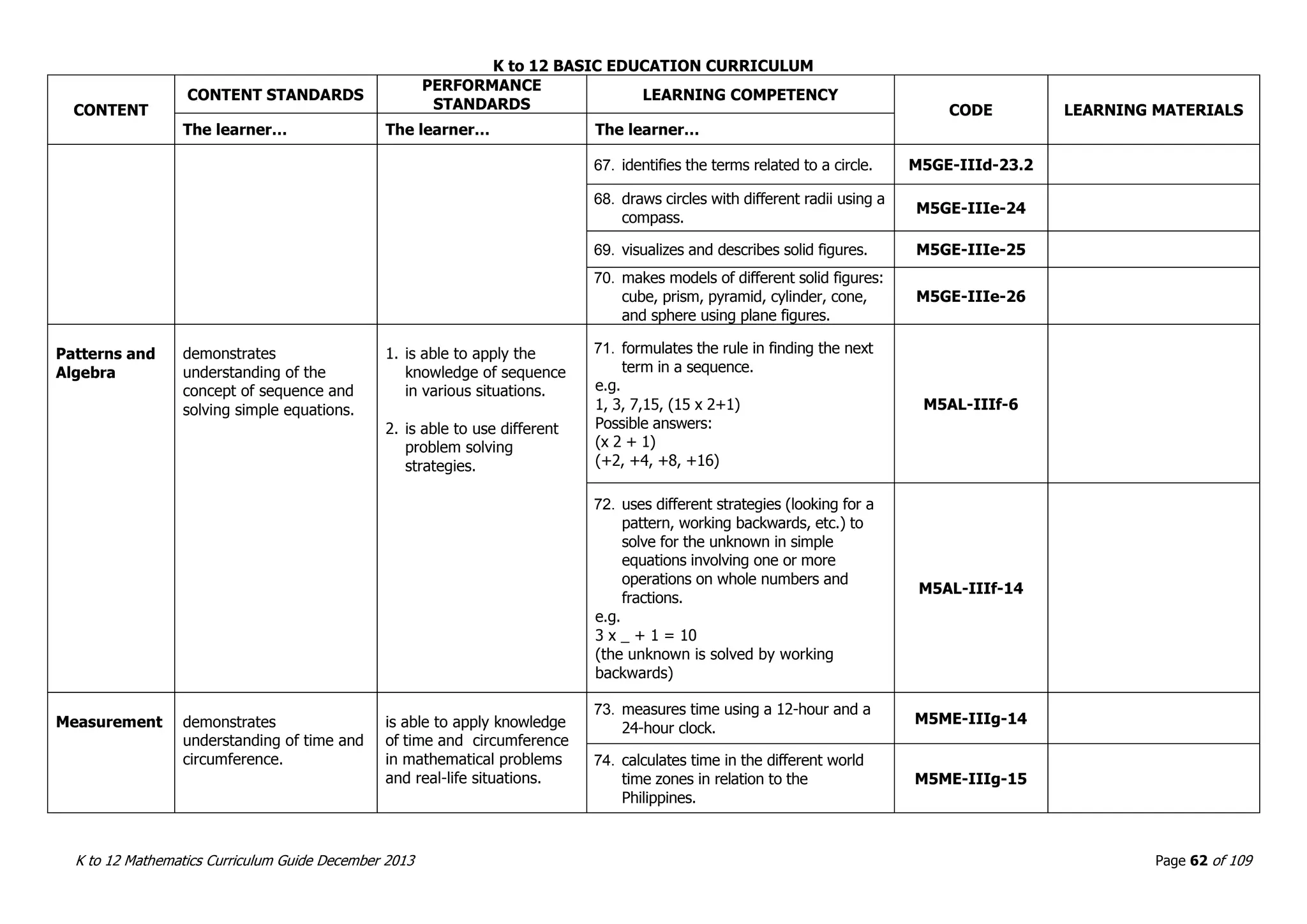
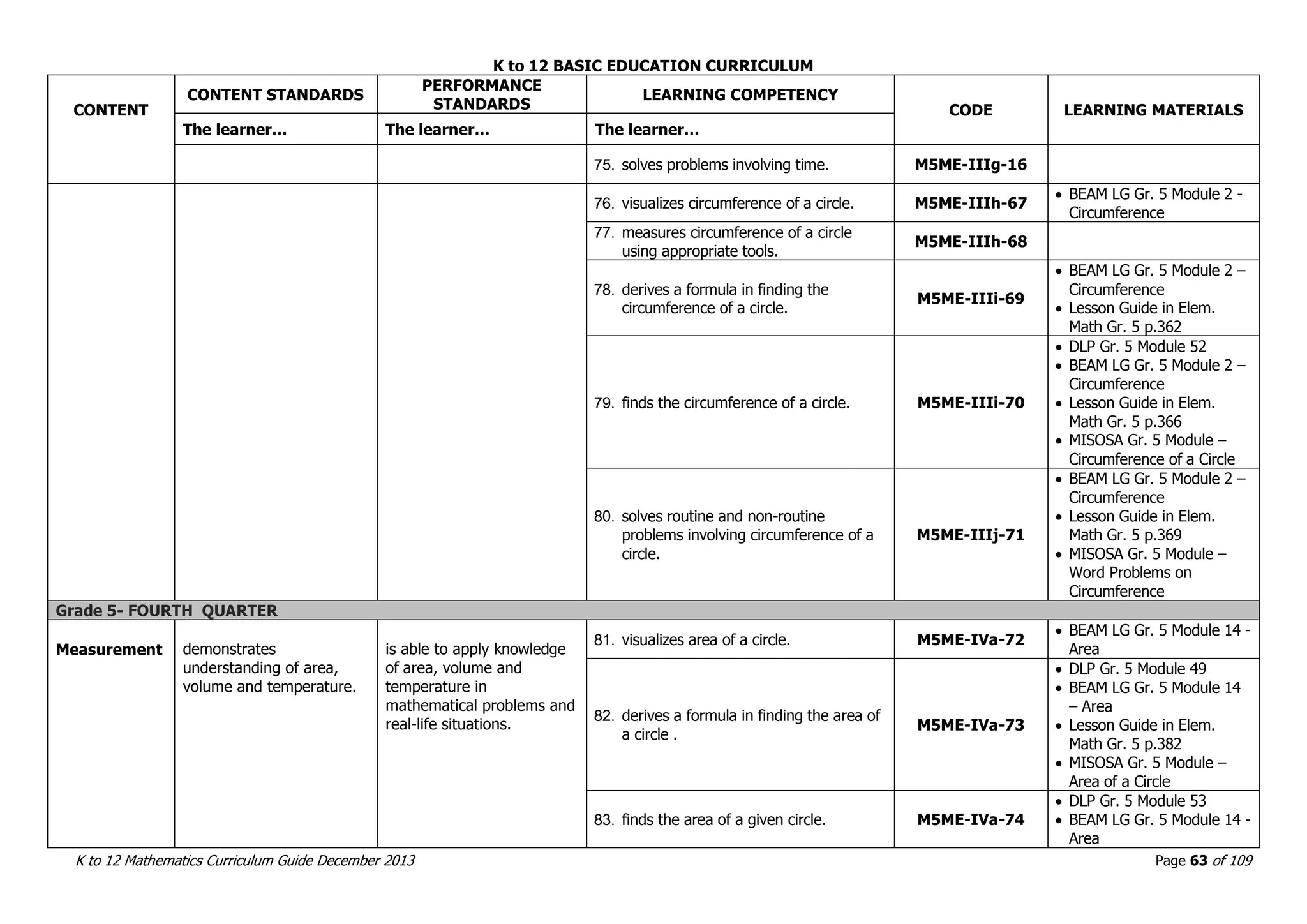
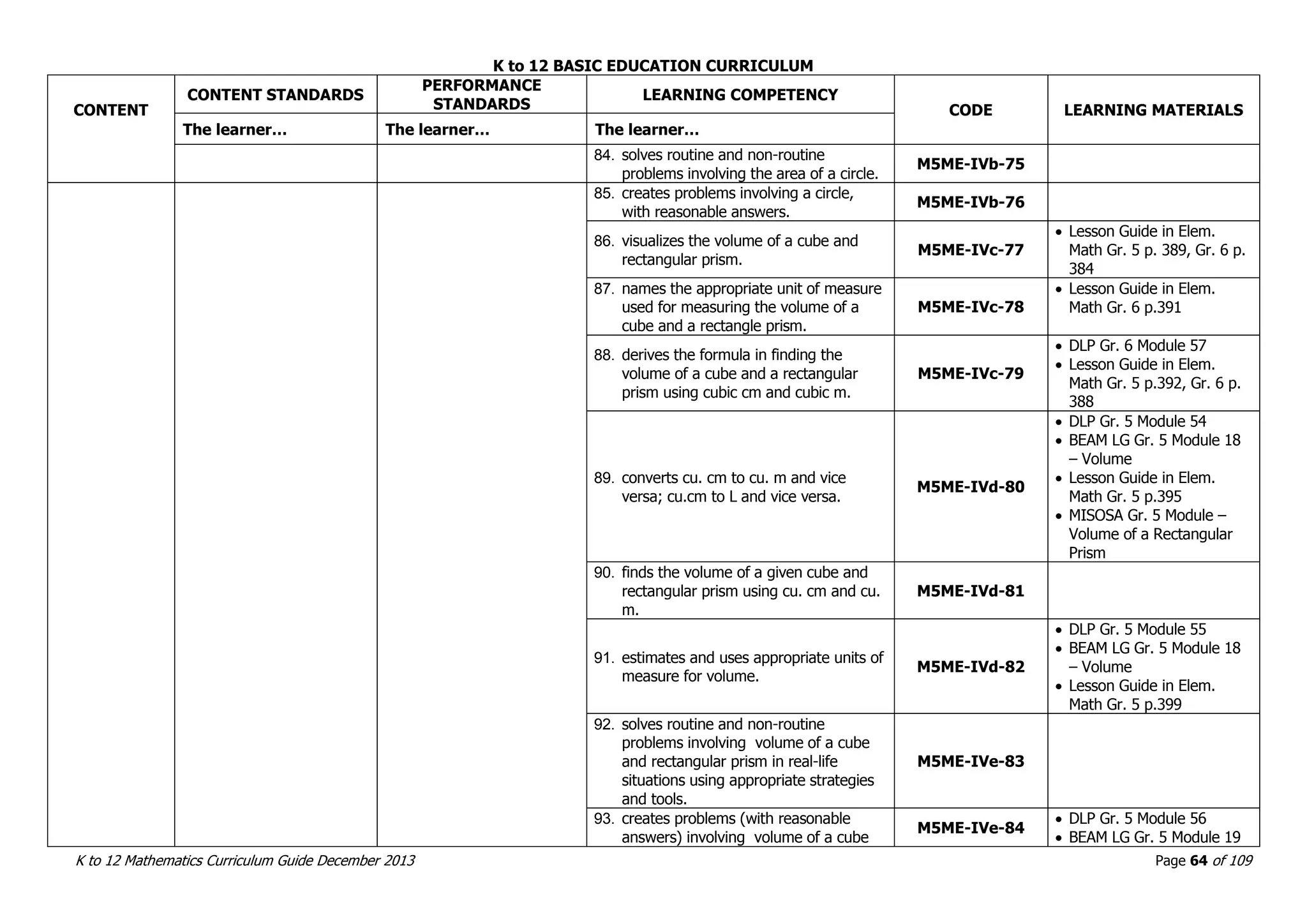
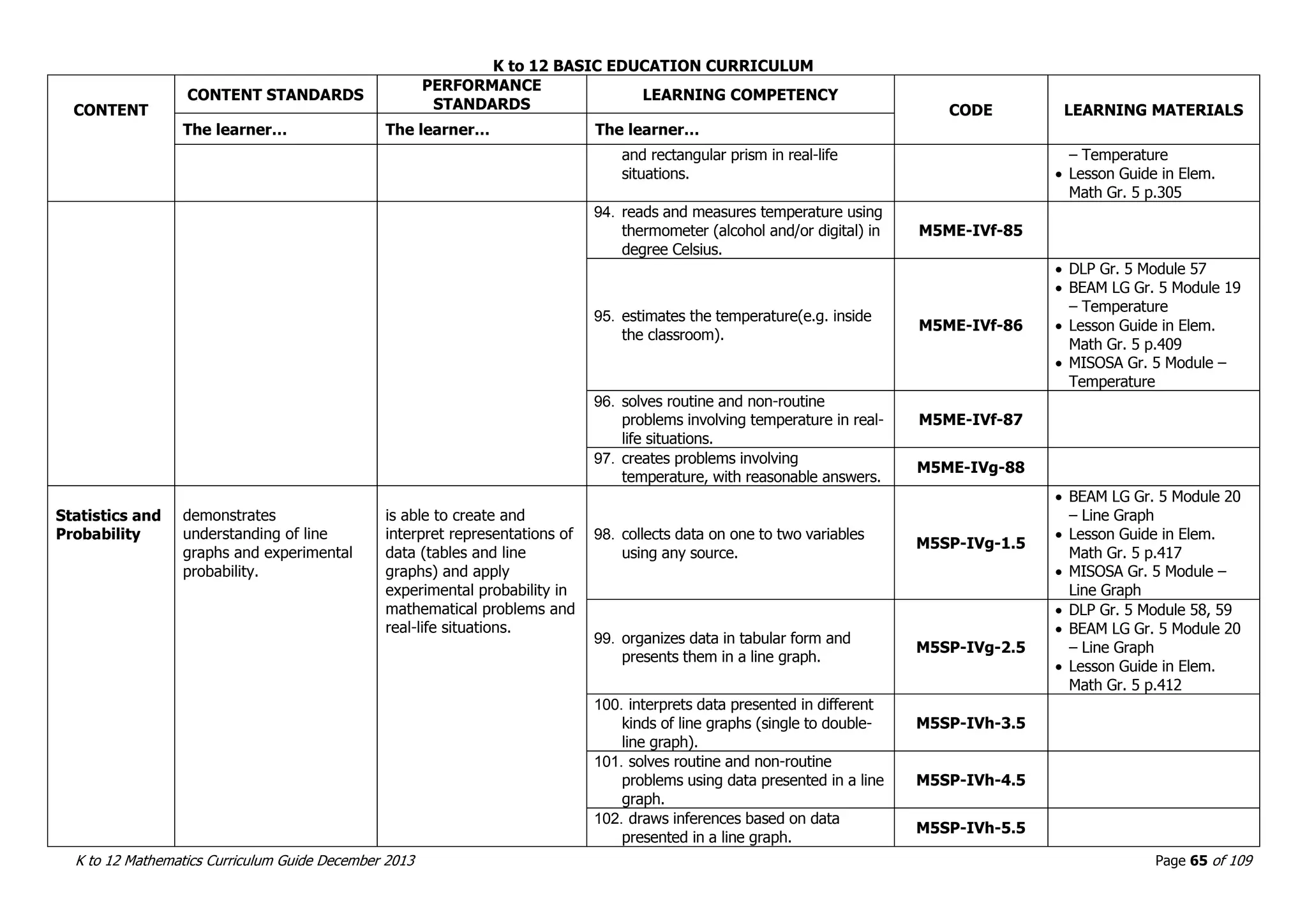
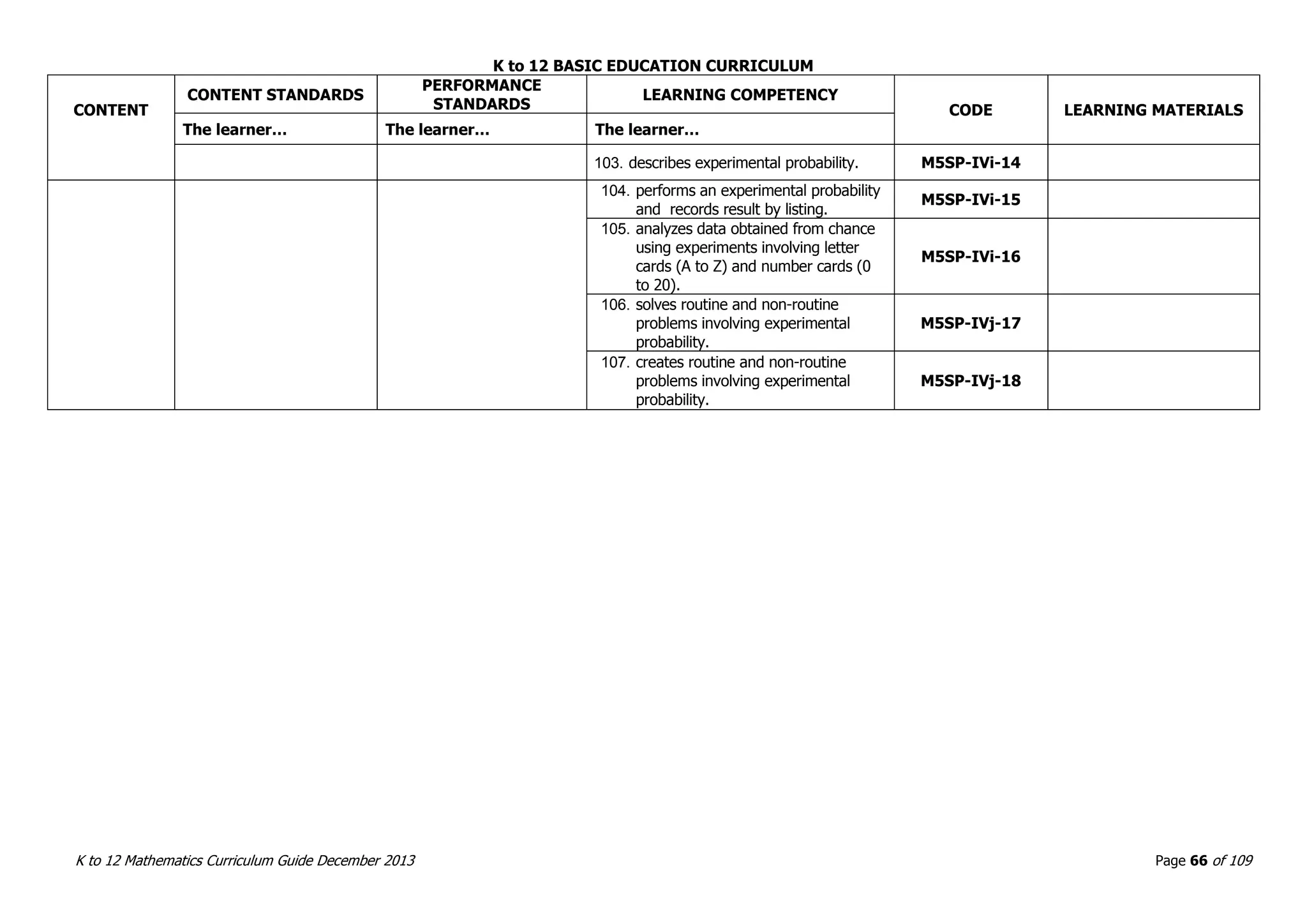
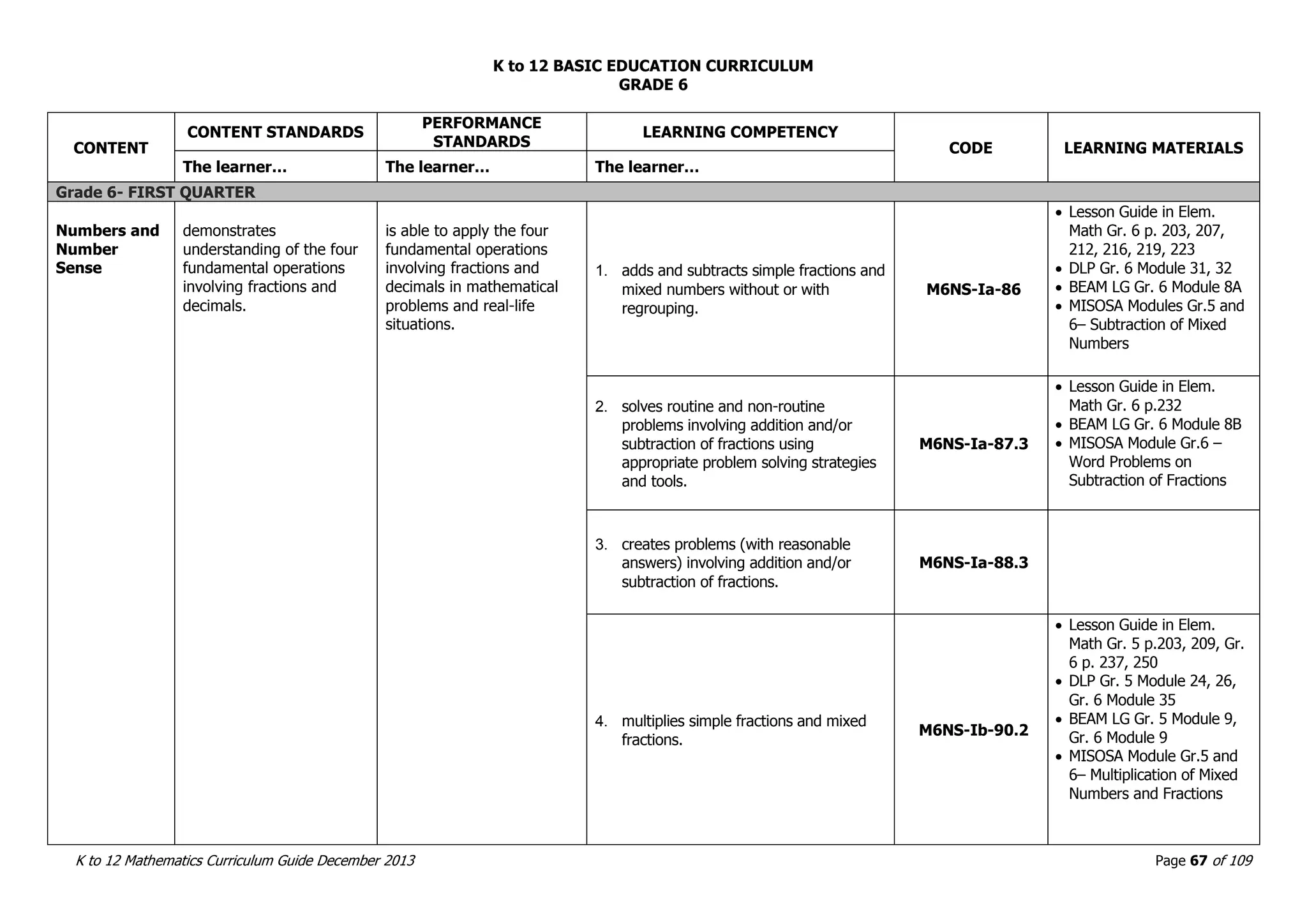
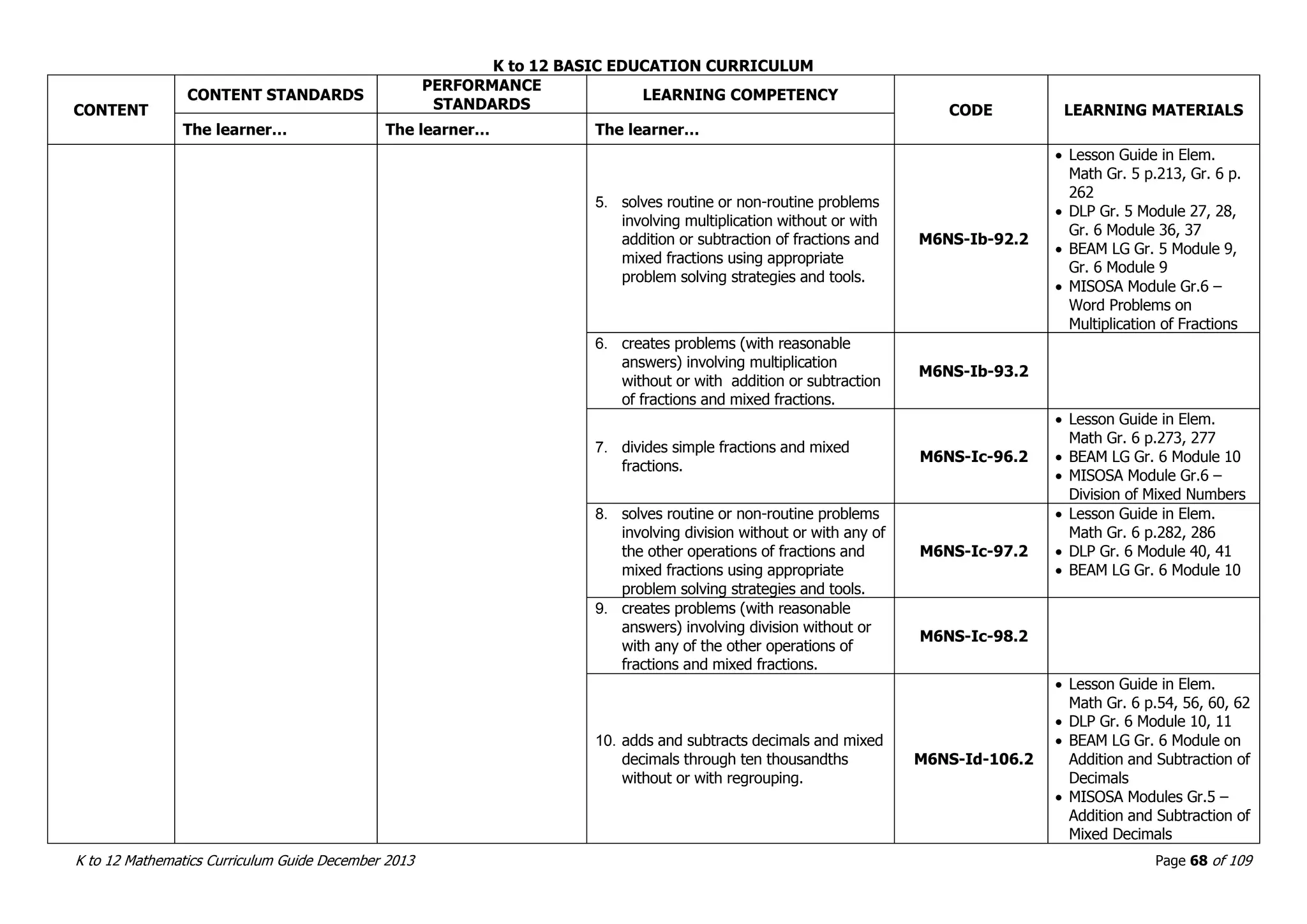
