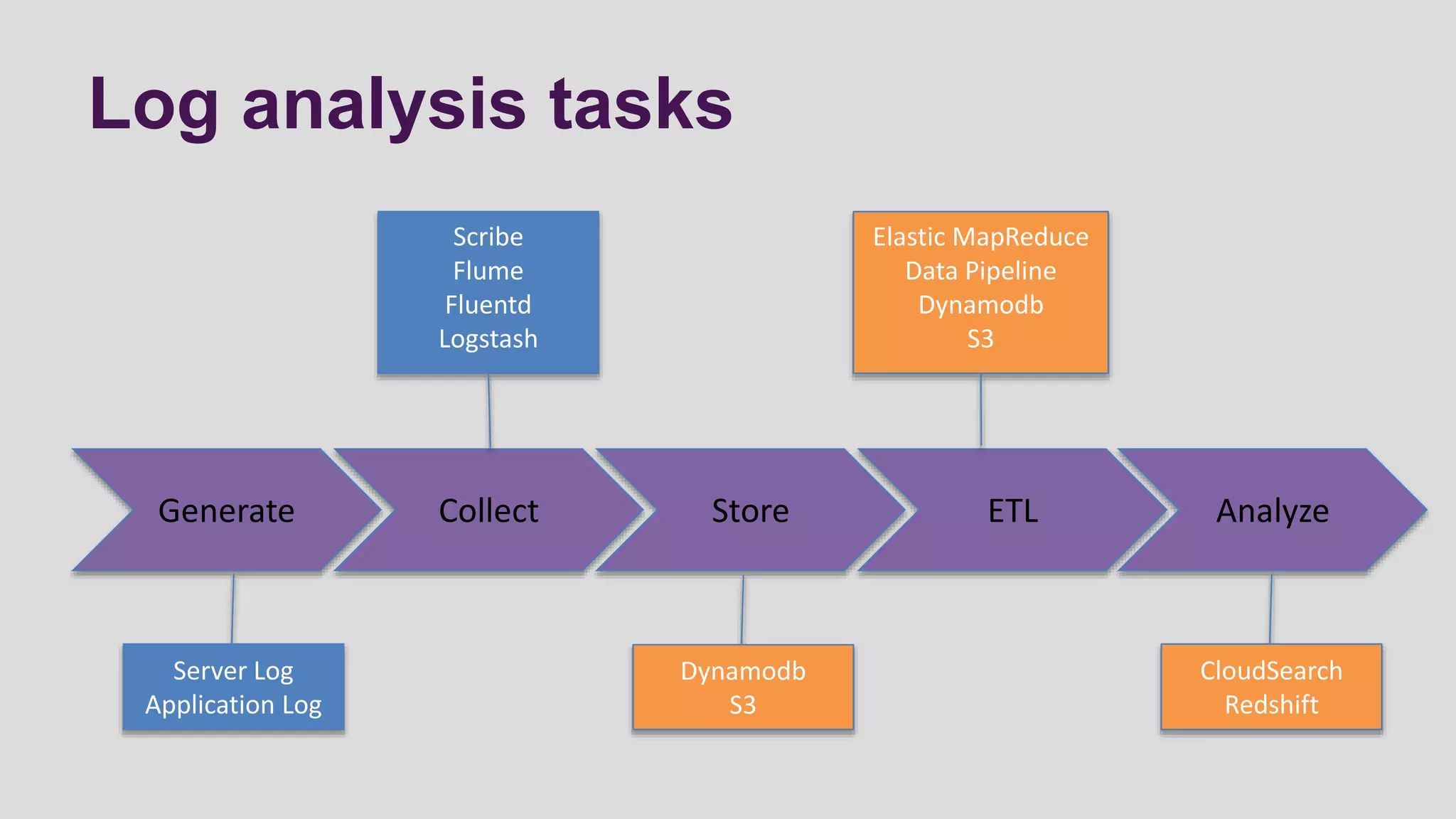
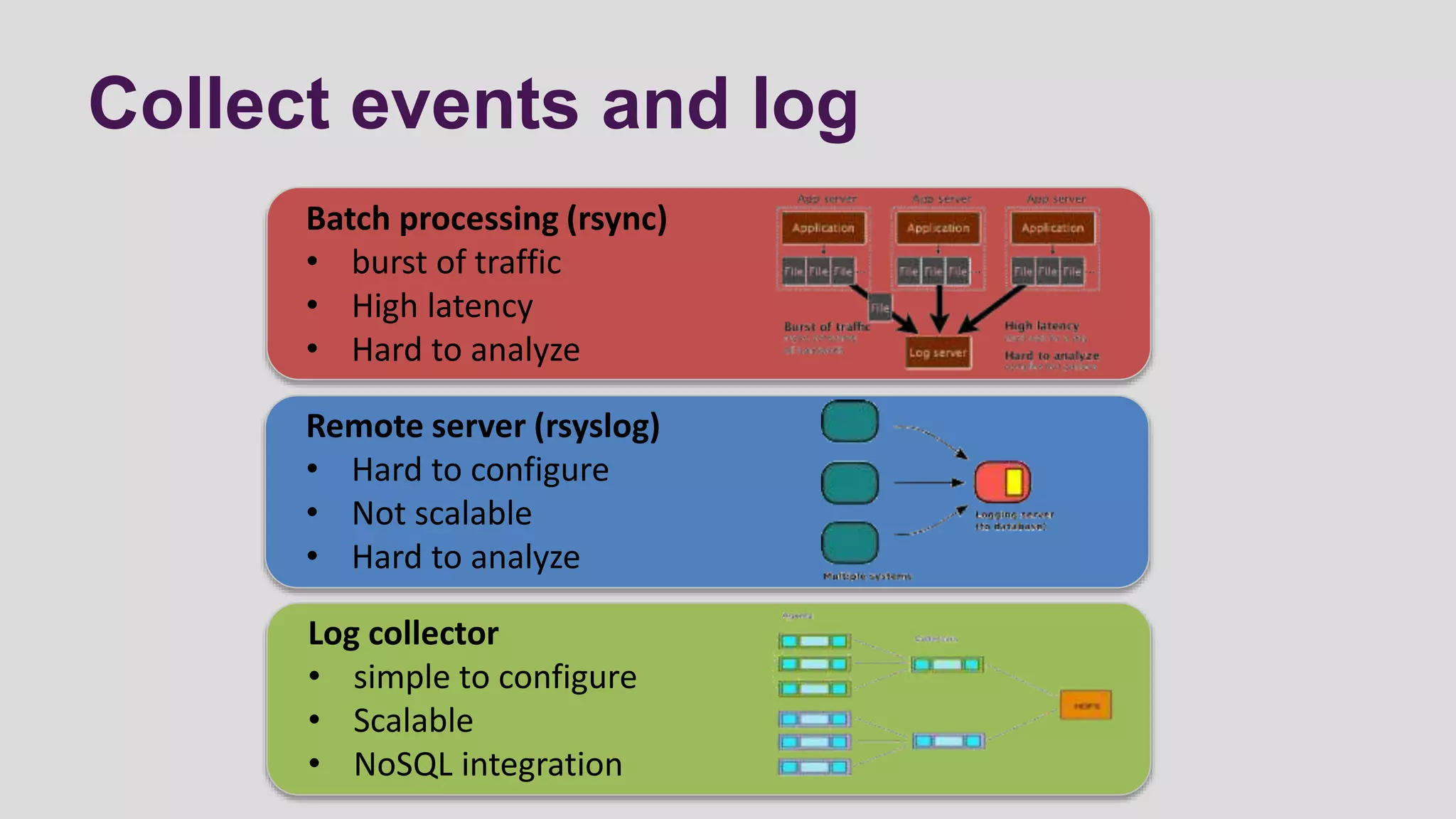
