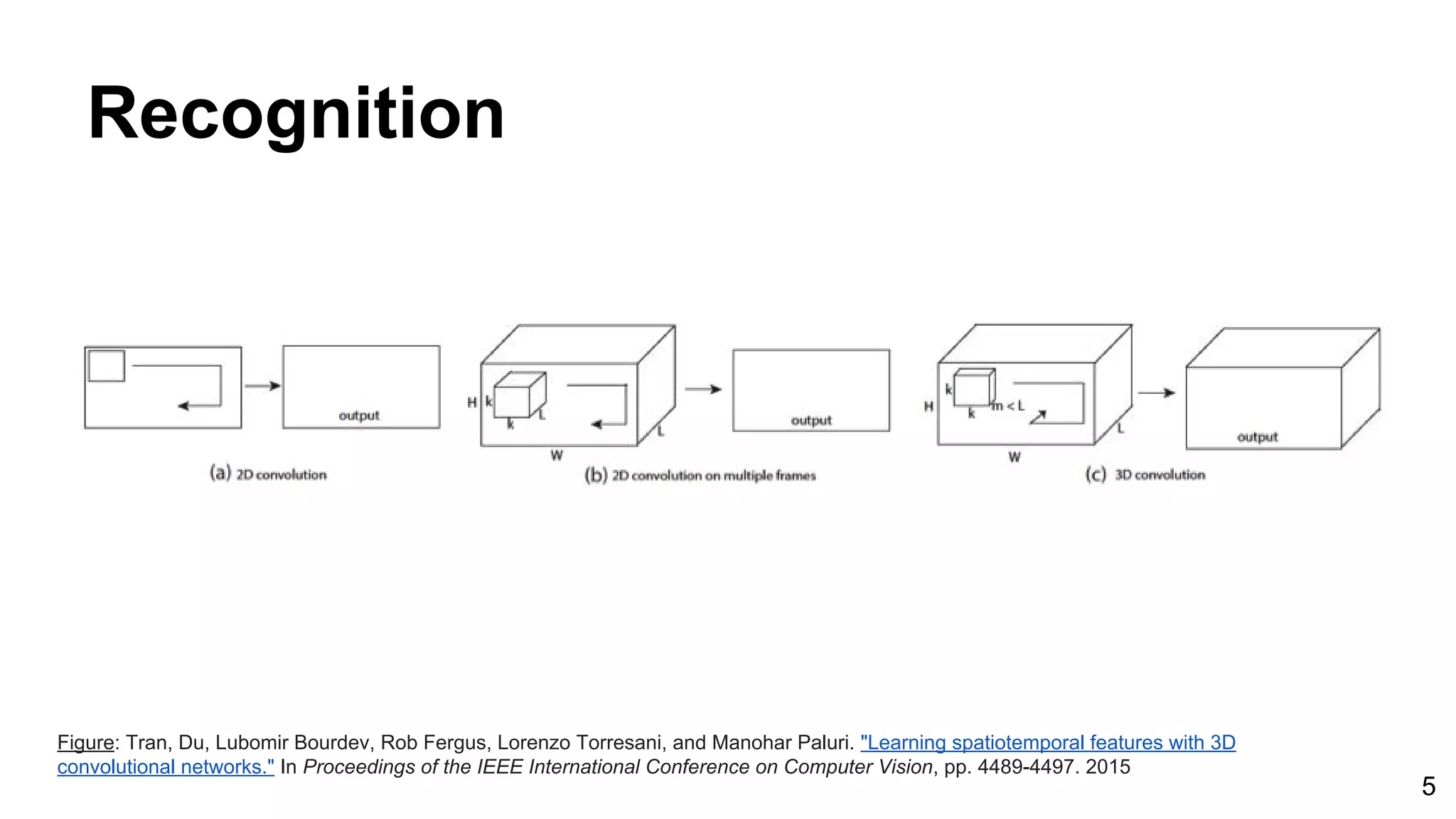
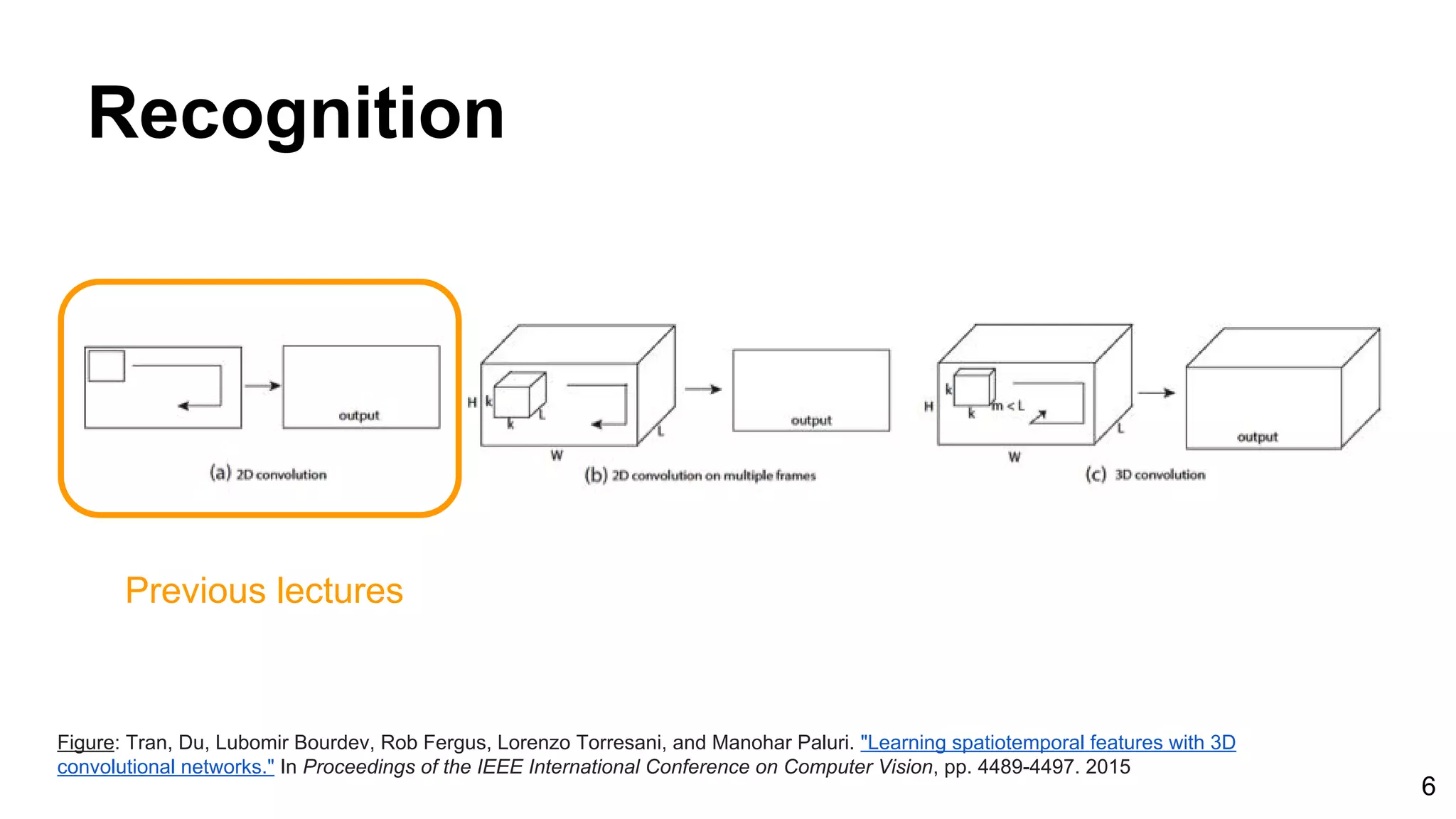
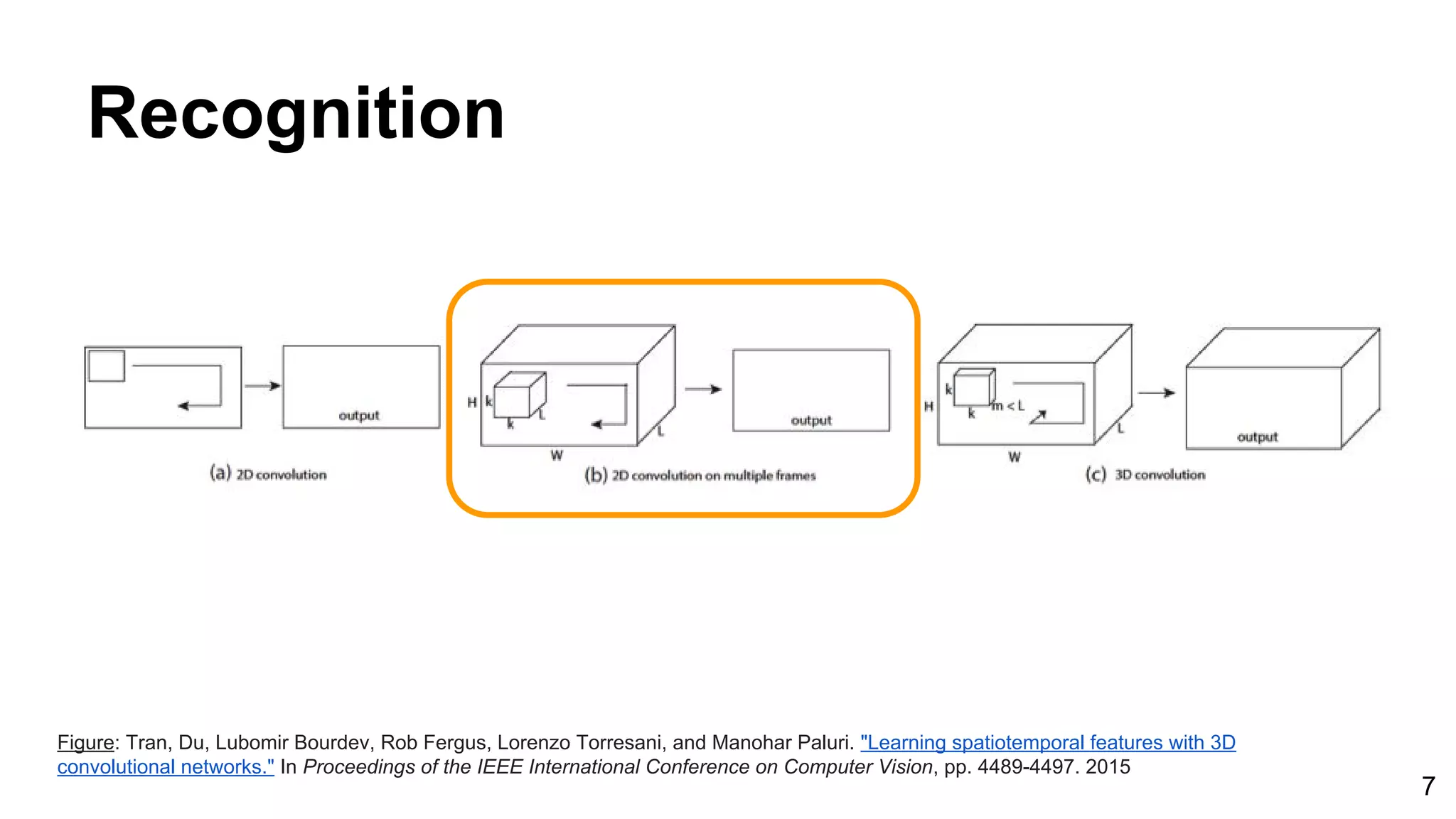
The document discusses advancements in deep learning techniques for computer vision, particularly focusing on video analytics. It covers various topics including recognition, optical flow algorithms, and object tracking methods, citing important works such as the use of convolutional neural networks for large-scale video classification. Additionally, it highlights the effectiveness of techniques like C3D networks and FlowNet for feature learning and video processing.





