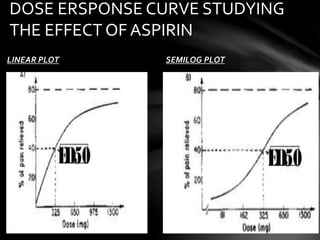
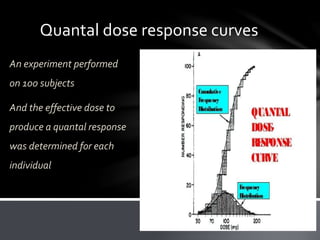
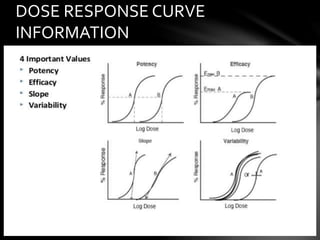
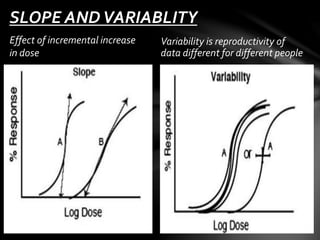
This document discusses dose-response relationships and dose-response curves. It defines dose as the amount of drug administered and response as the effect on the body. The relationship between dose and response can be illustrated with a dose-response curve, which is typically a rectangular hyperbola. Dose-response curves are used to determine the appropriate dose of a drug and compare effects across doses and individuals. The document also discusses factors like potency, efficacy, thresholds, and how dose-response curves can be graded or quantal depending on the type of response measured.



![WHAT IS DOSE RESPONSE
RELATIONSHIP
A RELATIONSHIP USED TO ANALYZE A KIND OF
RESPONSE OBTAINED AFTER ADMINISTERING
SPECIFIC DOSE OF DRUG
E.G If 10mg of ILLAPRAZOLE [ppi] is administered
response is it should inhibit formation of proton pumps at
10mg specifically
Dose response relationship has two components
[1] DOSE PLASMA CONCENTRATION RELATIONSHIP
[2] PLASMA CONCENTRATION RESPONSE
RELATIONSHIP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doseresponserelationship-141026060457-conversion-gate01/85/Dose-response-relationship-4-320.jpg)

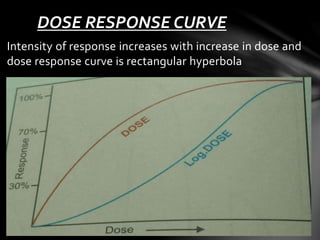
![WHY DOSE RESPONSE CURVE IS
RECTANGULAR HYPERBOLA
This is because drug-receptor interaction obeys law
of mass action, accordingly
E = Emax [D]
Kd [D]
Where
E = Observed effect of dose of drug
Emax = maximal response
Kd = dissociation constant of drug receptor
complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doseresponserelationship-141026060457-conversion-gate01/85/Dose-response-relationship-7-320.jpg)
![ADVANTAGES OF PLOTTING LOG DOSE RESPONSE
CURVES
[1] WIDE RANGE OF DRUG DOSES CAN BE DISPLAYED
ON GRAPH
[2] COMPARISON BETWEEN AGONIST AND
ANTAGONIST BECOMES EASIER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doseresponserelationship-141026060457-conversion-gate01/85/Dose-response-relationship-8-320.jpg)





![Drug potency and efficacy curves
[1] Drug B is less potent but equally
efficacious as drug A
[2] Drug C is less potent and less
efficacious than drug A ,But equally
potent and less efficacious than
drug B
[3] Drug D is more potent than drug
A,B,& C but less efficacious than
drugs A&B and equally efficacious
as drug C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doseresponserelationship-141026060457-conversion-gate01/85/Dose-response-relationship-18-320.jpg)

![Factors affecting drug response
[1] AGE
[2] WEIGHT
[3] GENDER
[4] ENVIRONMENT
[5] FEVER
[6] SHOCK](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doseresponserelationship-141026060457-conversion-gate01/85/Dose-response-relationship-21-320.jpg)
