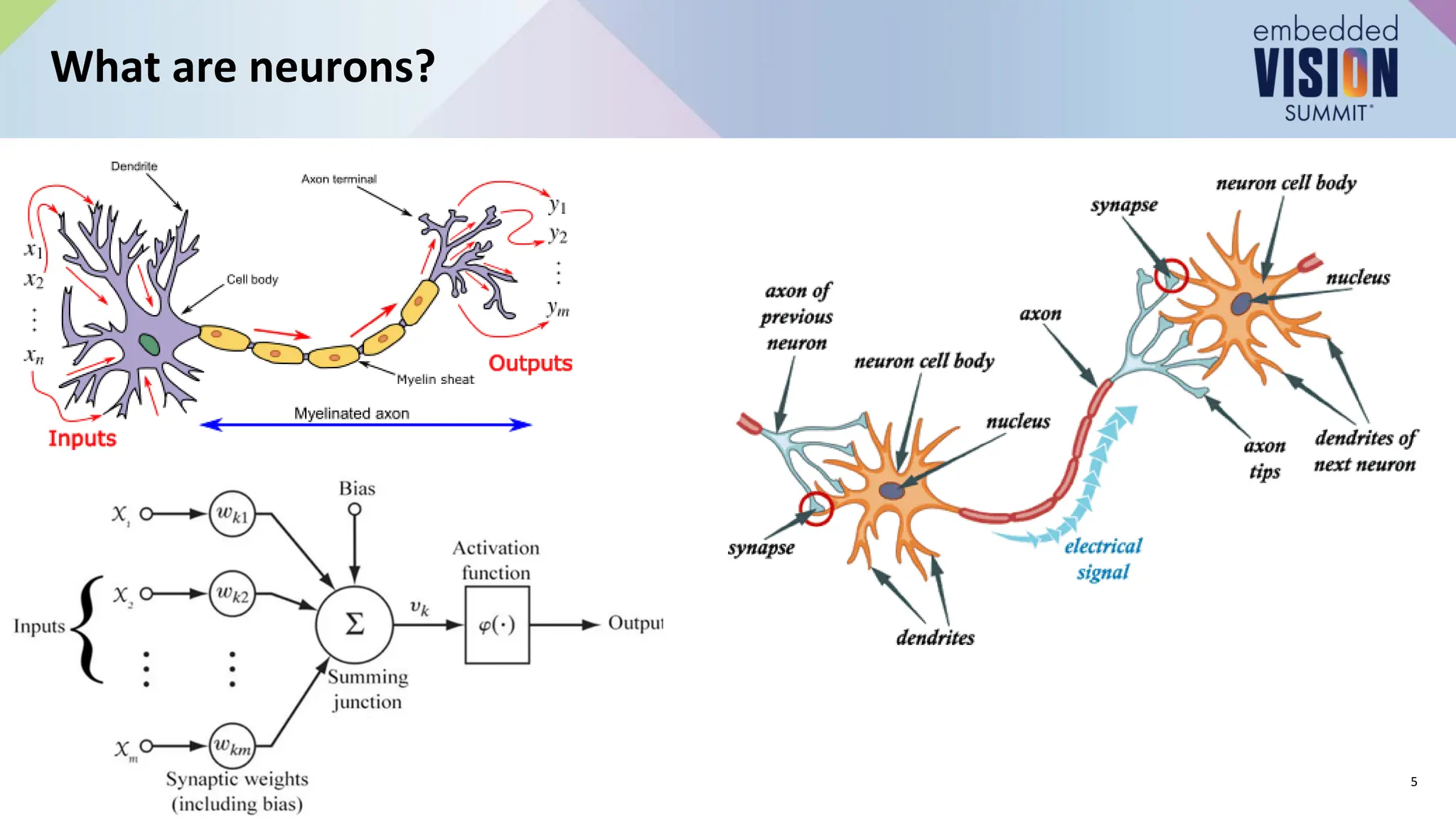
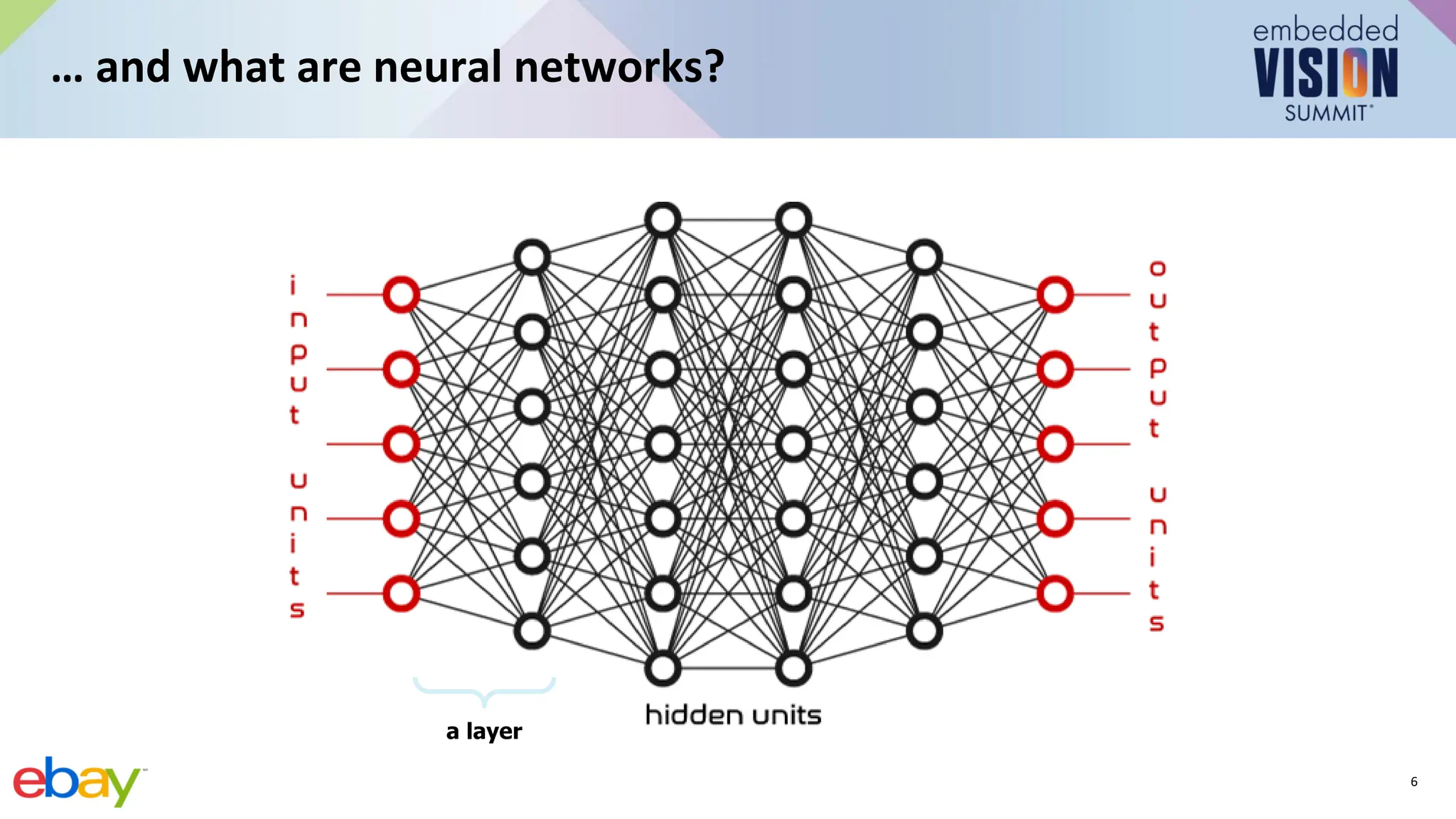
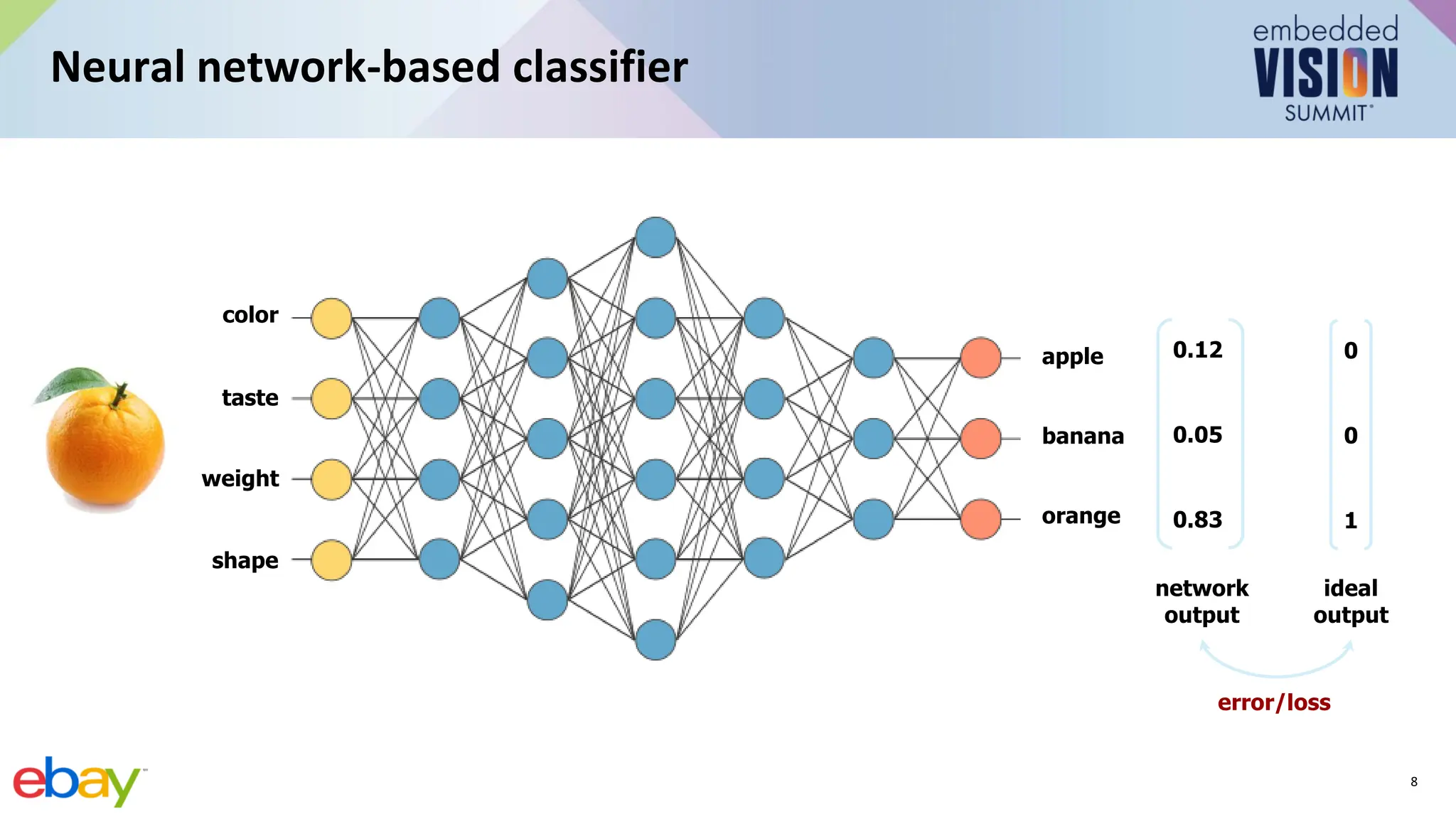
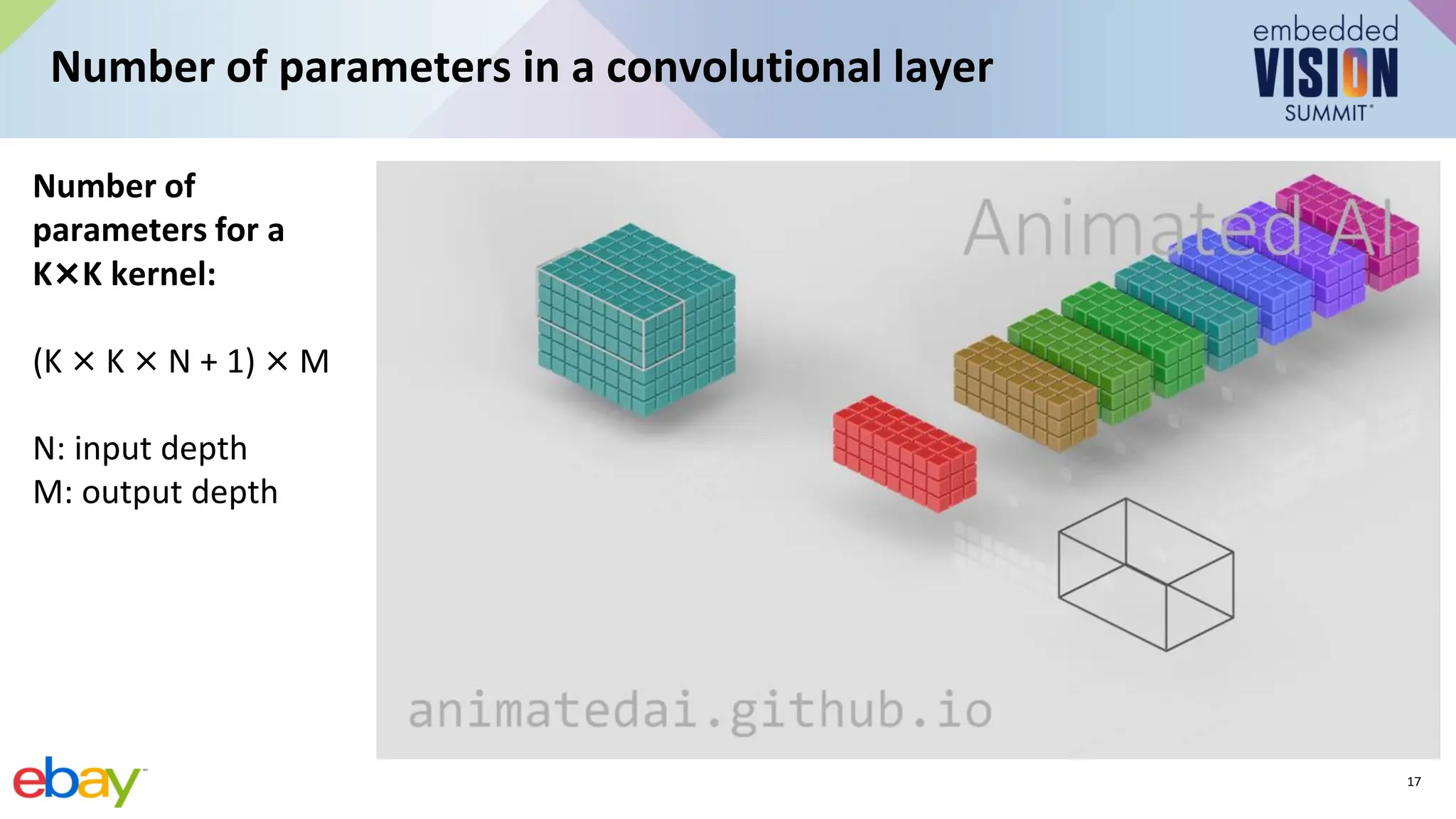