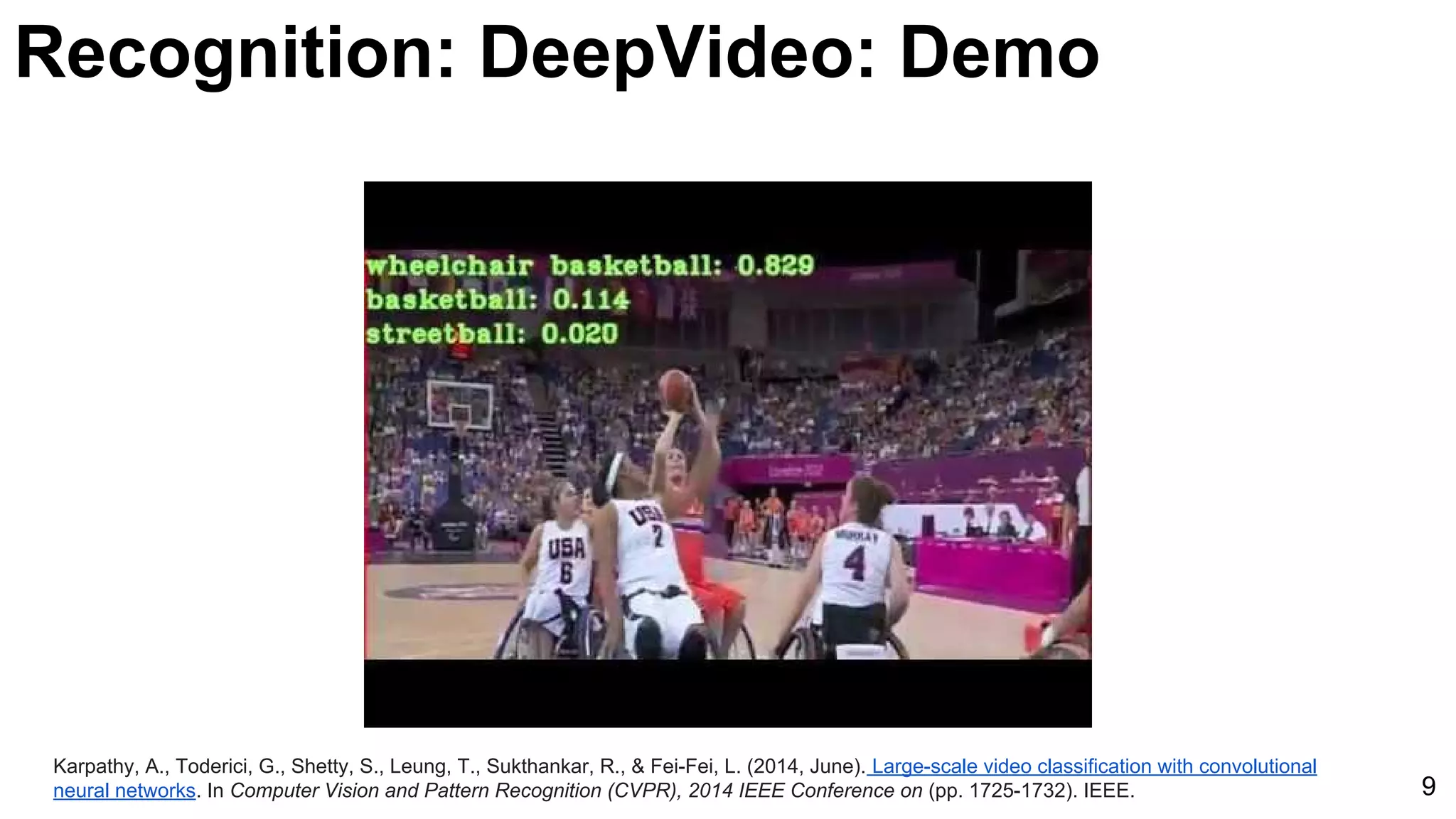
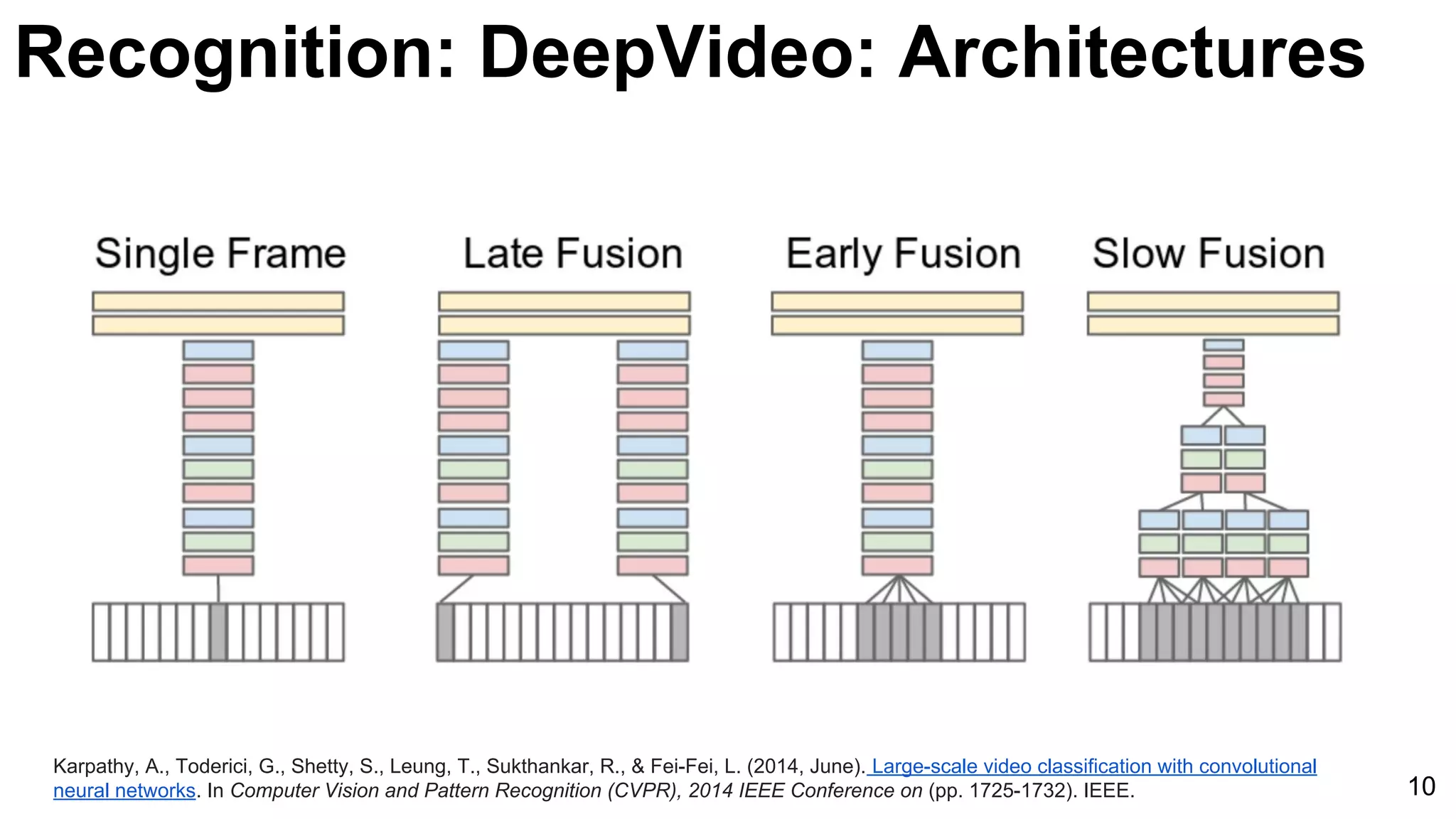
![Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Sukthankar, R., & Fei-Fei, L. (2014, June). Large-scale video classification with convolutional
neural networks. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2014 IEEE Conference on (pp. 1725-1732). IEEE. 11