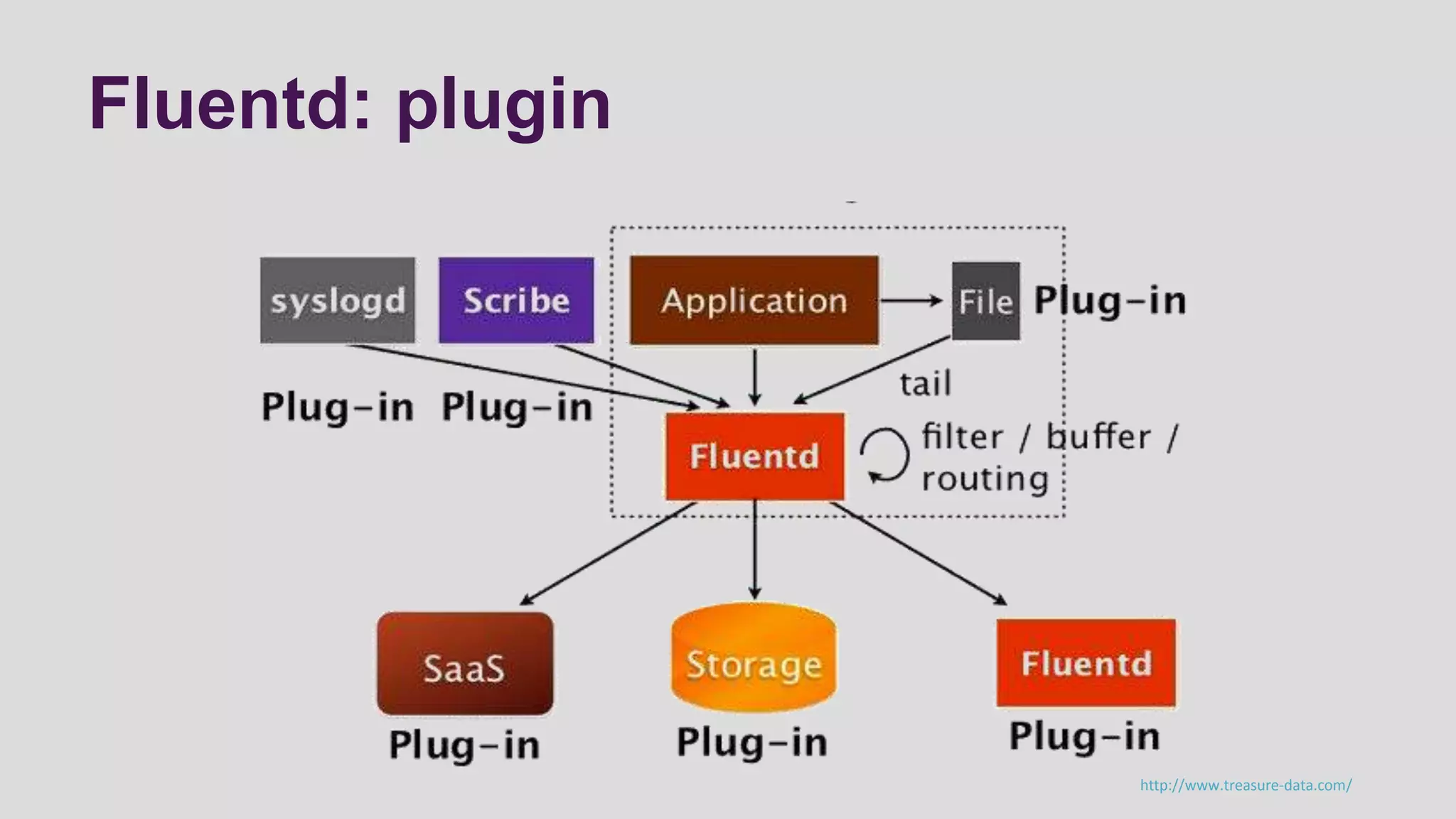
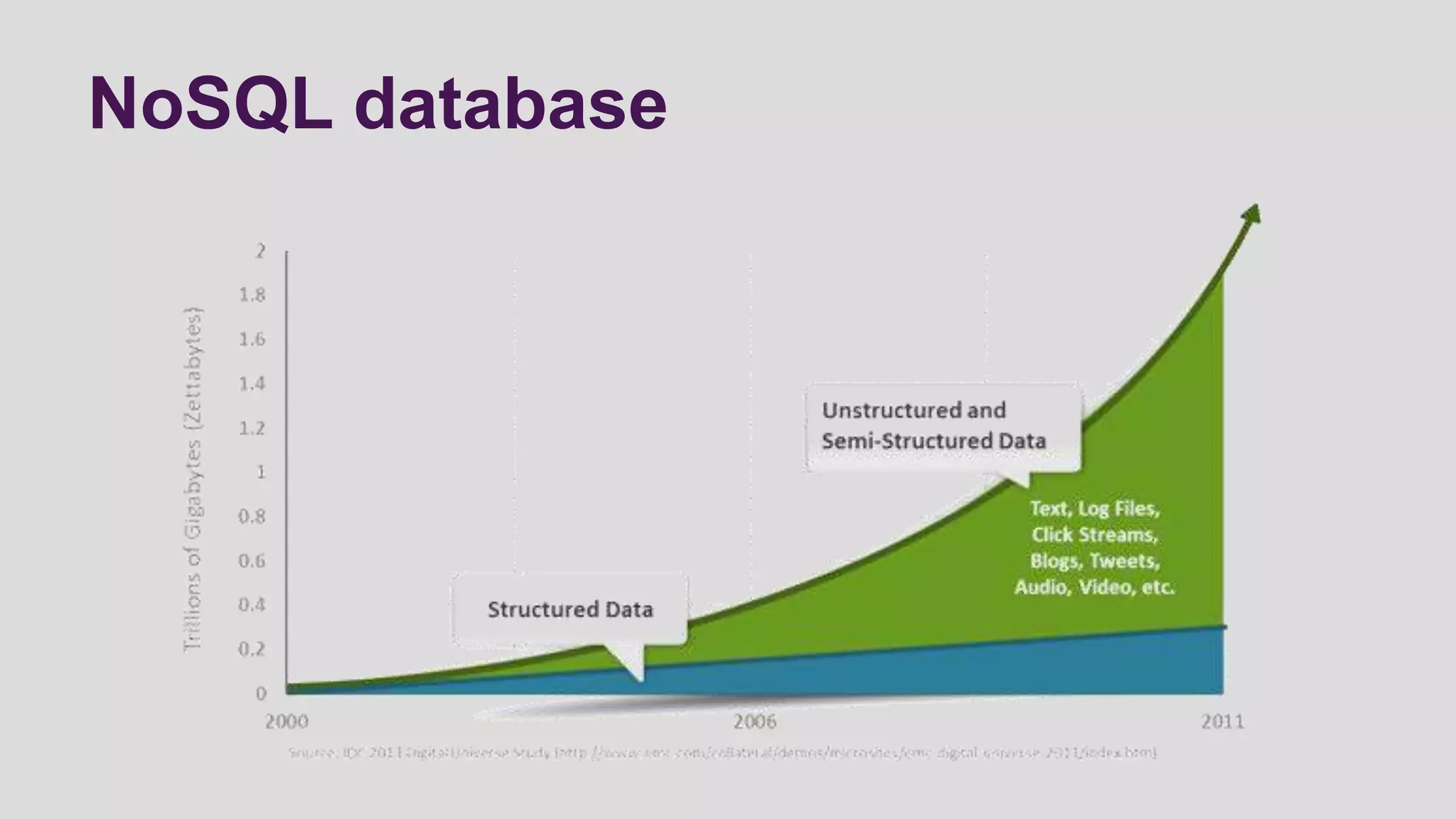
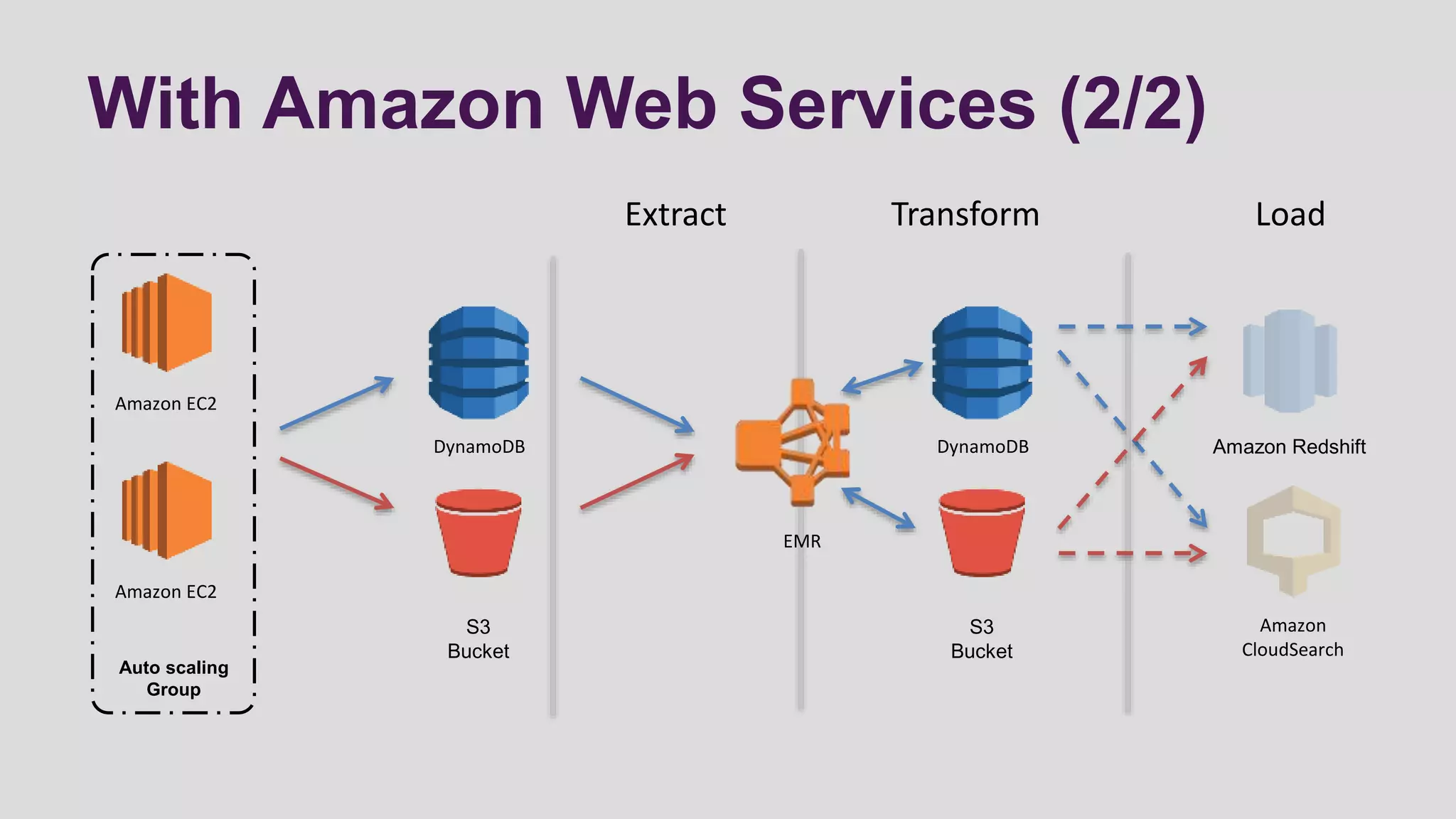
