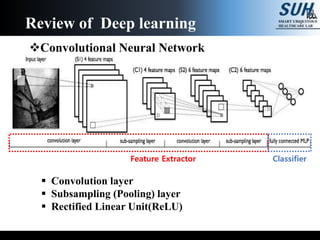
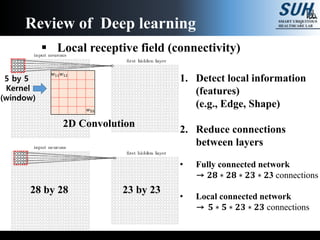
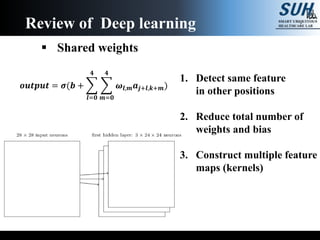
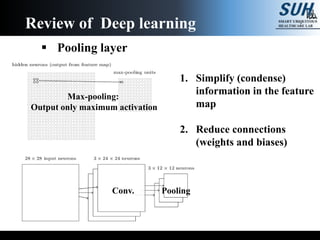
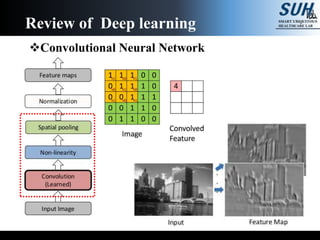
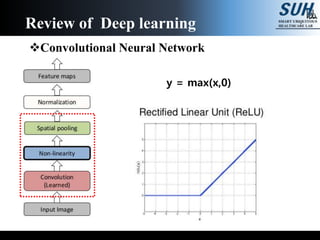
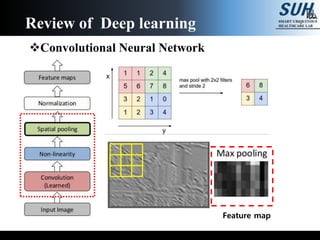
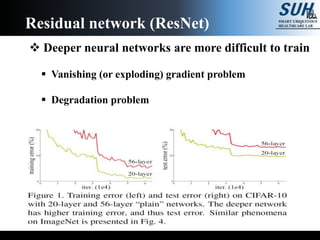
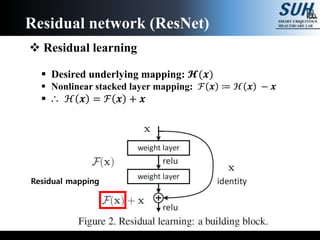
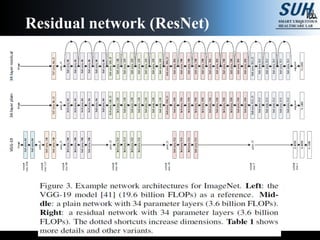
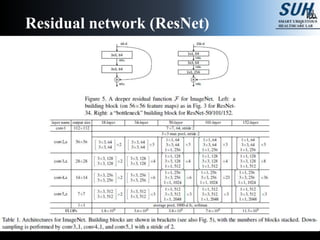
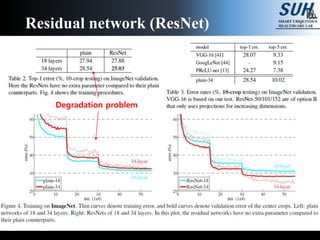
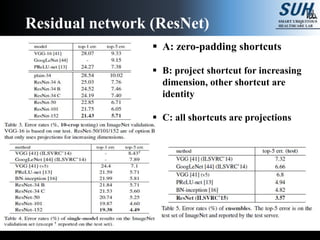
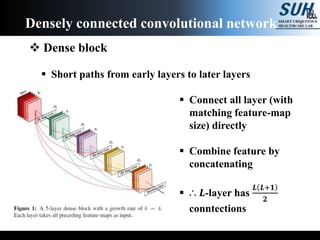
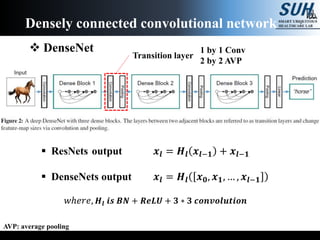
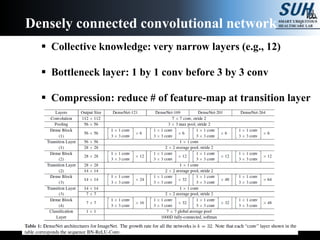
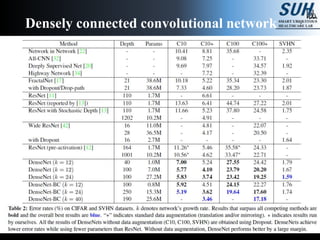
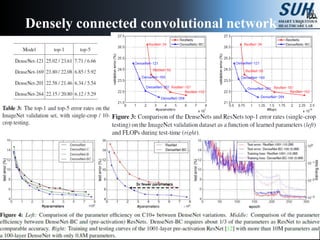
This document summarizes recent developments in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image recognition, including residual networks (ResNets) and densely connected convolutional networks (DenseNets). It reviews CNN structure and components like convolution, pooling, and ReLU. ResNets address degradation problems in deep networks by introducing identity-based skip connections. DenseNets connect each layer to every other layer to encourage feature reuse, addressing vanishing gradients. The document outlines the structures of ResNets and DenseNets and their advantages over traditional CNNs.