Unsupervised learning [Le at al’11] Supervised learning [Karpathy et al’14]
Recognition: DeepVideo: Features](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-11-2048.jpg)
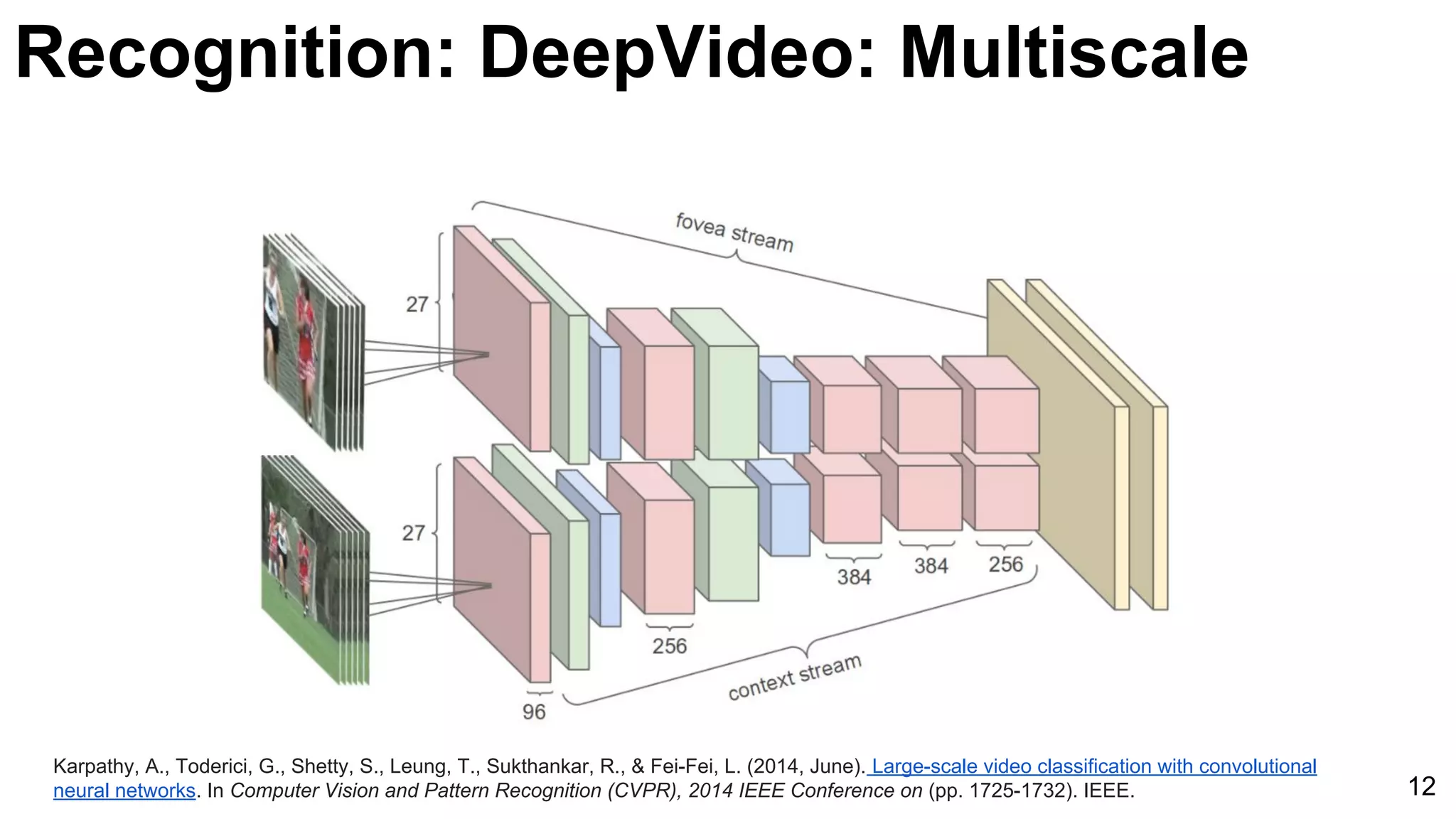
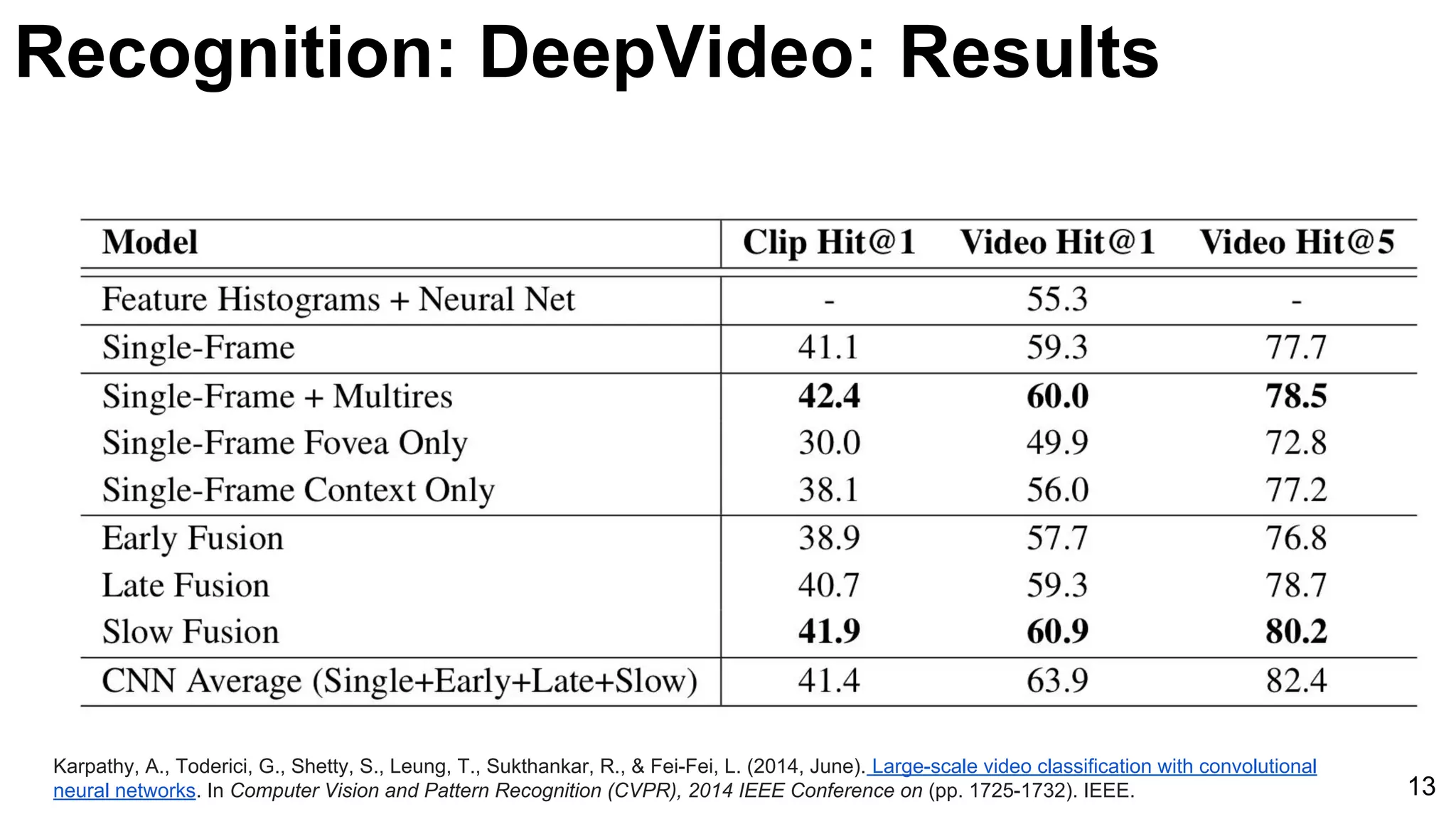
