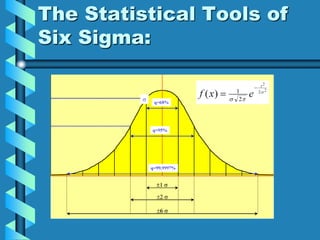
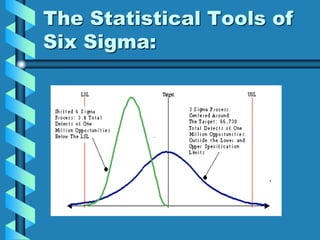
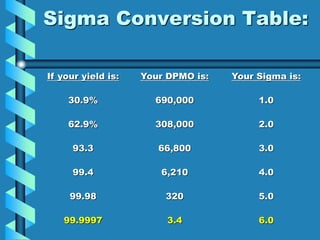
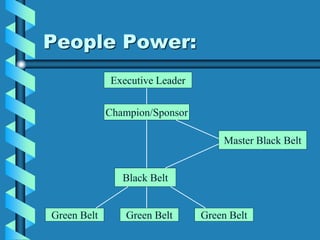
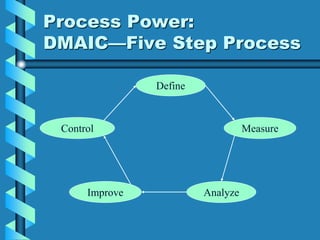
Six Sigma is a quality management program developed by Motorola to reduce defects through statistical process analysis. It aims for 3.4 defects per million opportunities. The statistical tools of Six Sigma include defining requirements, measuring defects, determining yield, and calculating sigma level. Six Sigma programs involve executive leaders, champions, master black belts, black belts, and green belts who follow the DMAIC process of define, measure, analyze, improve, and control processes. An example success story is GE, which improved operating margins using Six Sigma.