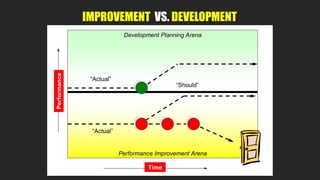
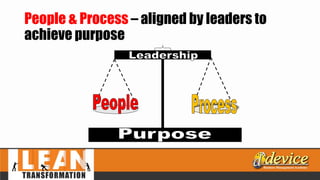
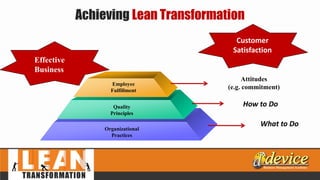
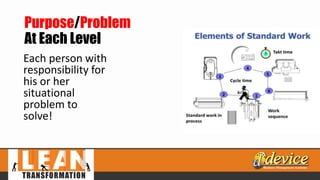
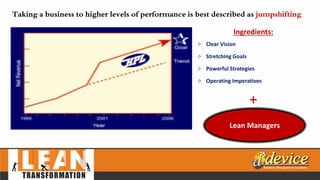
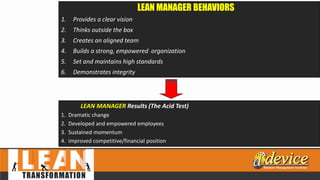
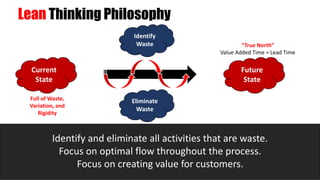
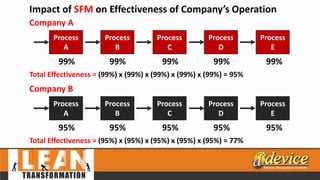
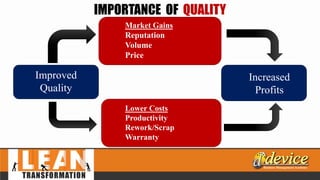
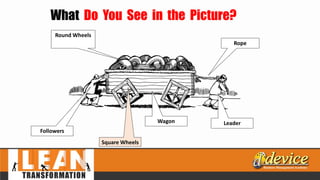
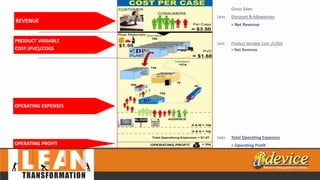
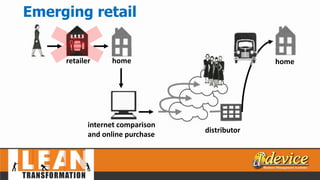
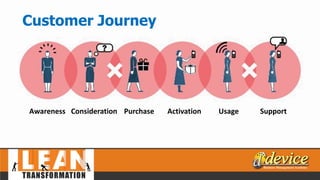
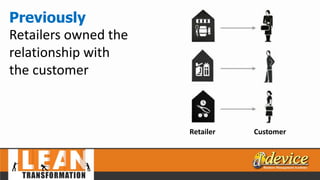
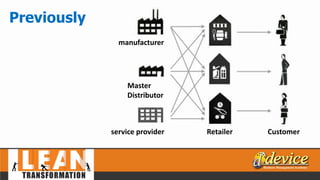
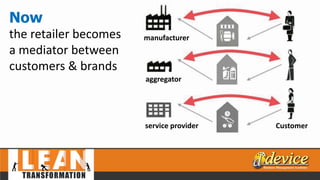
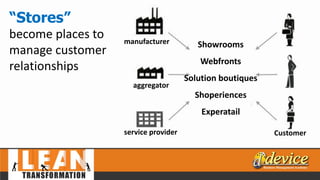
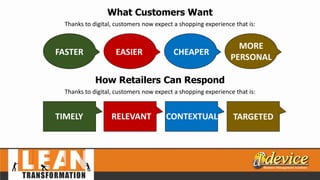
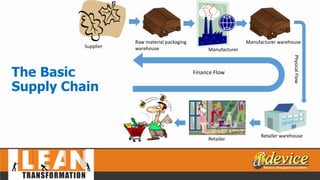
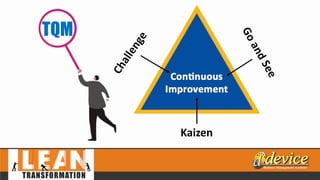
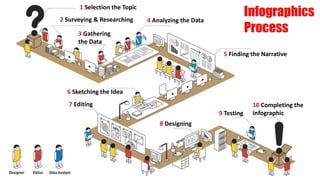
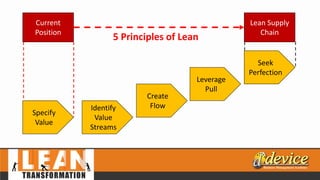
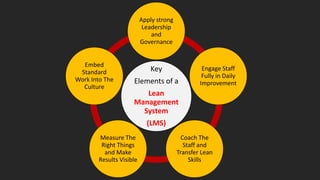
The document discusses lean management principles aimed at improving organizational efficiency and competitive advantage by eliminating waste and creating value from the customer's perspective. It outlines the importance of engaging employees, developing a clear vision, and implementing continuous improvement practices to drive transformation. Key components include establishing metrics for performance, aligning purpose and processes, and fostering a culture of empowerment and innovation.