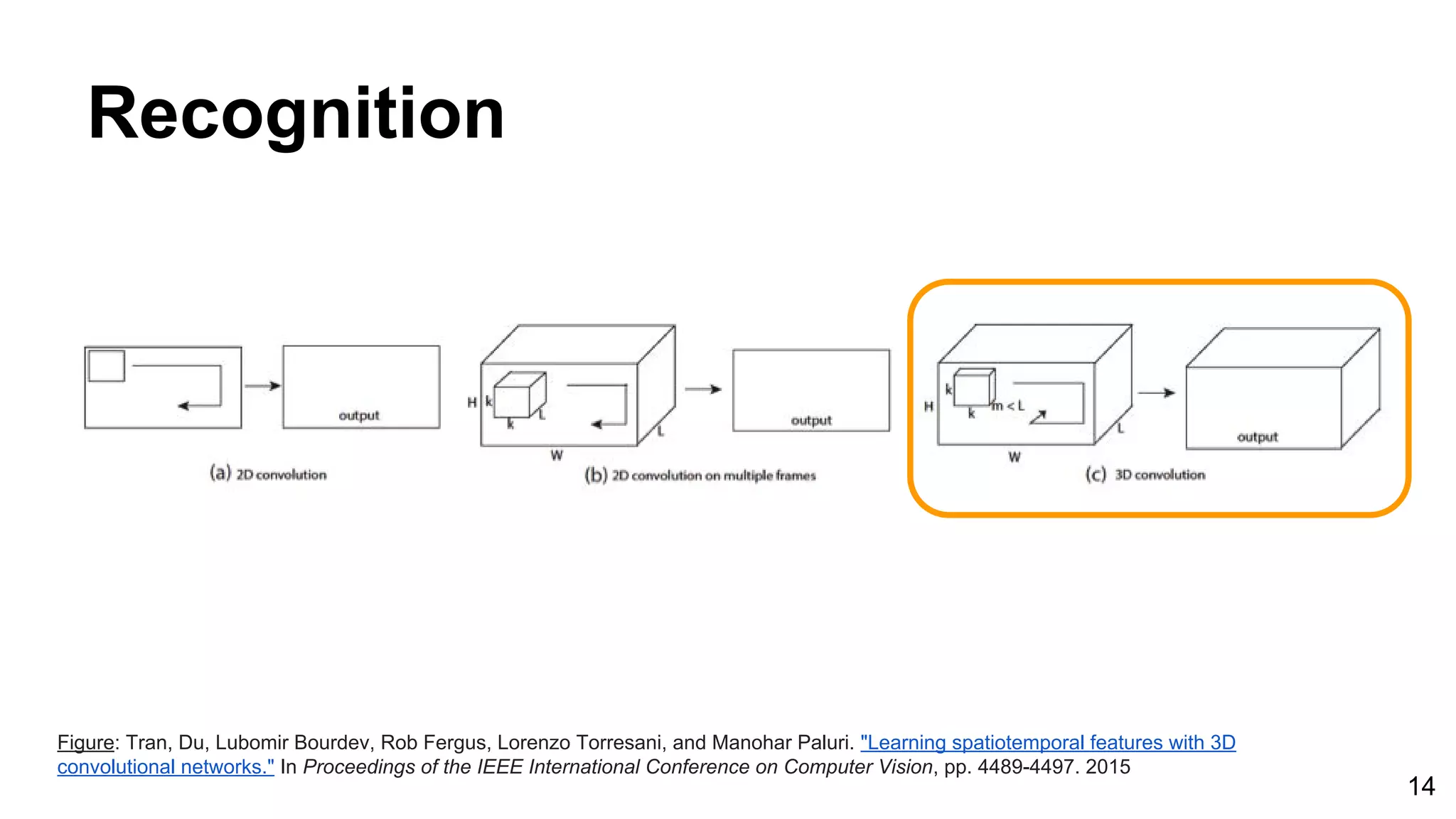

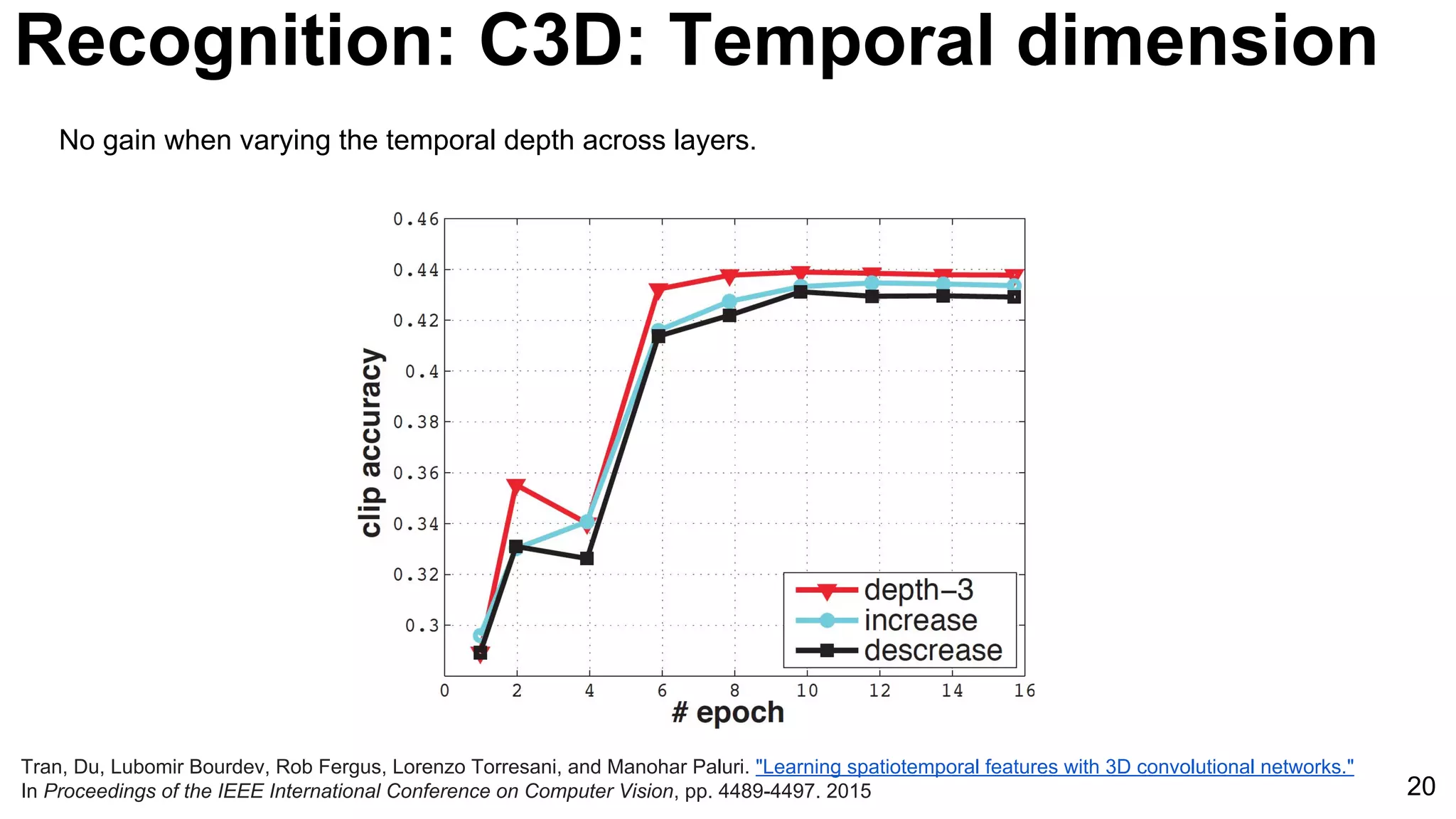
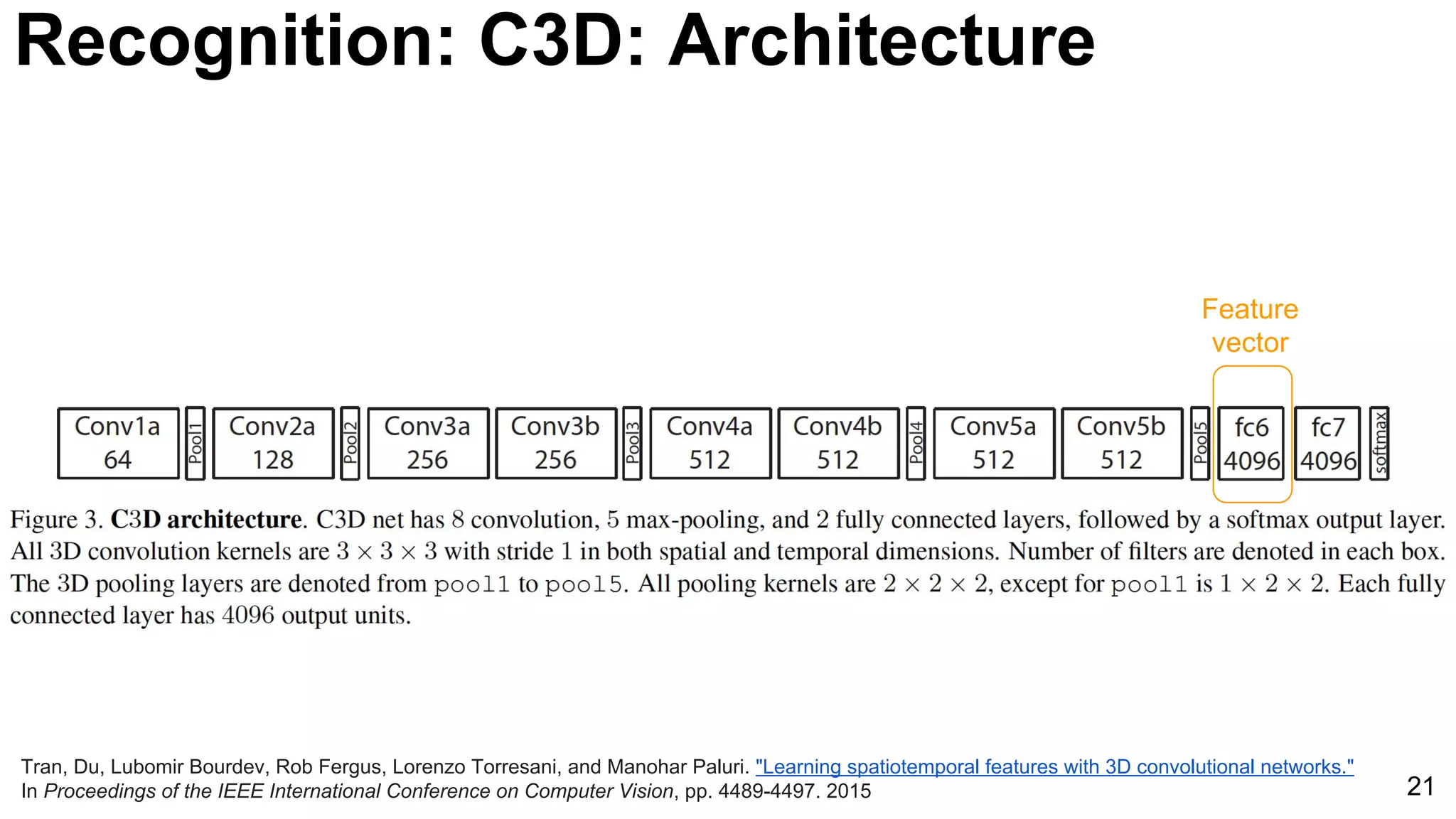
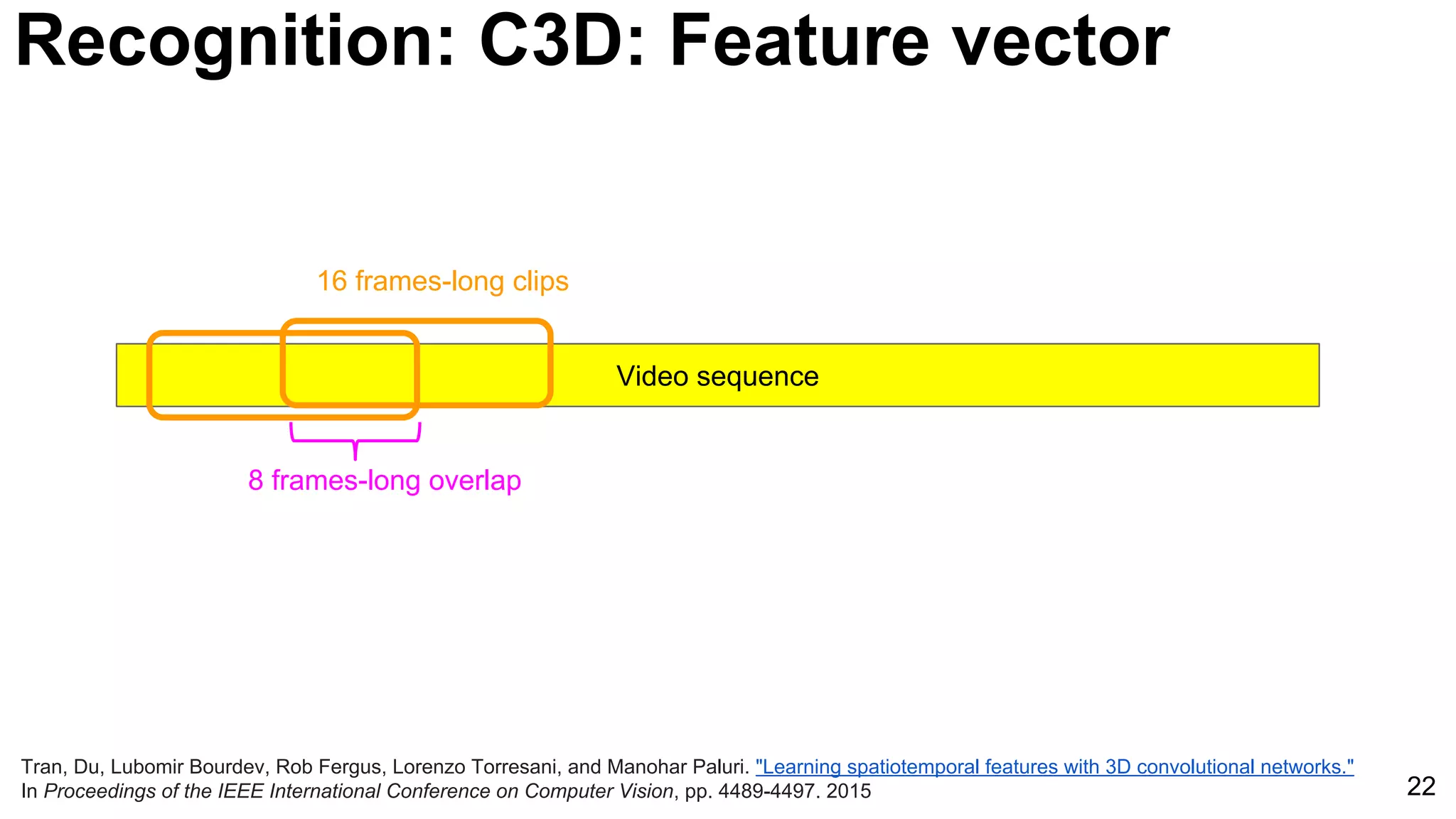
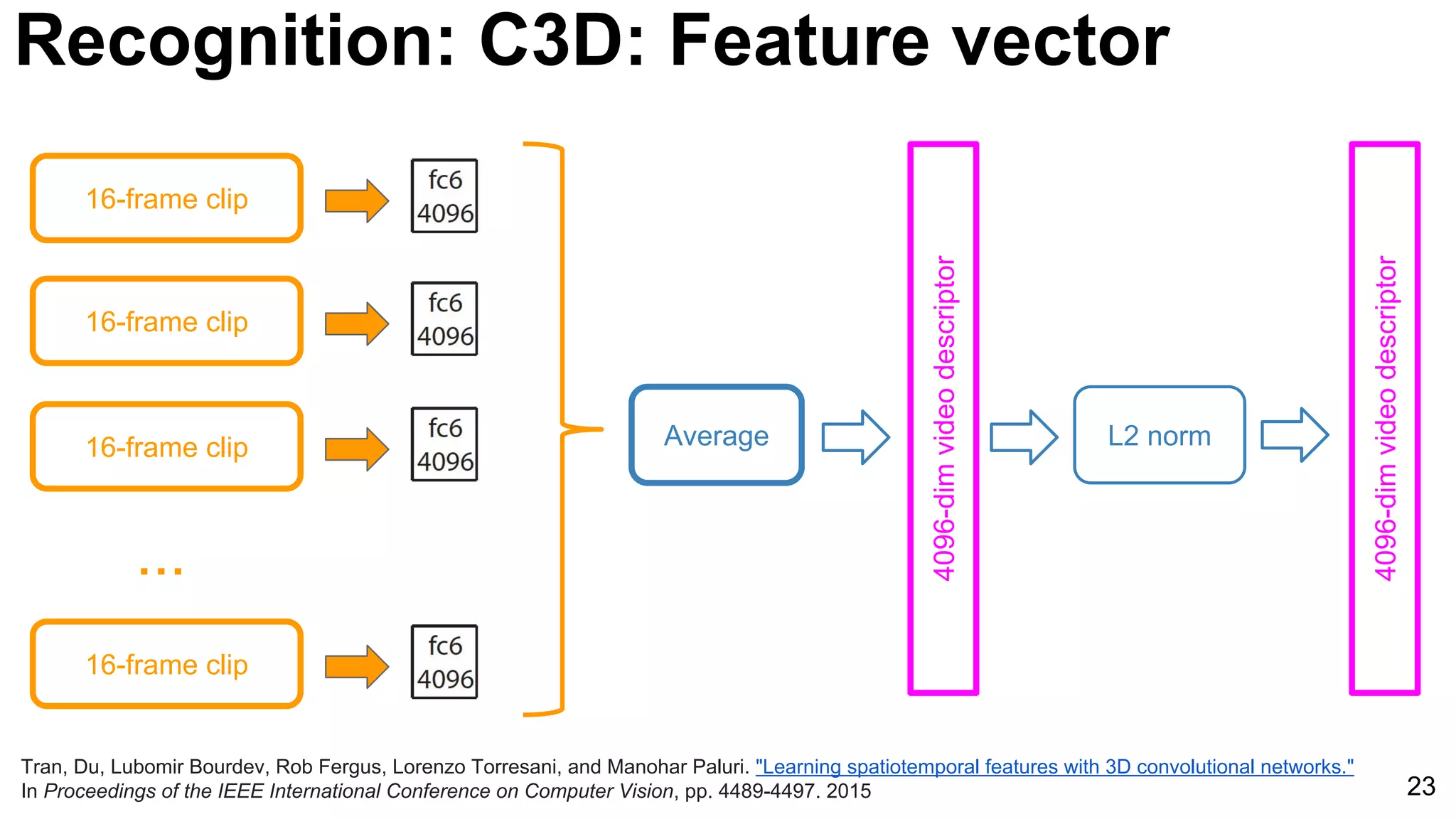
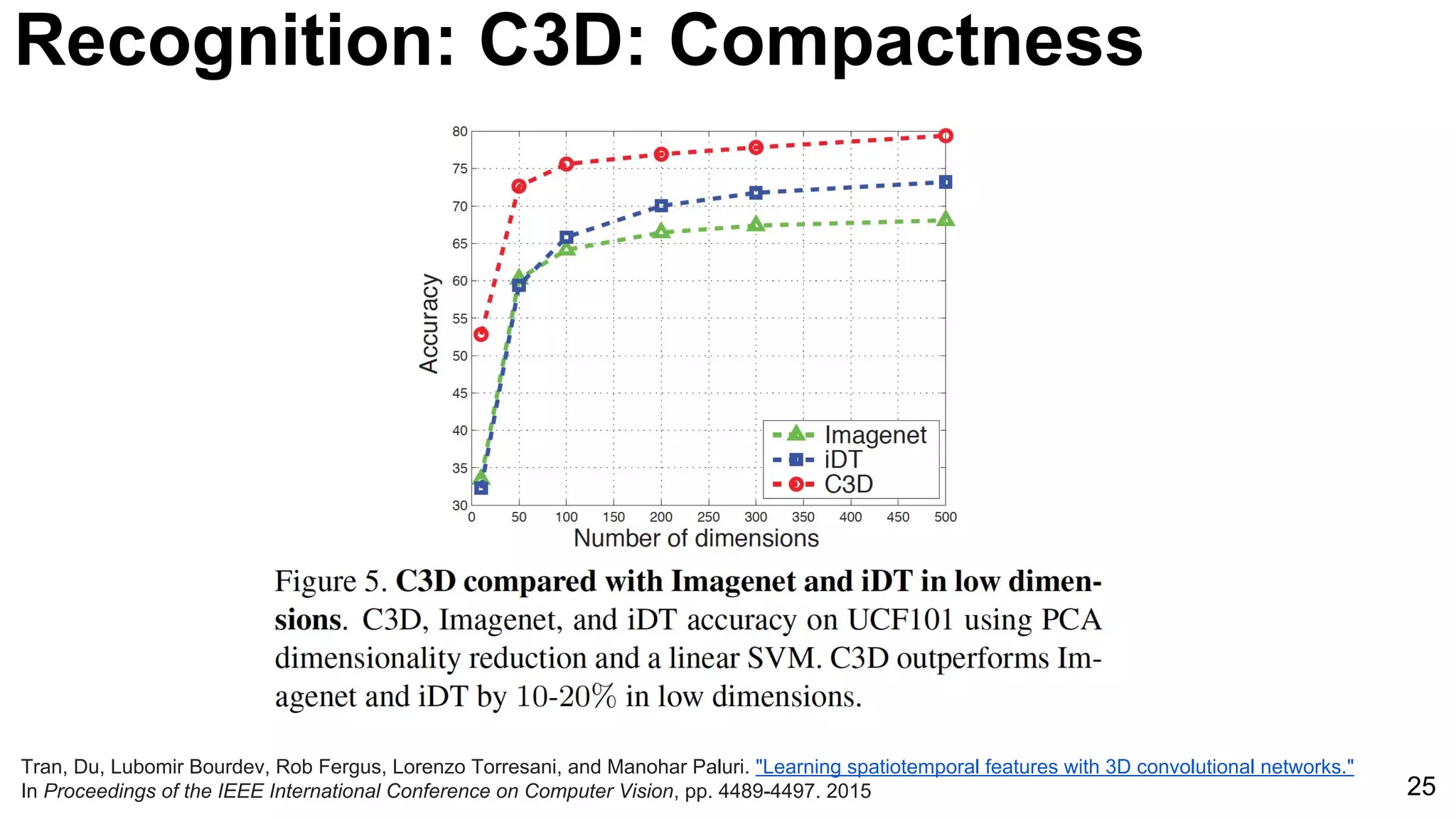
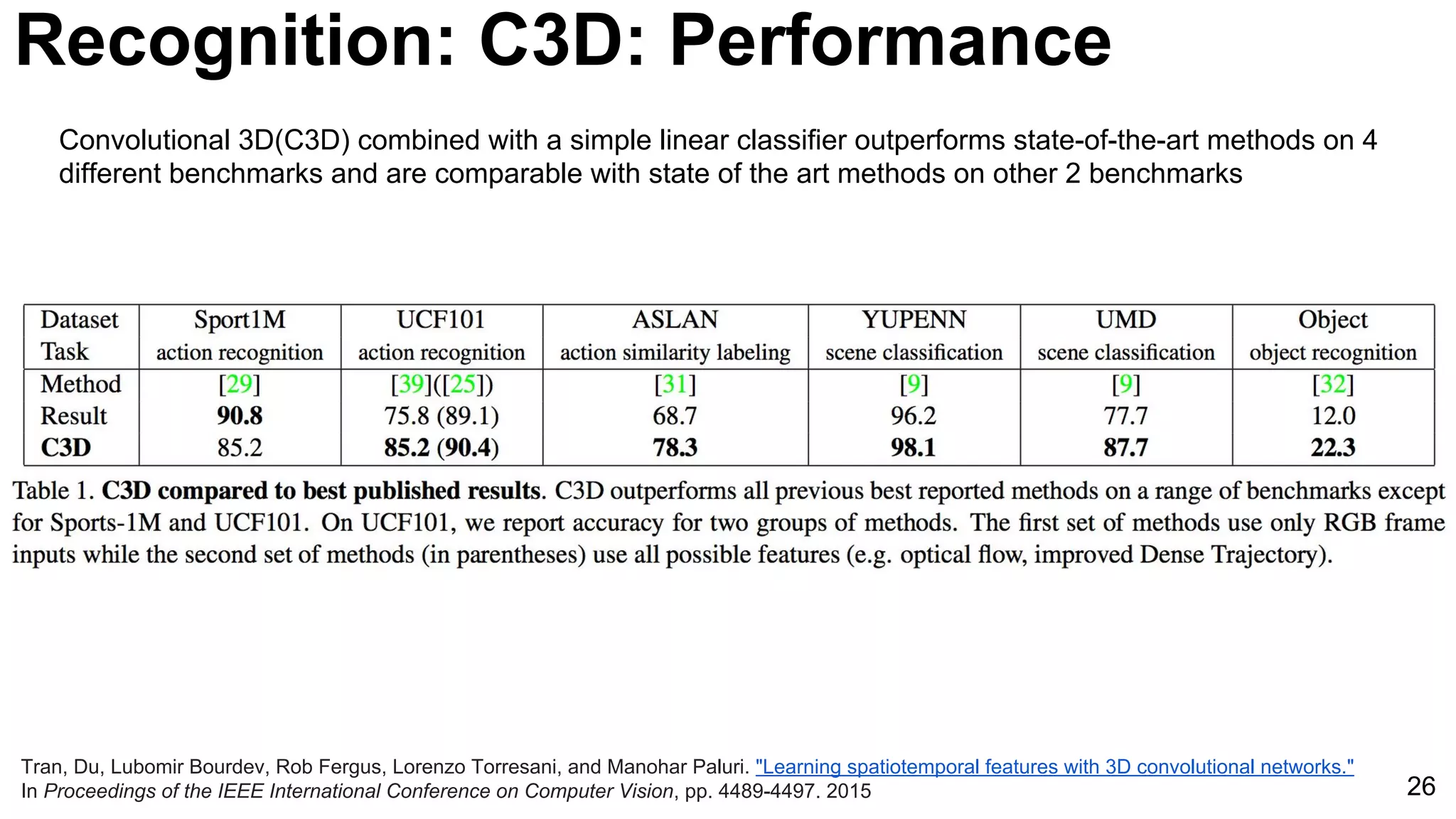
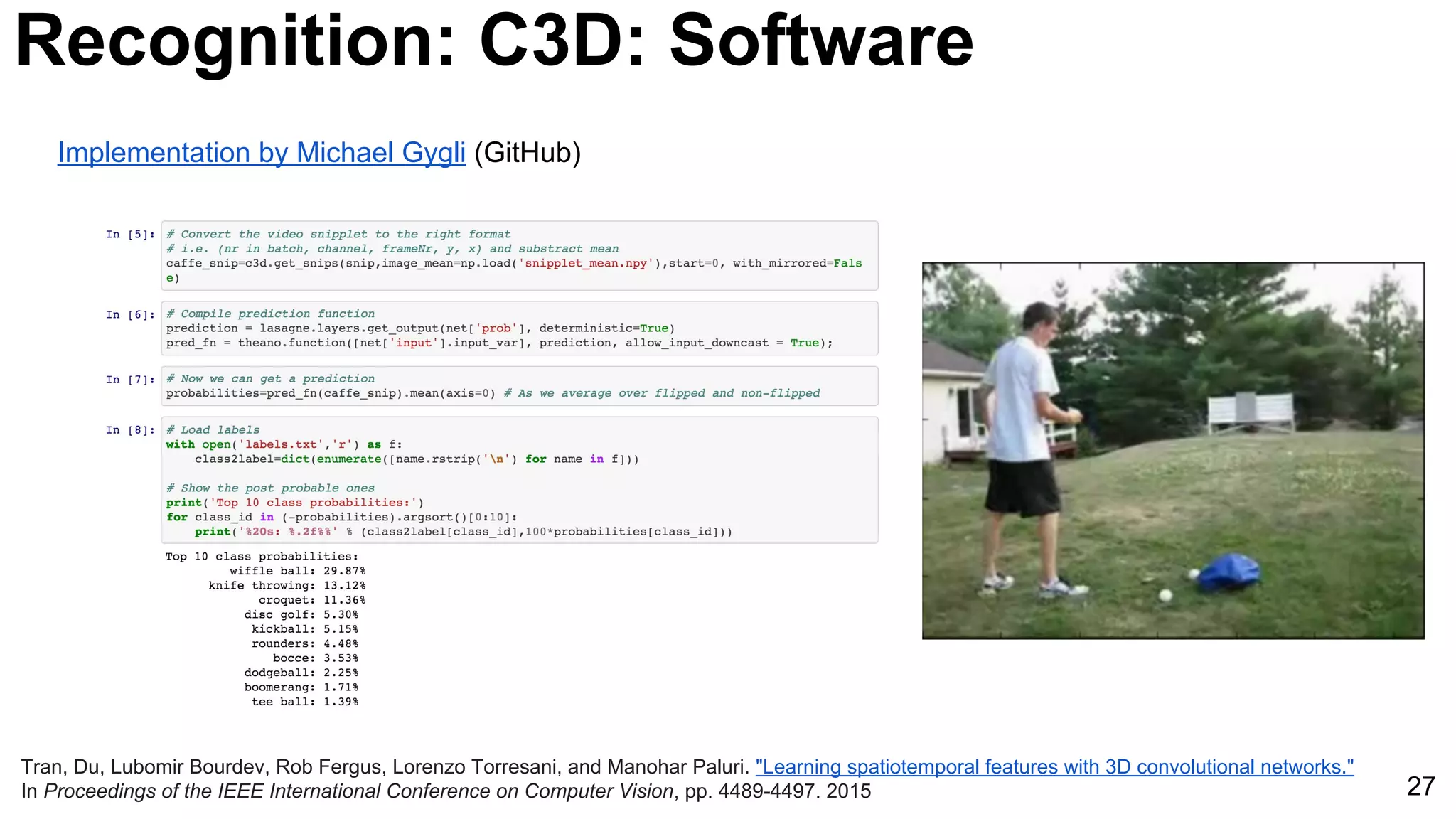
