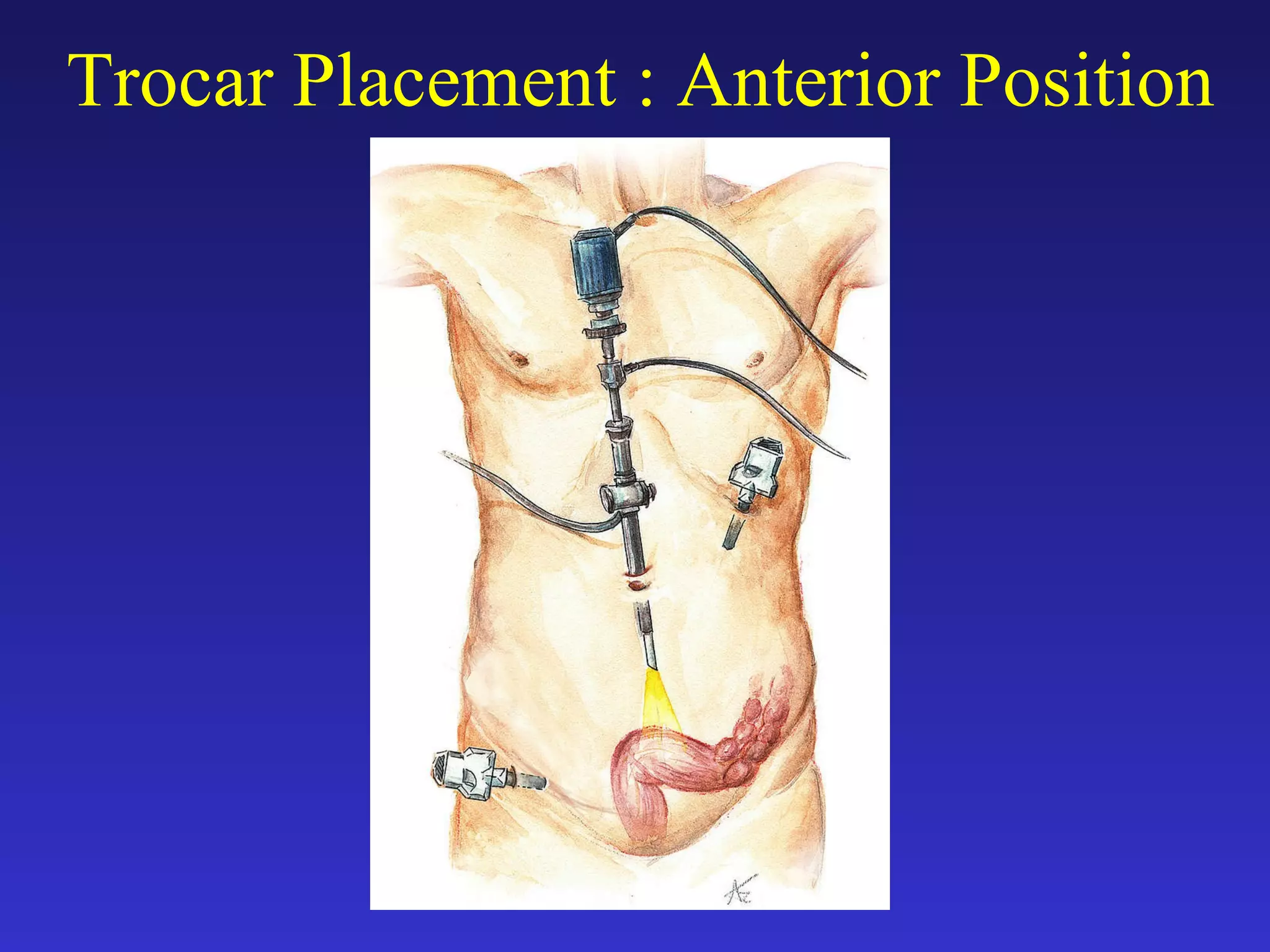
