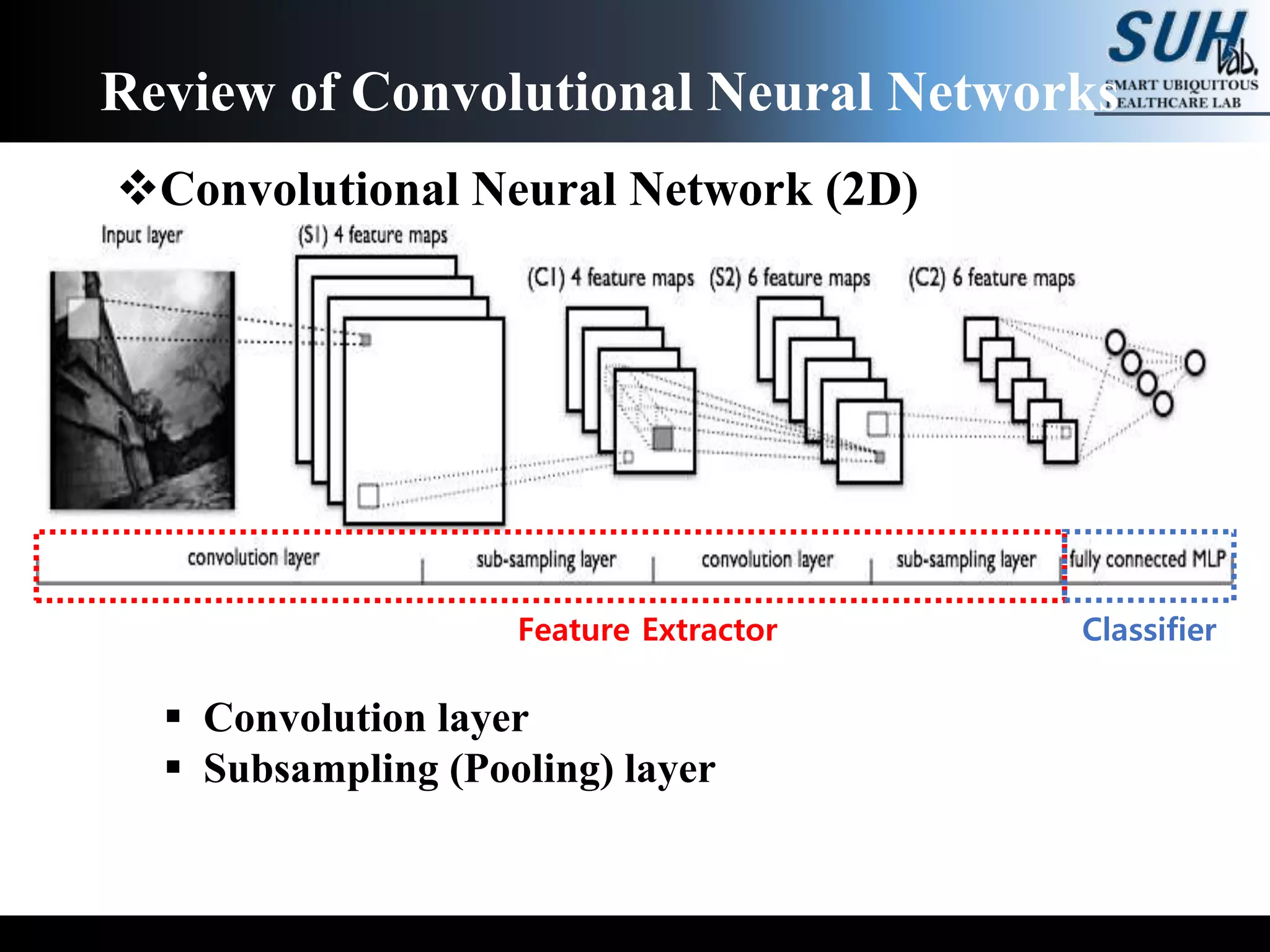
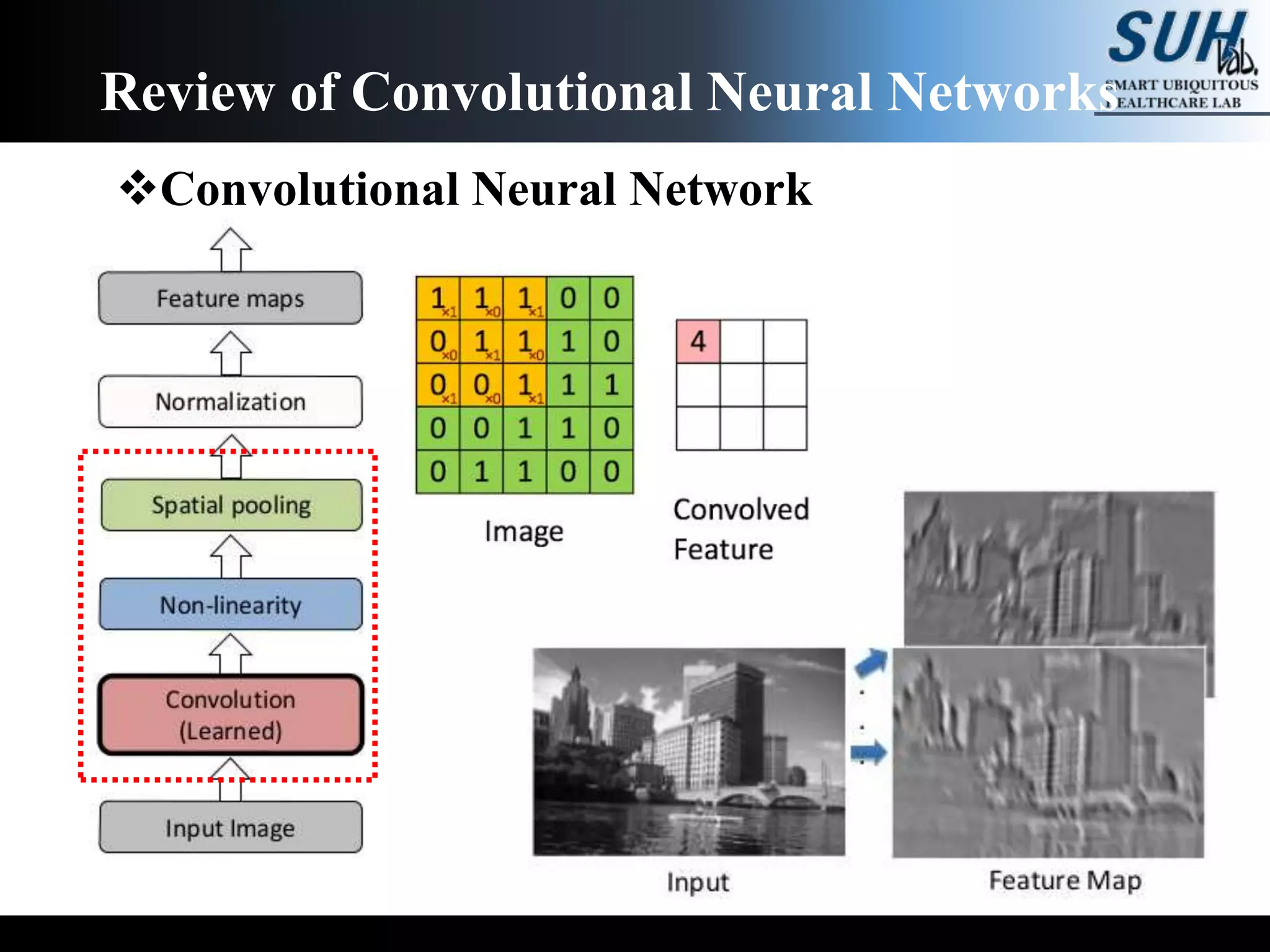
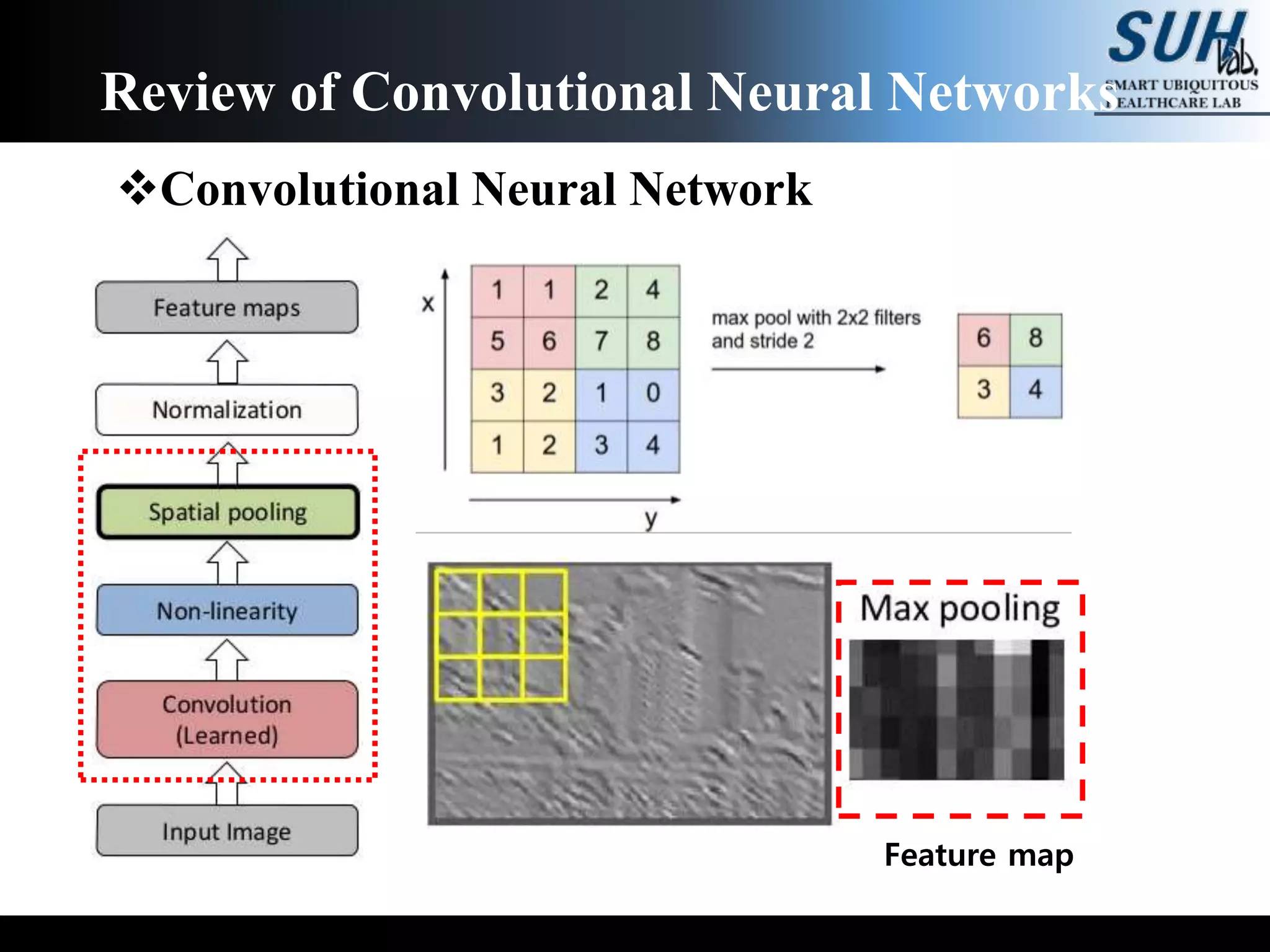
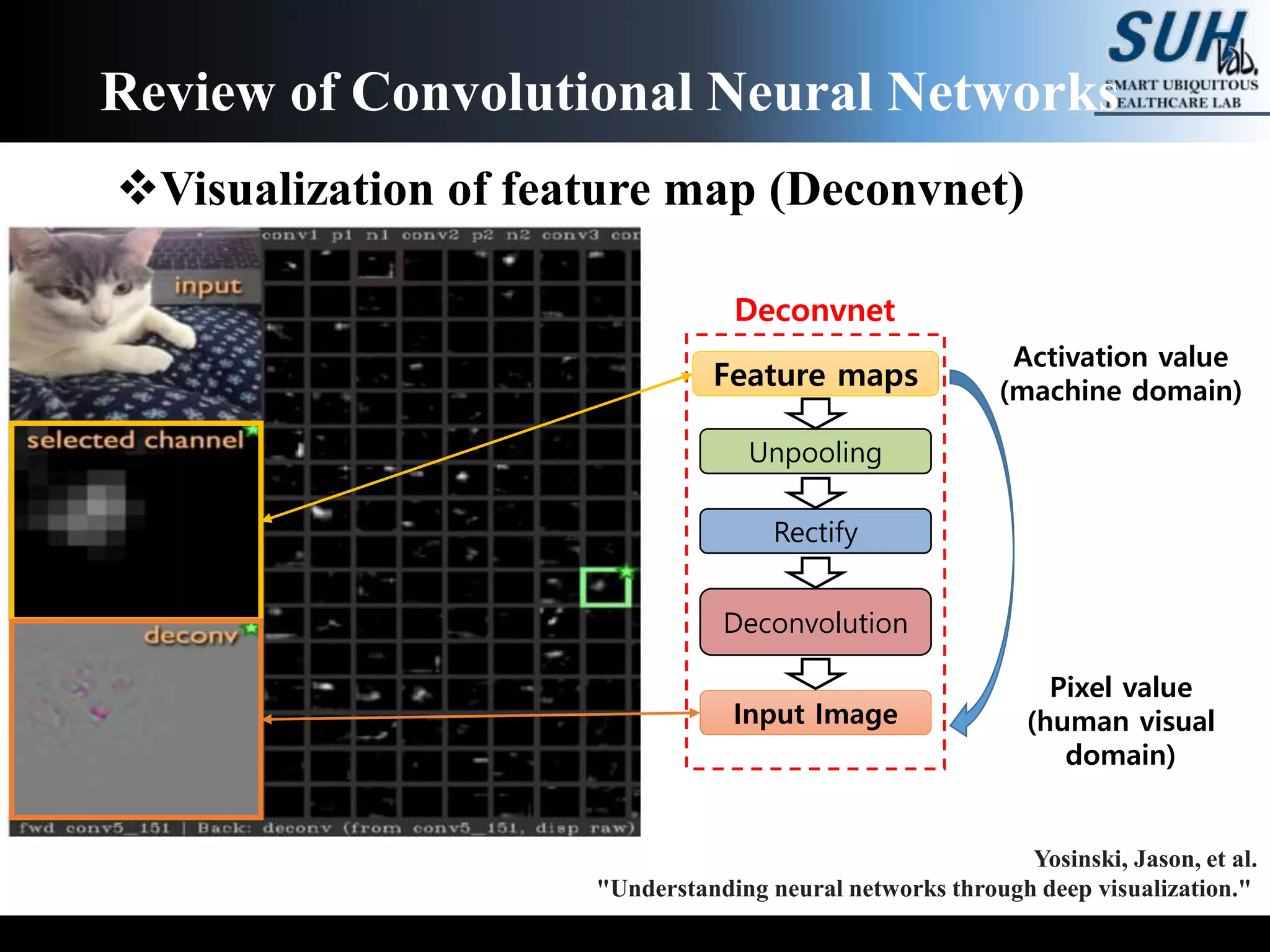