![24
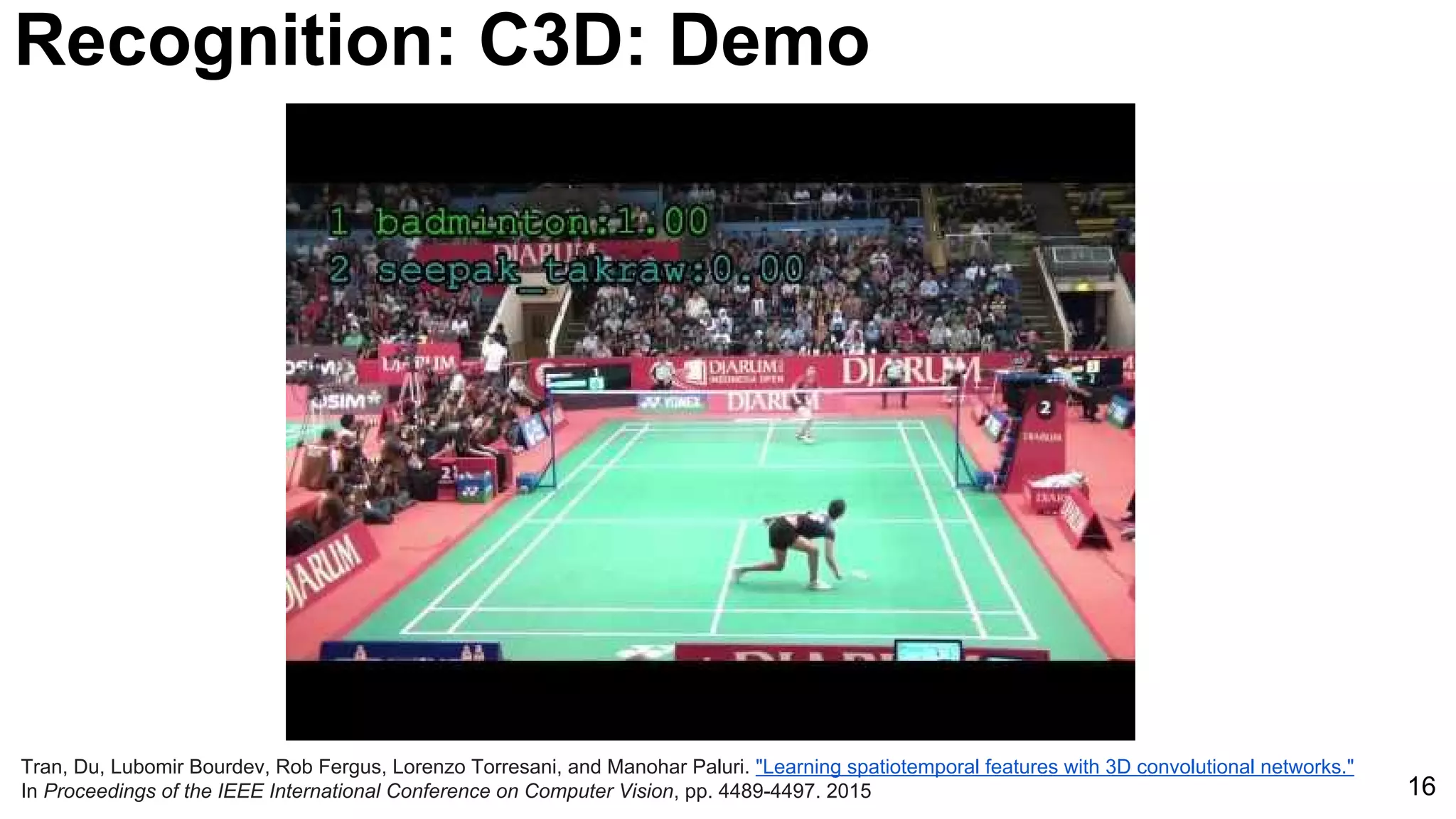
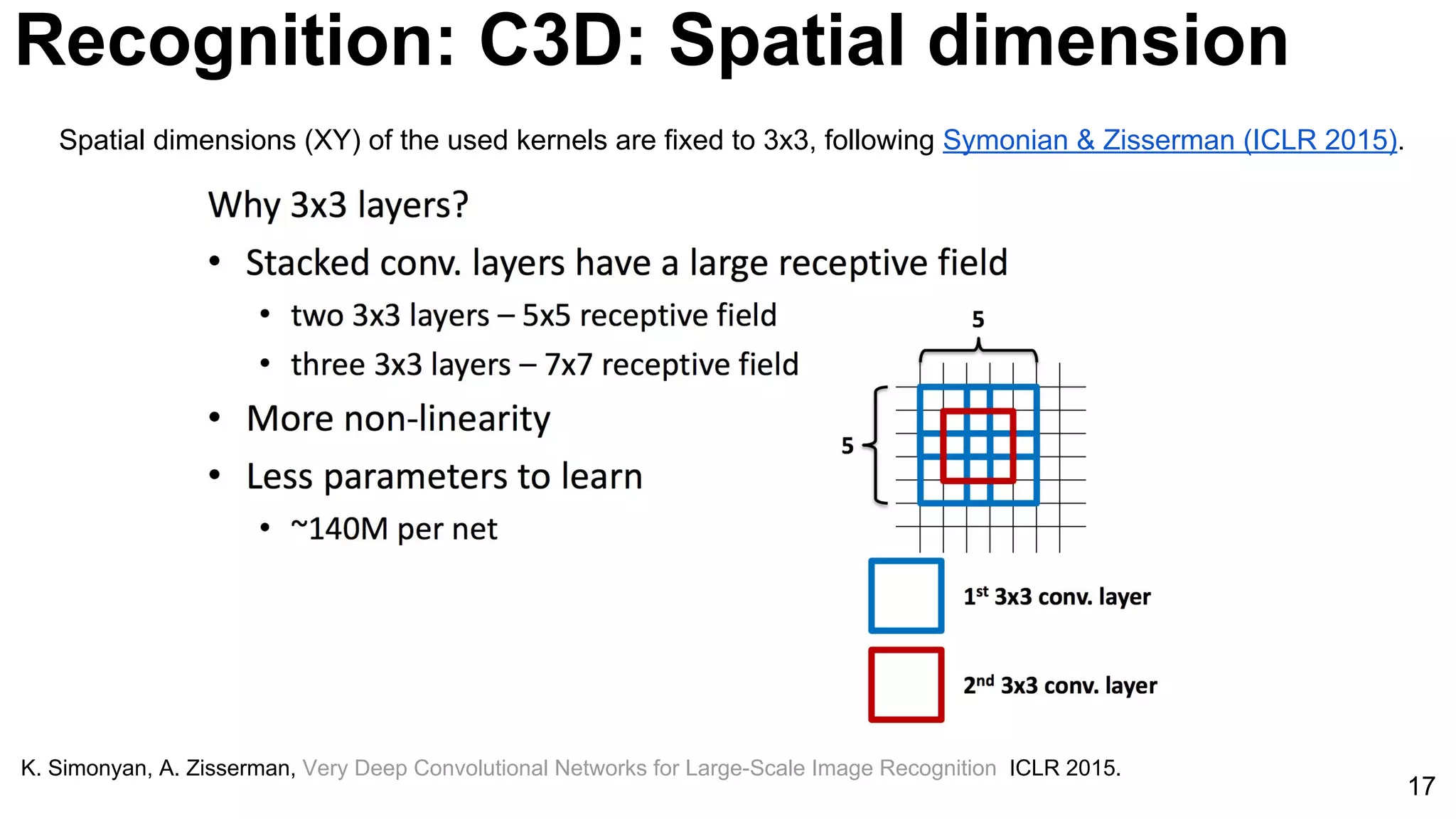
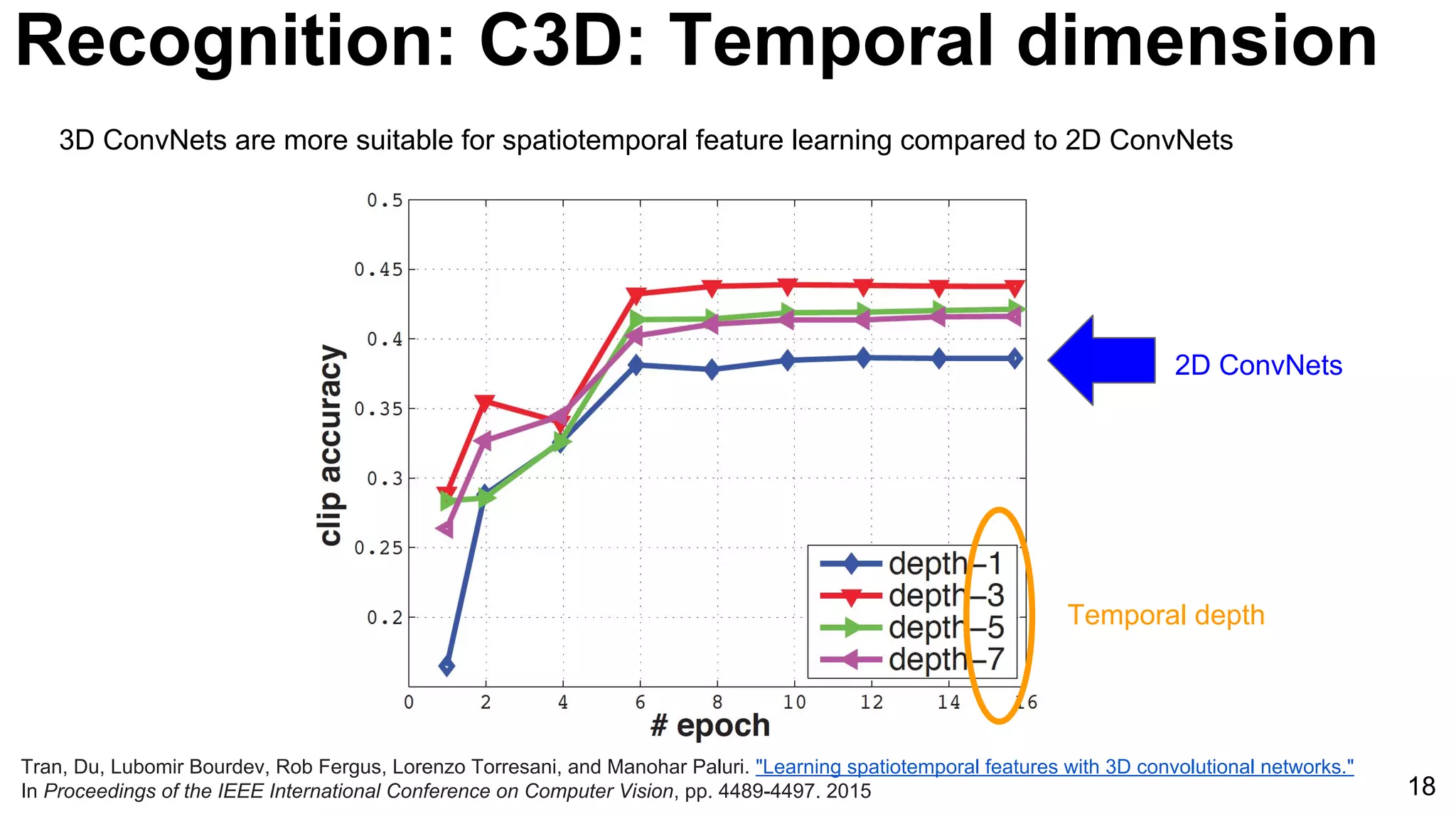
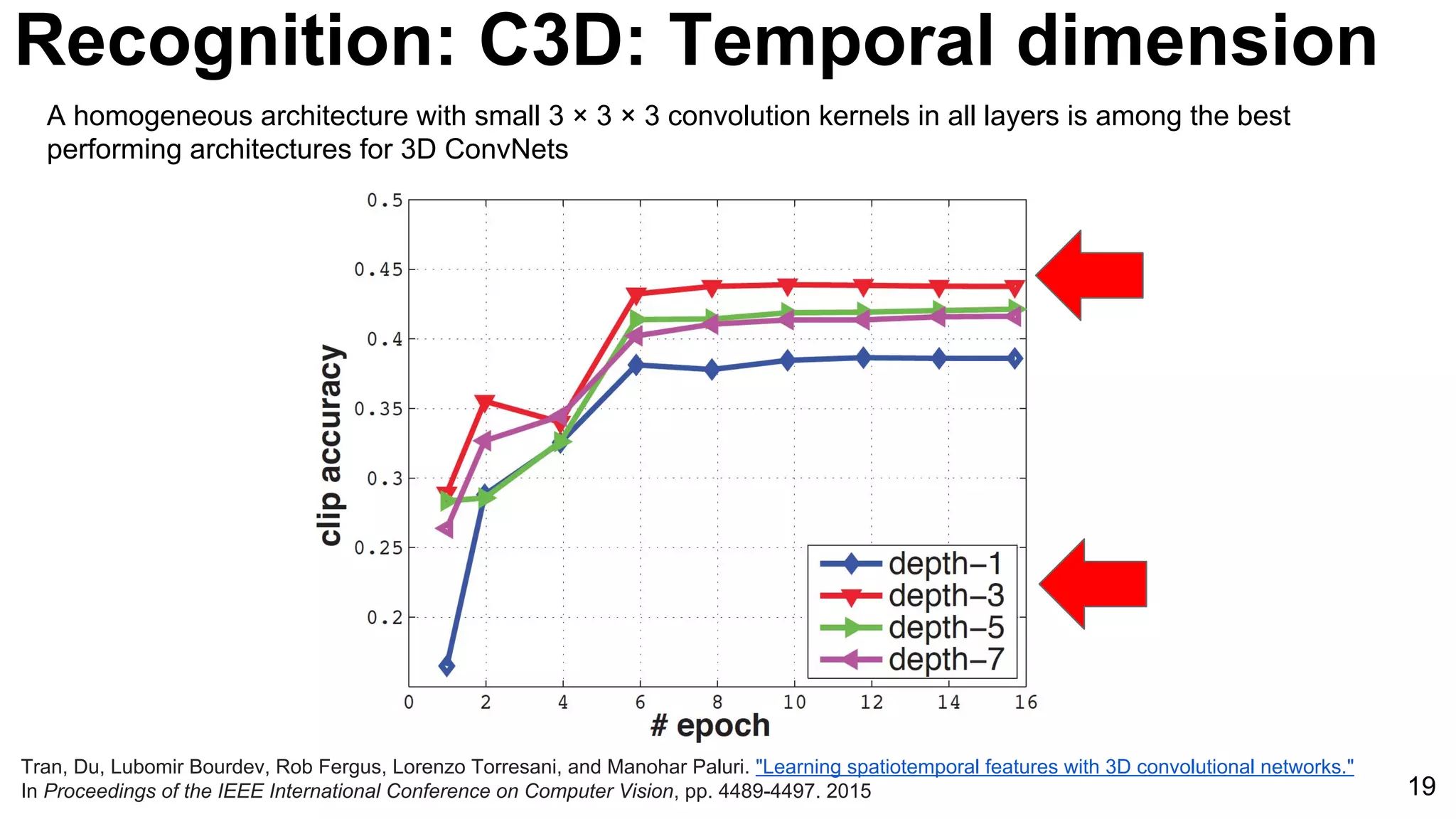
Tran, Du, Lubomir Bourdev, Rob Fergus, Lorenzo Torresani, and Manohar Paluri. "Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks."