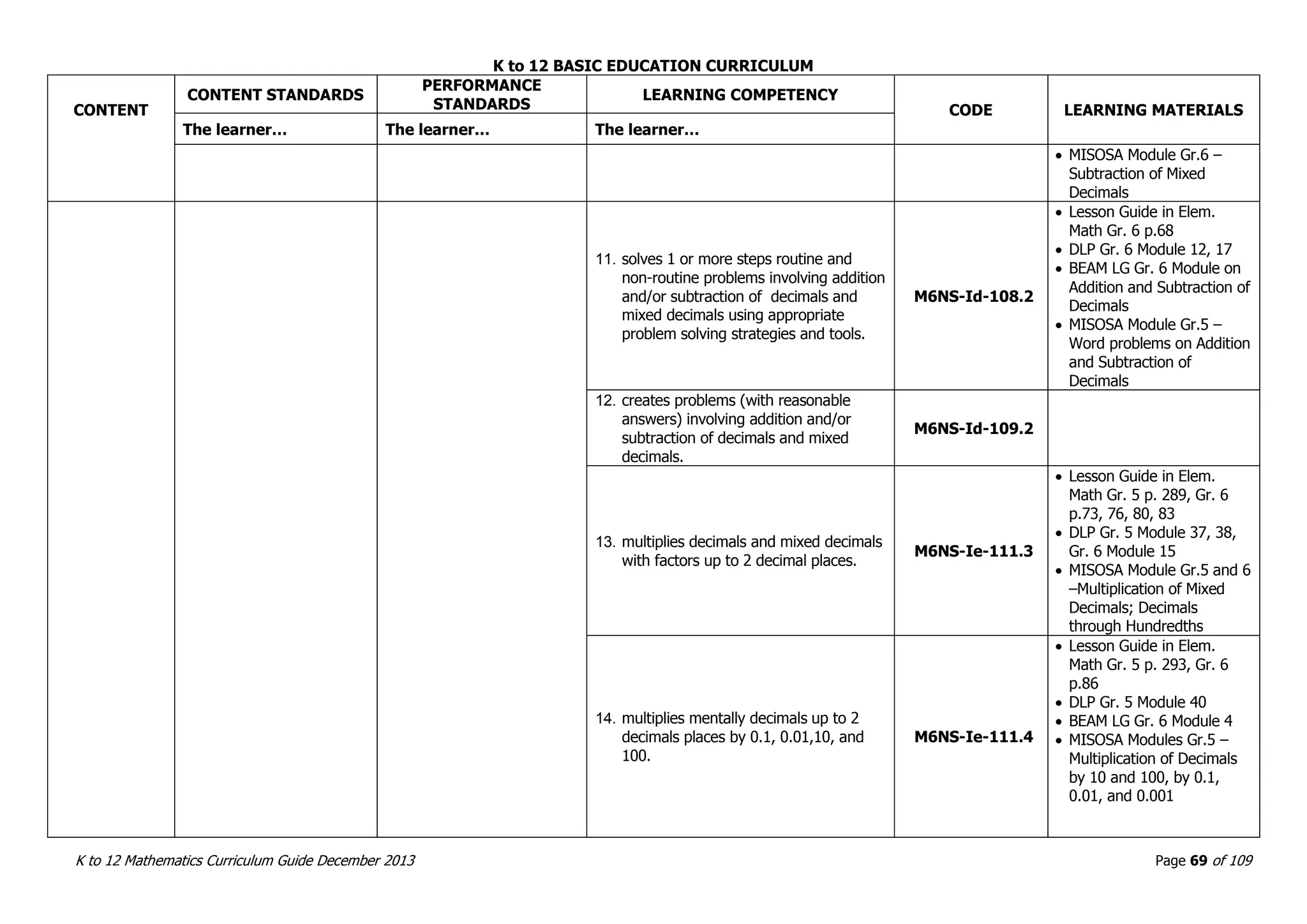
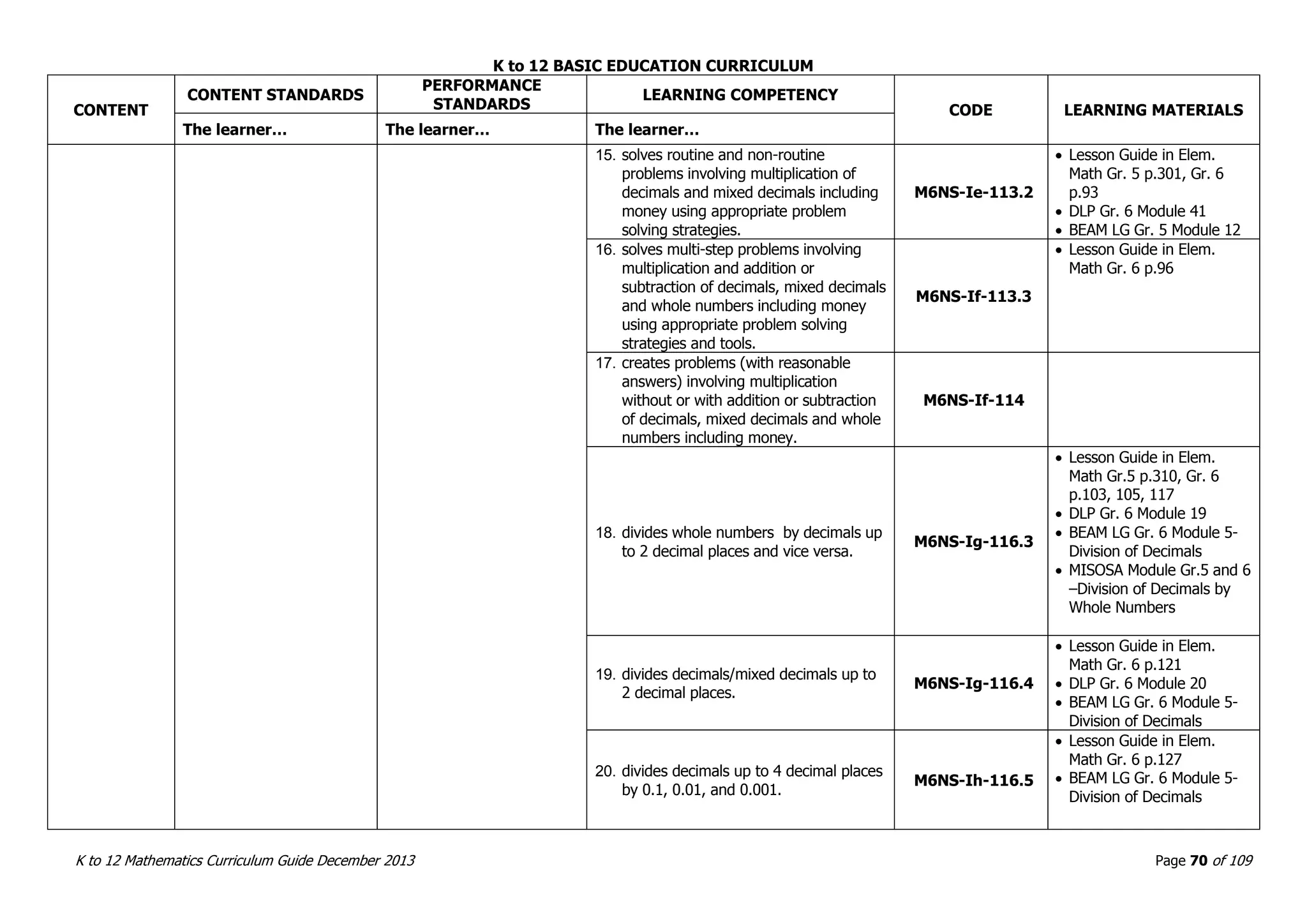
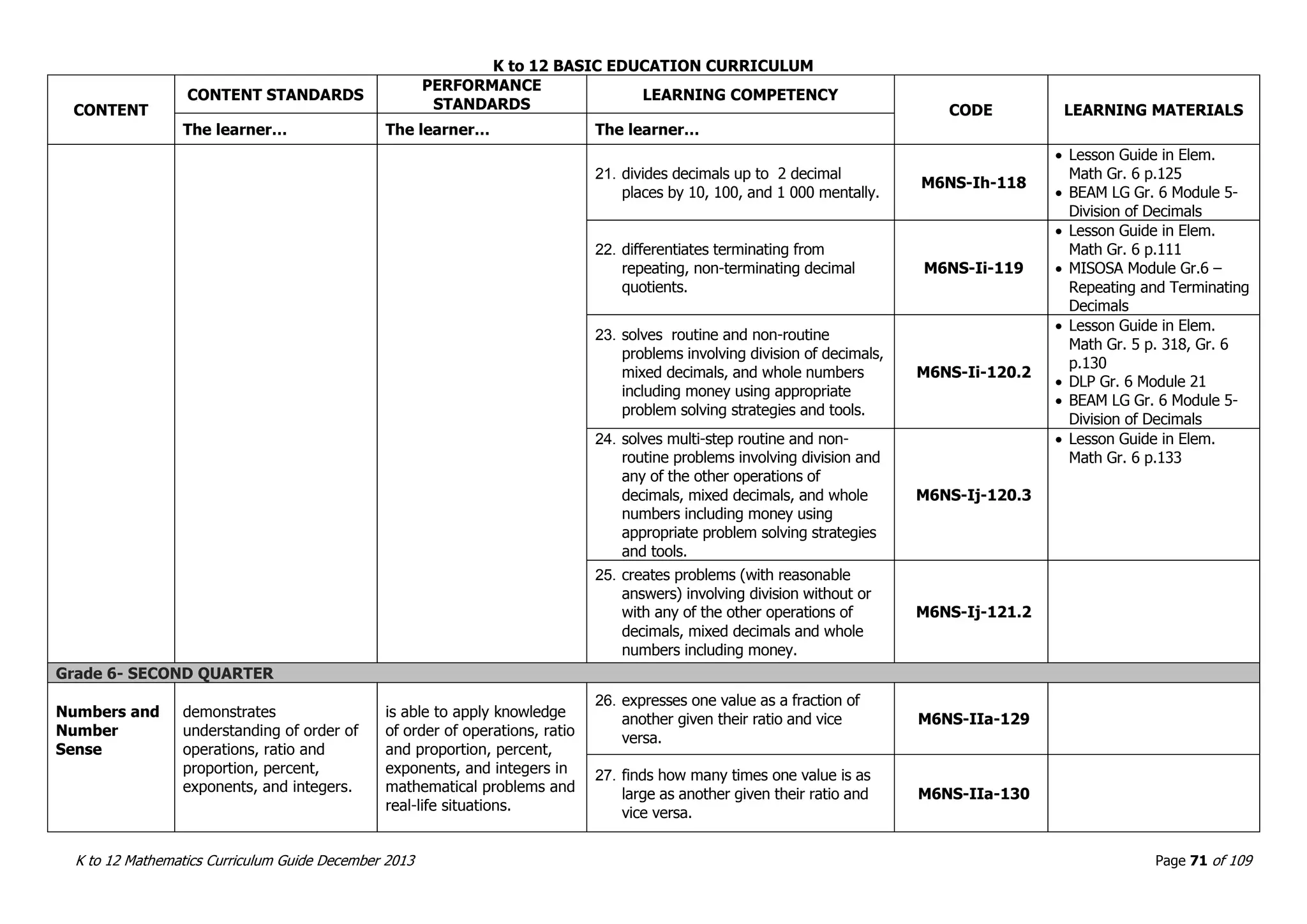
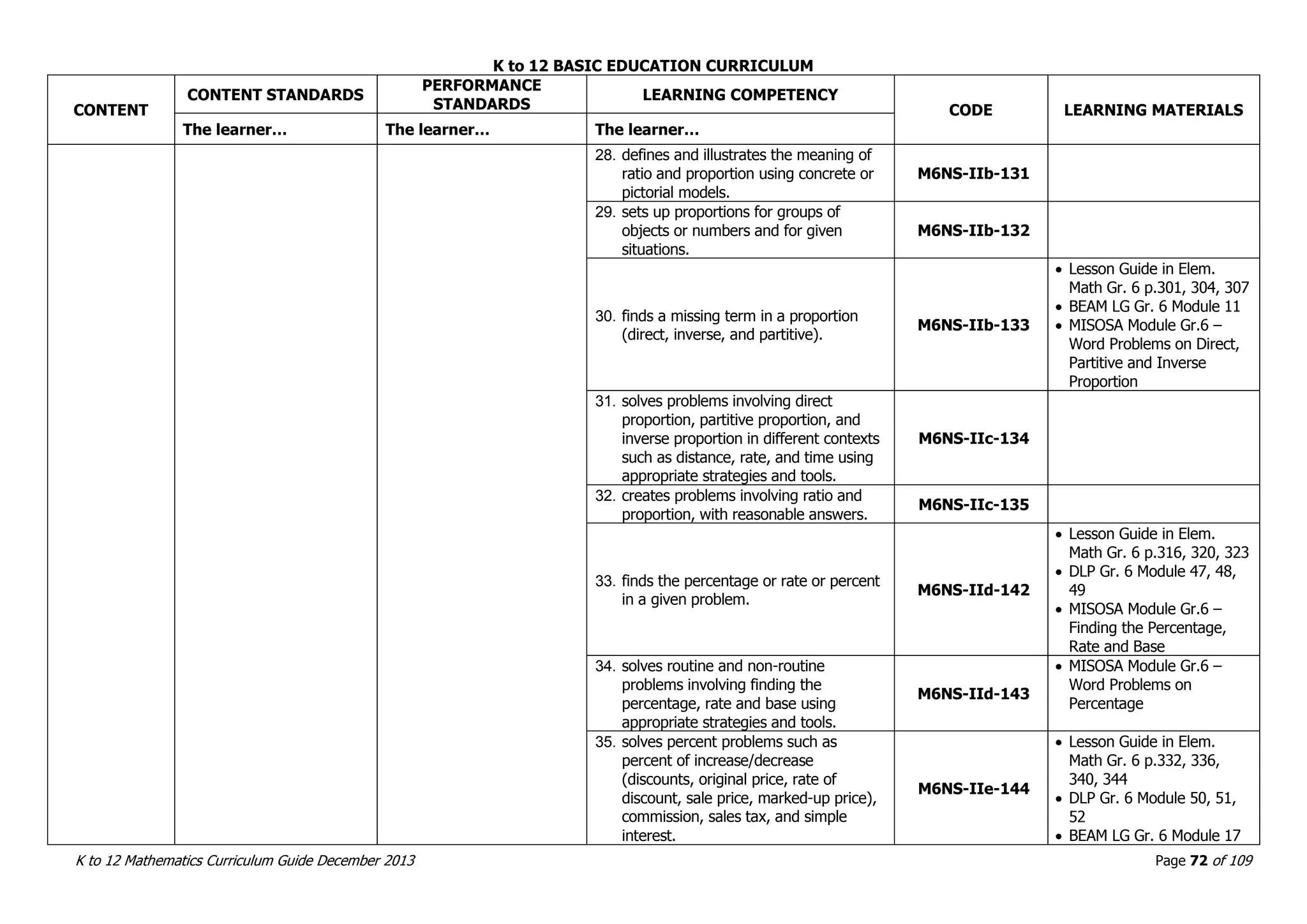
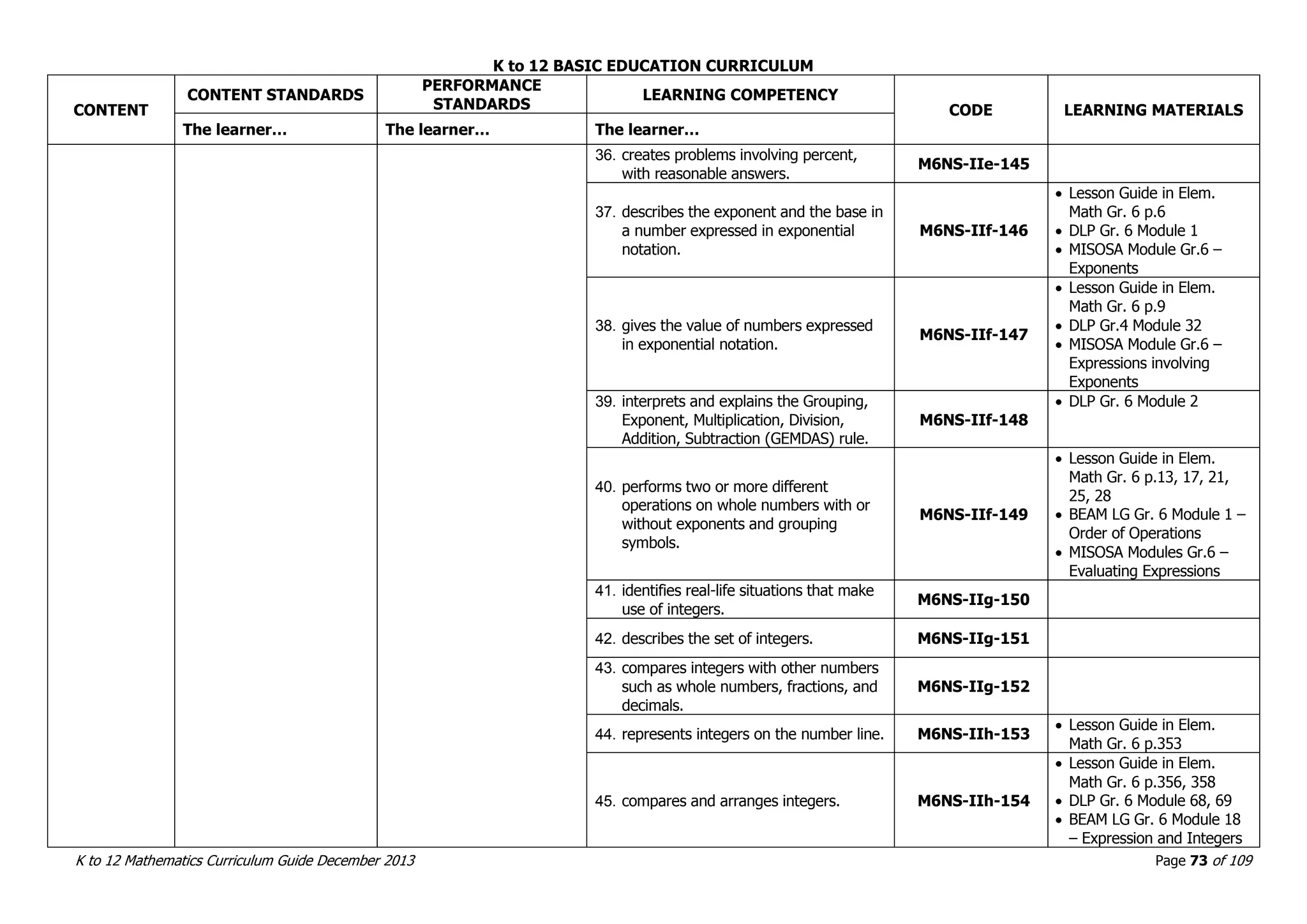
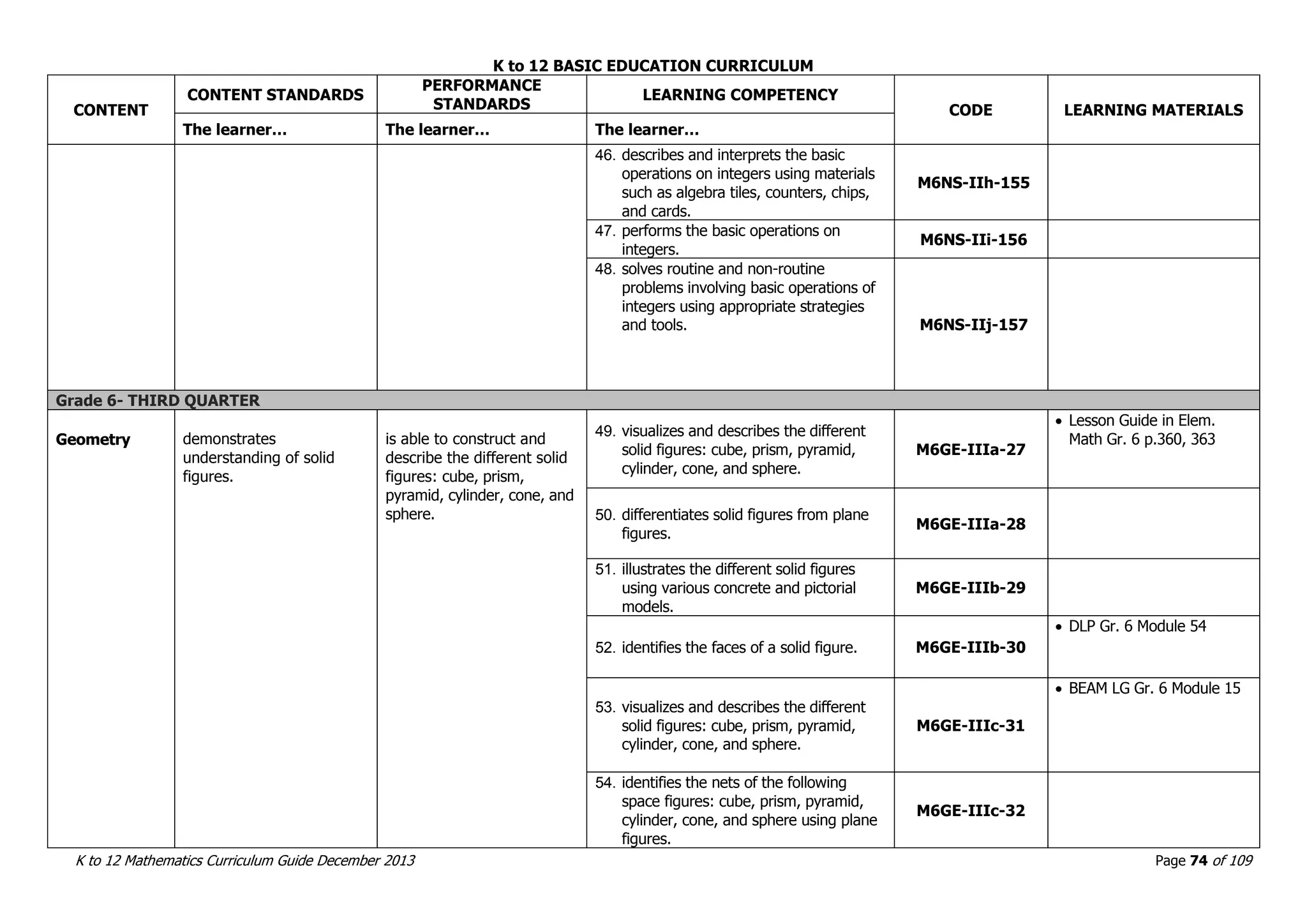
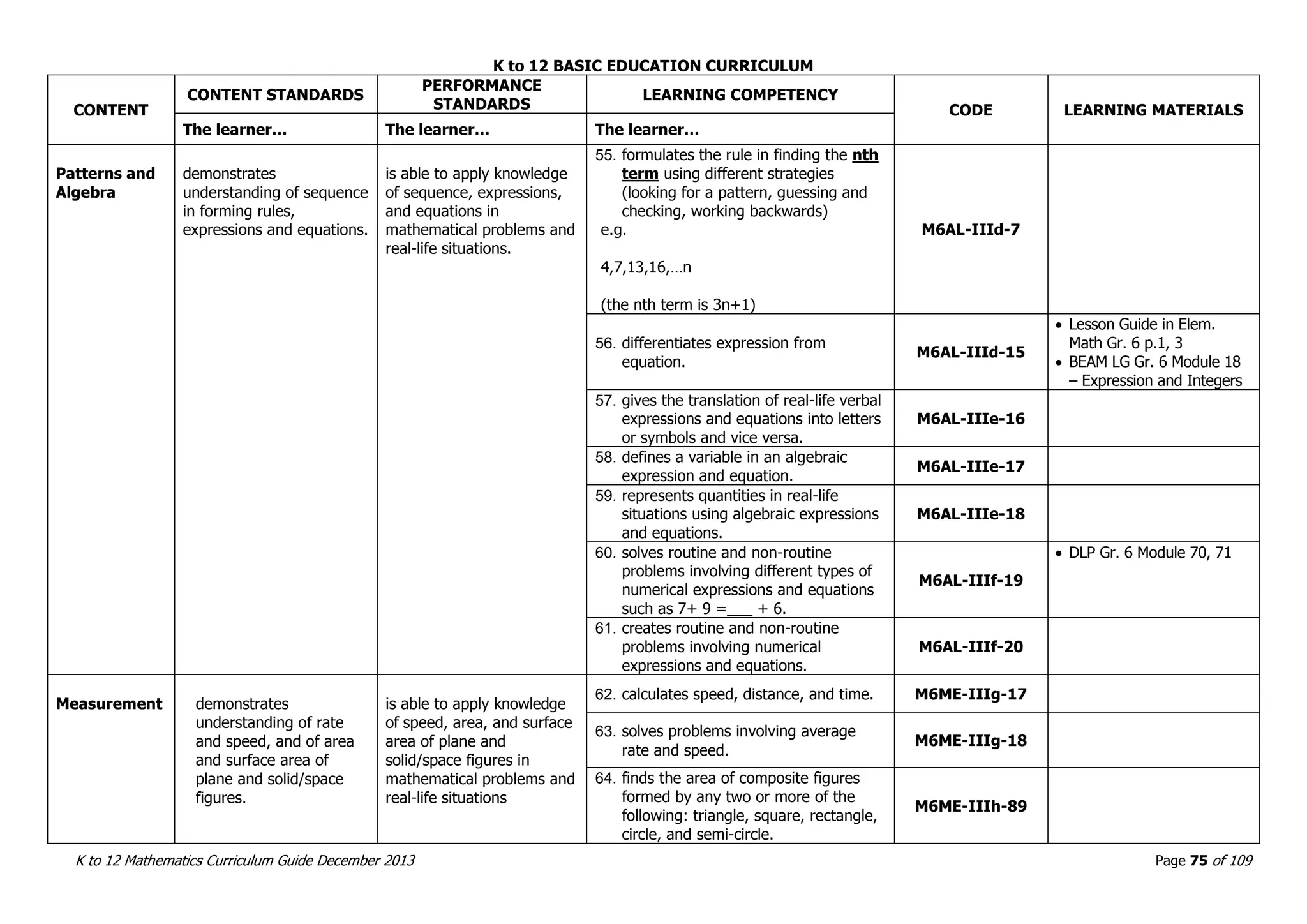
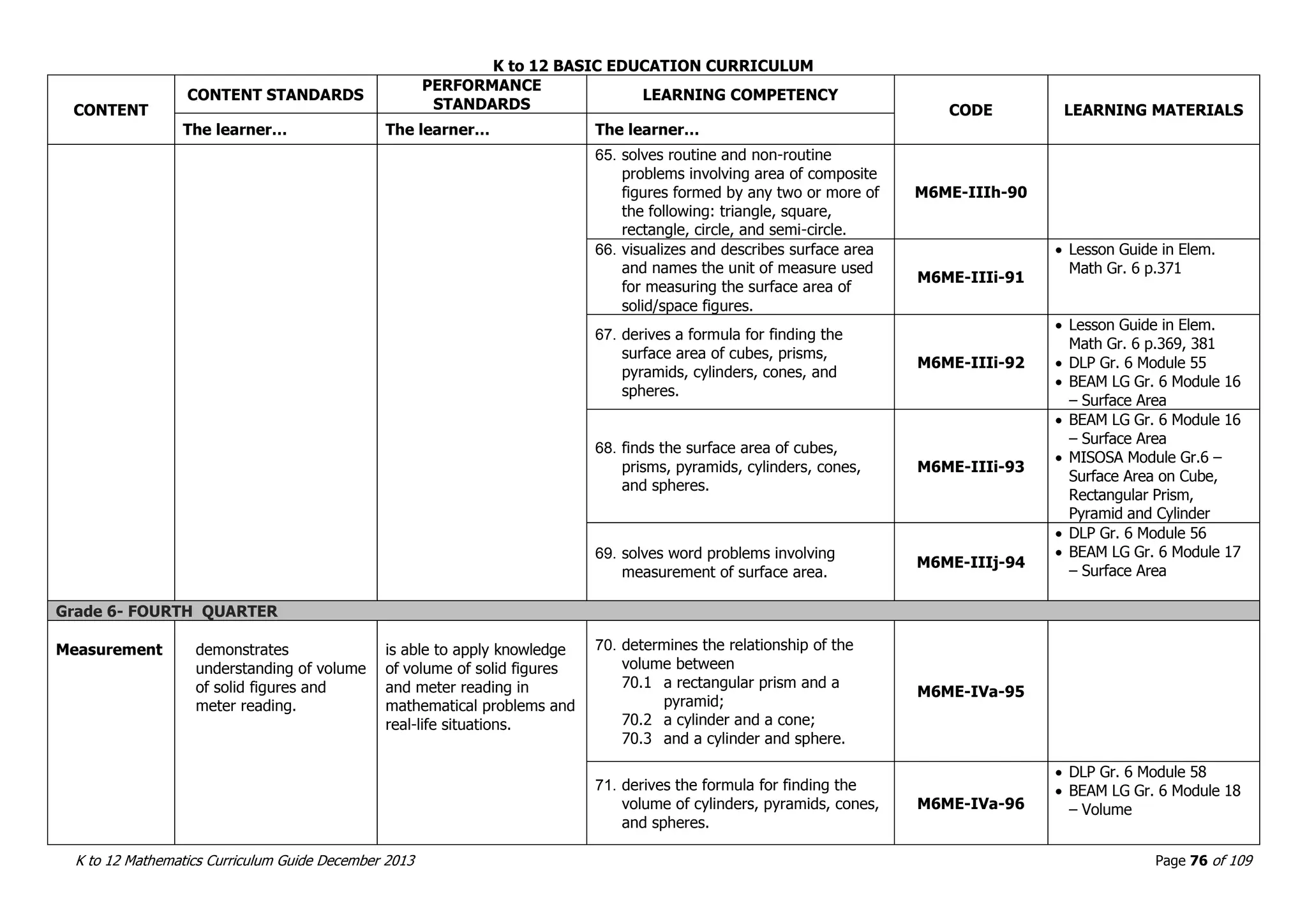