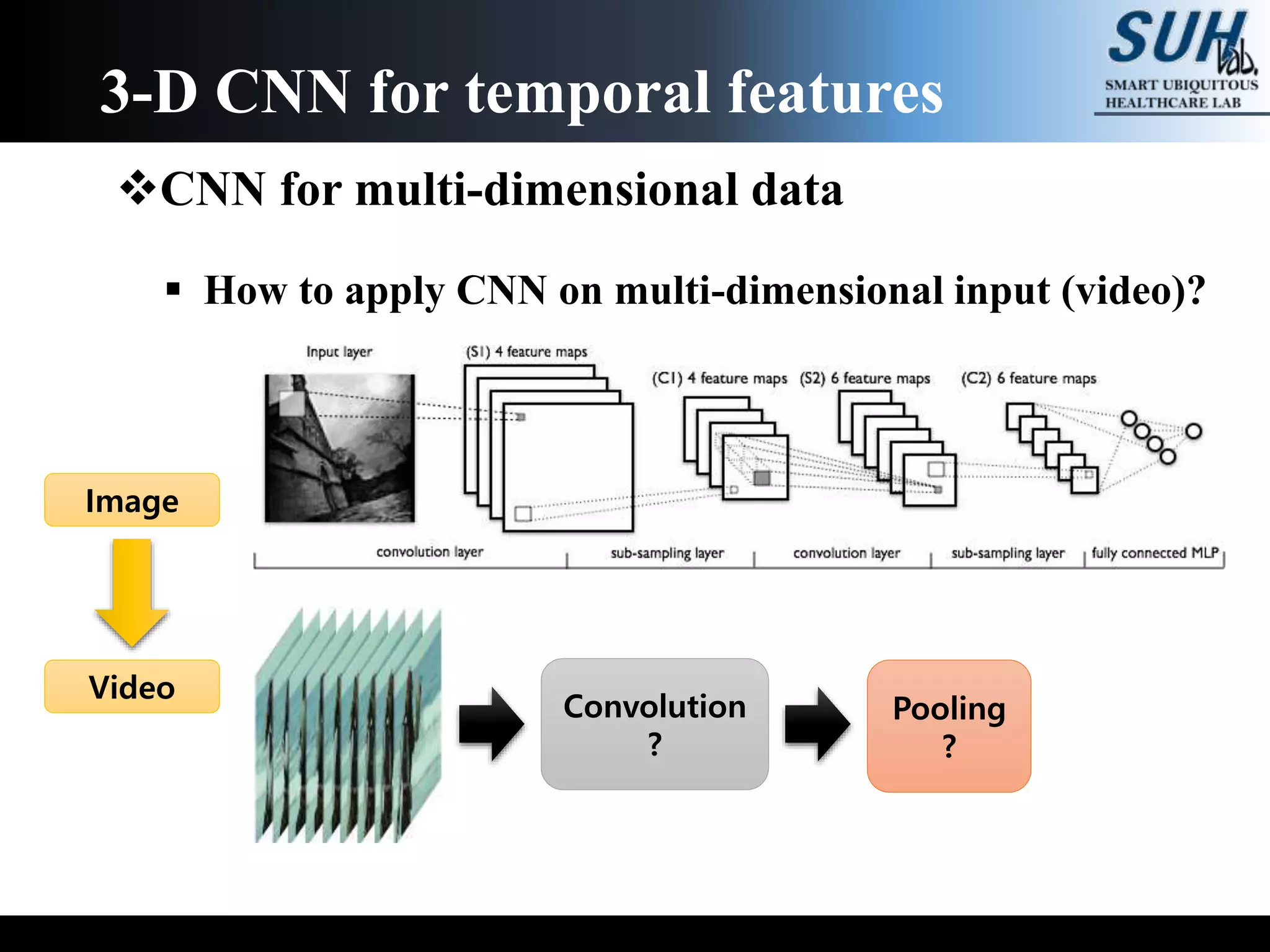
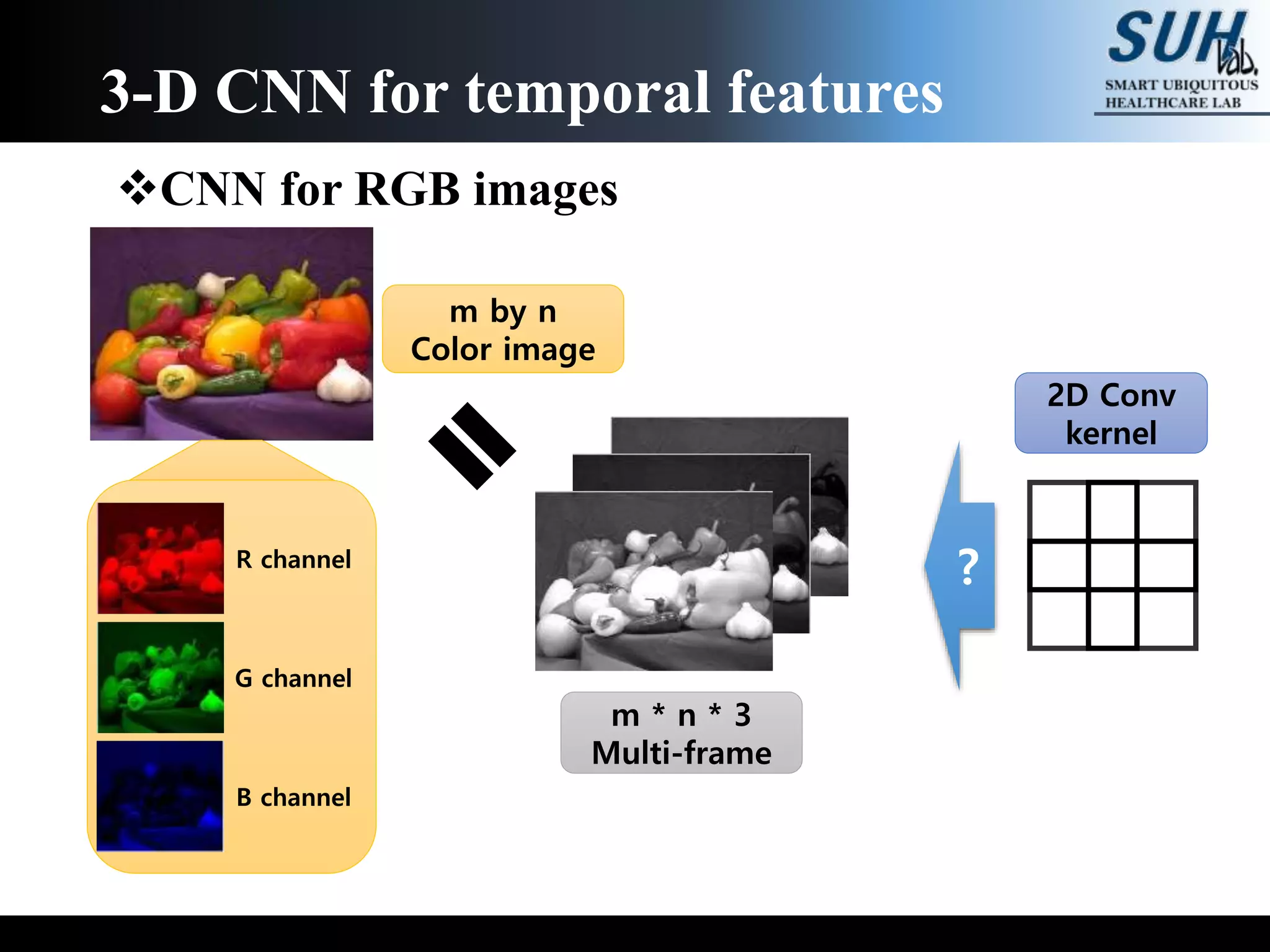
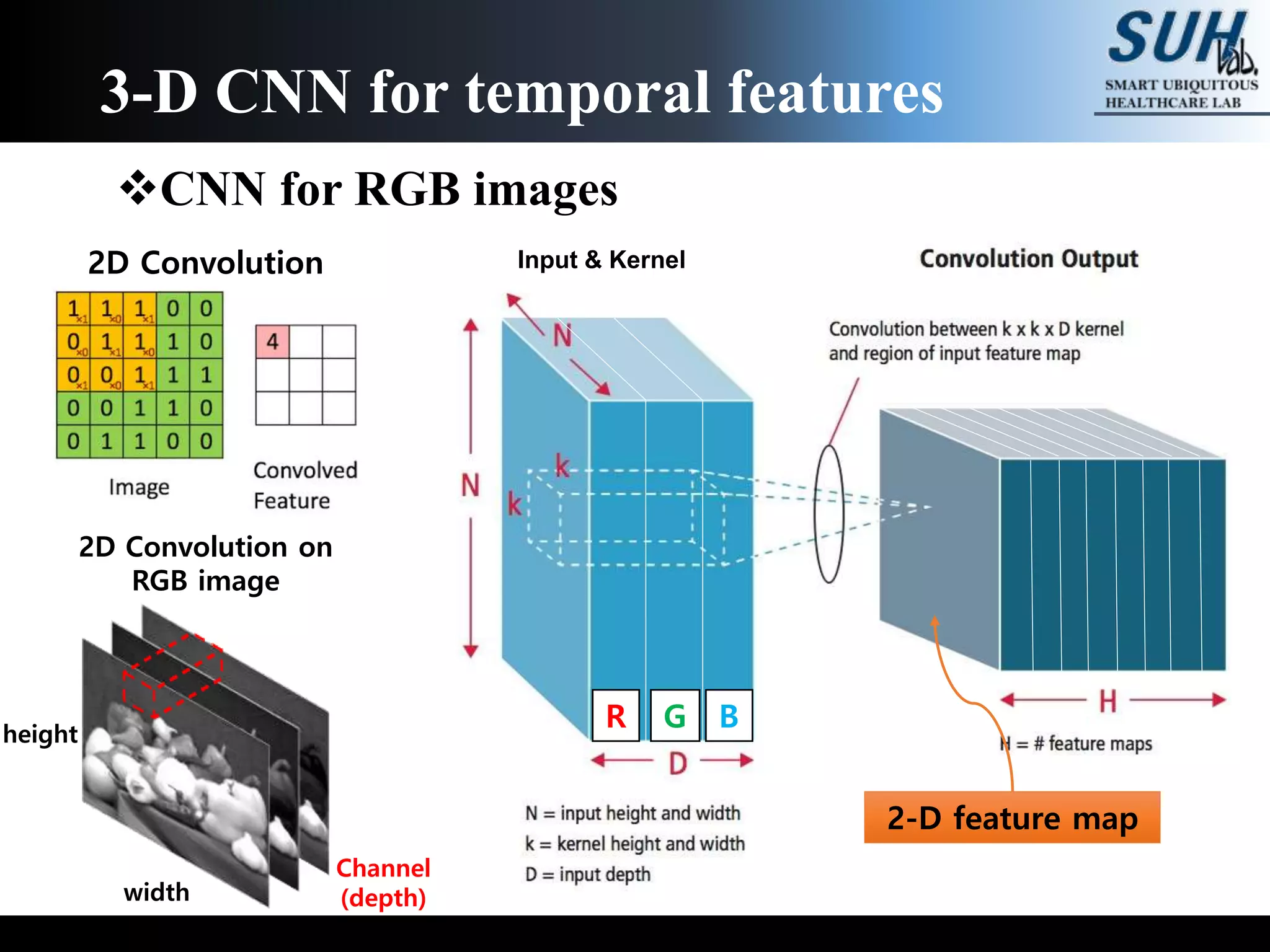
