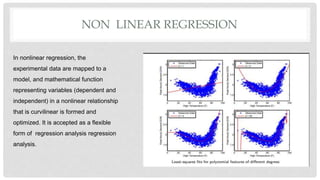
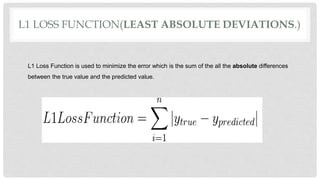
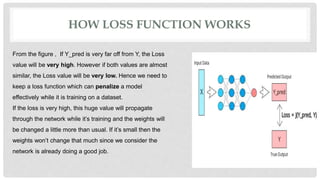
L1 and L2 loss functions are used to minimize error during machine learning model training. The L1 loss function minimizes the sum of the absolute differences between true and predicted values, while the L2 loss function minimizes the sum of squared differences. These loss functions help the model adjust its parameters to reduce error via backpropagation. The L1 loss function is generally better when outliers are present in the data, as it is not as heavily influenced by outliers as the L2 loss function.