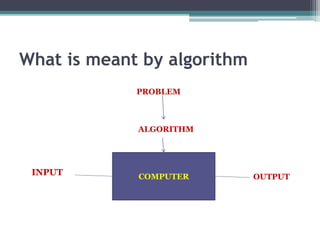
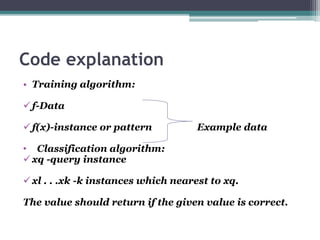
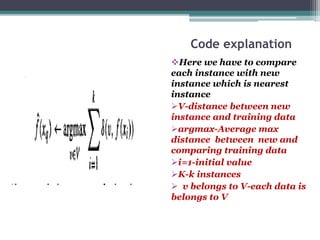
The document provides an overview of the k-nearest neighbor (k-NN) algorithm in machine learning, detailing its functionality, types of algorithms, and the instance-based learning approach. It explains the steps involved in implementing the k-NN algorithm, including distance calculation and classification, and discusses the positives and negatives of using k-NN. The document also contains examples illustrating how to classify new instances based on training data.