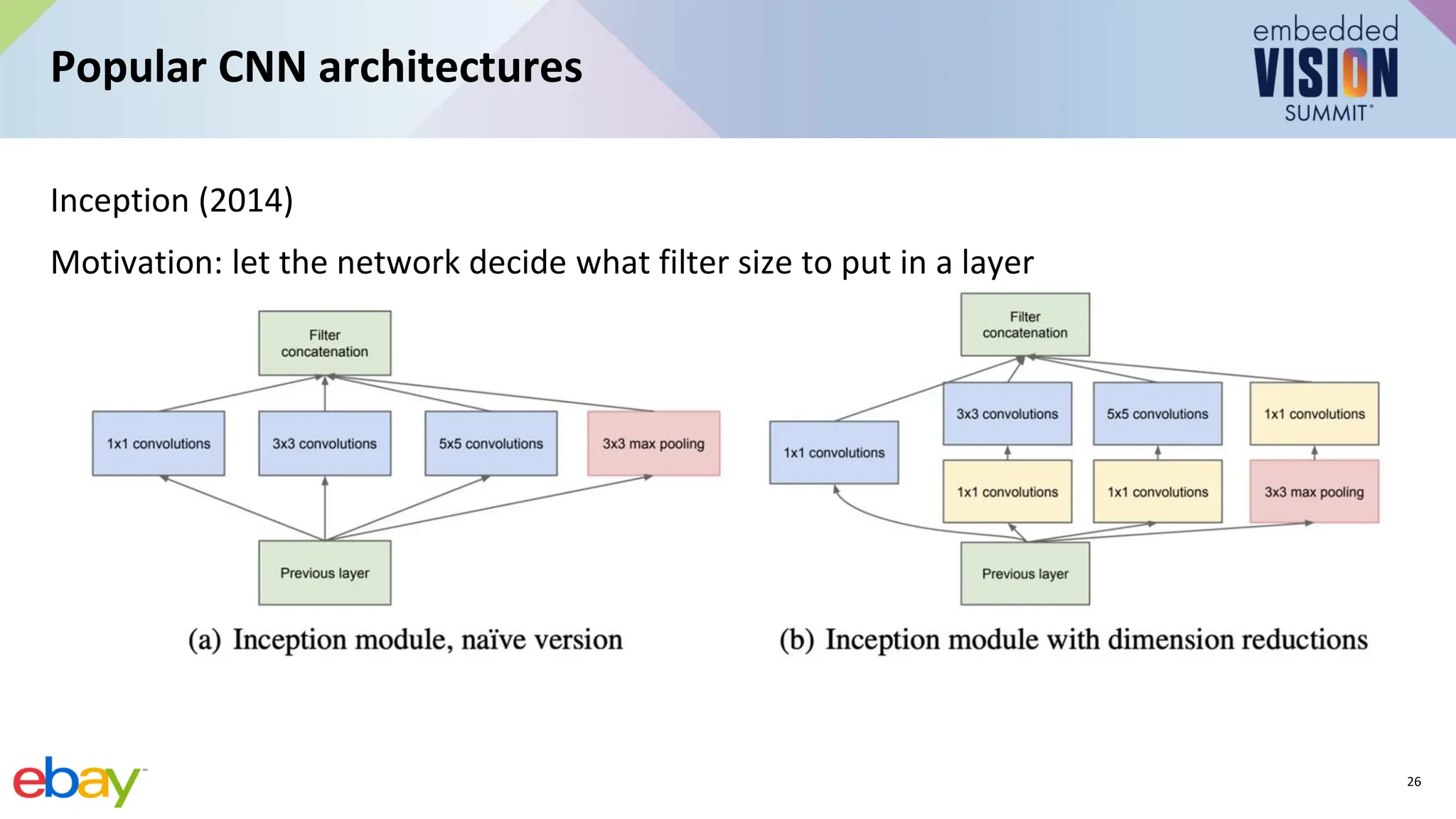
This document provides an introduction to computer vision using convolutional neural networks (CNNs), covering fundamental concepts, neural network training, and architectural variations such as AlexNet, VGG, and MobileNets. It discusses applications of CNNs in image classification, object detection, and segmentation, emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate models for specific applications. Additionally, it highlights the impact of model efficiency in edge devices and provides resources for further learning.