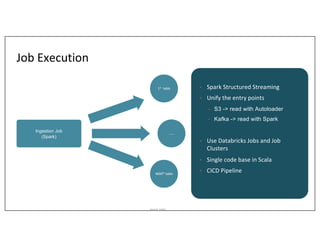
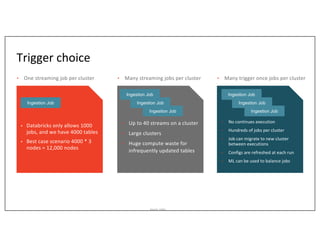
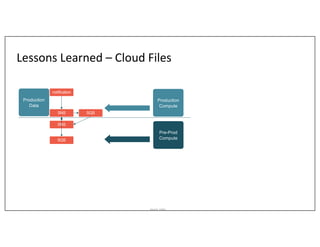
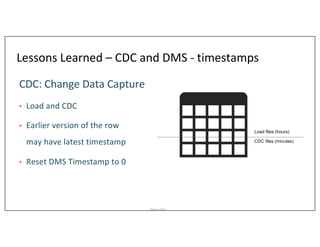
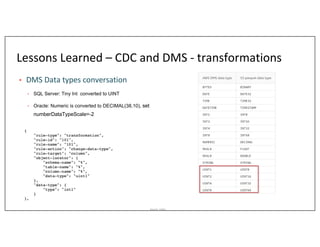
This document outlines Asurion's large-scale lakehouse implementation using structured streaming, detailing their architecture and data ingestion strategies across multiple sources. It highlights the challenges faced, lessons learned during the process, and the technology stack employed, including Apache Spark, AWS, and Delta Lake. Key points include optimizing job execution, managing cloud files, and addressing limitations with change data capture and Kafka integration.