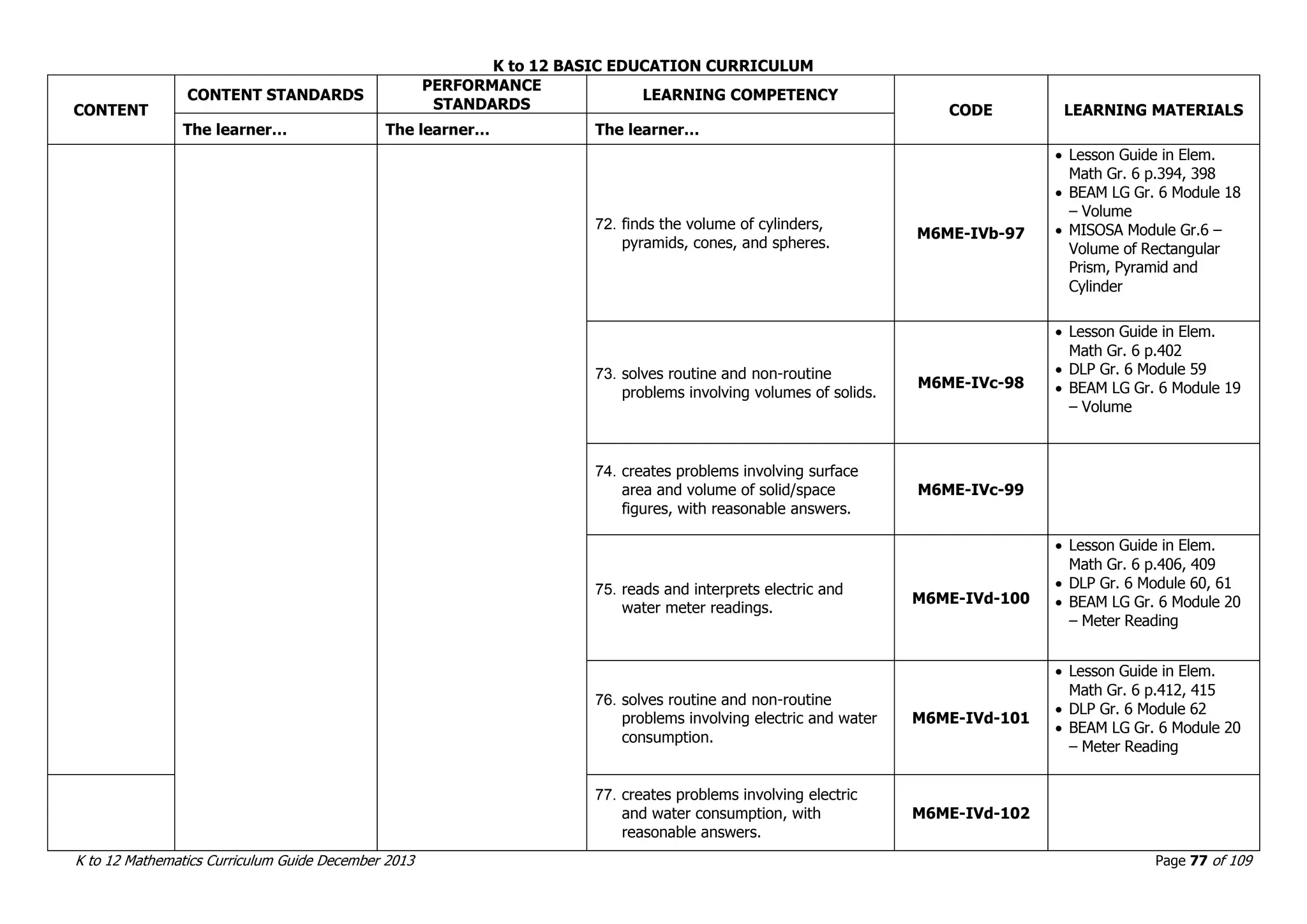
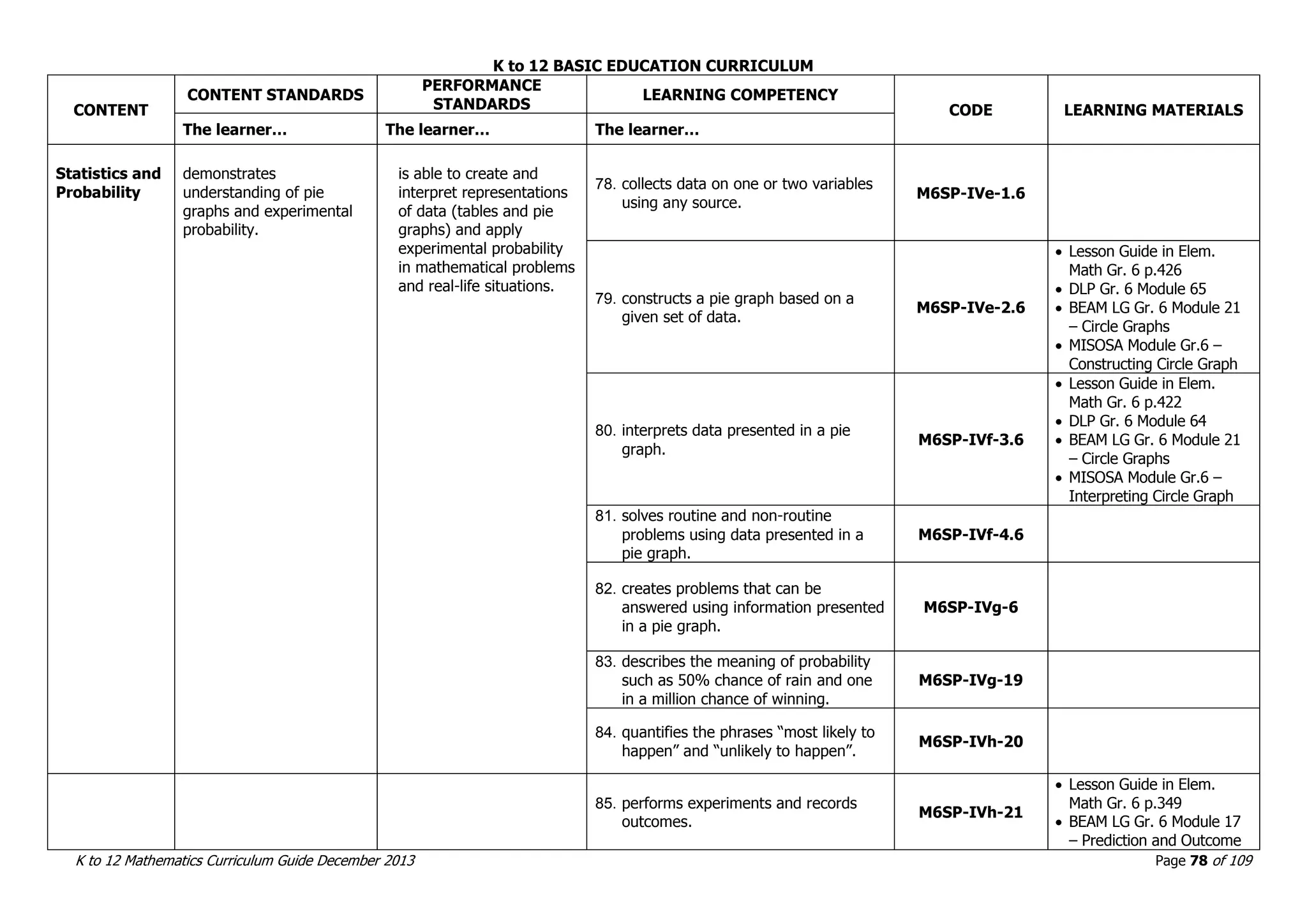
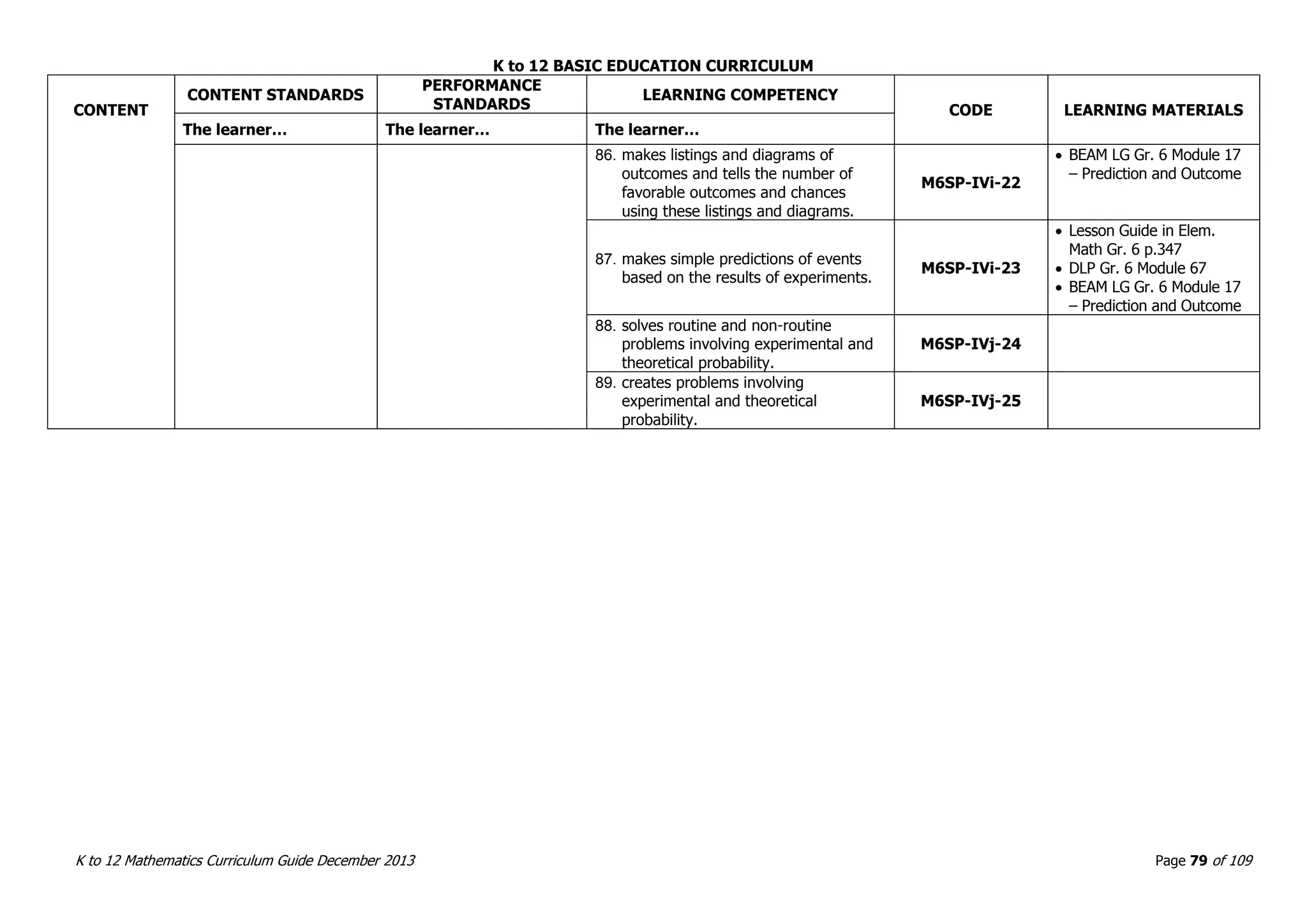
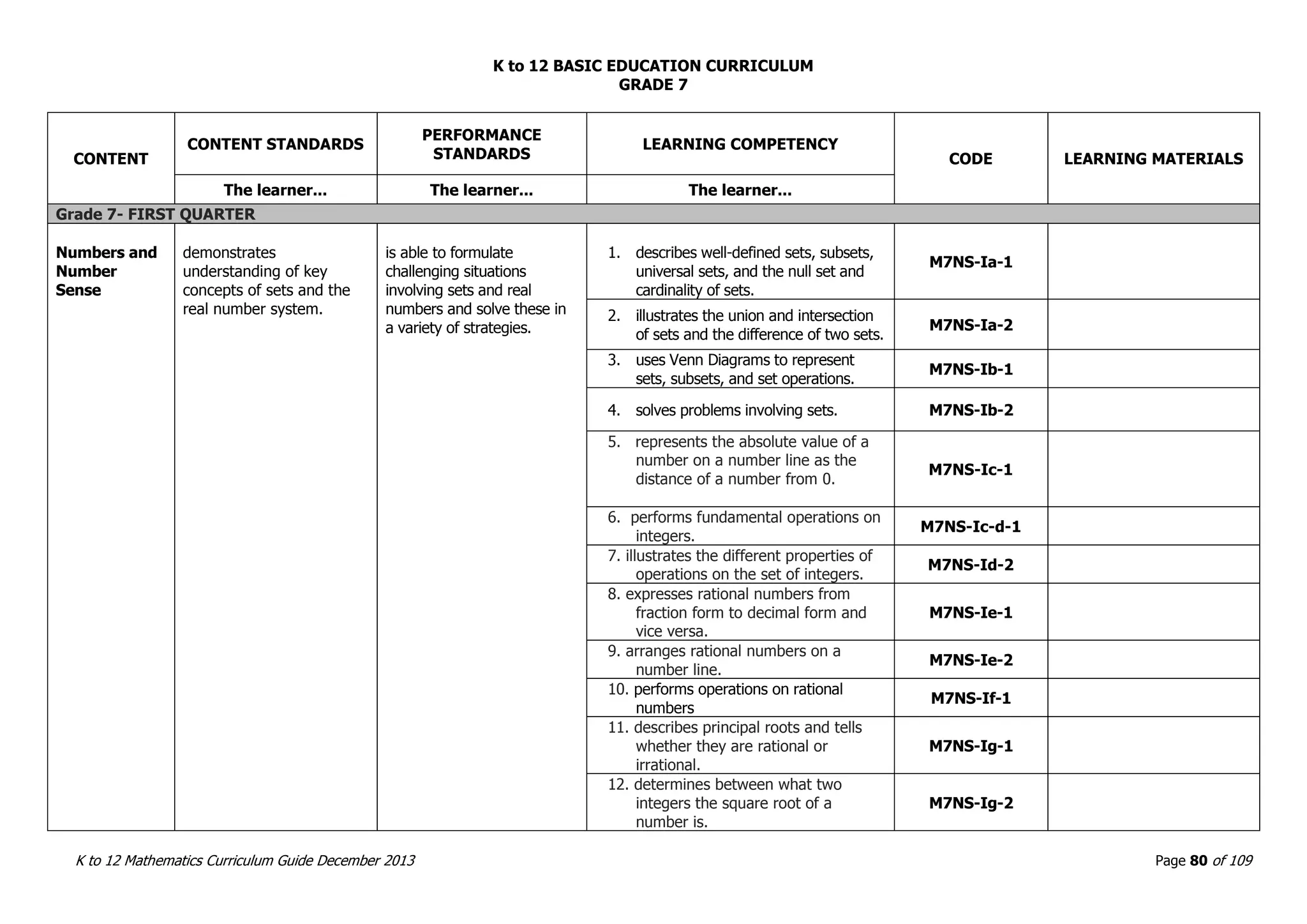
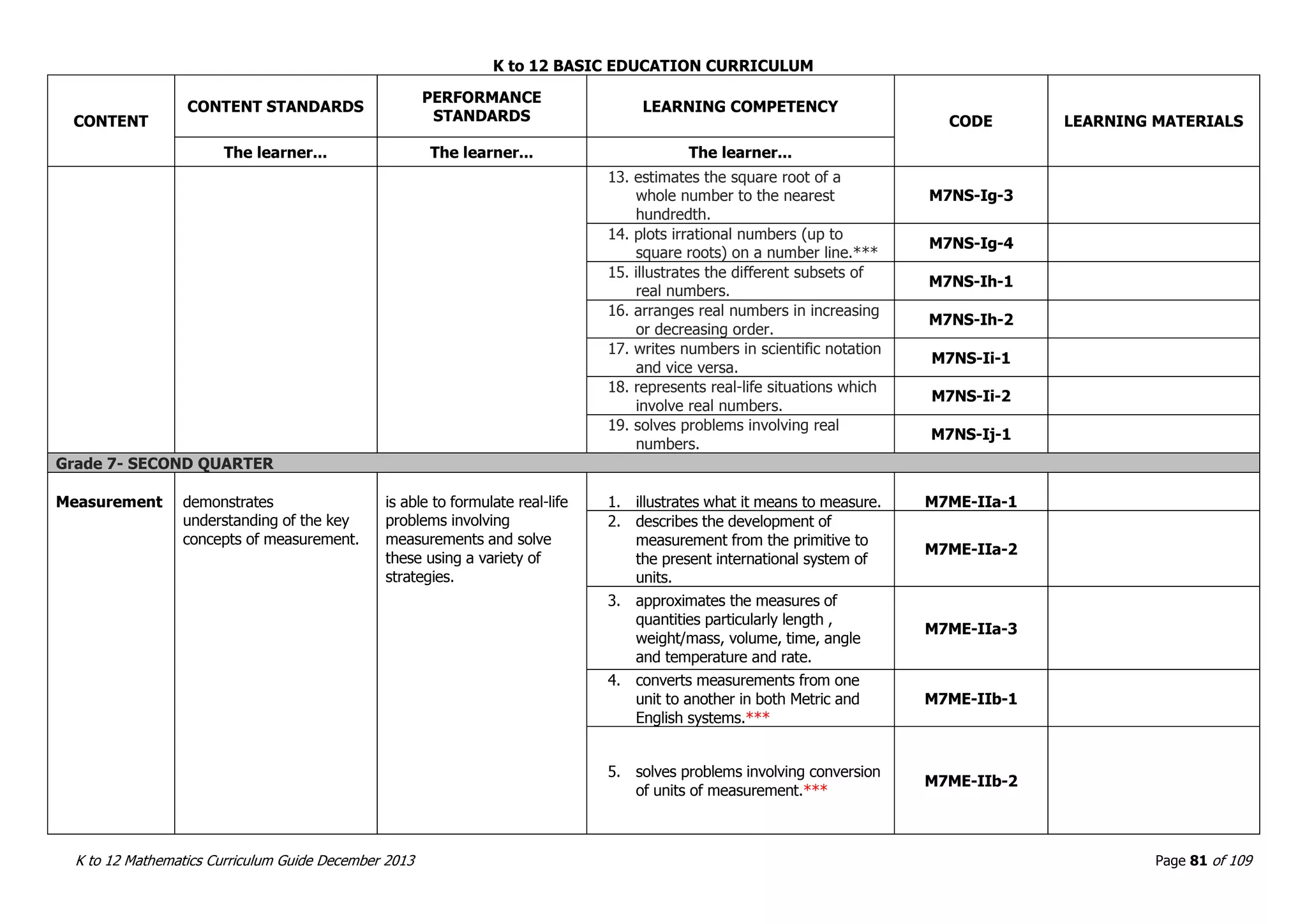
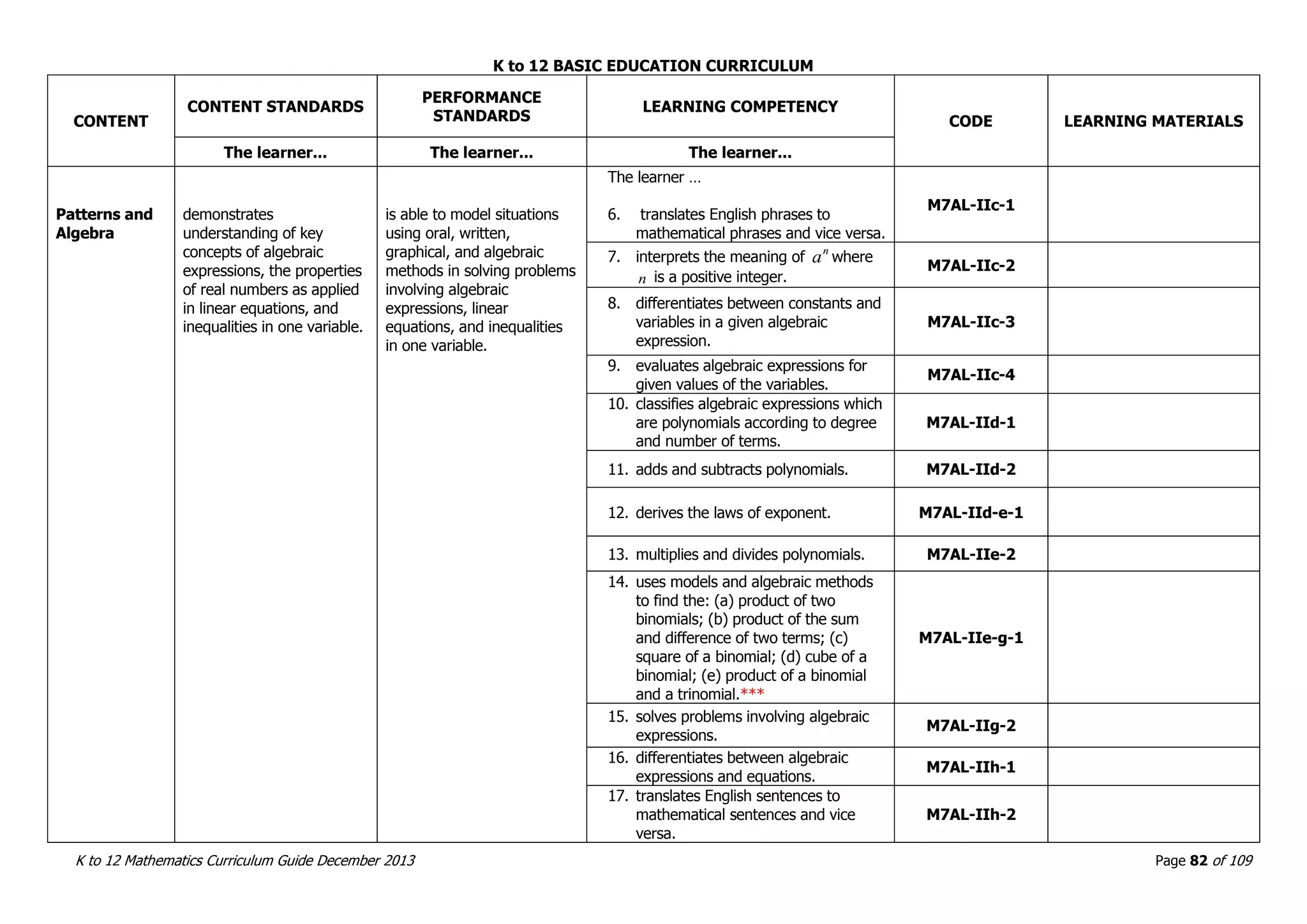
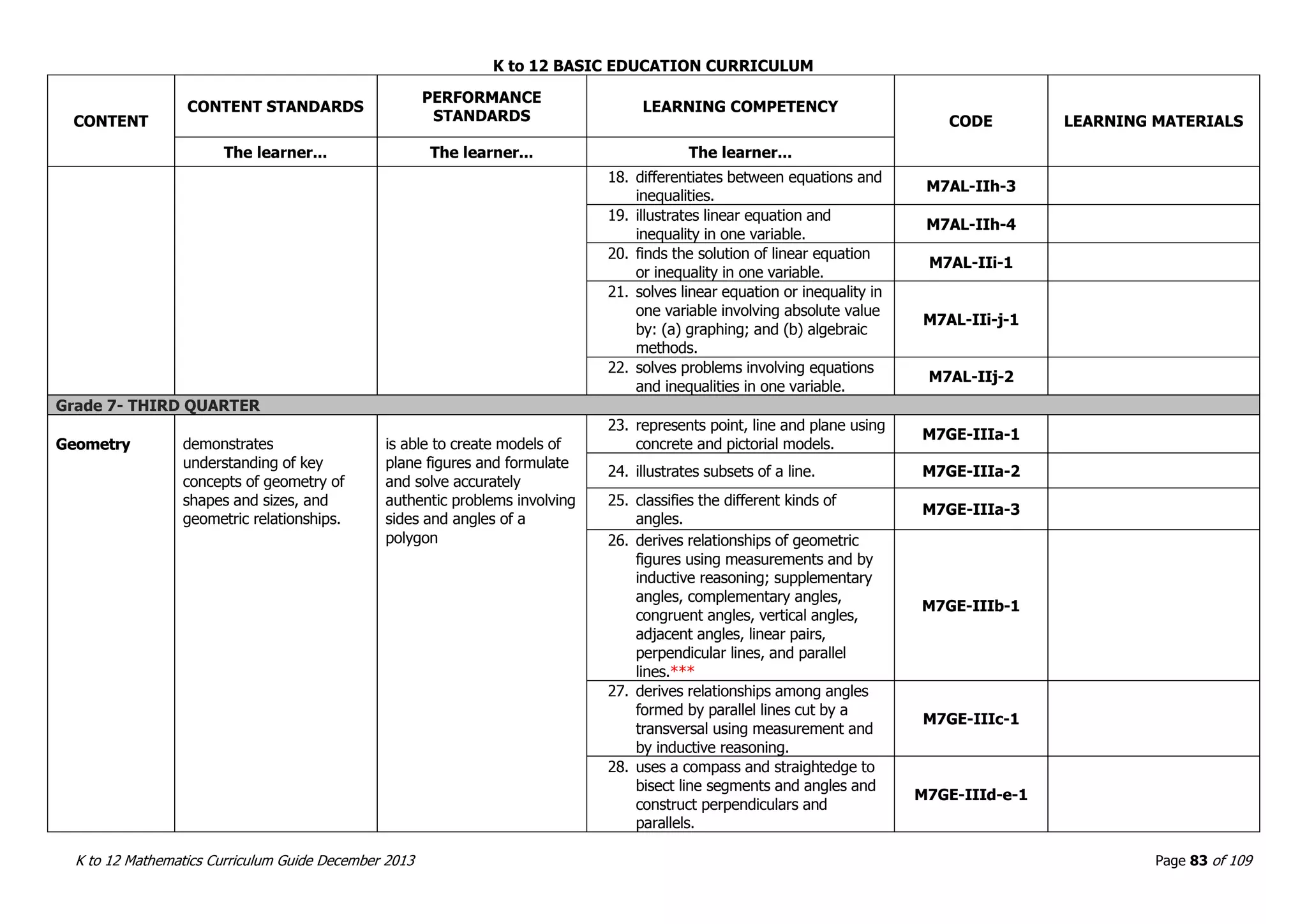
