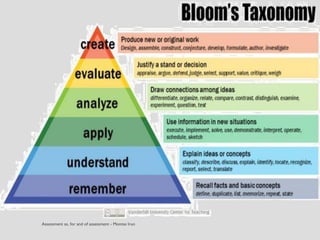
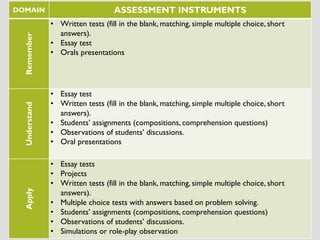
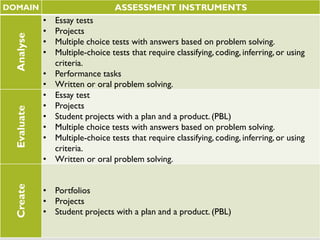
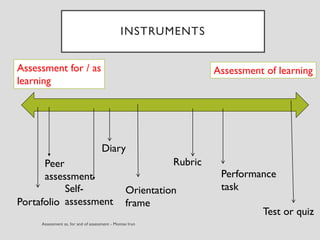
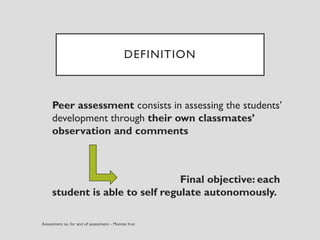
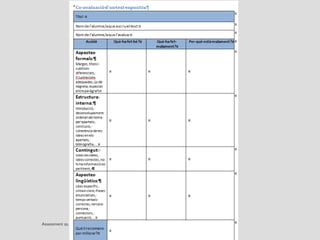
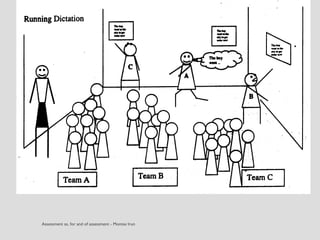
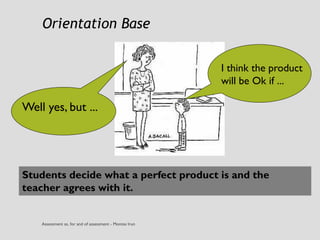
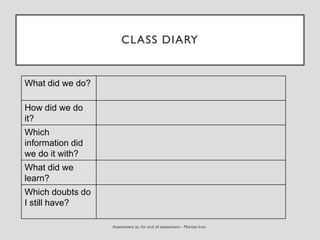
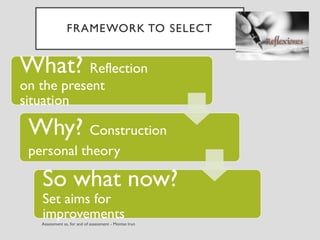
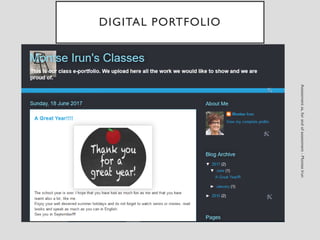
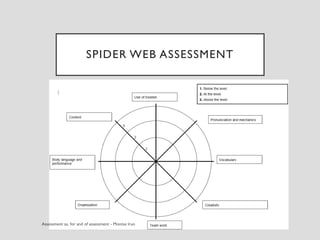
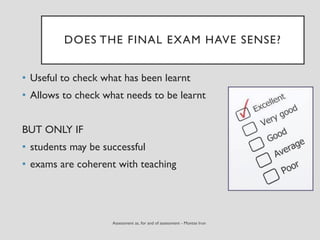
This document discusses various assessment instruments that can be used for 21st century learners. It begins by classifying common assessment instruments according to their level of cognitive complexity, from remembering to creating. It then discusses the functions of different assessment types, such as for learning versus of learning. The rest of the document explores specific assessment instruments and strategies in more detail, including rubrics, portfolios, diaries, peer assessment, and various testing formats. The overall aim is to suggest a range of options for holistically assessing students' competencies rather than just facts.