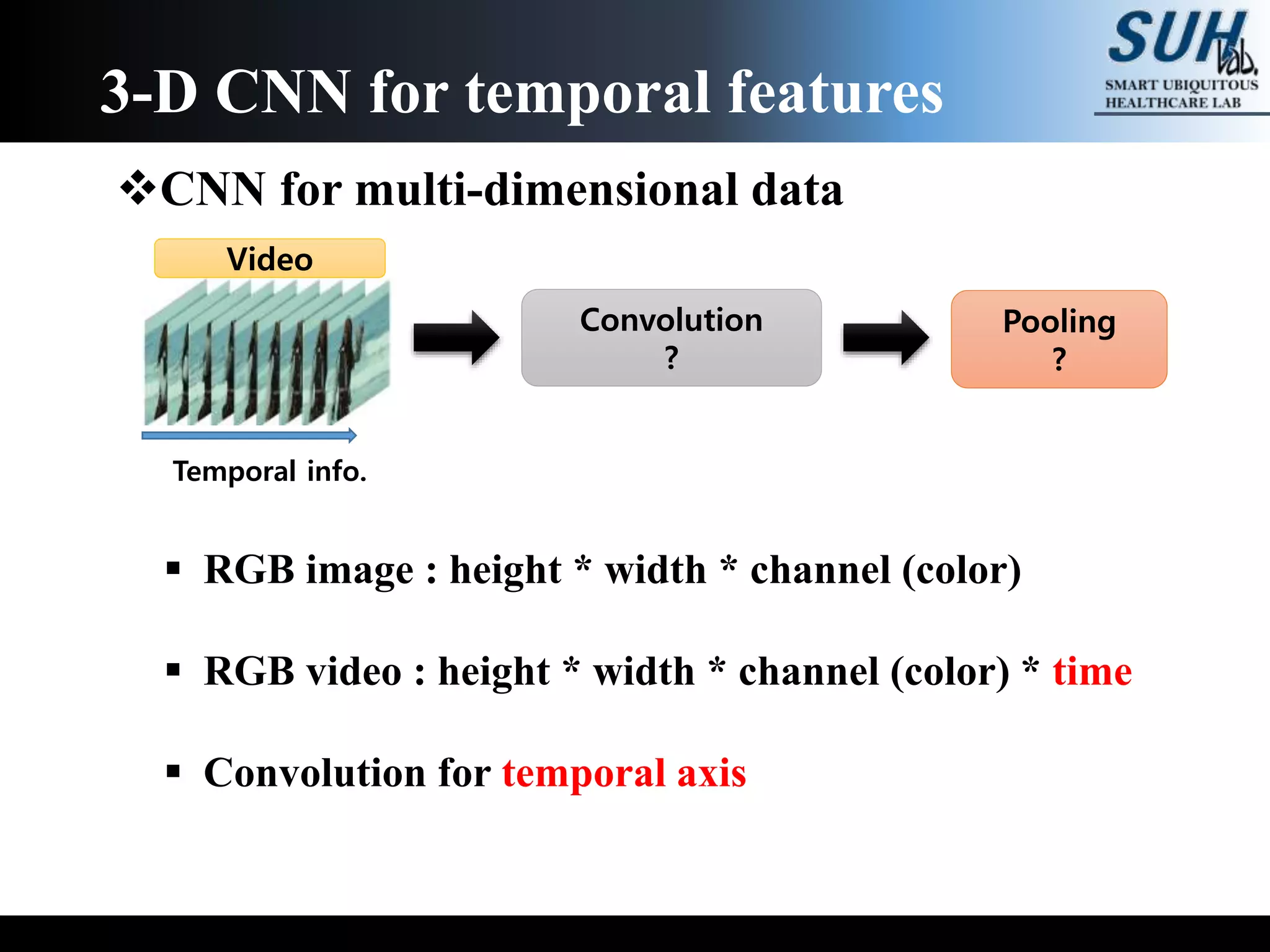
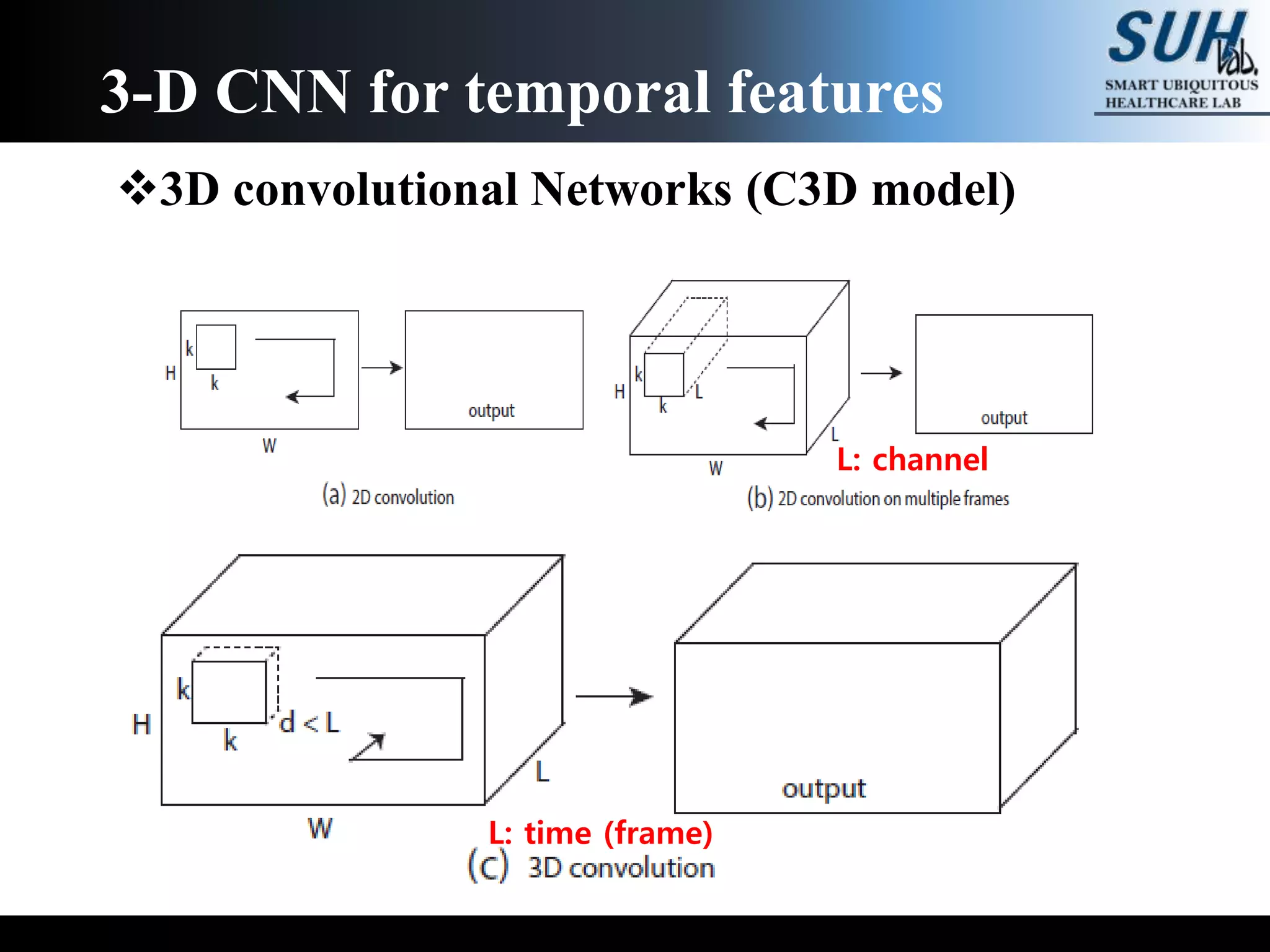
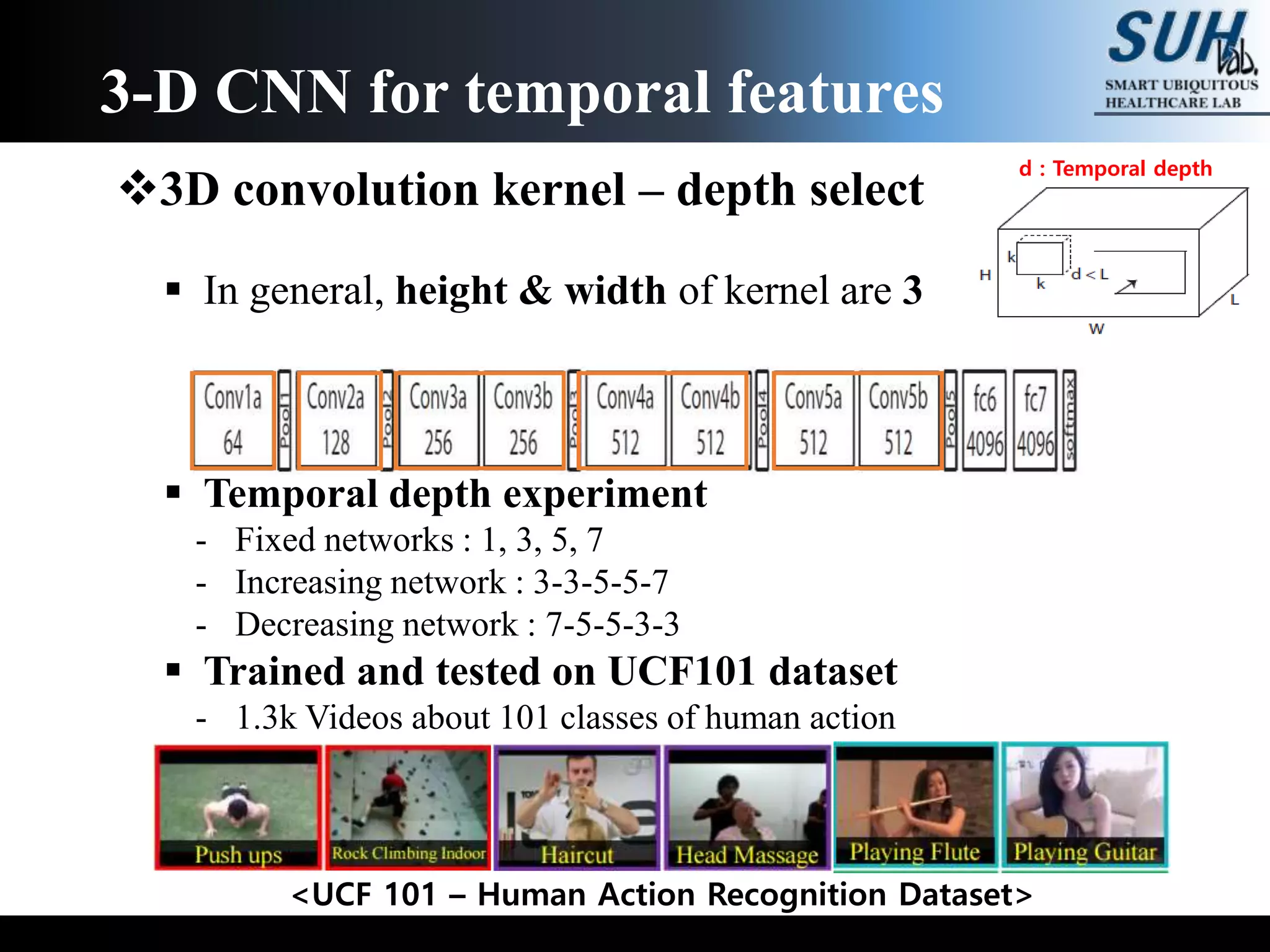
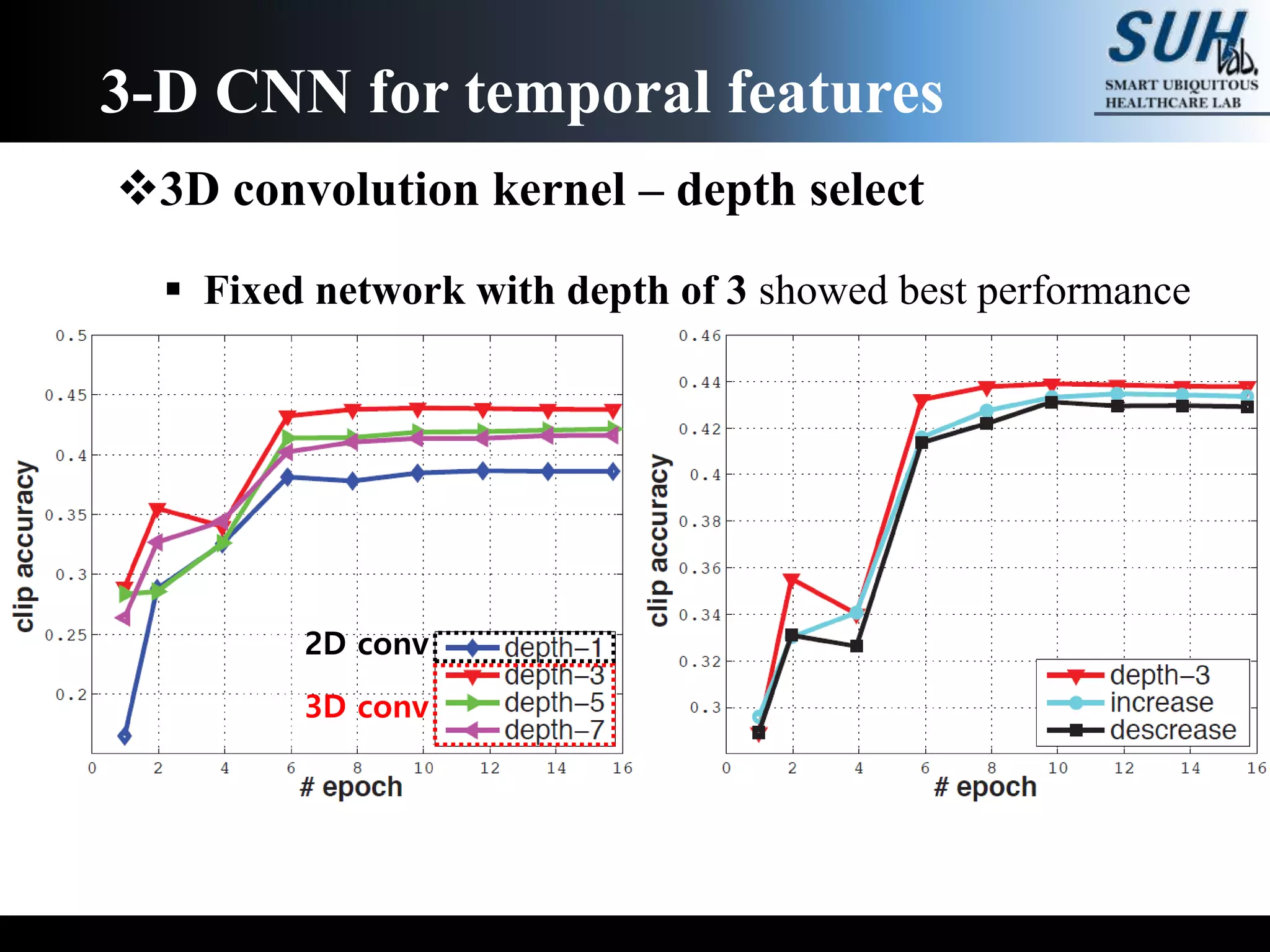