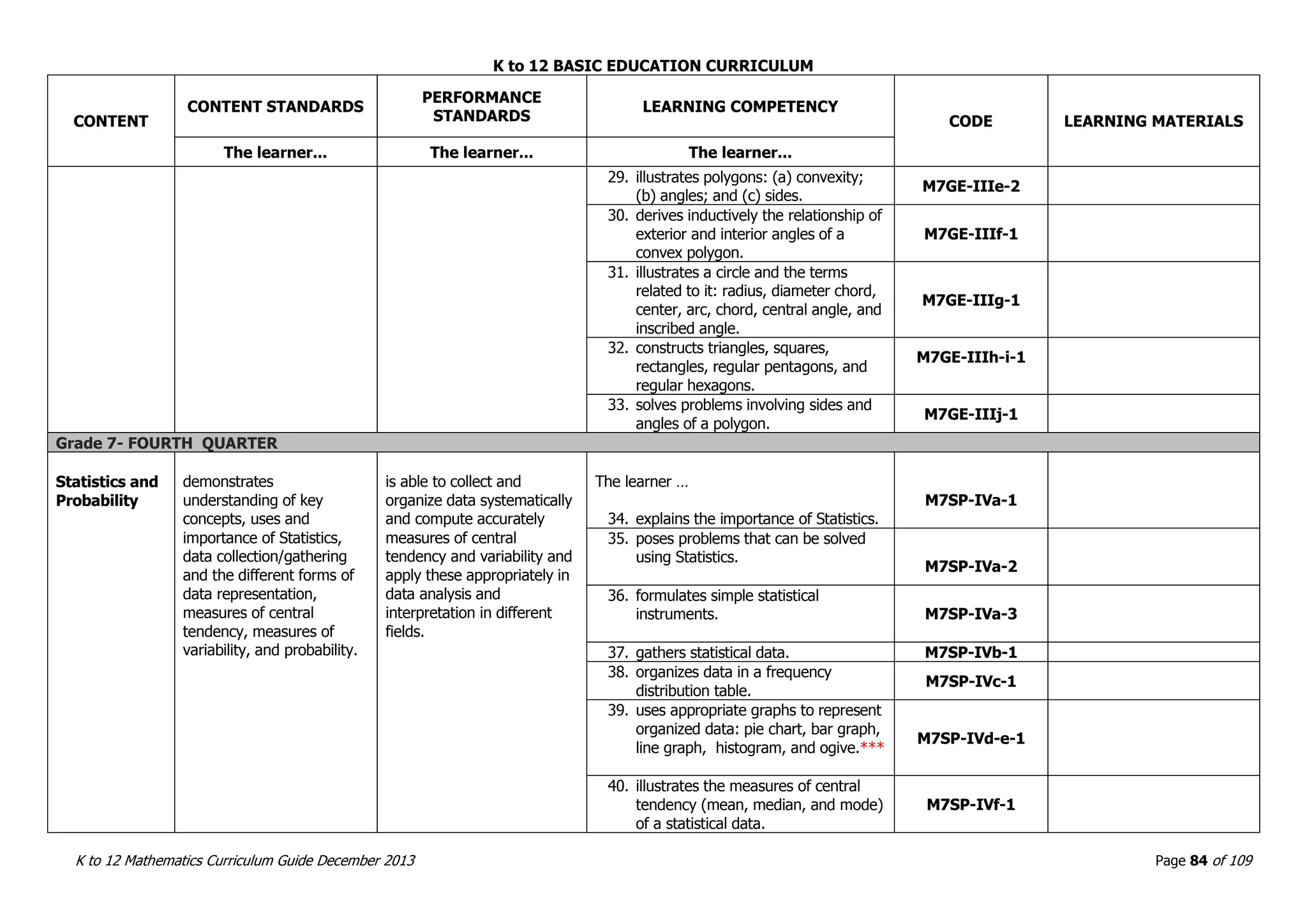
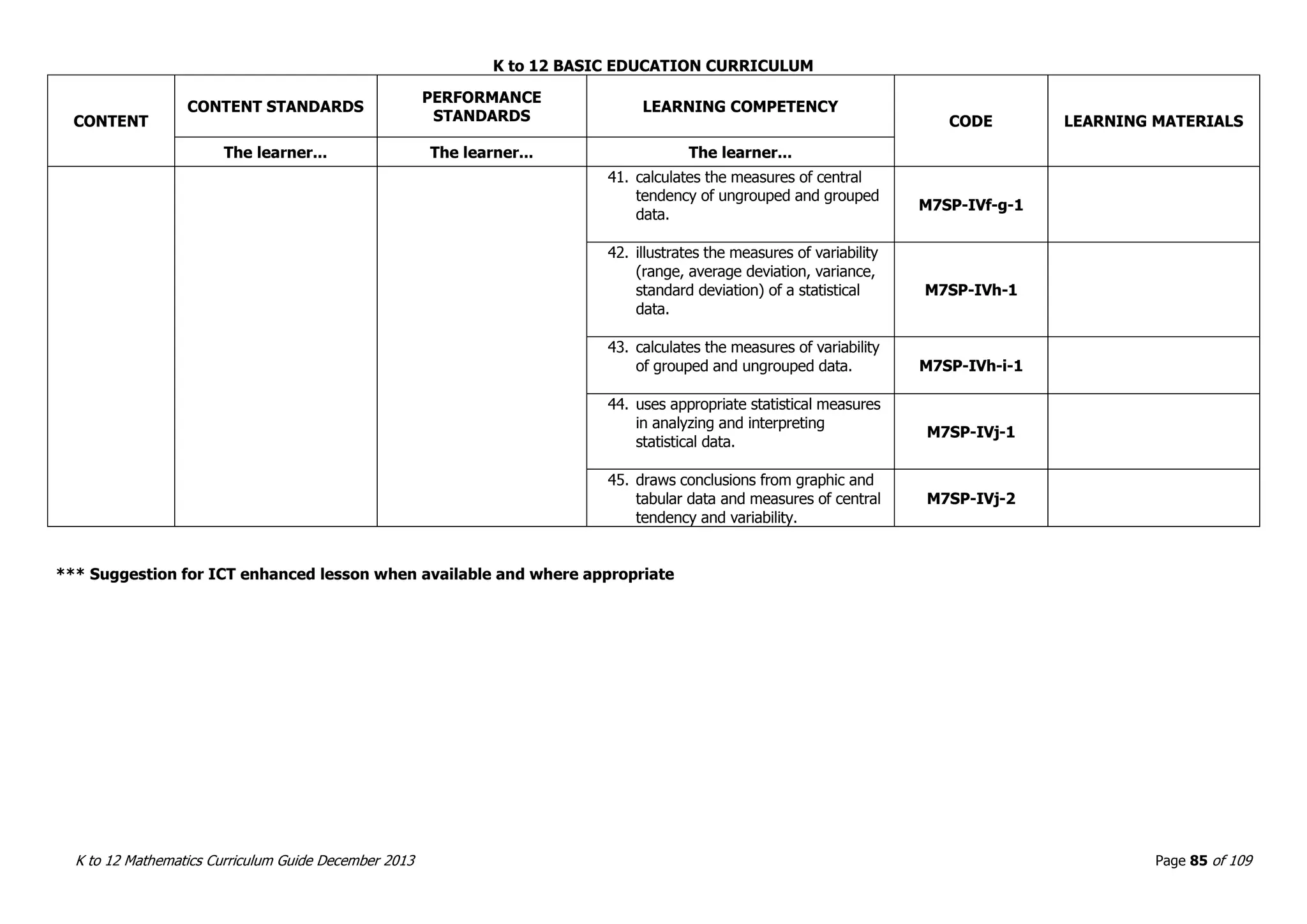
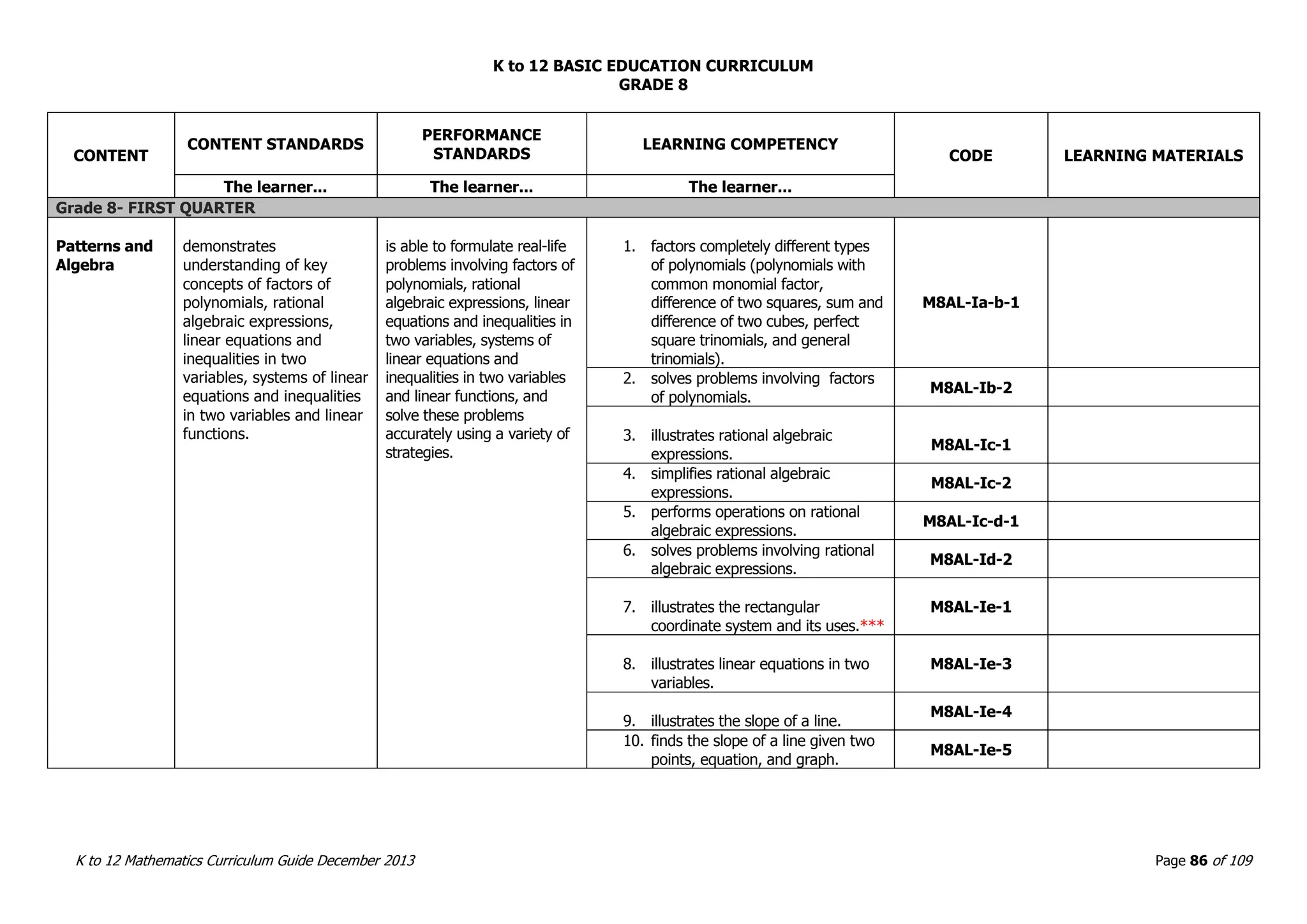
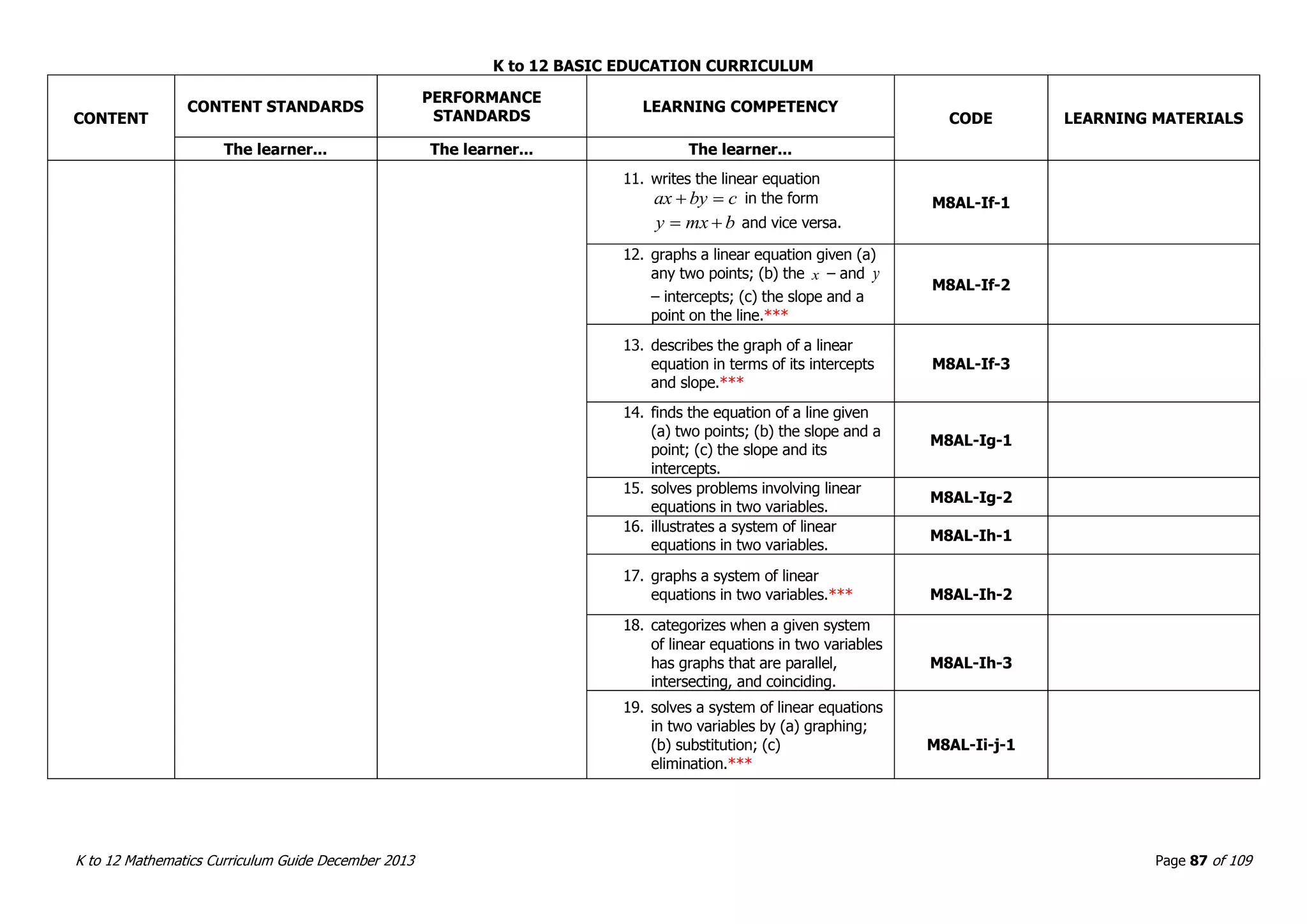
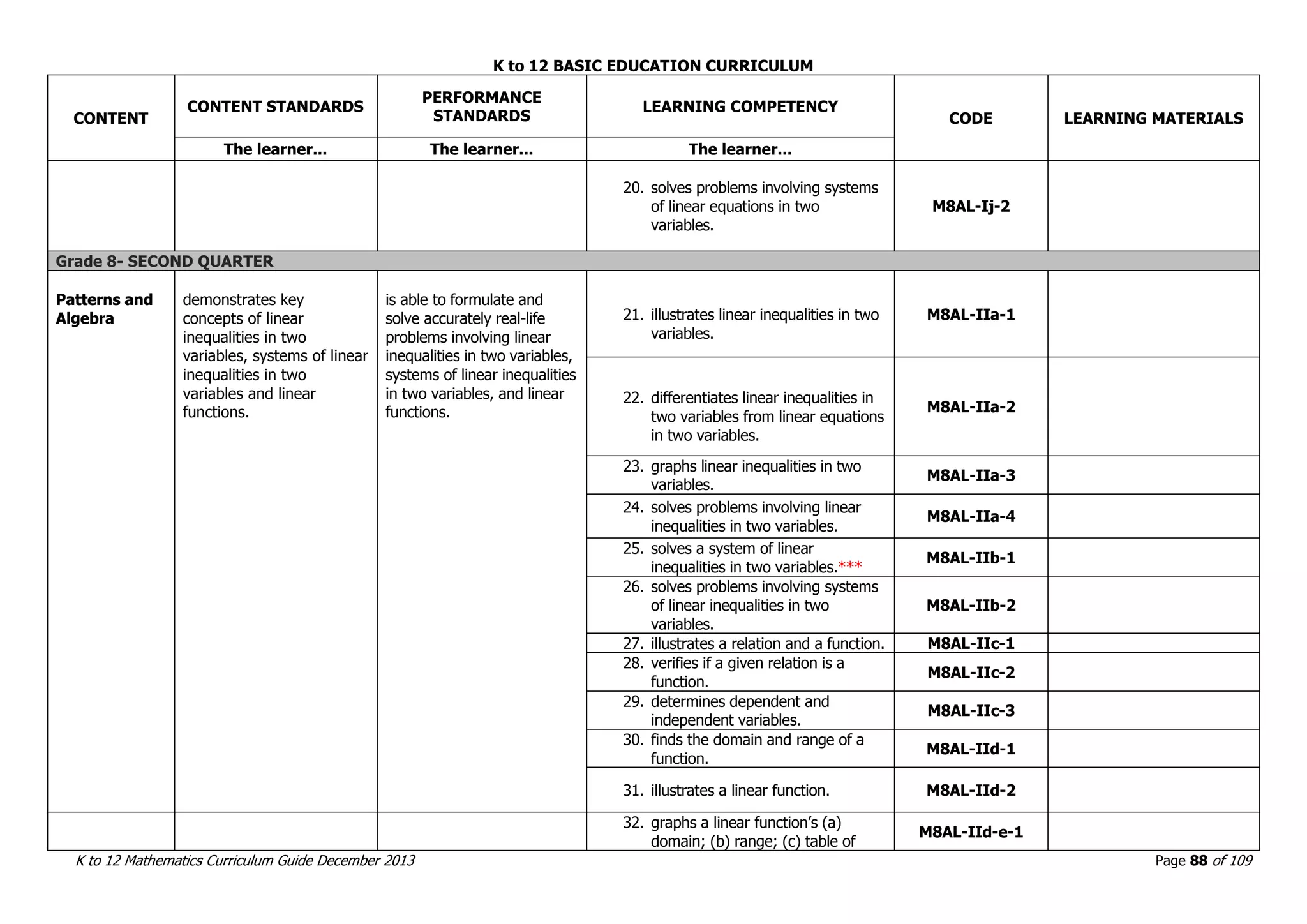
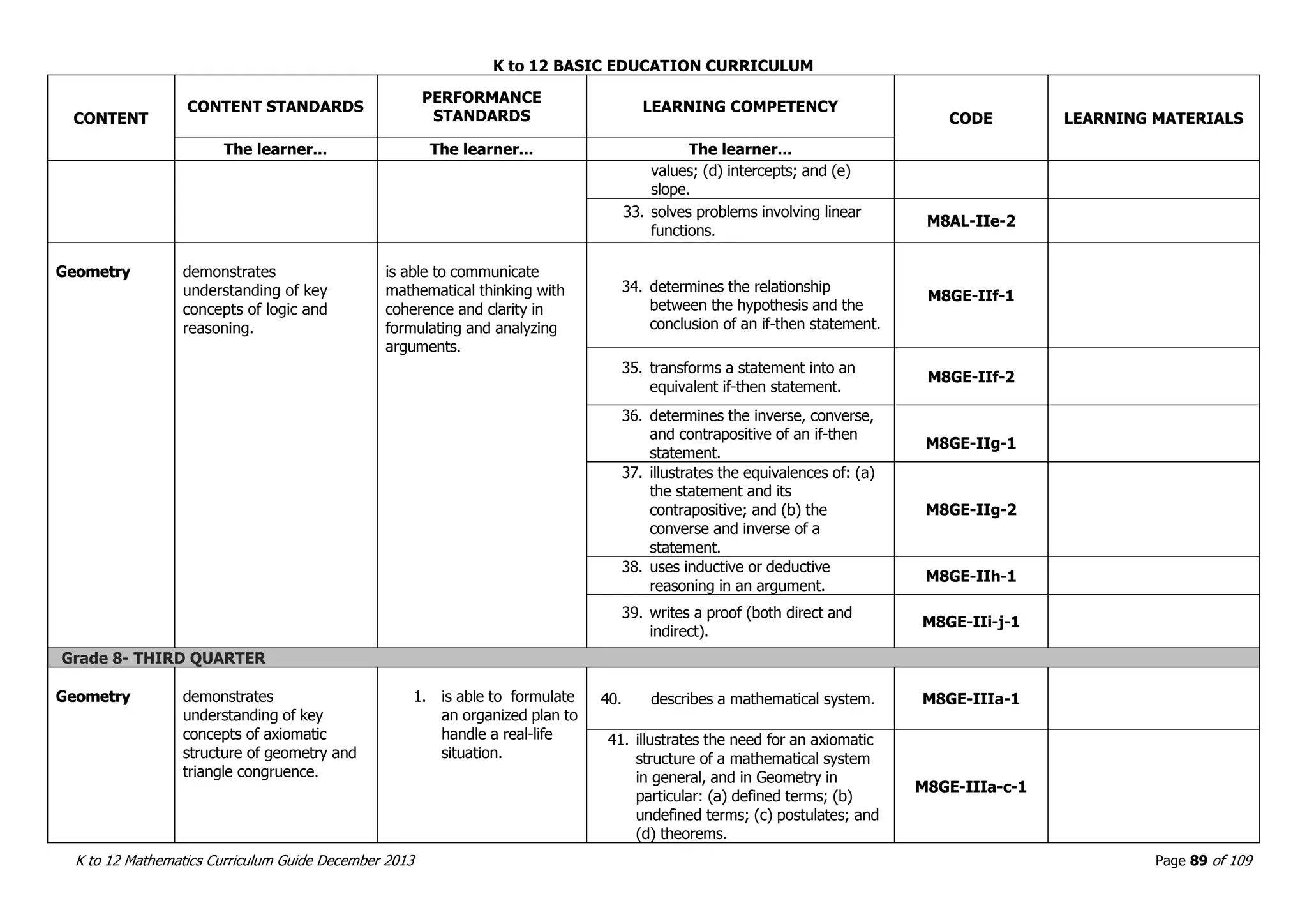
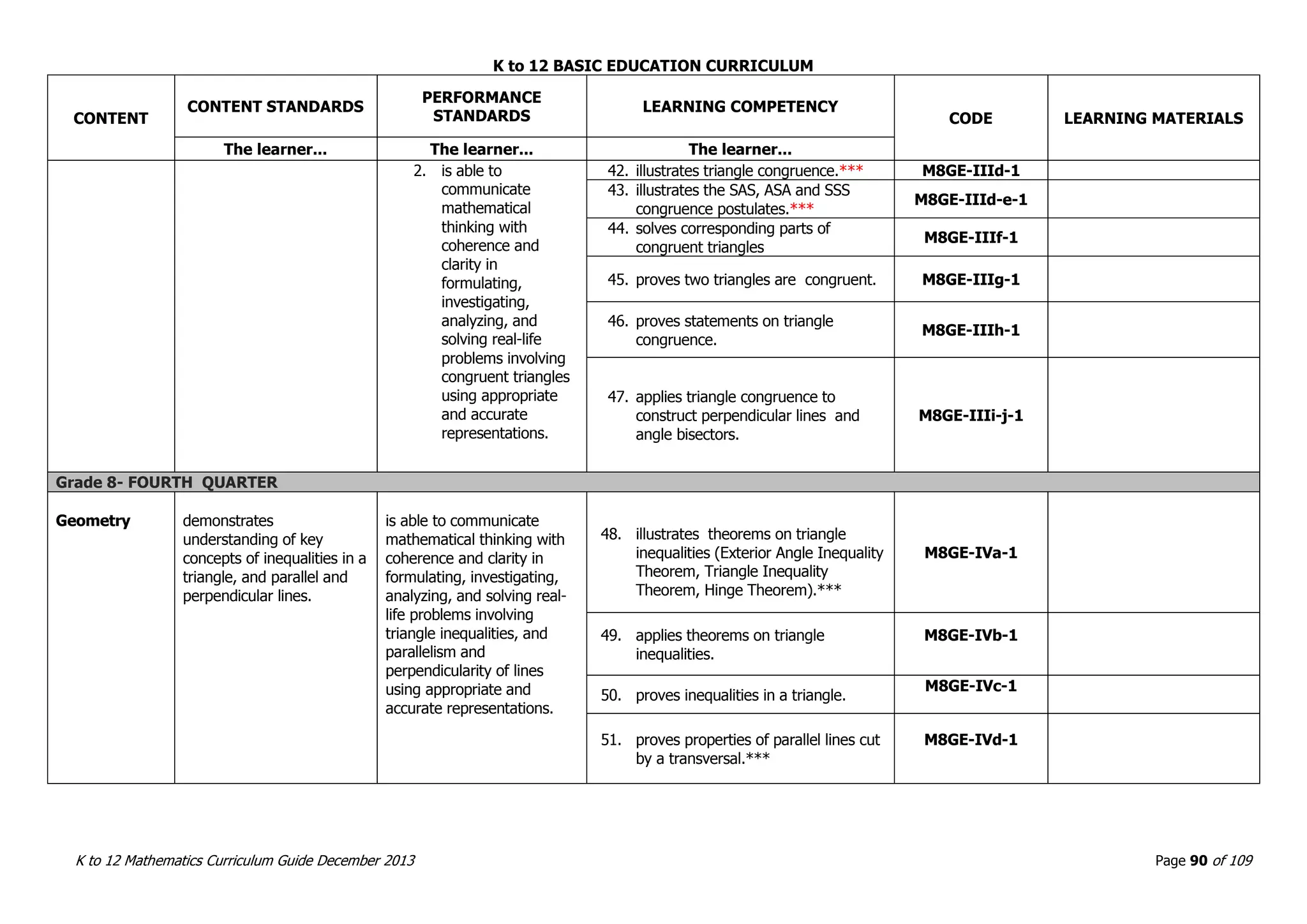
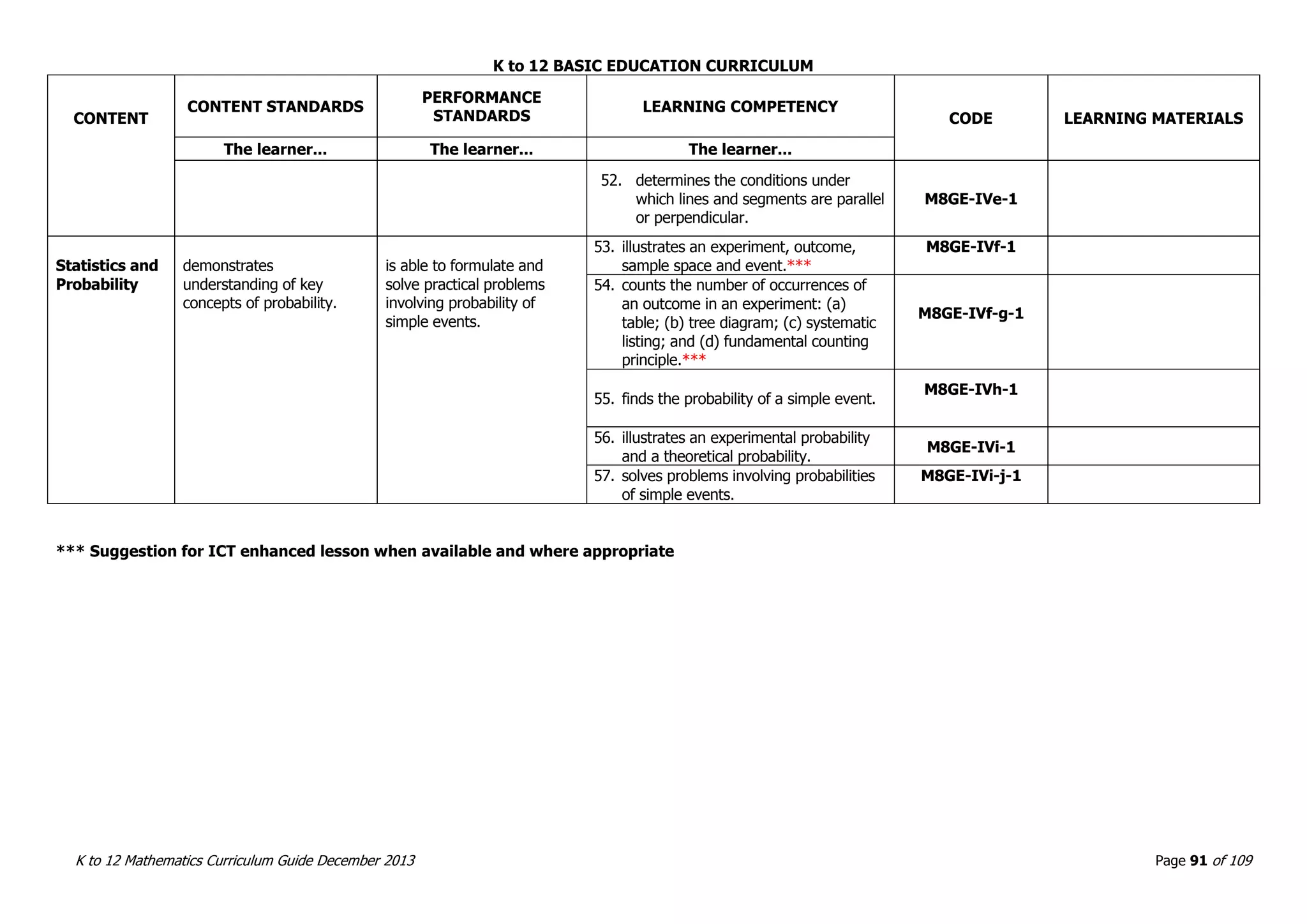