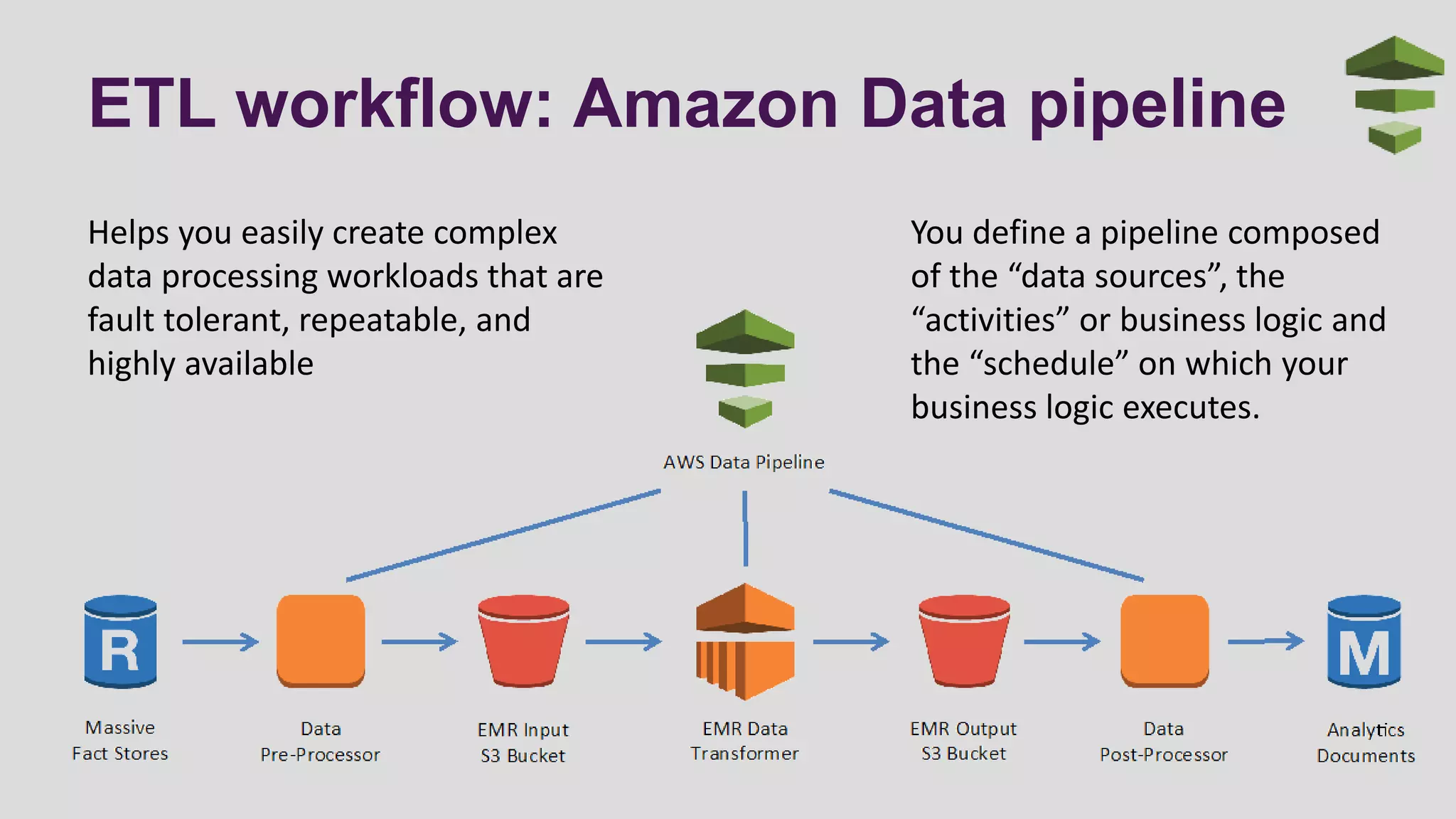
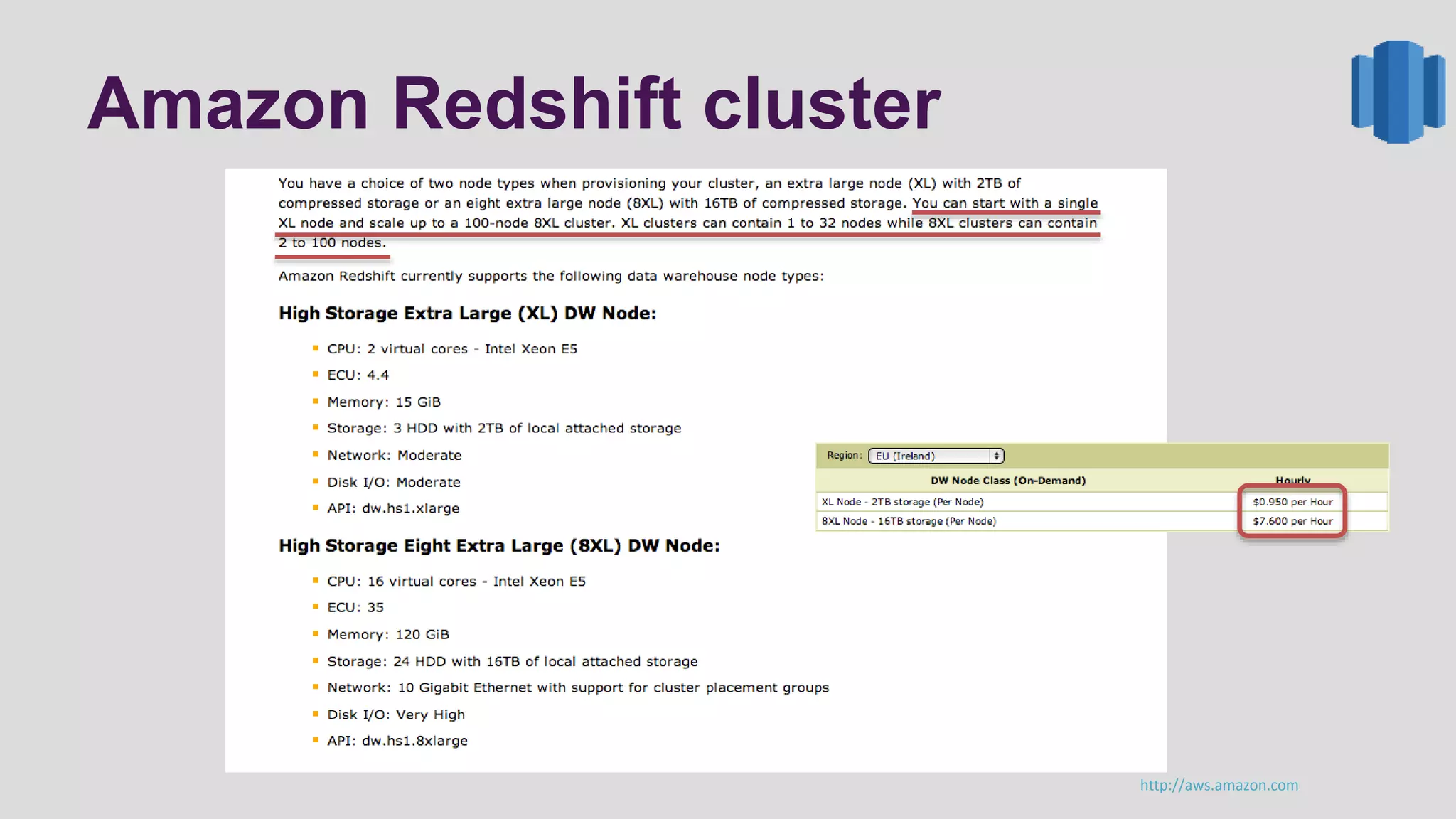