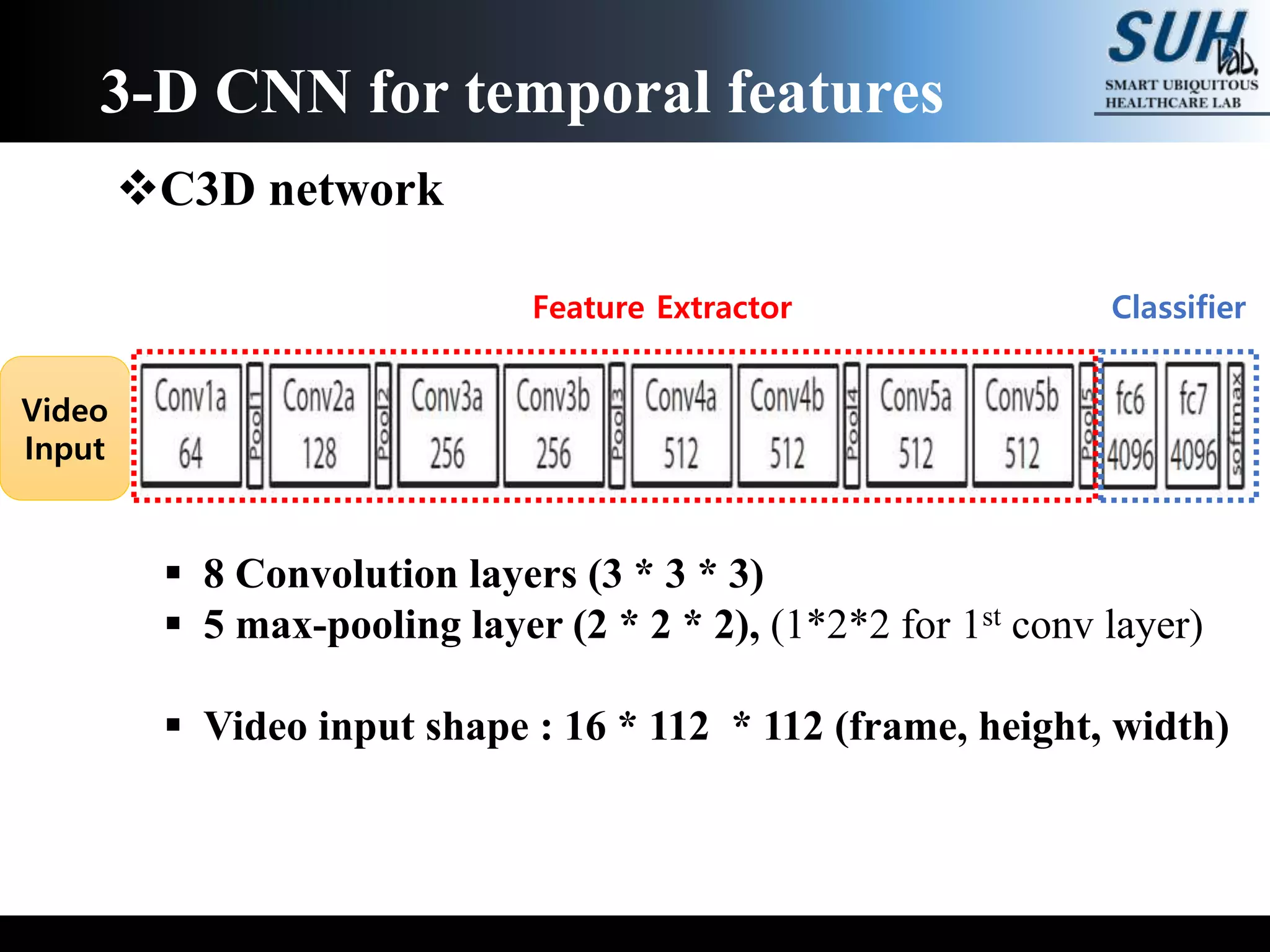
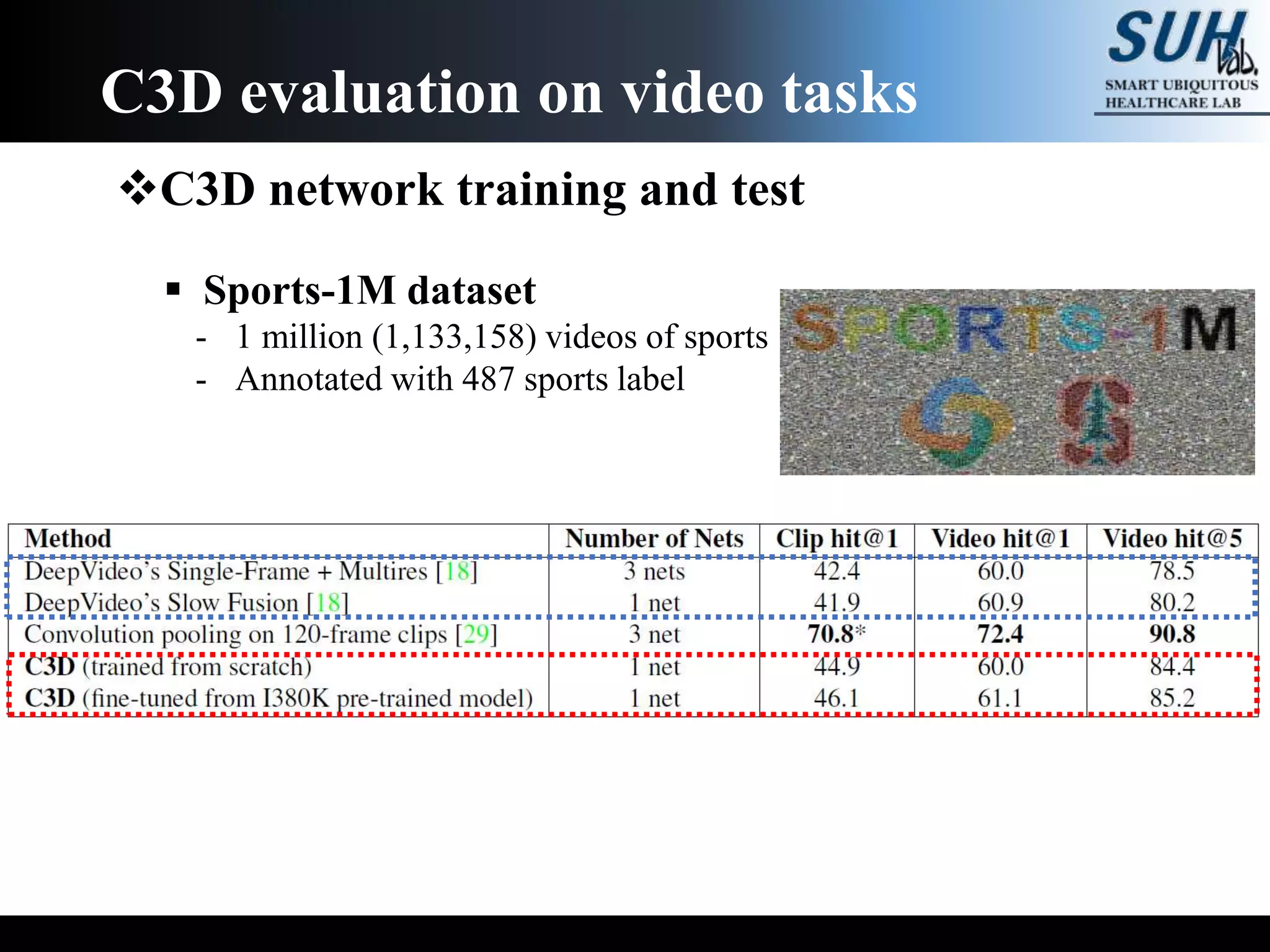
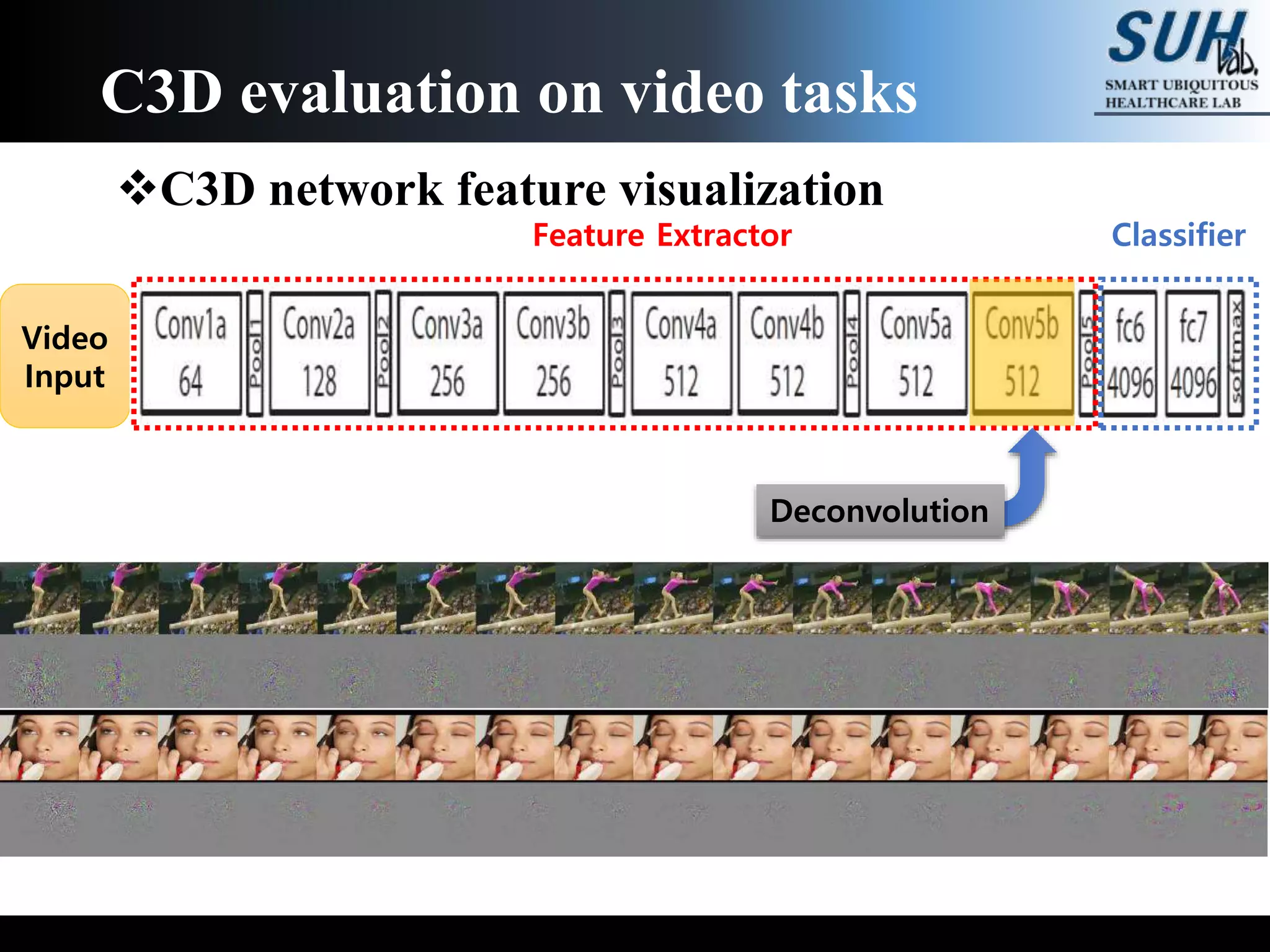
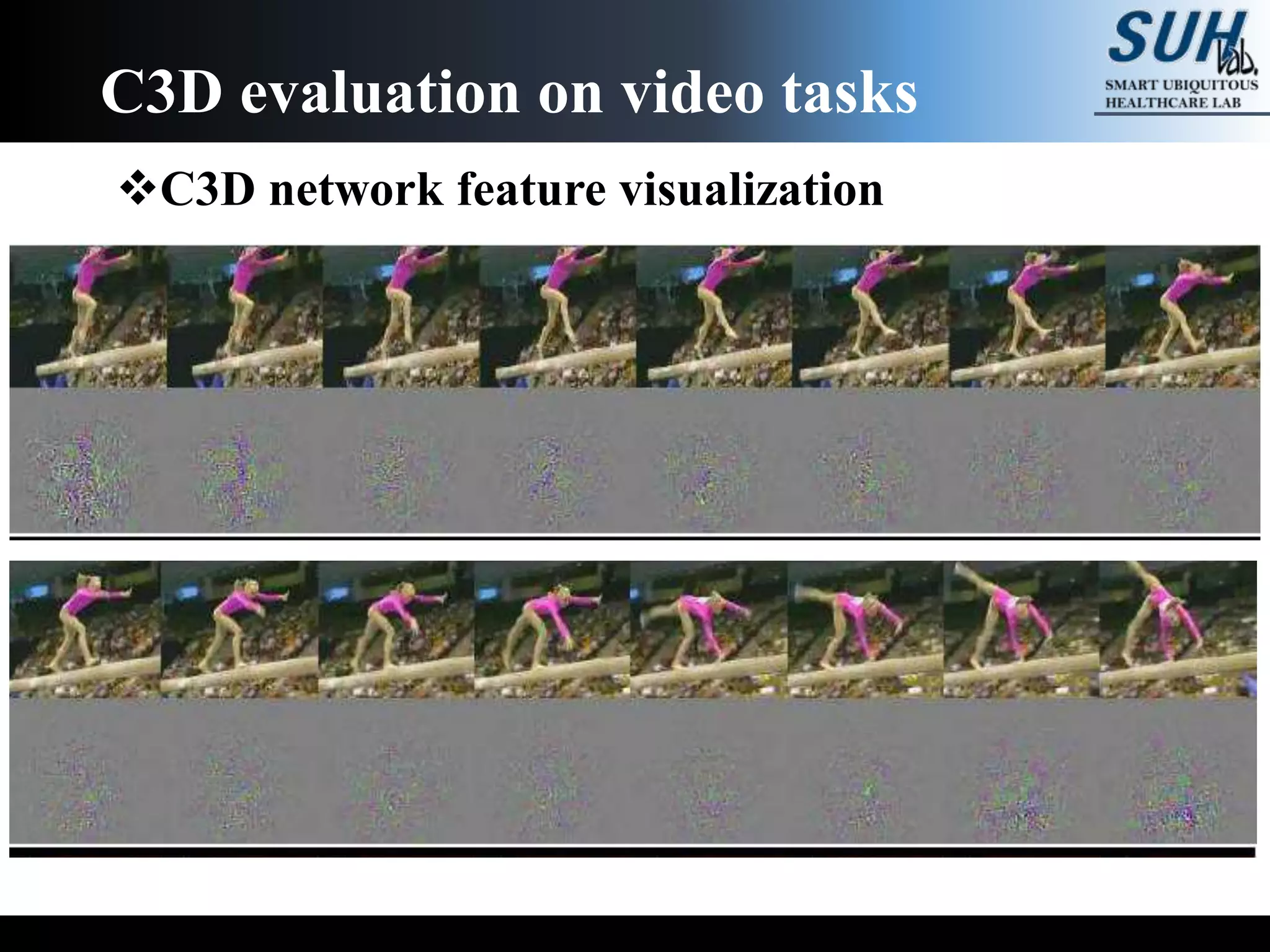