In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4489-4497. 2015
Recognition: C3D: Visualization
Based on Deconvnets by Zeiler and Fergus [ECCV 2014] - See [ReadCV Slides] for more details.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-24-2048.jpg)

![29
Recognition: ImageNet Video
[ILSVRC 2015 Slides and videos]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-29-2048.jpg)
![30
Recognition: ImageNet Video
[ILSVRC 2015 Slides and videos]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-30-2048.jpg)
![31
Recognition: ImageNet Video
[ILSVRC 2015 Slides and videos]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-31-2048.jpg)
![32
Recognition: ImageNet Video
Kai Kang et al, Object Detection in Videos with TubeLets and Multi-Context Cues (ILSVRC 2015) [video] [poster]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-32-2048.jpg)
![33
Recognition: ImageNet Video
Kai Kang et al, Object Detection in Videos with TubeLets and Multi-Context Cues (ILSVRC 2015) [video] [poster]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-33-2048.jpg)
![34
Recognition: ImageNet Video
Kai Kang et al, Object Detection in Videos with TubeLets and Multi-Context Cues (ILSVRC 2015) [video] [poster]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-34-2048.jpg)
![35
Recognition: ImageNet Video
Kai Kang et al, Object Detection in Videos with TubeLets and Multi-Context Cues (ILSVRC 2015) [video] [poster]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-35-2048.jpg)
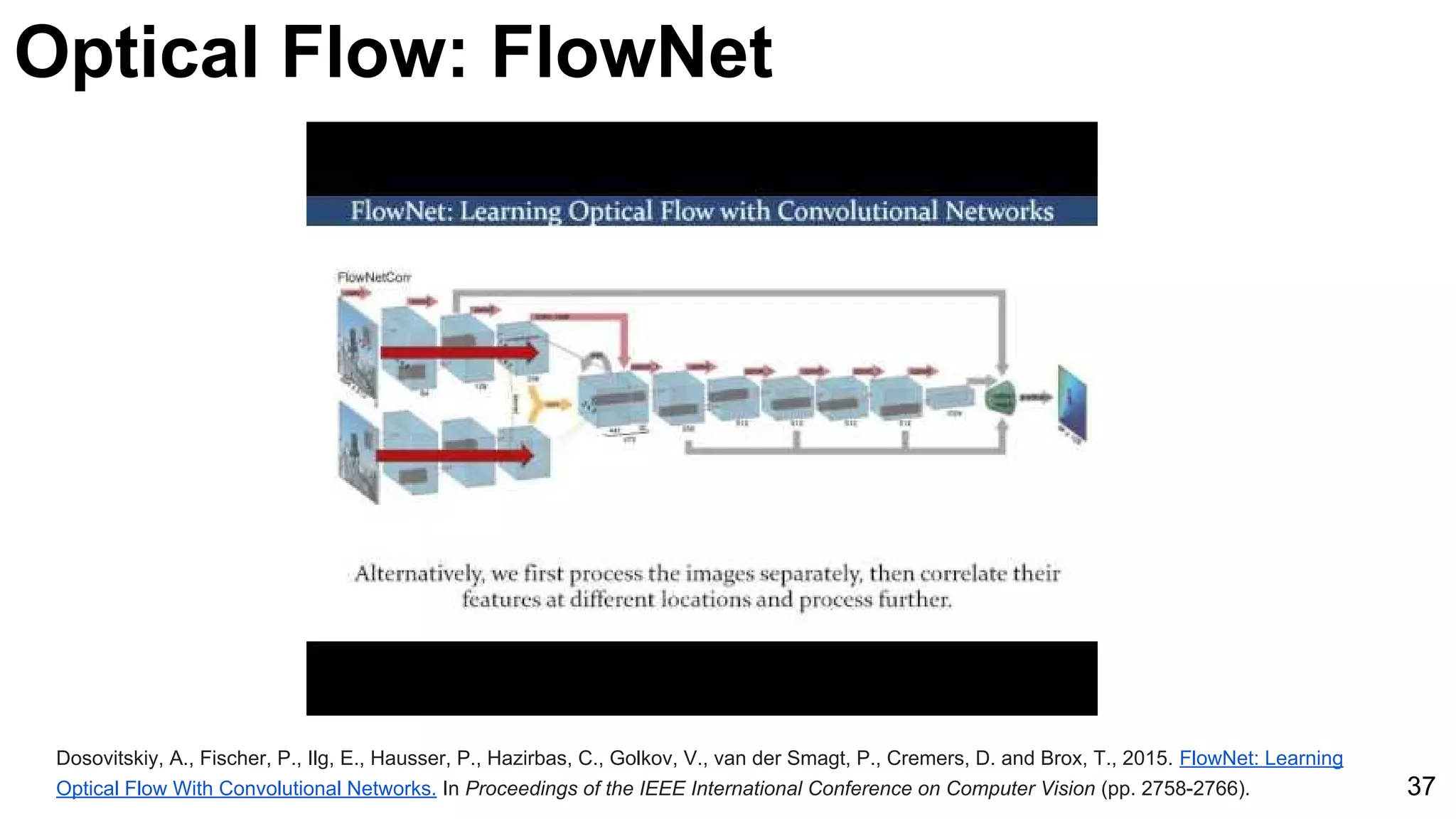
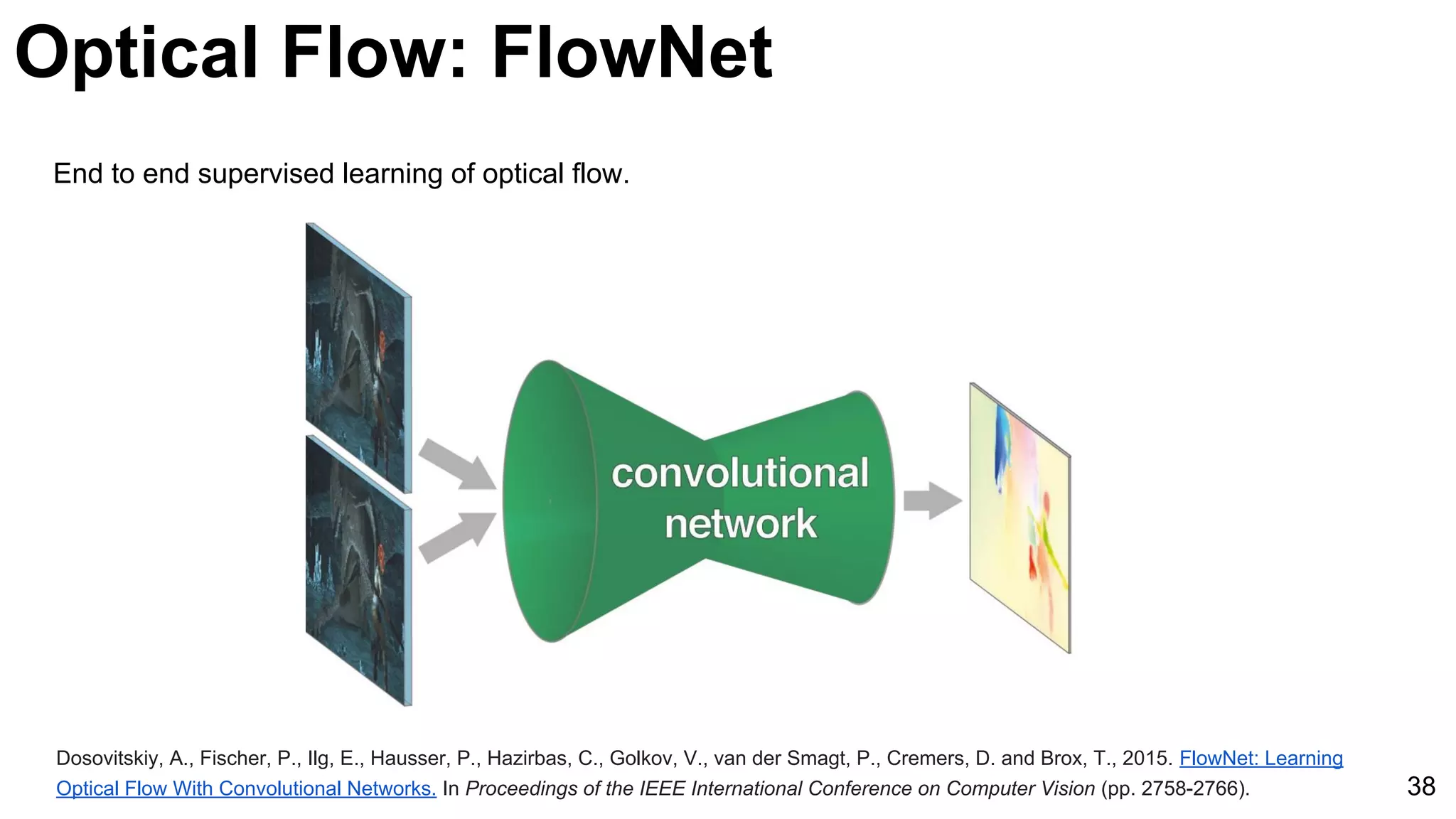
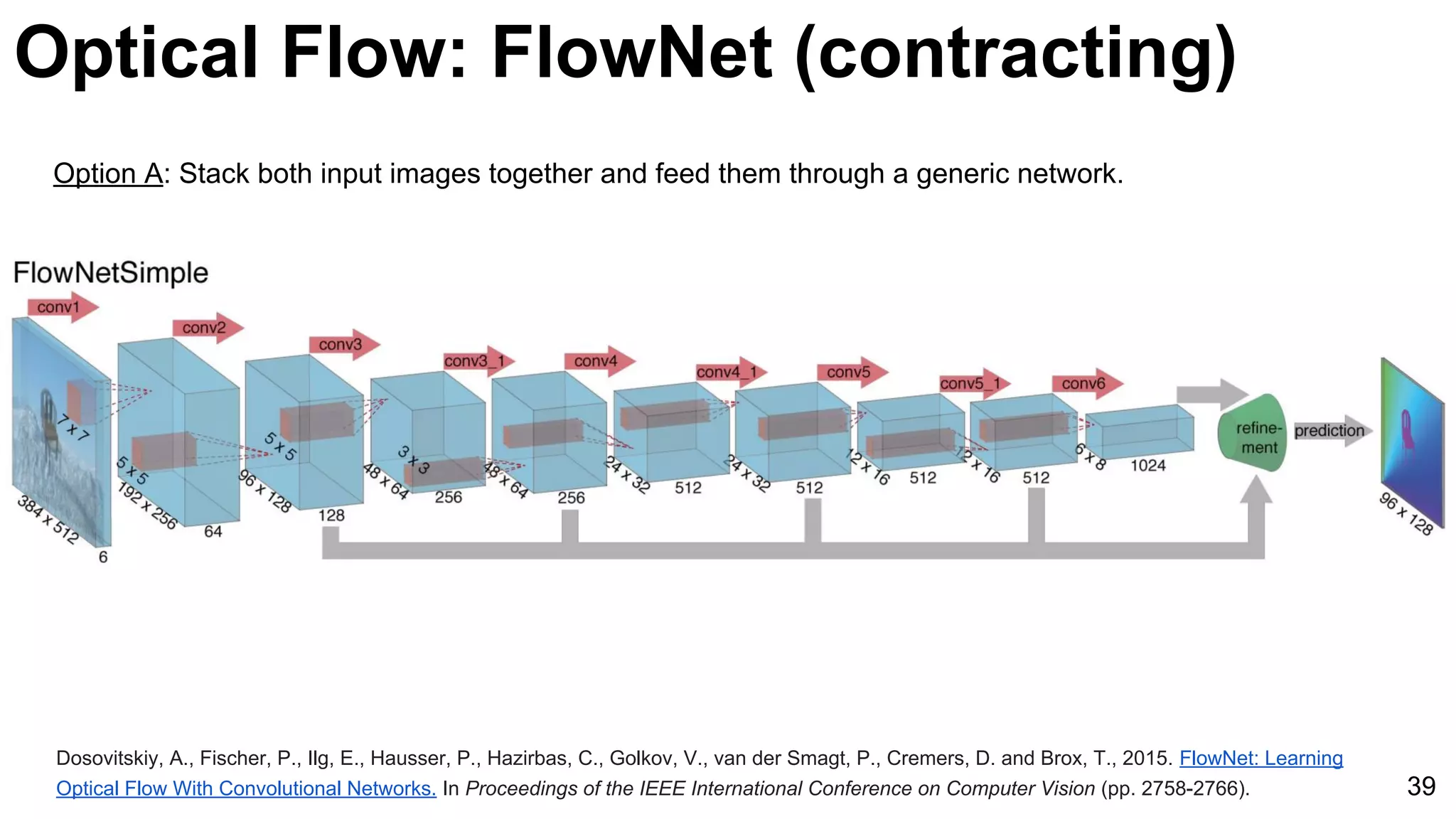
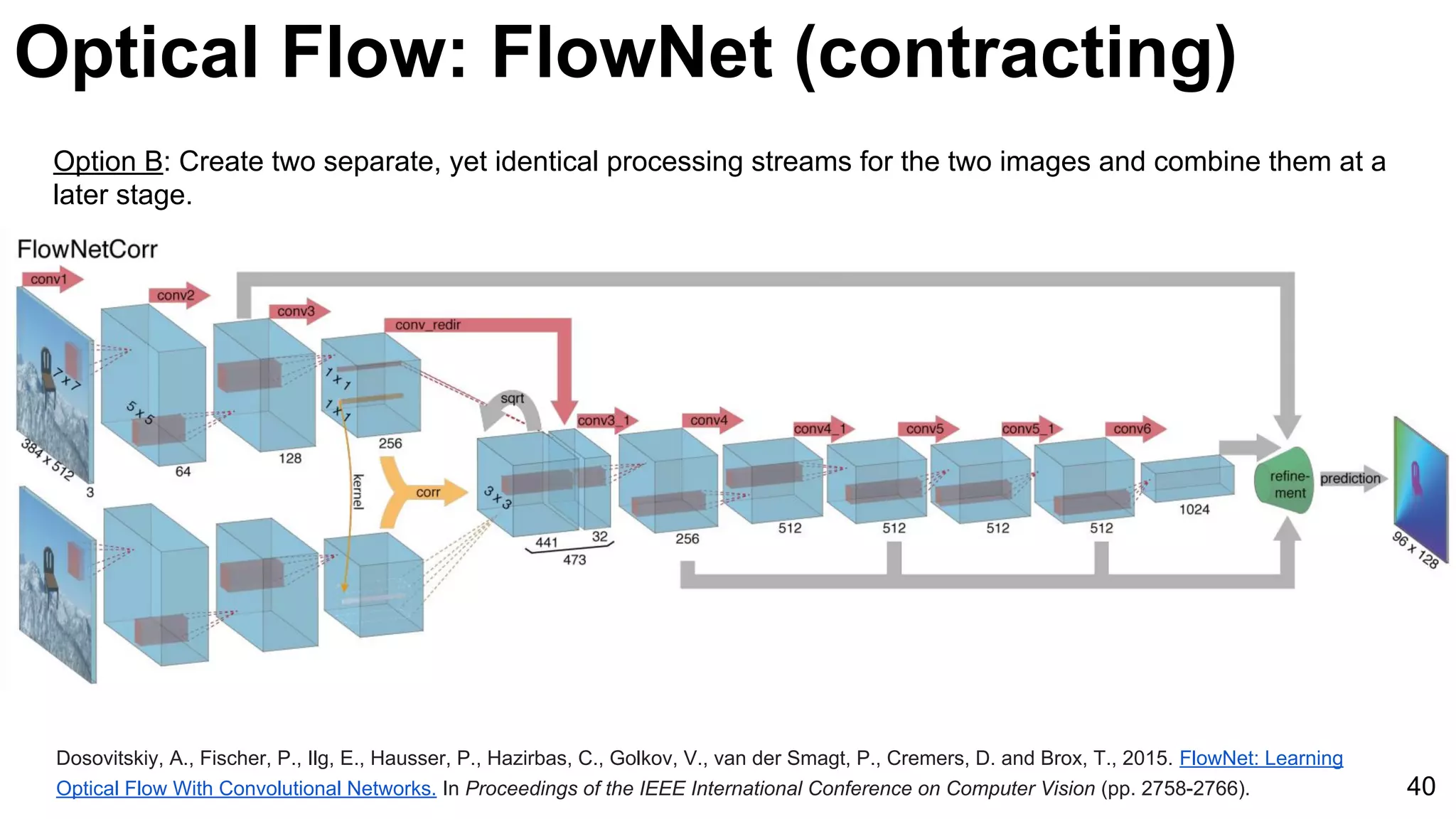
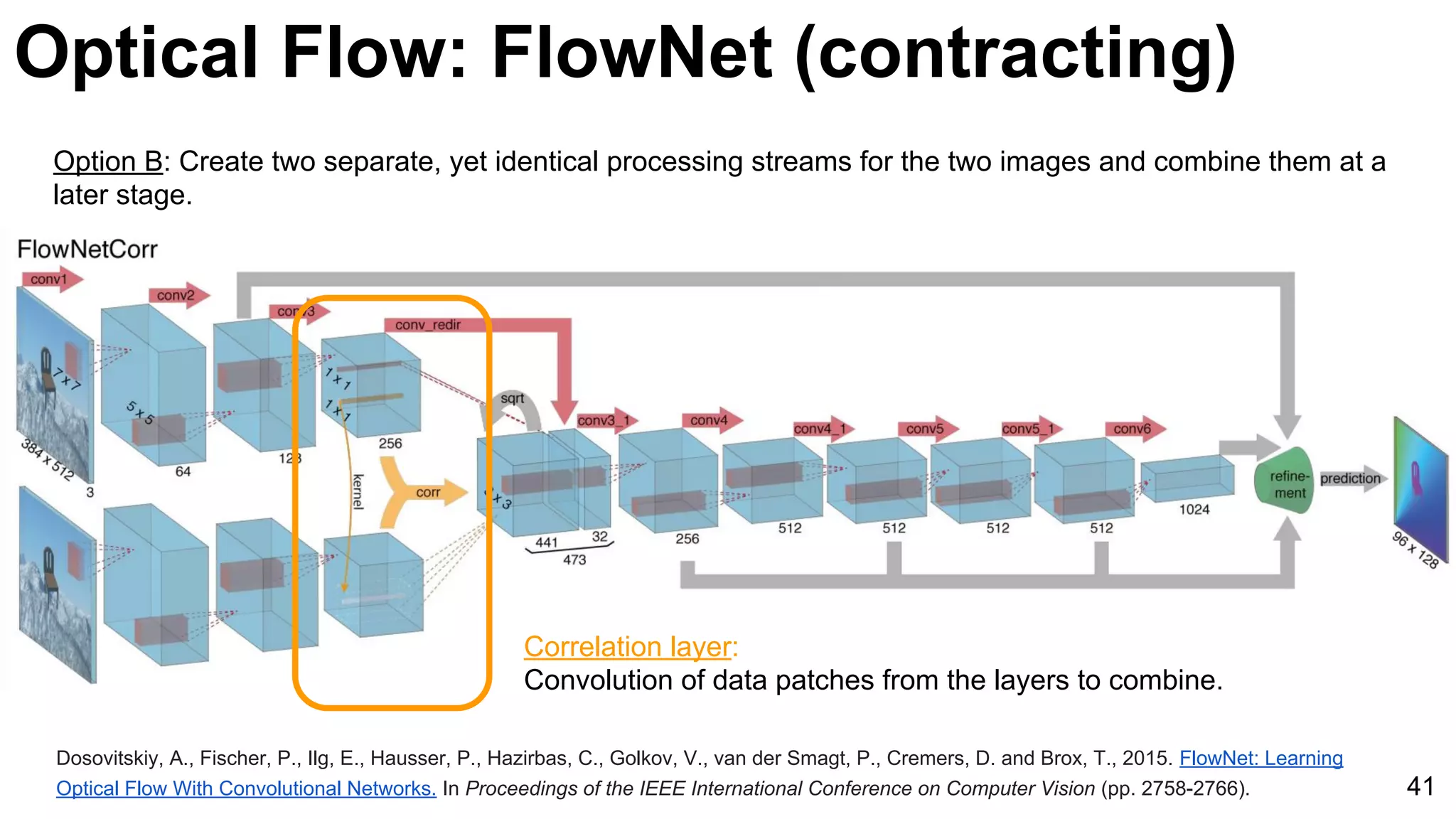
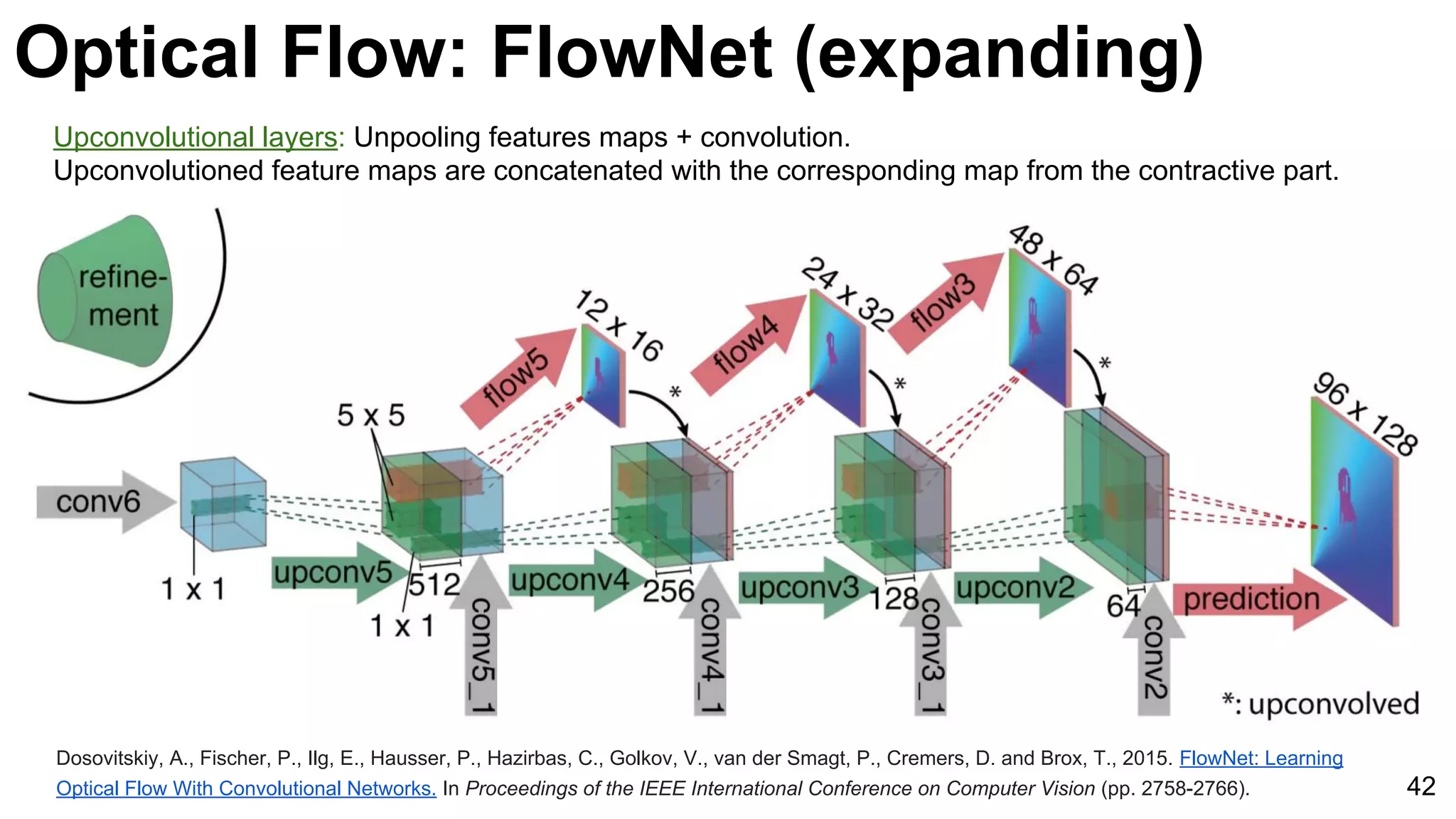
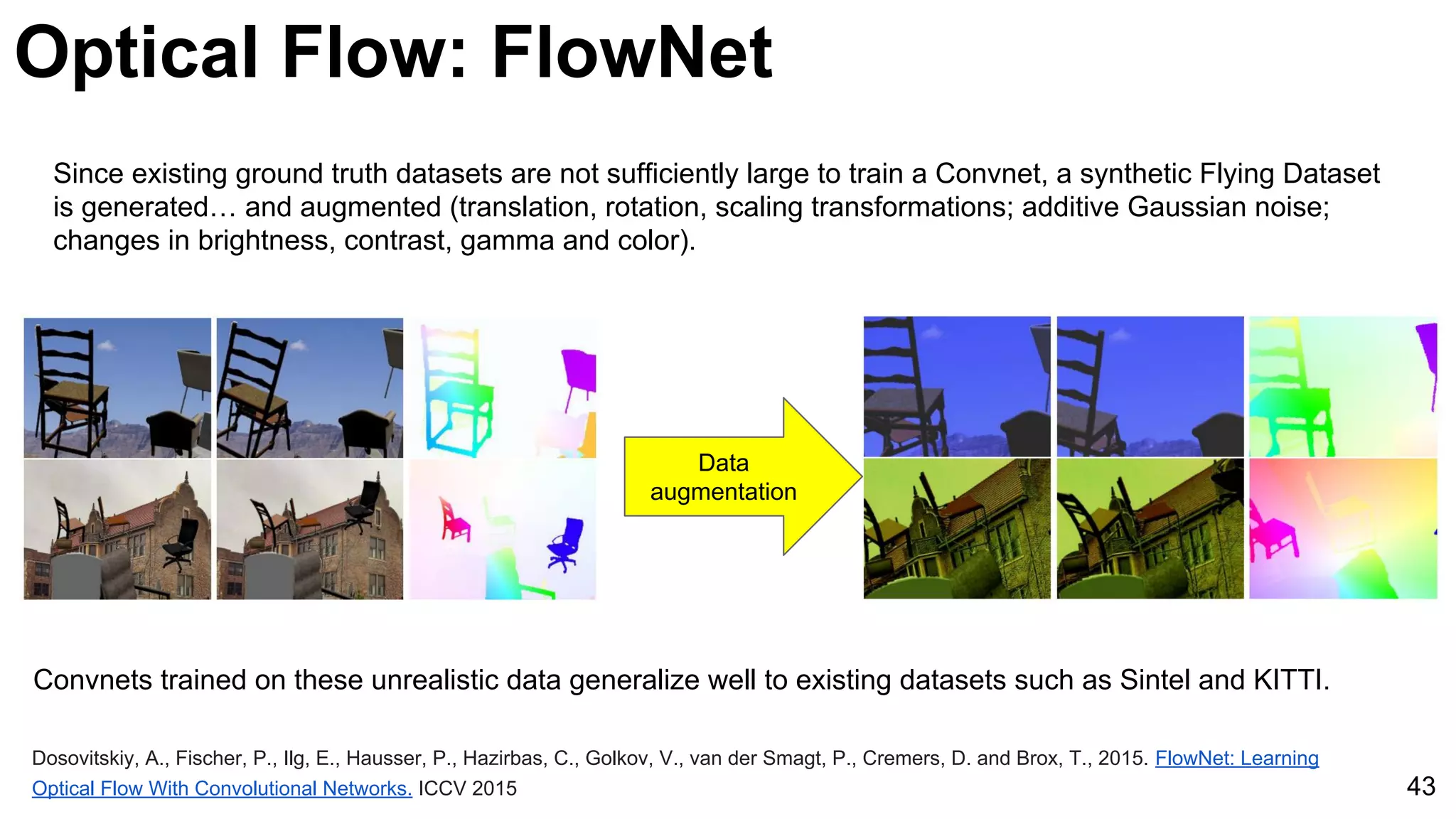
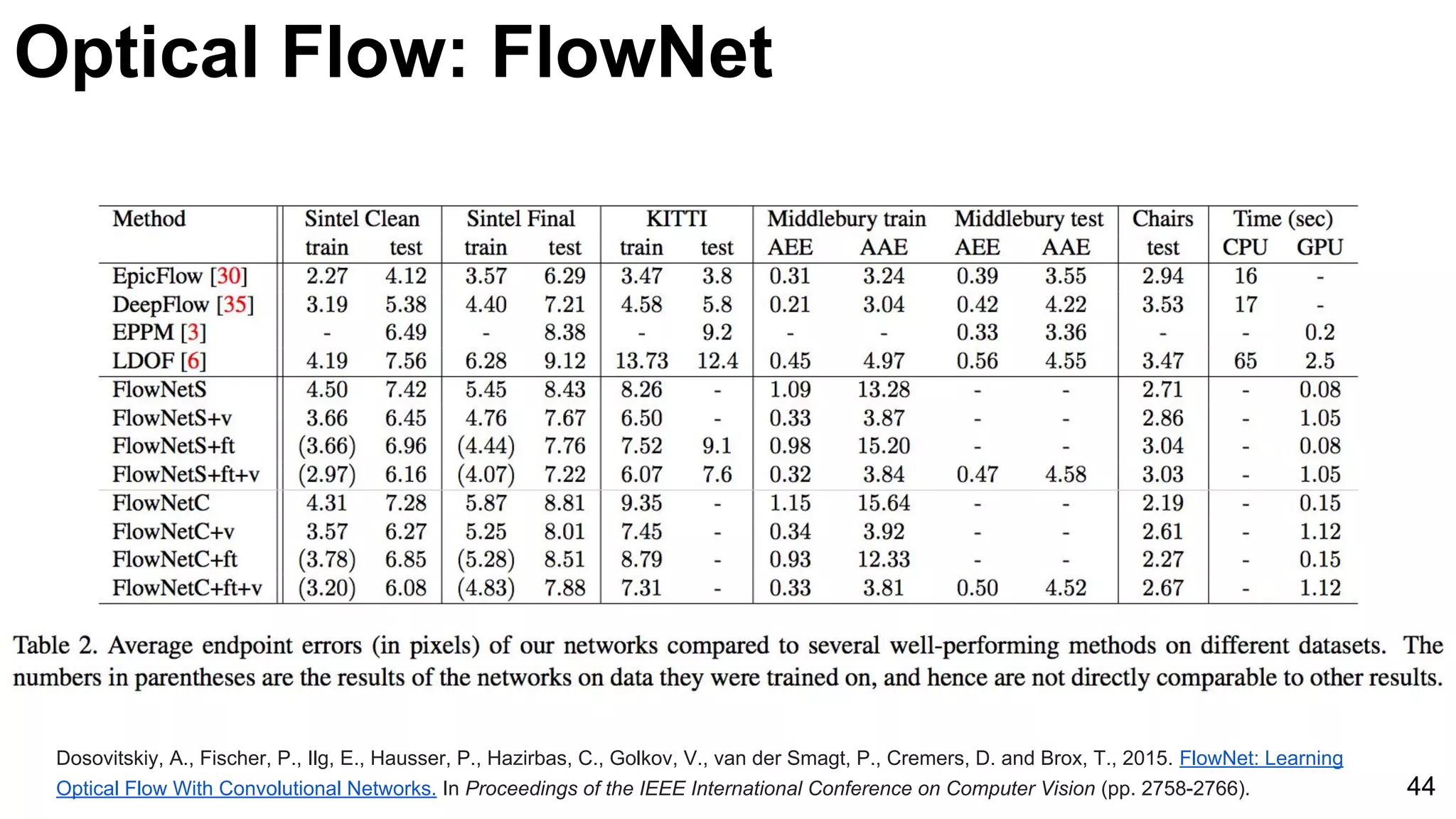
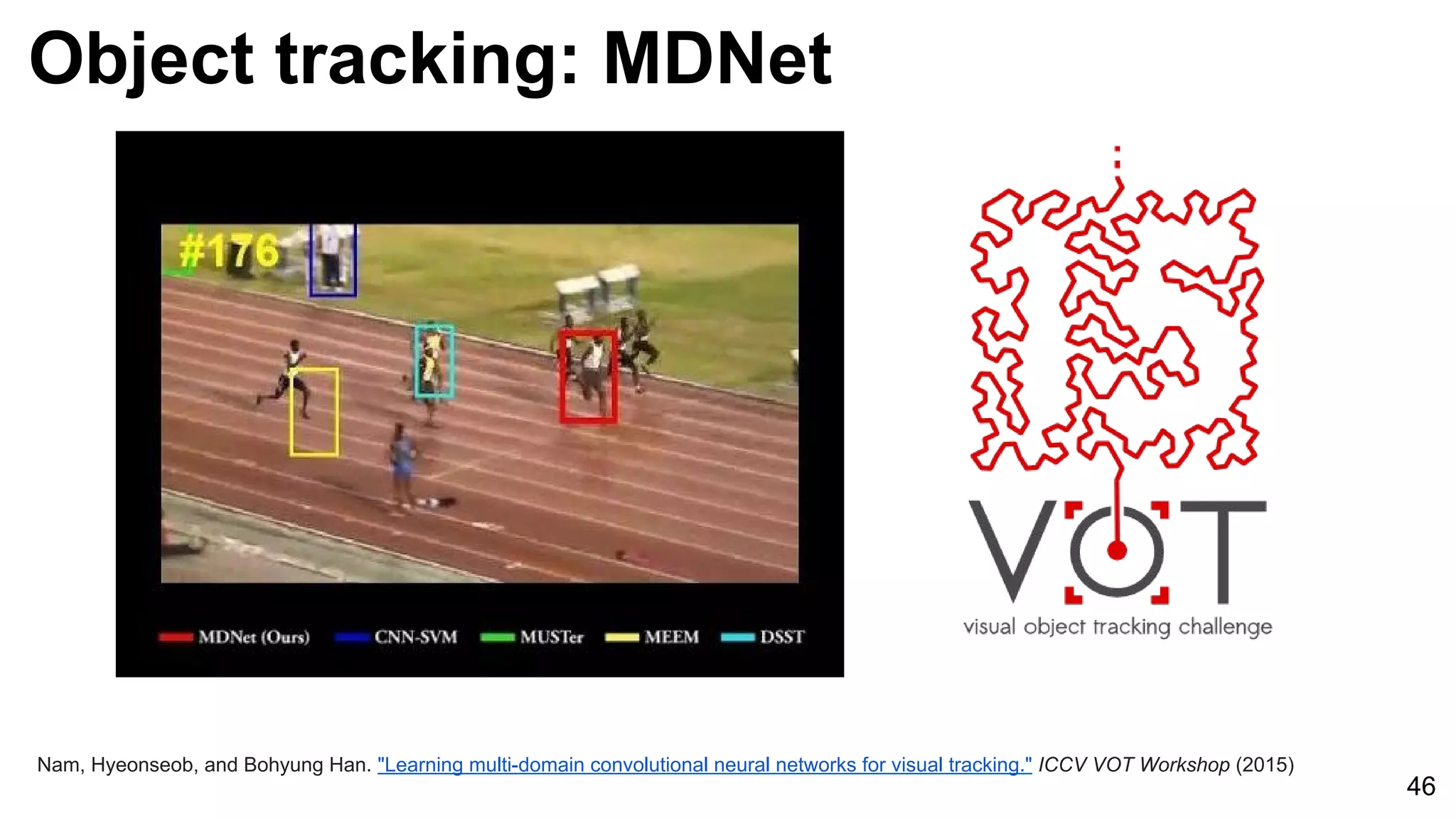
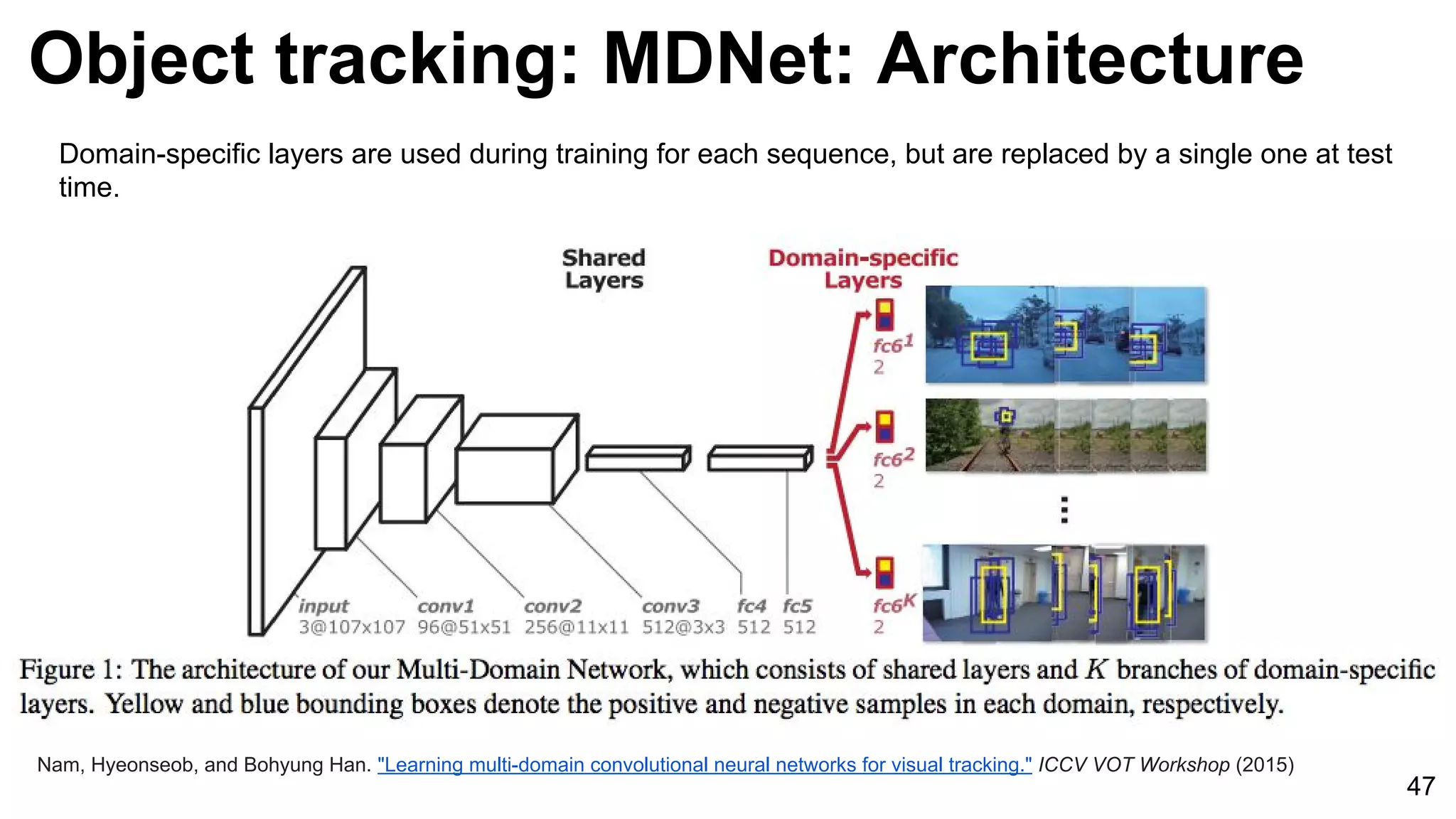
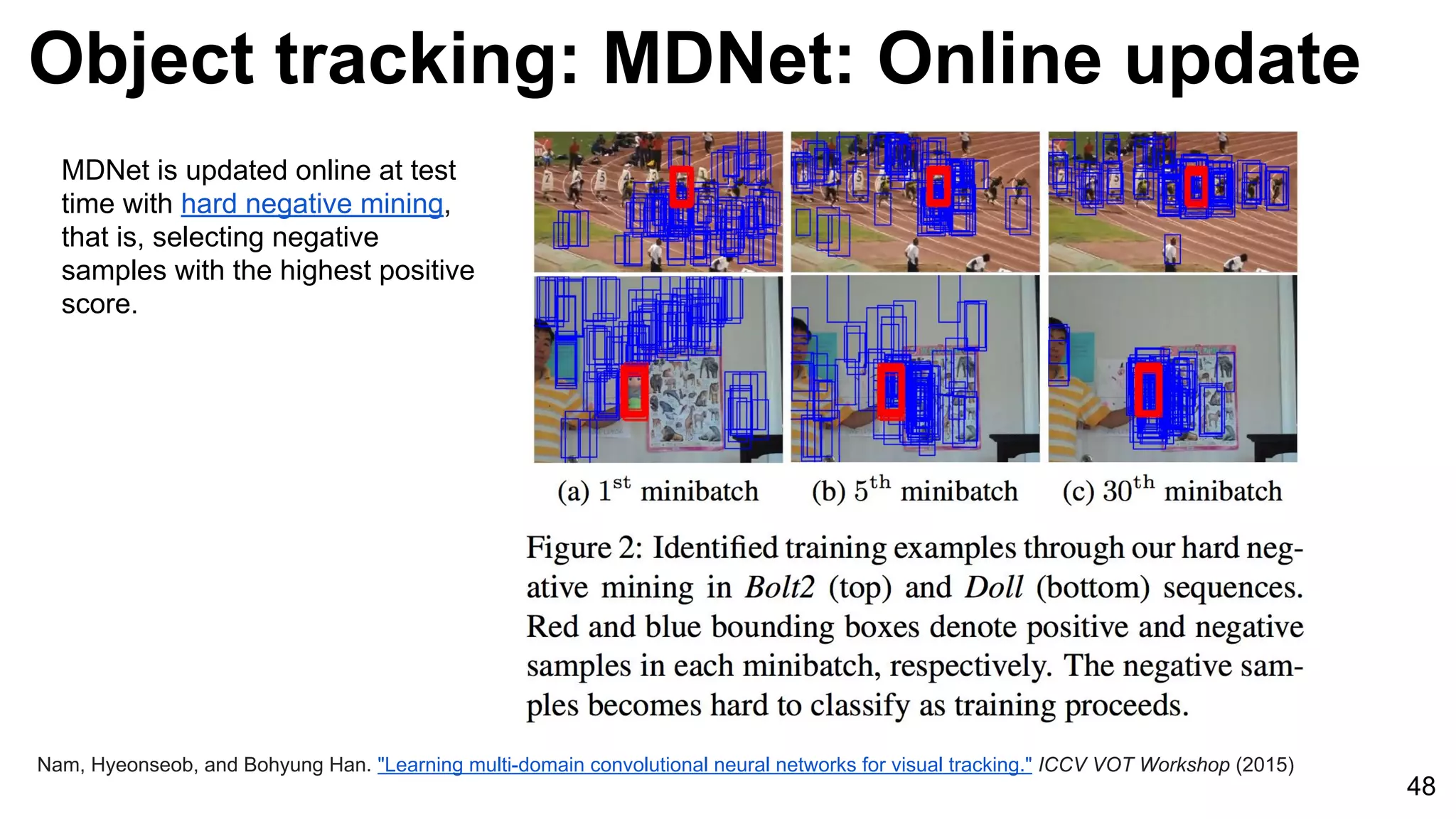
![Object tracking: FCNT
49
Wang, Lijun, Wanli Ouyang, Xiaogang Wang, and Huchuan Lu. "Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks." ICCV 2015 [code]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-49-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: FCNT