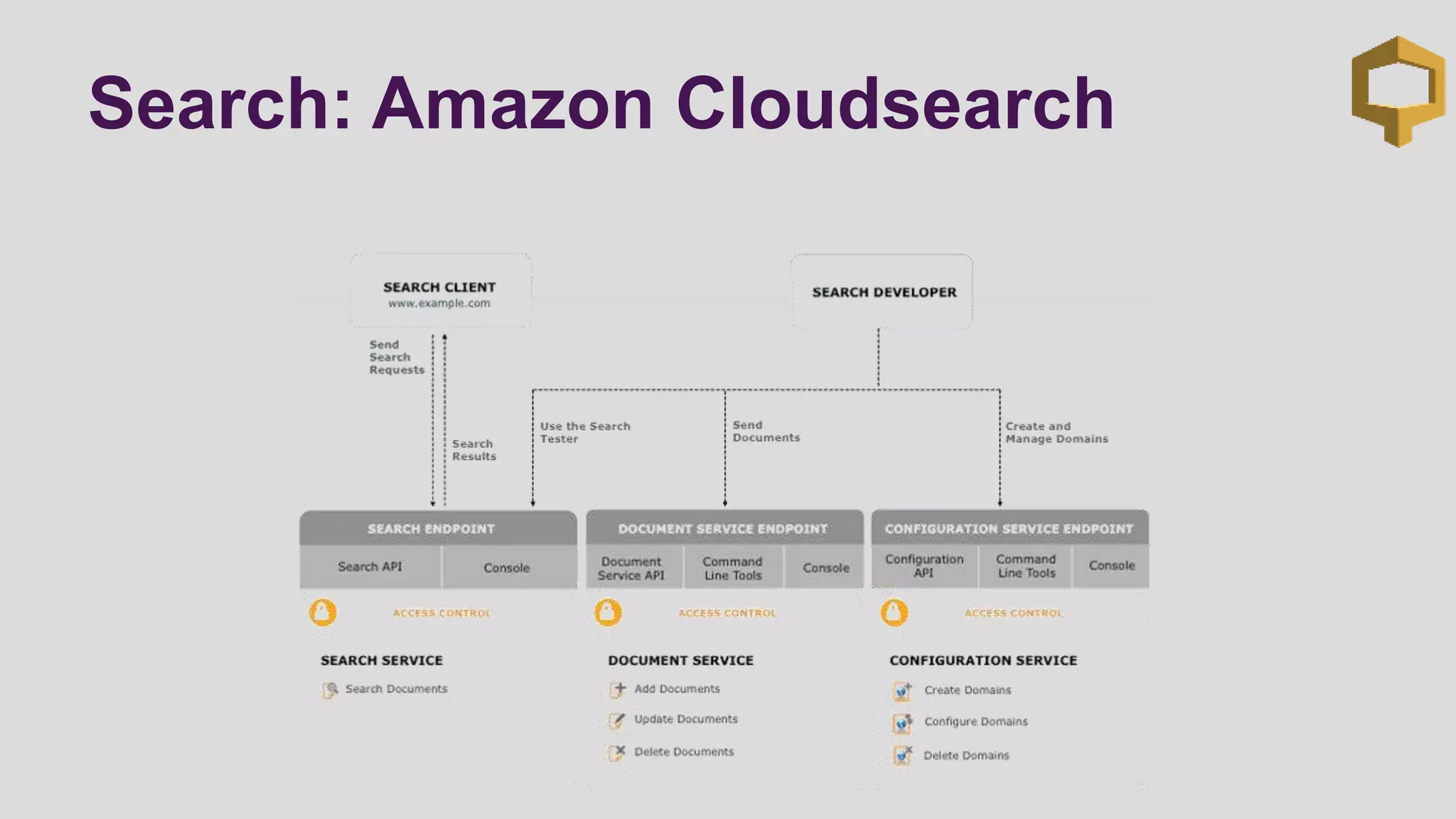
This document discusses logging scenarios using DynamoDB and Elastic MapReduce. It covers collecting log data in real-time using tools like Fluentd and storing it in DynamoDB. It then describes using EMR to perform ETL processes on the data, extracting from DynamoDB, transforming the data across EC2 instances, and loading to S3 or DynamoDB. Finally, it discusses analyzing the data using Redshift for queries or CloudSearch for search capabilities.