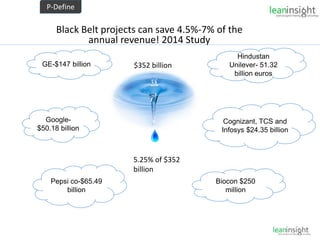
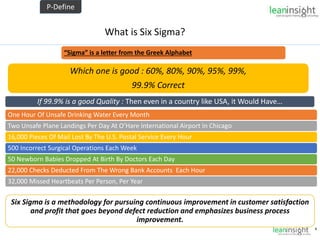
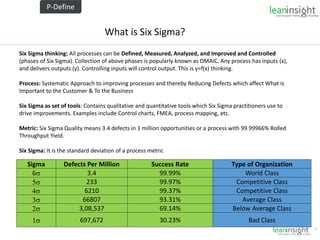
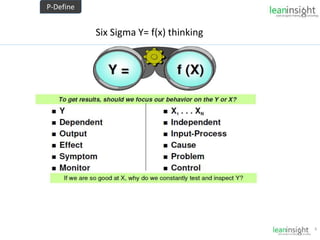
The document outlines the significance of Six Sigma methodology in enhancing customer satisfaction and profitability through continuous improvement and defect reduction. It emphasizes the importance of understanding processes, metrics, and the roles of various Six Sigma practitioners including Black Belts and Master Black Belts. Additionally, it highlights the financial benefits associated with successful Six Sigma projects and provides a training opportunity in Bangalore.