50
Wang, Lijun, Wanli Ouyang, Xiaogang Wang, and Huchuan Lu. "Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks." In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3119-3127. 2015 [code]
Focus on conv4-3 and conv5-3 of VGG-16 network pre-trained for ImageNet image classification.
conv4-3 conv5-3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-50-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: FCNT: Specialization
51
Wang, Lijun, Wanli Ouyang, Xiaogang Wang, and Huchuan Lu. "Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks." In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3119-3127. 2015 [code]
Most feature maps in VGG-16 conv4-3 and conv5-3 are not related to the foreground regions in a tracking
sequence.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-51-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: FCNT: Localization
52
Wang, Lijun, Wanli Ouyang, Xiaogang Wang, and Huchuan Lu. "Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks." In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3119-3127. 2015 [code]
Although trained for image classification, feature maps in conv5-3 enable object localization…
...but is not discriminative enough to different objects of the same category.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-52-2048.jpg)
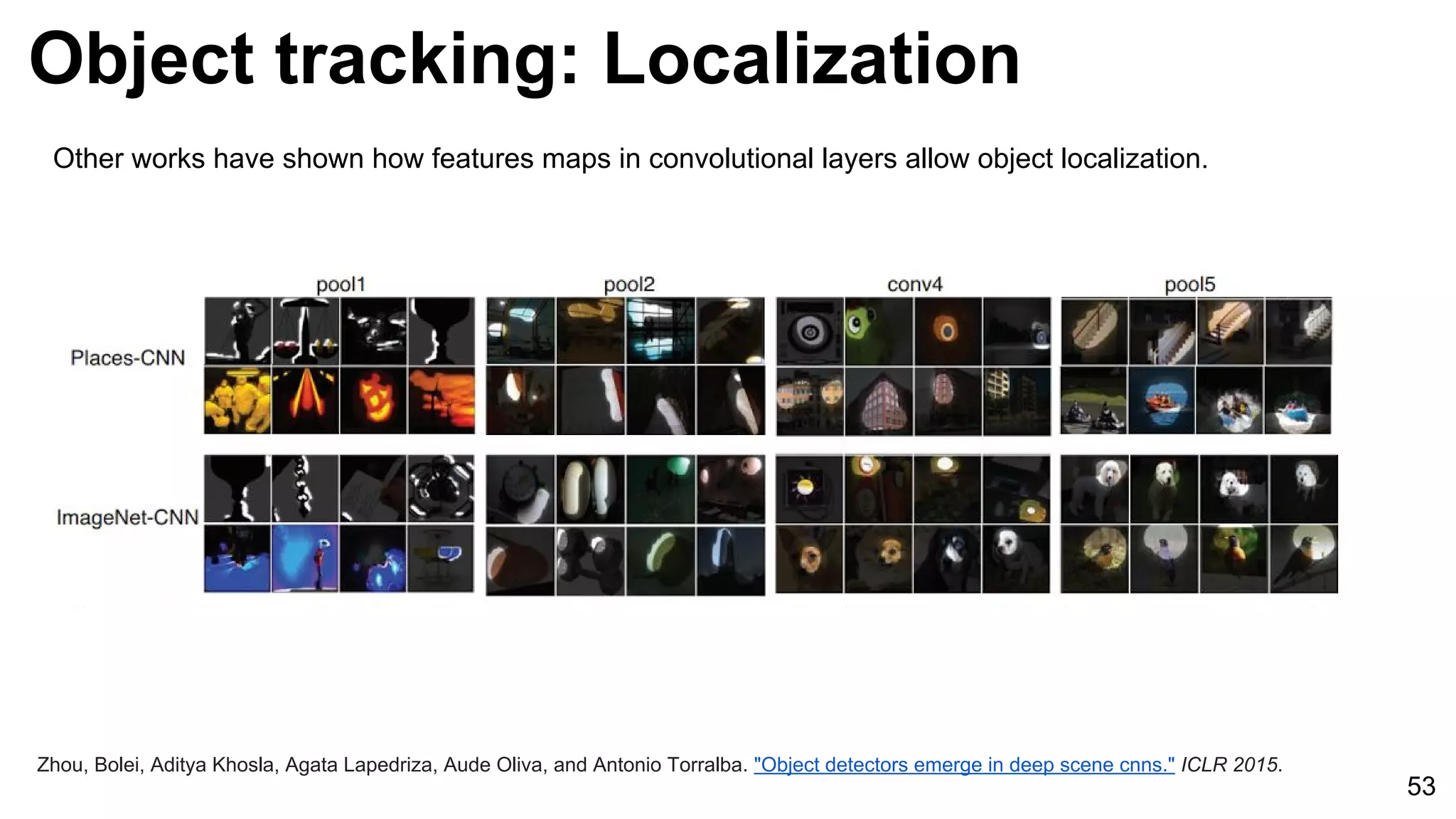
![Object tracking: FCNT: Localization
54
Wang, Lijun, Wanli Ouyang, Xiaogang Wang, and Huchuan Lu. "Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks." In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3119-3127. 2015 [code]
On the other hand, feature maps from conv4-3 are more sensitive to intra-class appearance variation…
conv4-3 conv5-3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-54-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: FCNT: Architecture
55
Wang, Lijun, Wanli Ouyang, Xiaogang Wang, and Huchuan Lu. "Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks." In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3119-3127. 2015 [code]