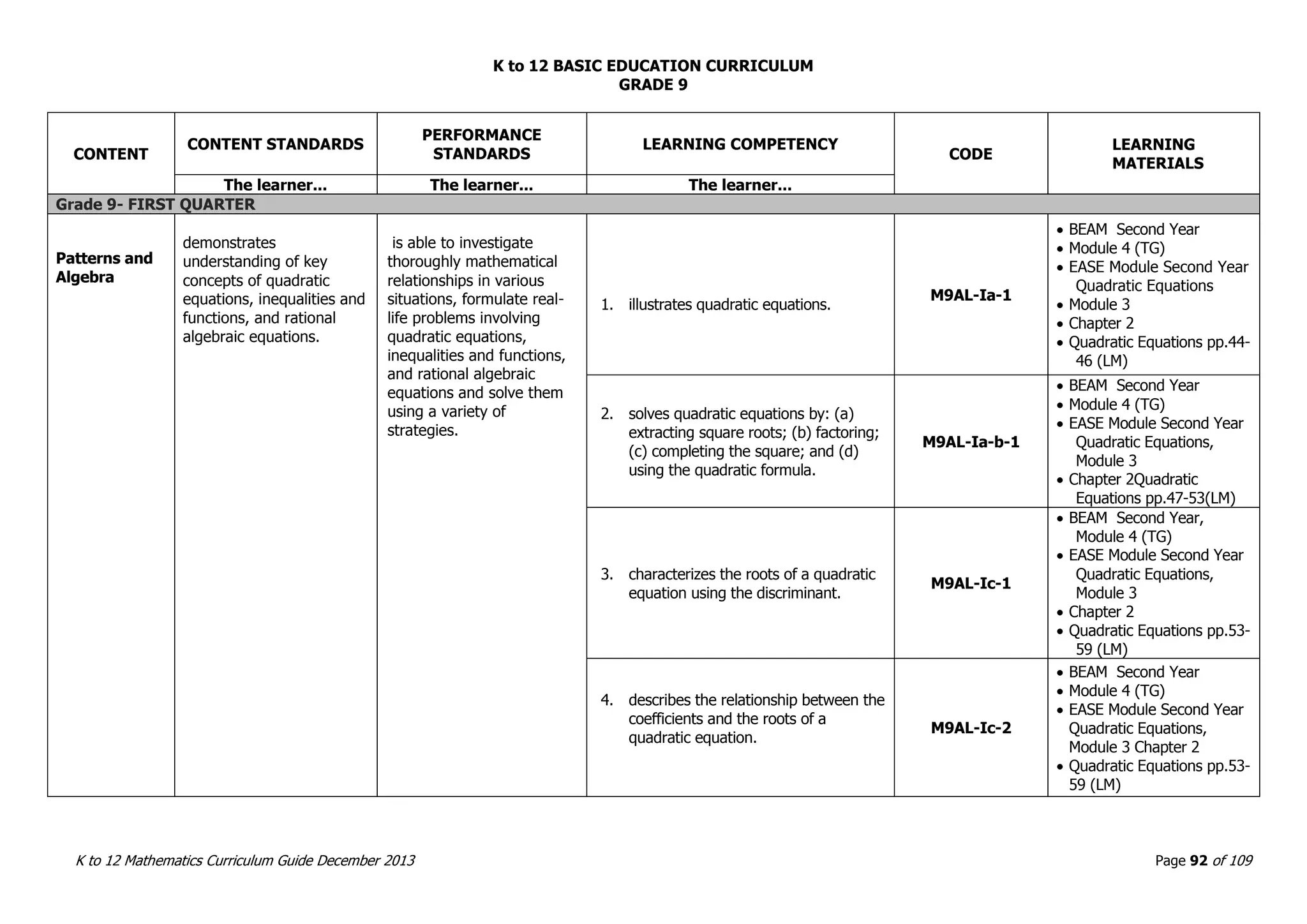
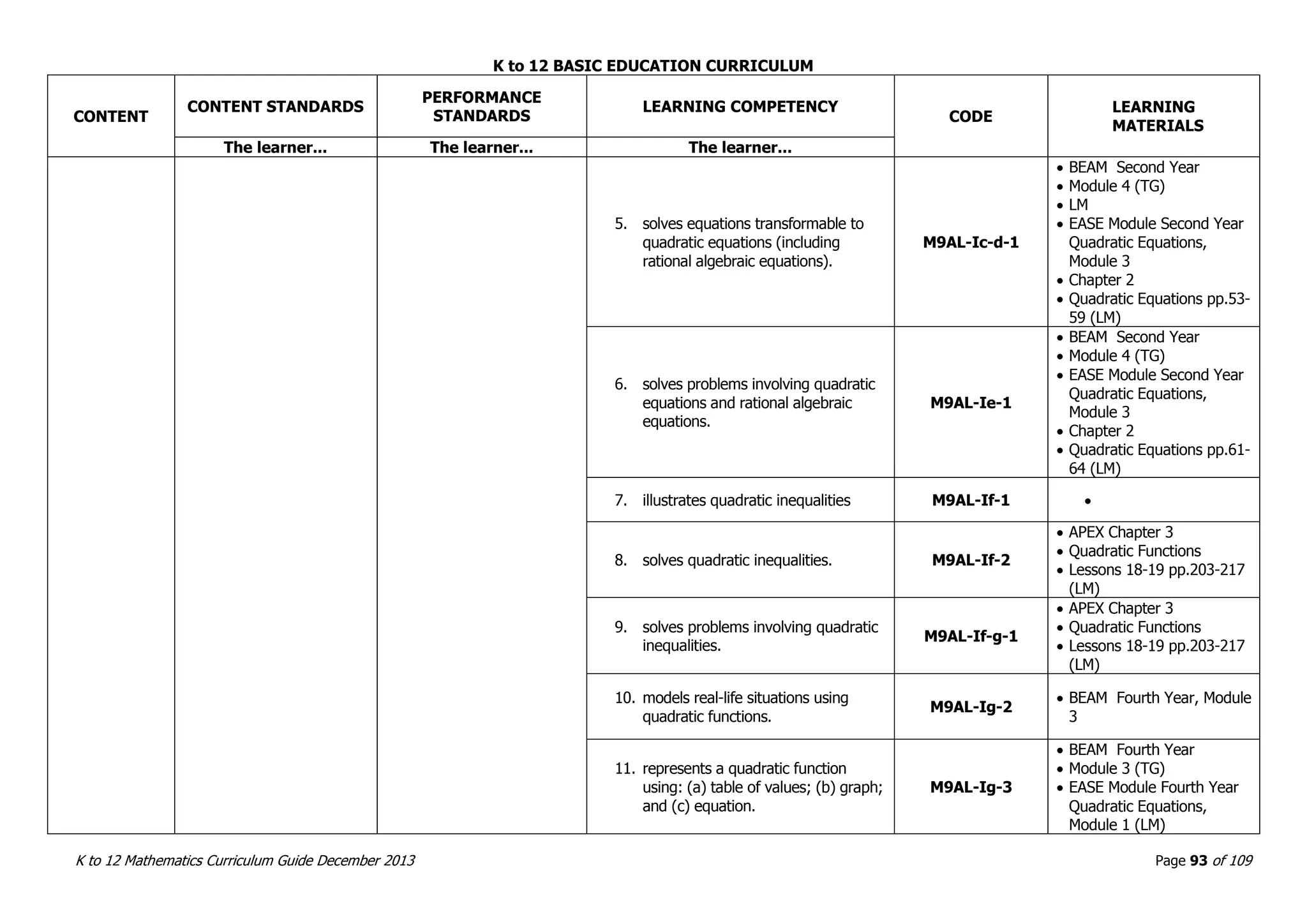
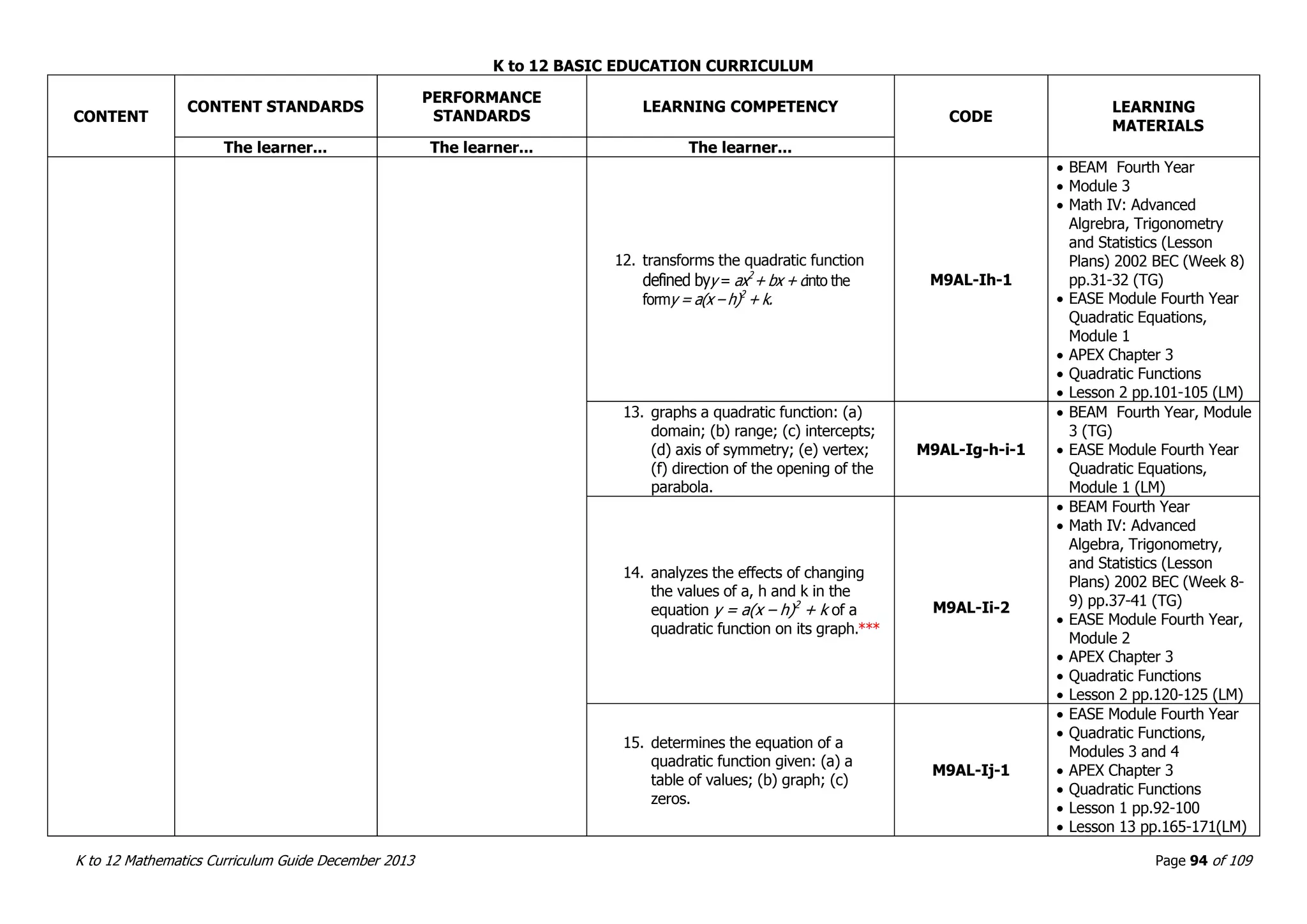
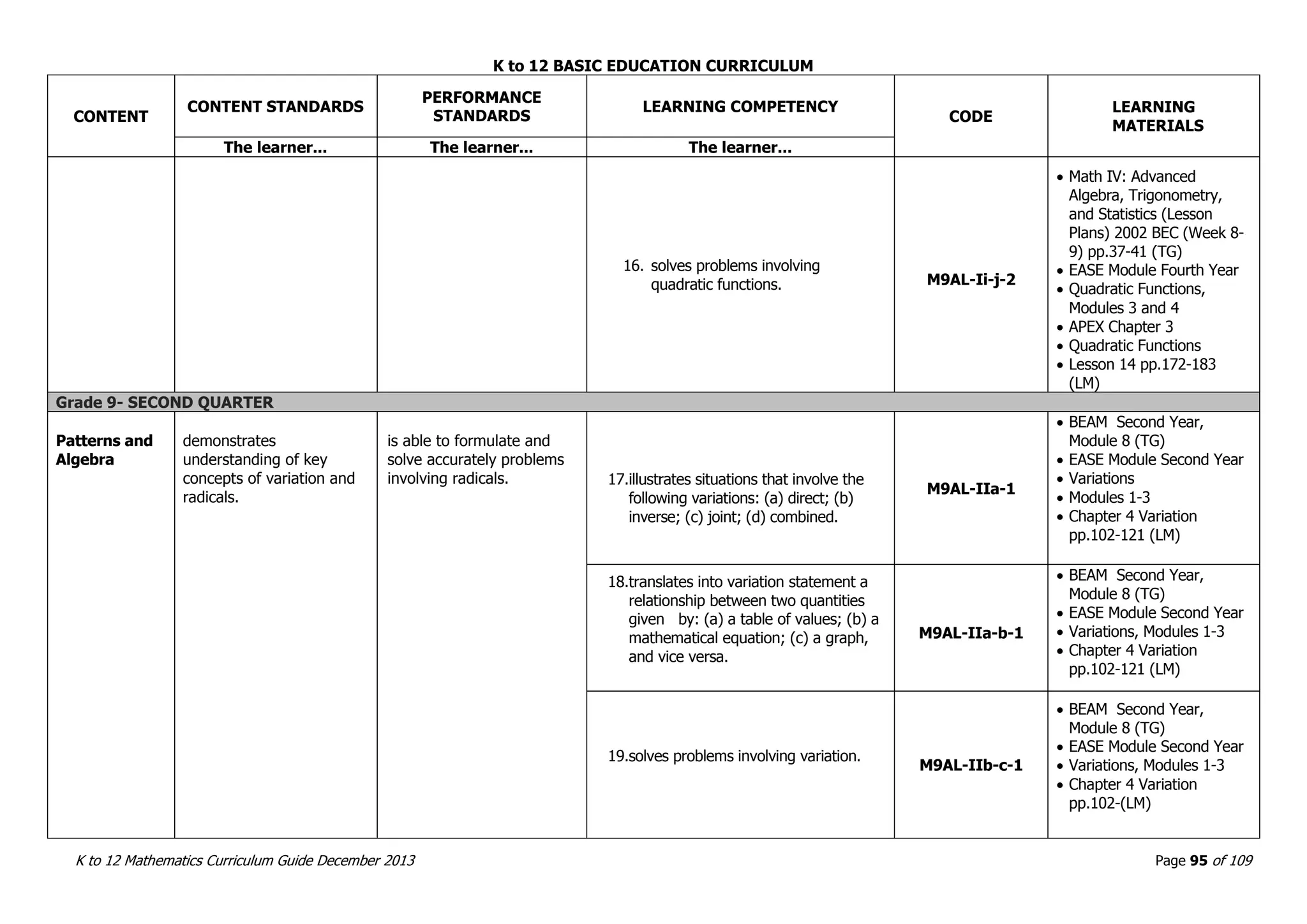
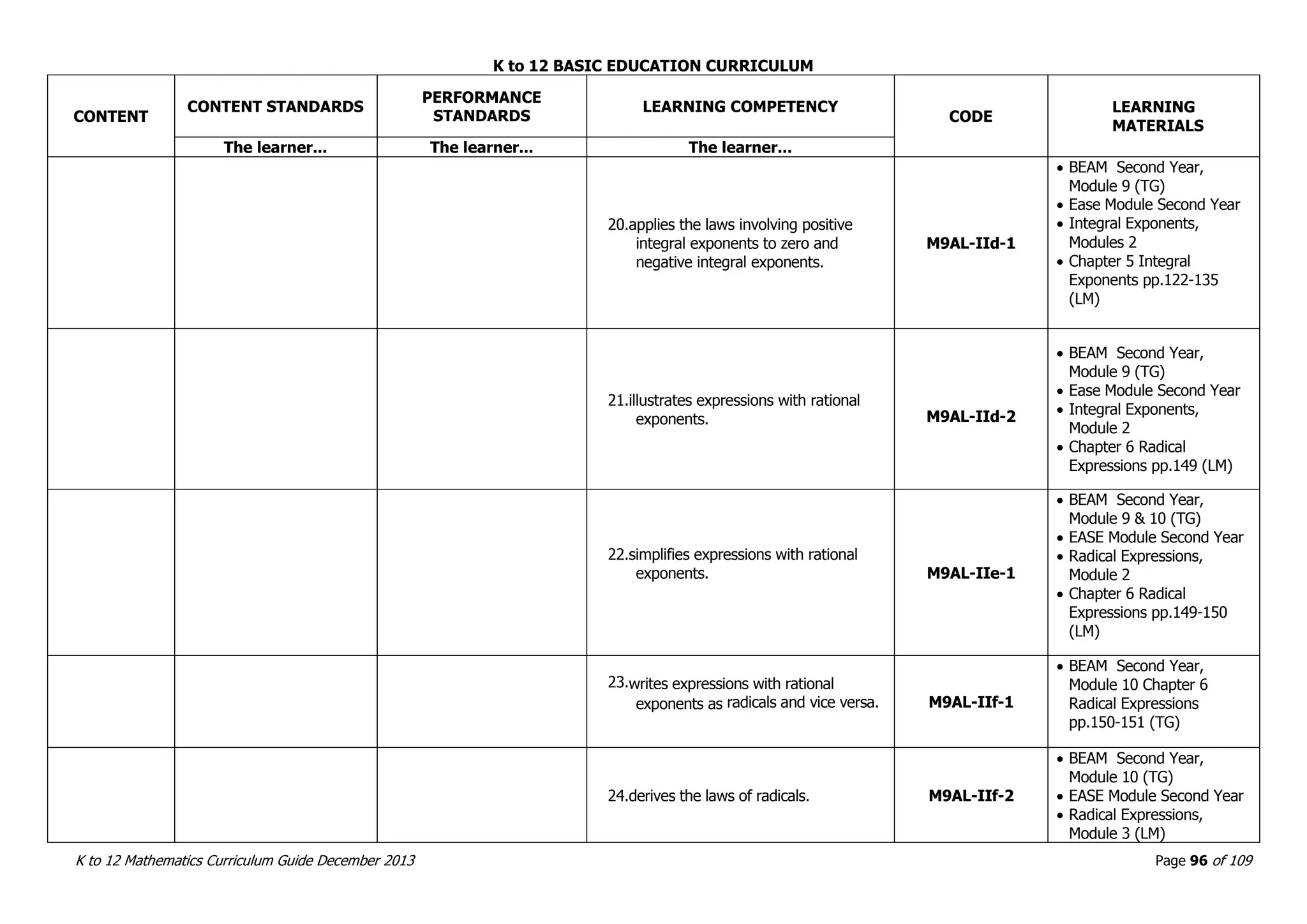
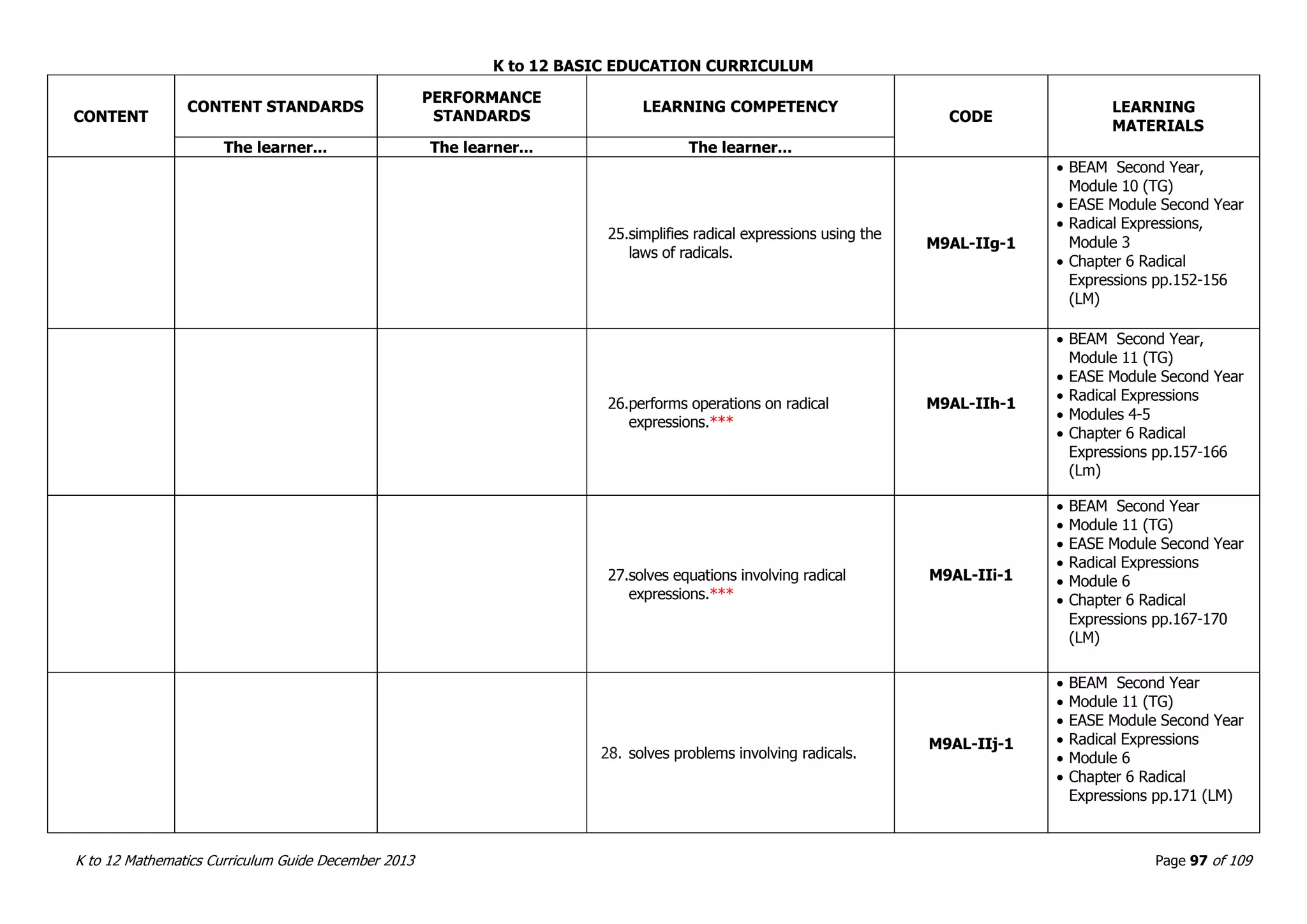
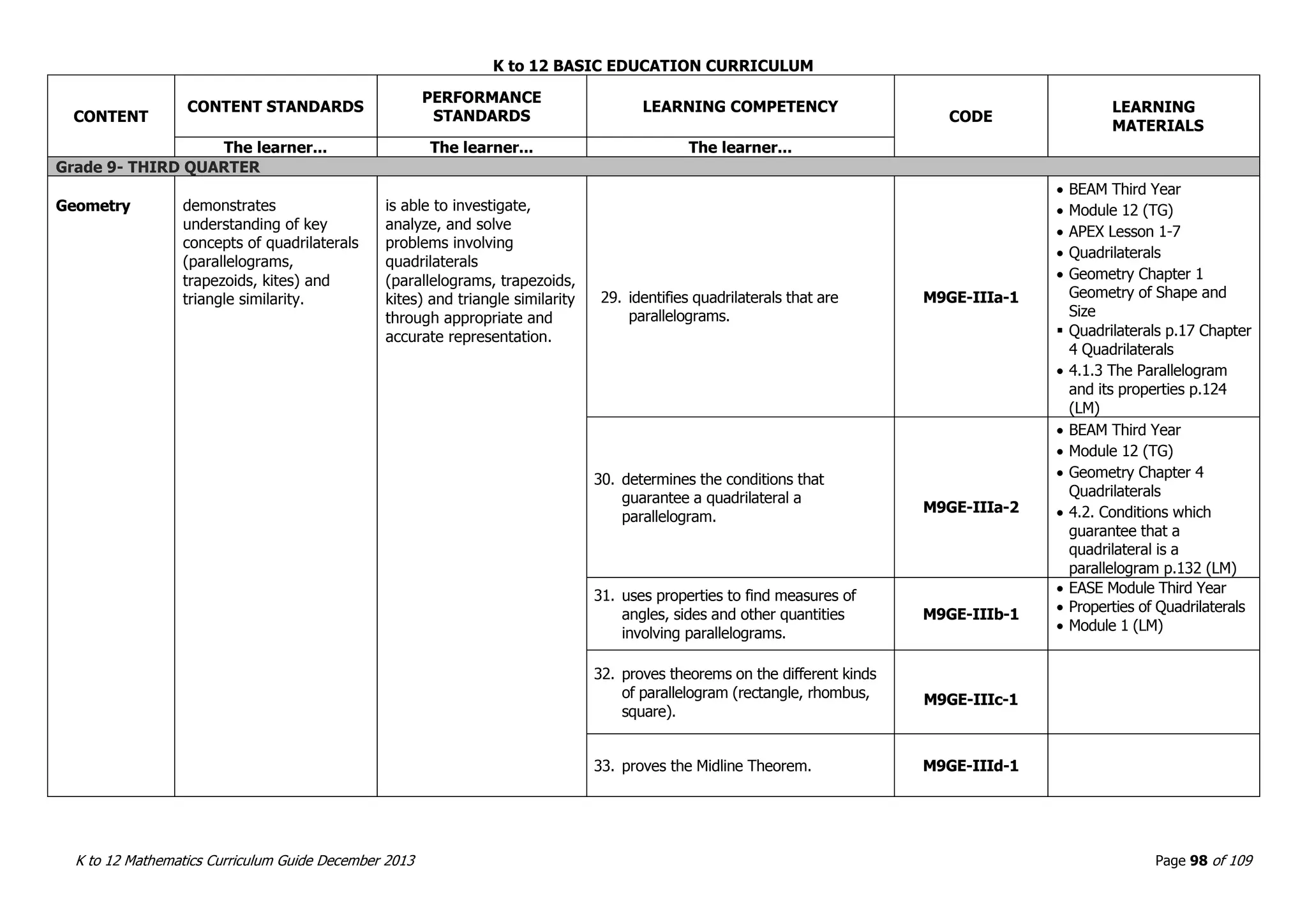