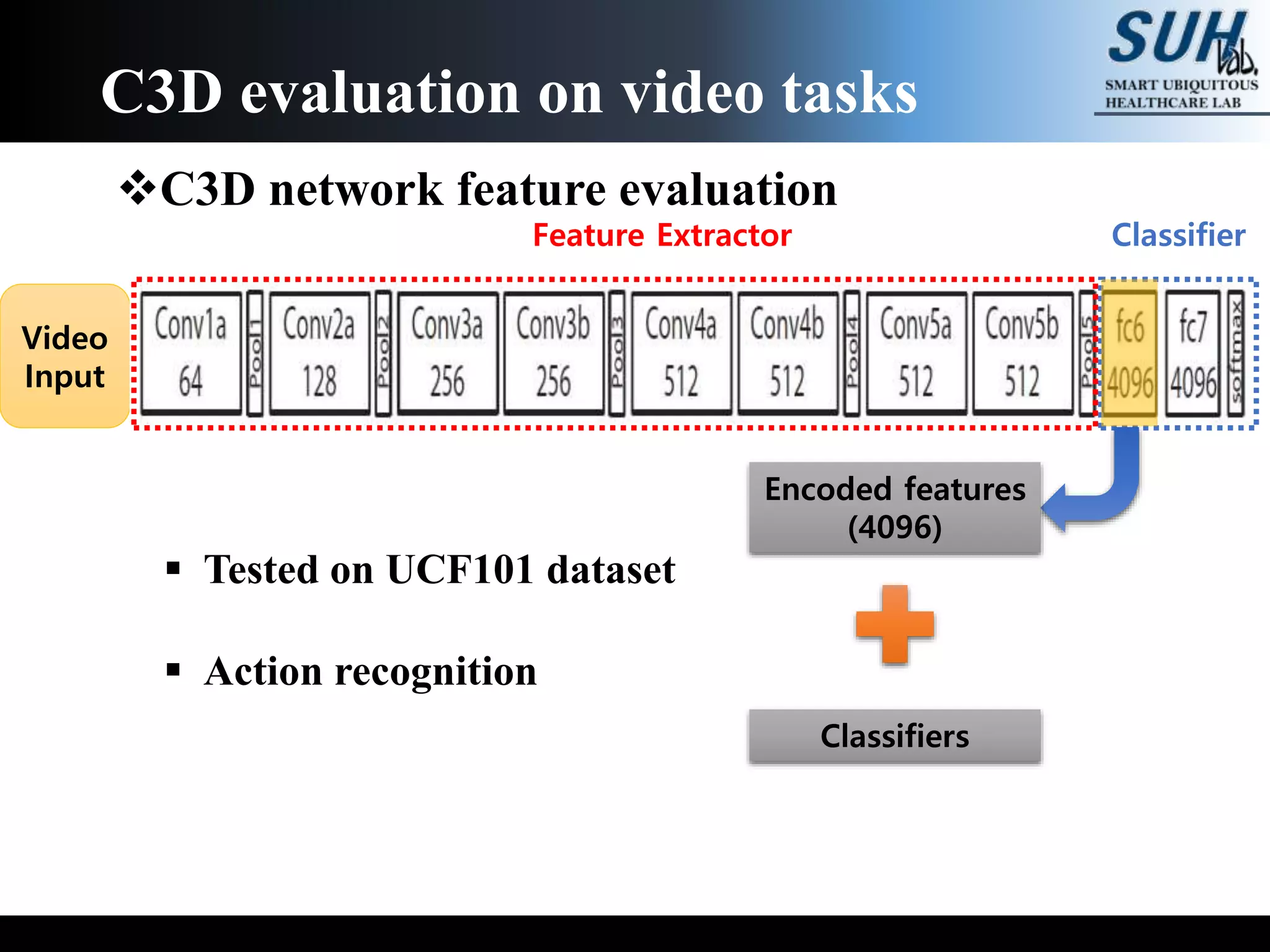
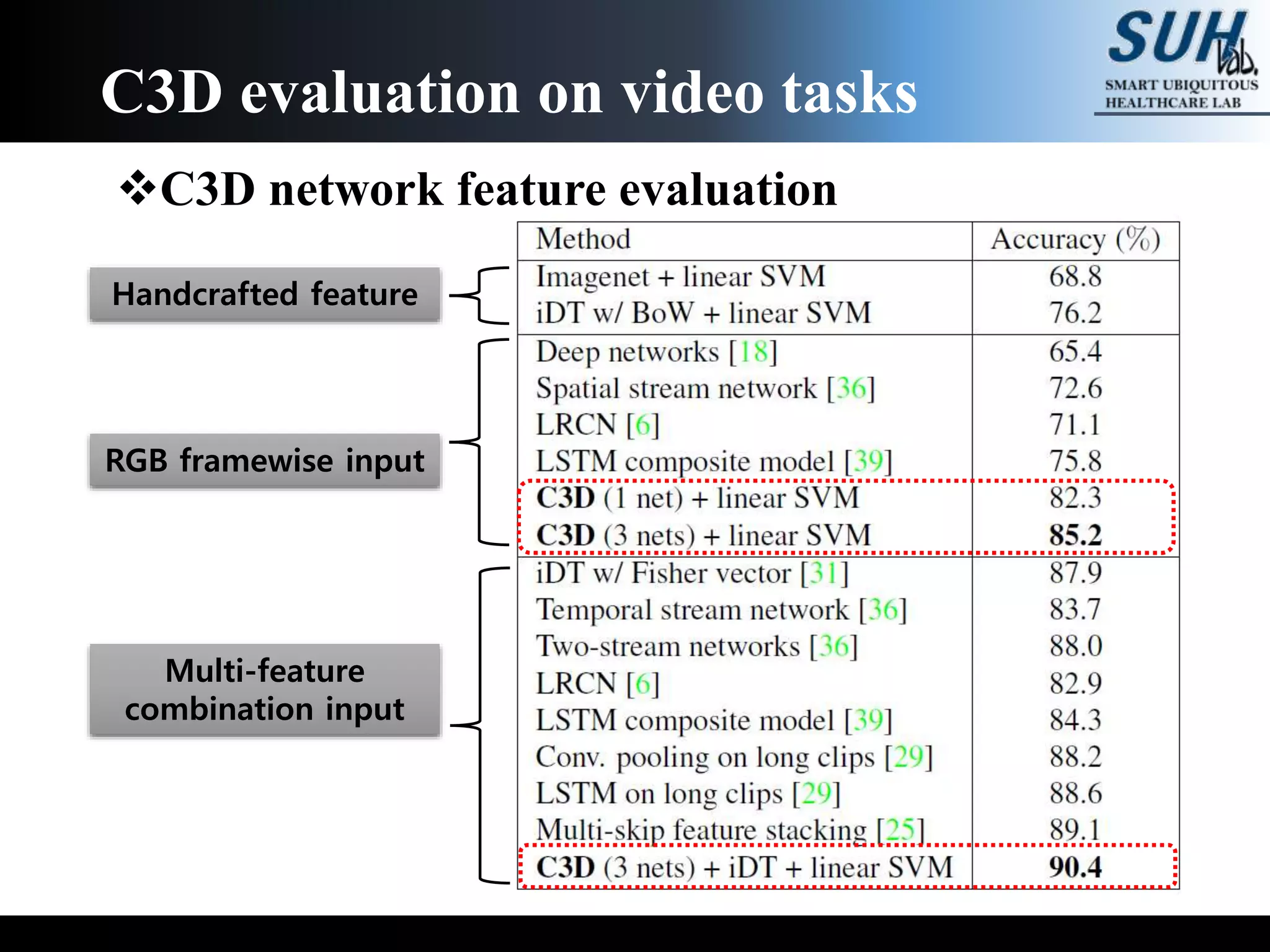
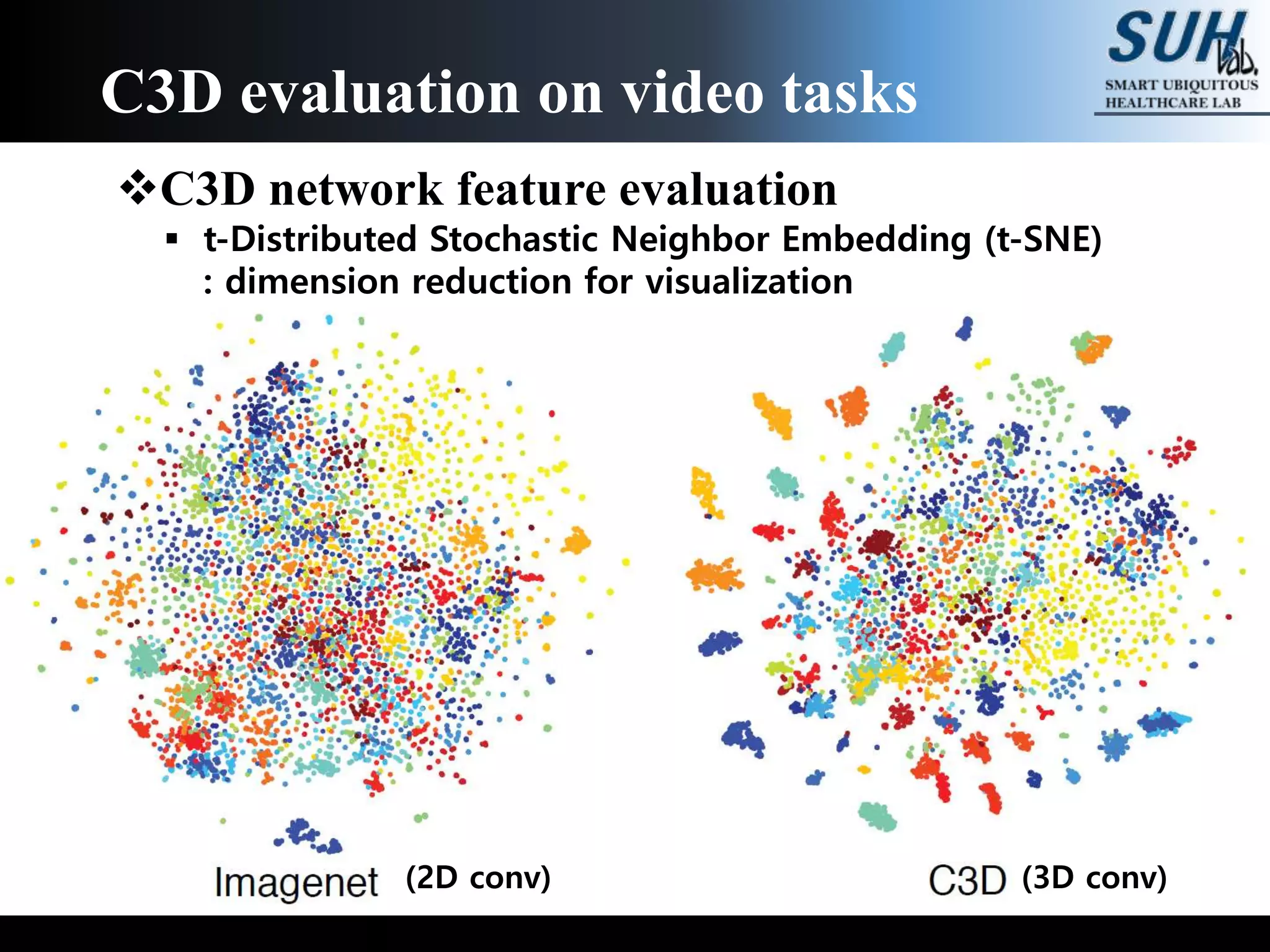