SNet=Specific Network (online update)
GNet=General Network (fixed)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-55-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: FCNT: Results
56
Wang, Lijun, Wanli Ouyang, Xiaogang Wang, and Huchuan Lu. "Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks." In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3119-3127. 2015 [code]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-56-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: DeepTracking
57
P. Ondruska and I. Posner, “Deep Tracking: Seeing Beyond Seeing Using Recurrent Neural Networks,” in The Thirtieth
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Phoenix, Arizona USA, 2016. [code]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-57-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: DeepTracking
58
P. Ondruska and I. Posner, “Deep Tracking: Seeing Beyond Seeing Using Recurrent Neural Networks,” in The Thirtieth
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Phoenix, Arizona USA, 2016. [code]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-58-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: DeepTracking
59
P. Ondruska and I. Posner, “Deep Tracking: Seeing Beyond Seeing Using Recurrent Neural Networks,” in The Thirtieth
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Phoenix, Arizona USA, 2016. [code]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-59-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: DeepTracking
60
P. Ondruska and I. Posner, “Deep Tracking: Seeing Beyond Seeing Using Recurrent Neural Networks,” in The Thirtieth
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Phoenix, Arizona USA, 2016. [code]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-60-2048.jpg)
![Object tracking: Compact features
61
Wang, Naiyan, and Dit-Yan Yeung. "Learning a deep compact image representation for visual tracking." NIPS 2013 [Project page with code]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03lasallemmmdlcv-videoanalytics-160505221440/75/Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-3-4-Video-Analytics-laSalle-2016-61-2048.jpg)