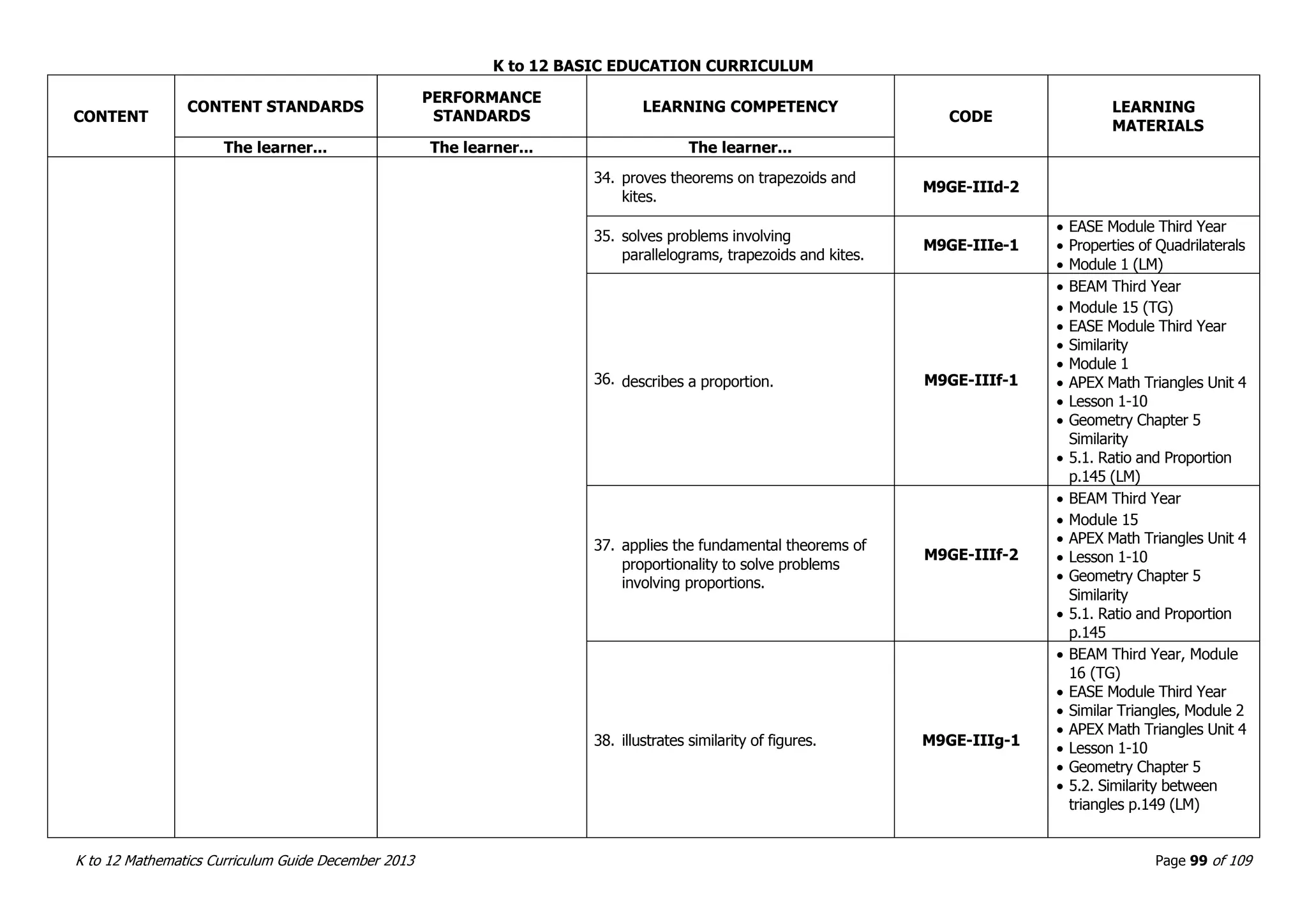
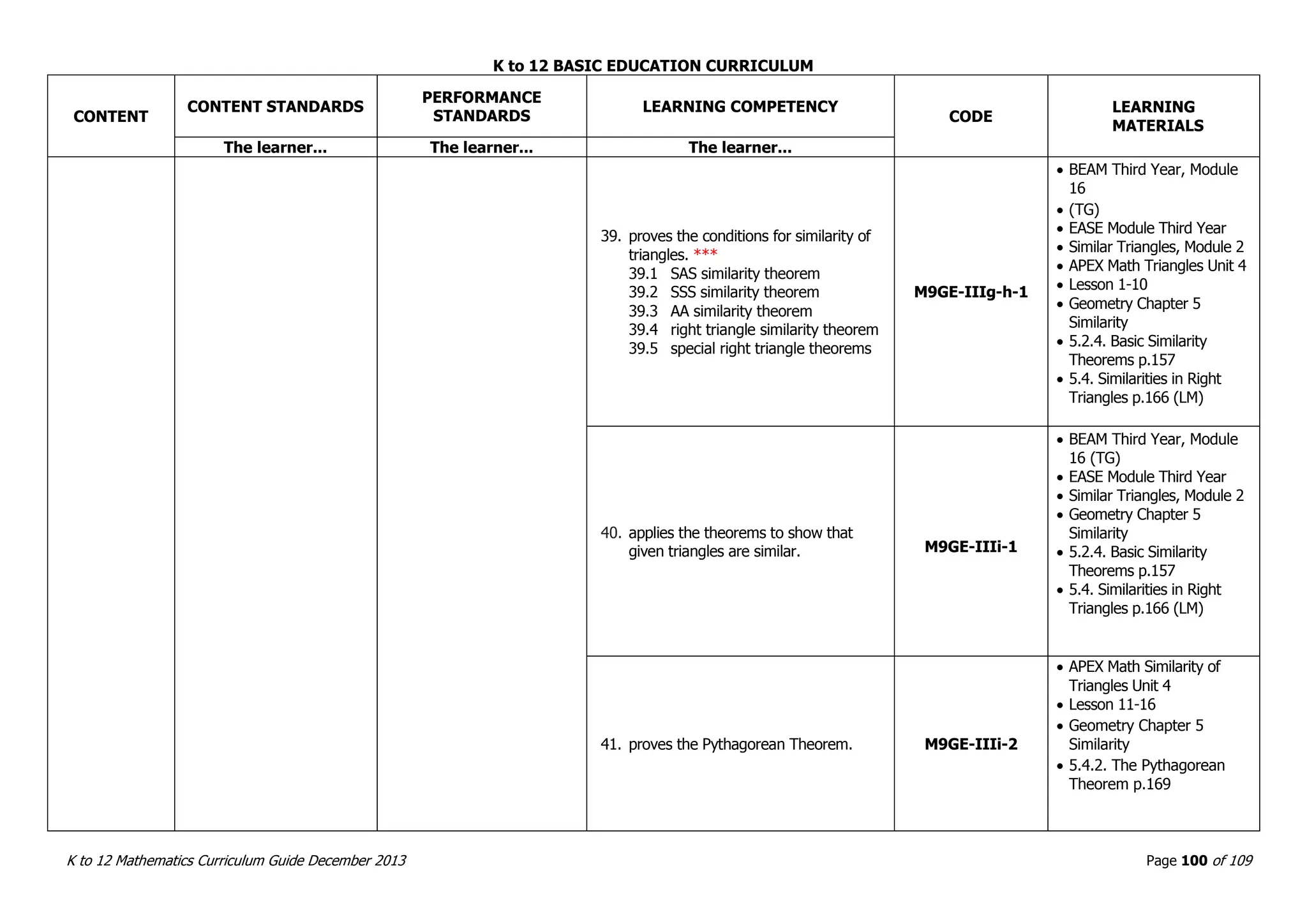
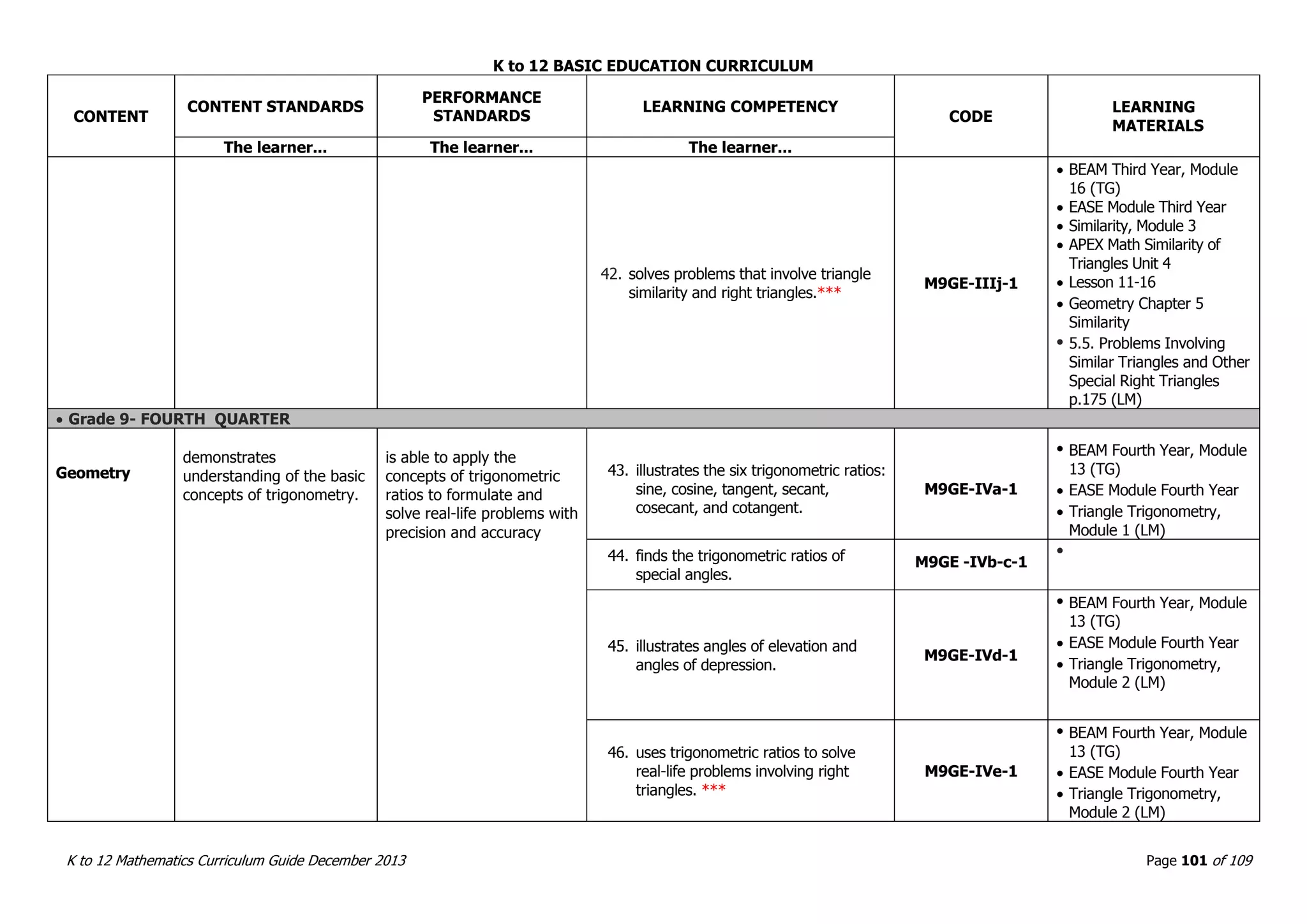
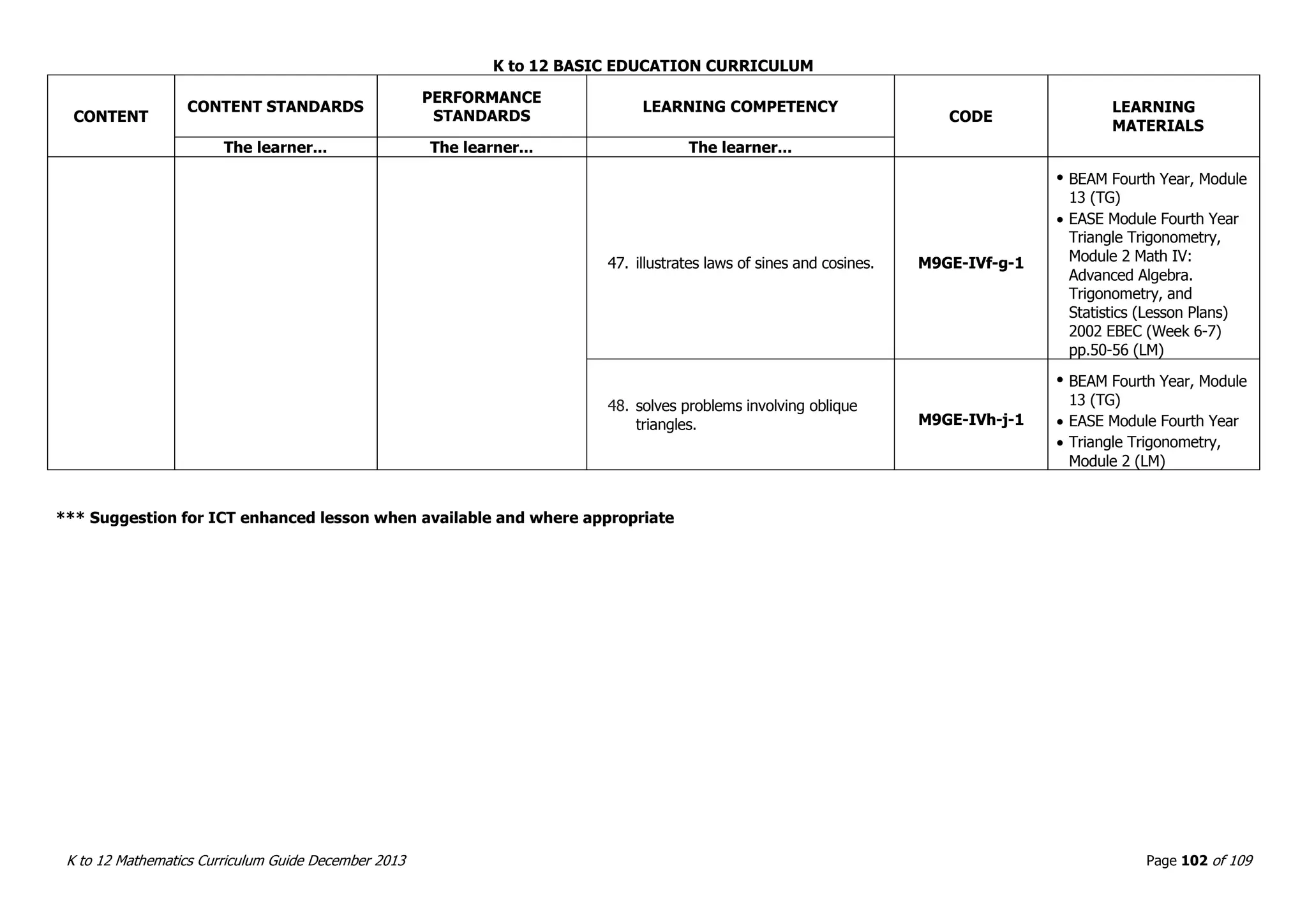
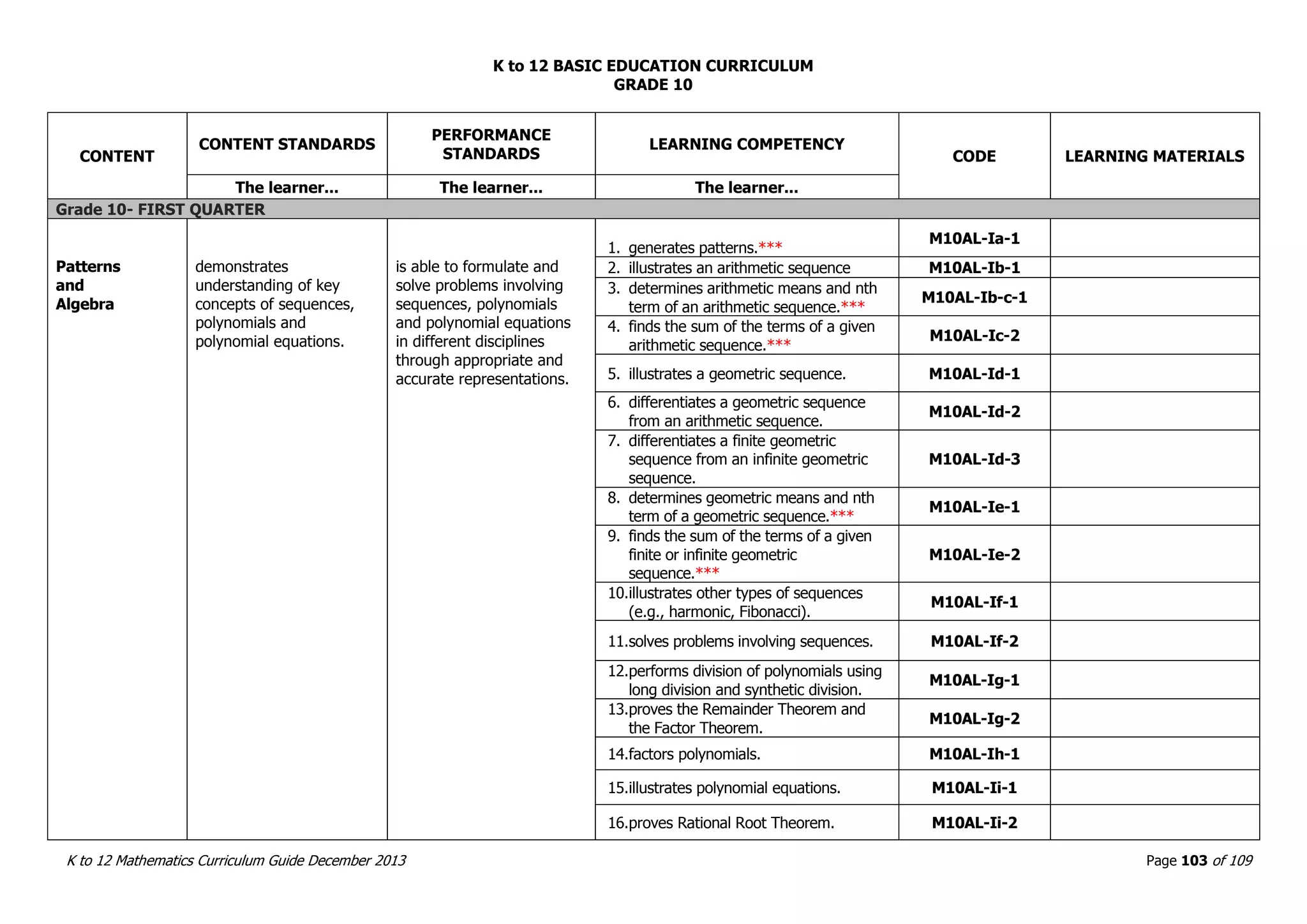
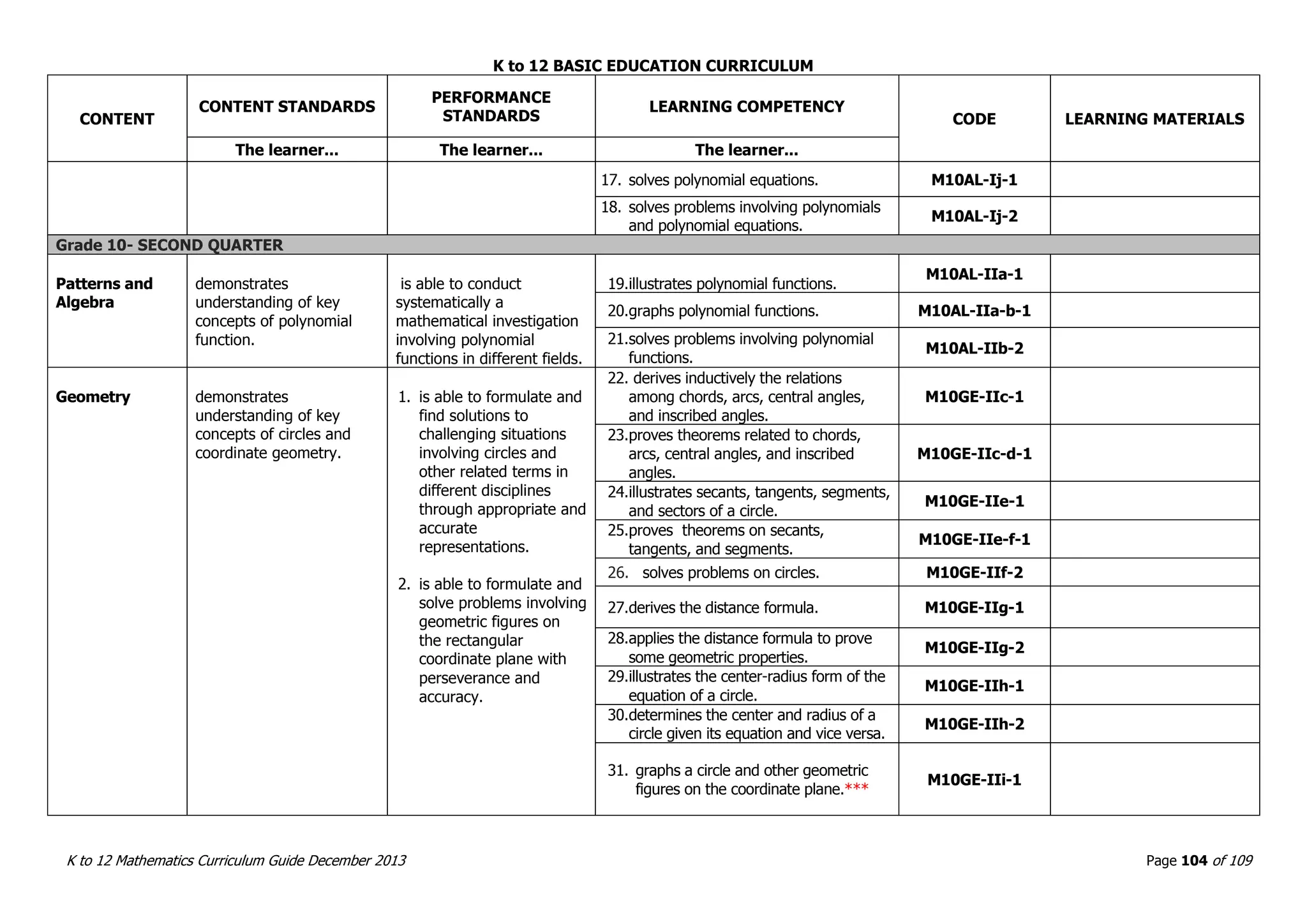
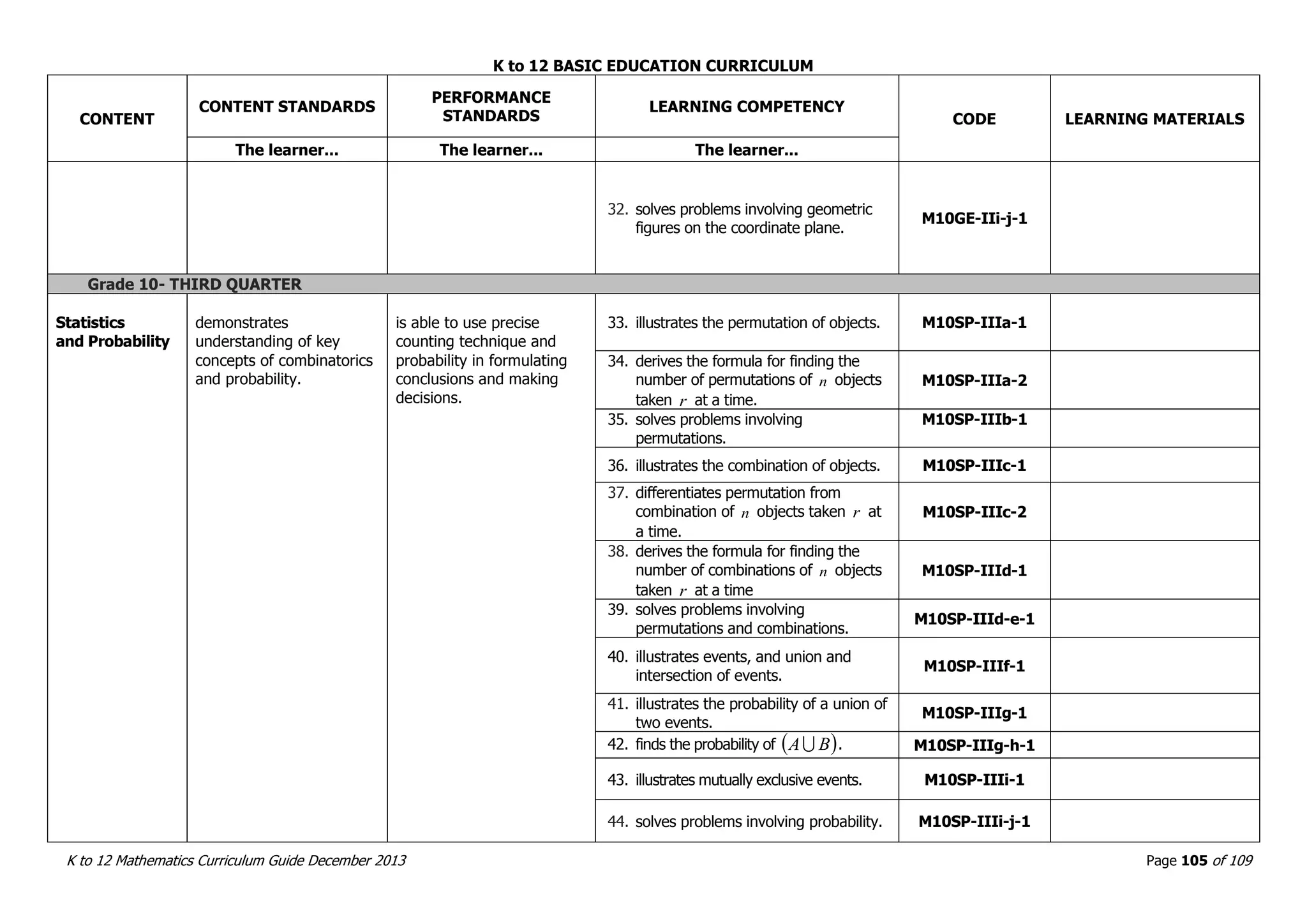
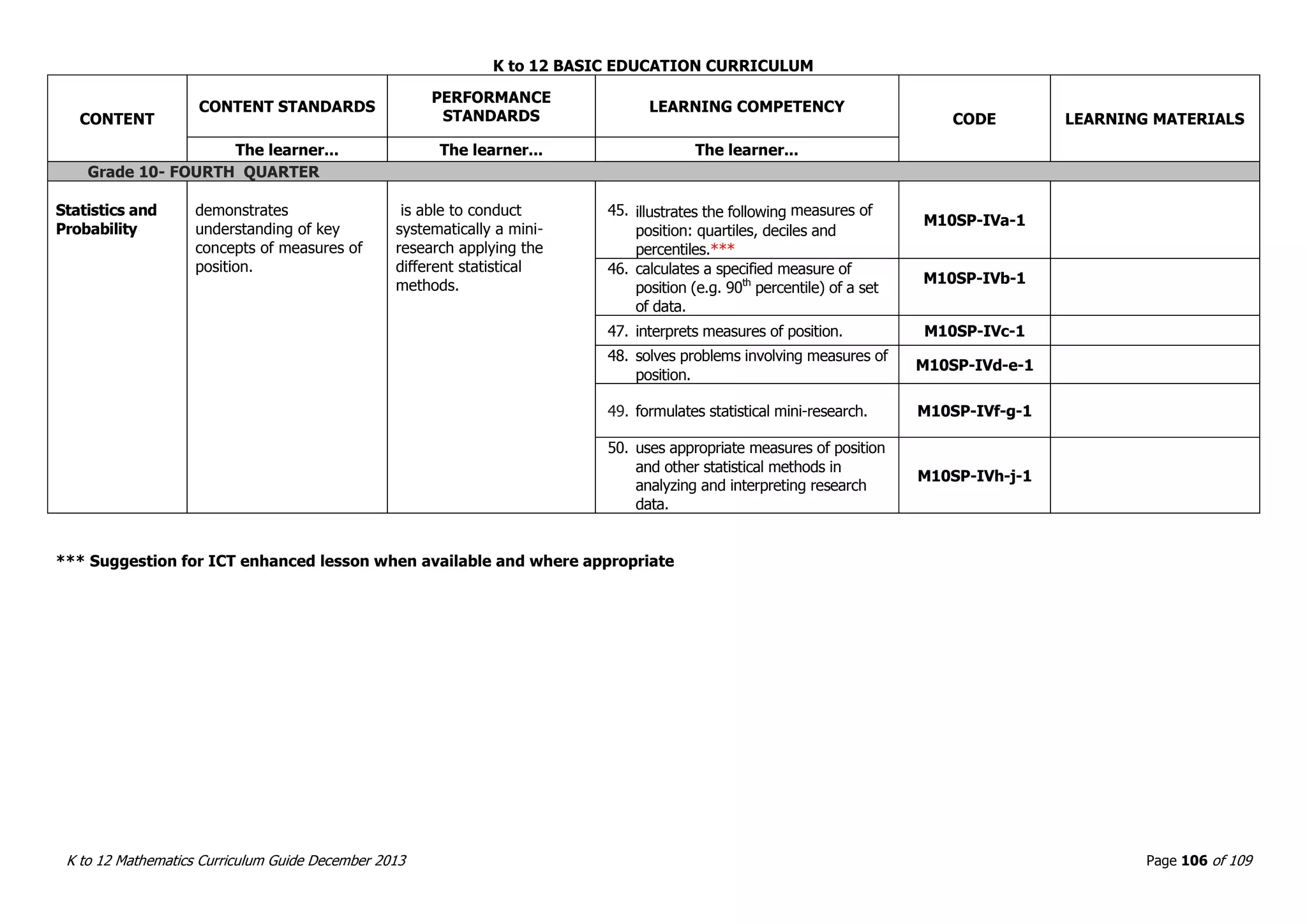