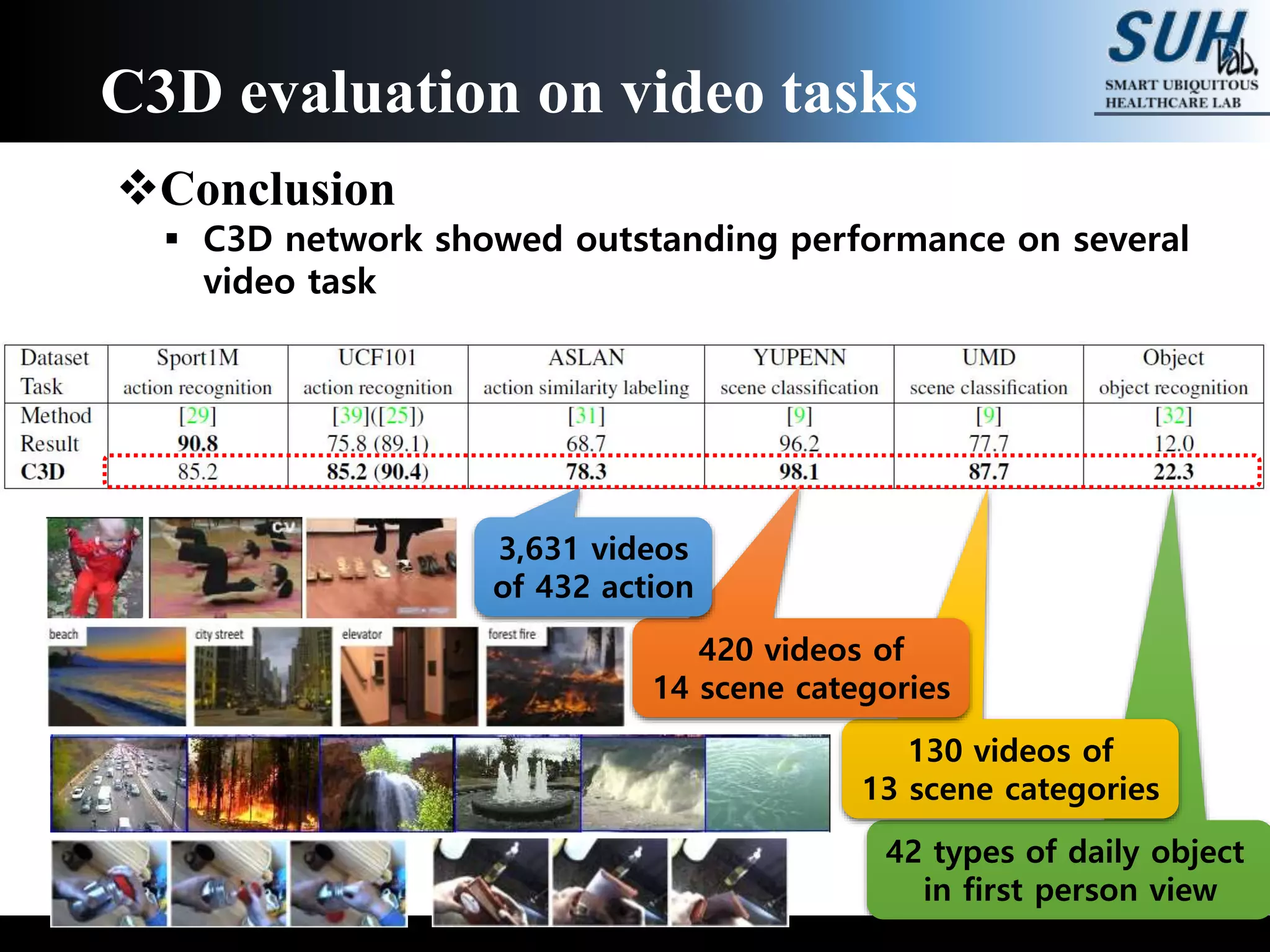
The document discusses convolutional neural networks (CNNs), focusing on the development and evaluation of 3D CNNs for video data. Specifically, it reviews the architecture of the C3D model, its training on datasets such as UCF101 and Sports-1M, and evaluates its performance in action recognition tasks. The findings highlight the effectiveness of 3D CNNs in extracting spatiotemporal features from video inputs.