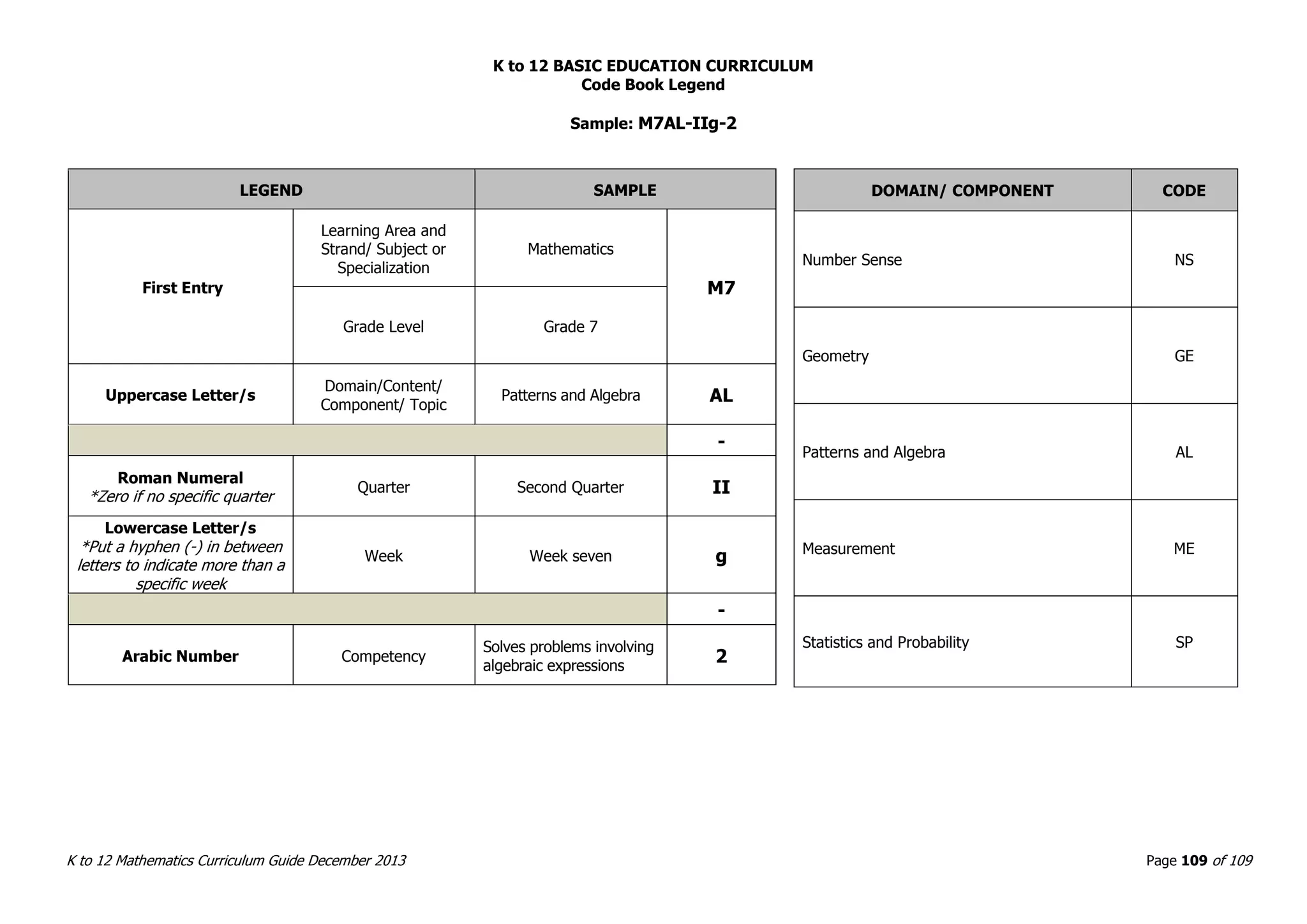
This document outlines the K to 12 mathematics curriculum for grades 1 to 10 in the Philippines. It discusses the goals of critical thinking and problem solving. It describes the content areas of numbers and number sense, measurement, geometry, patterns and algebra, and probability and statistics. It provides the standards and competencies for each grade level, with a focus on applying mathematical concepts to real-life problem solving. Time allotment for mathematics is 4 hours per week for grades 1 to 6 and 50 minutes daily for grades 7 to 10.