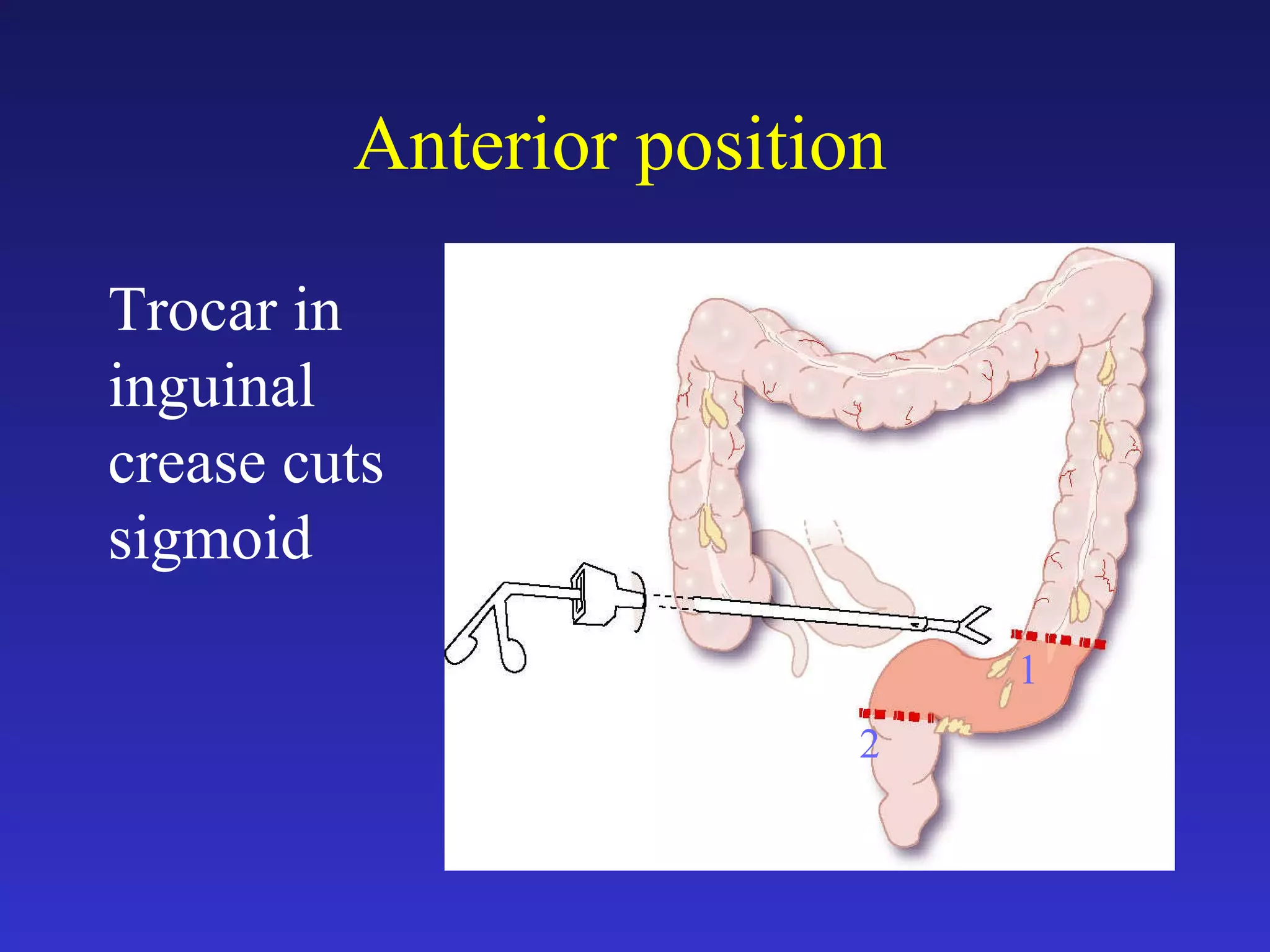
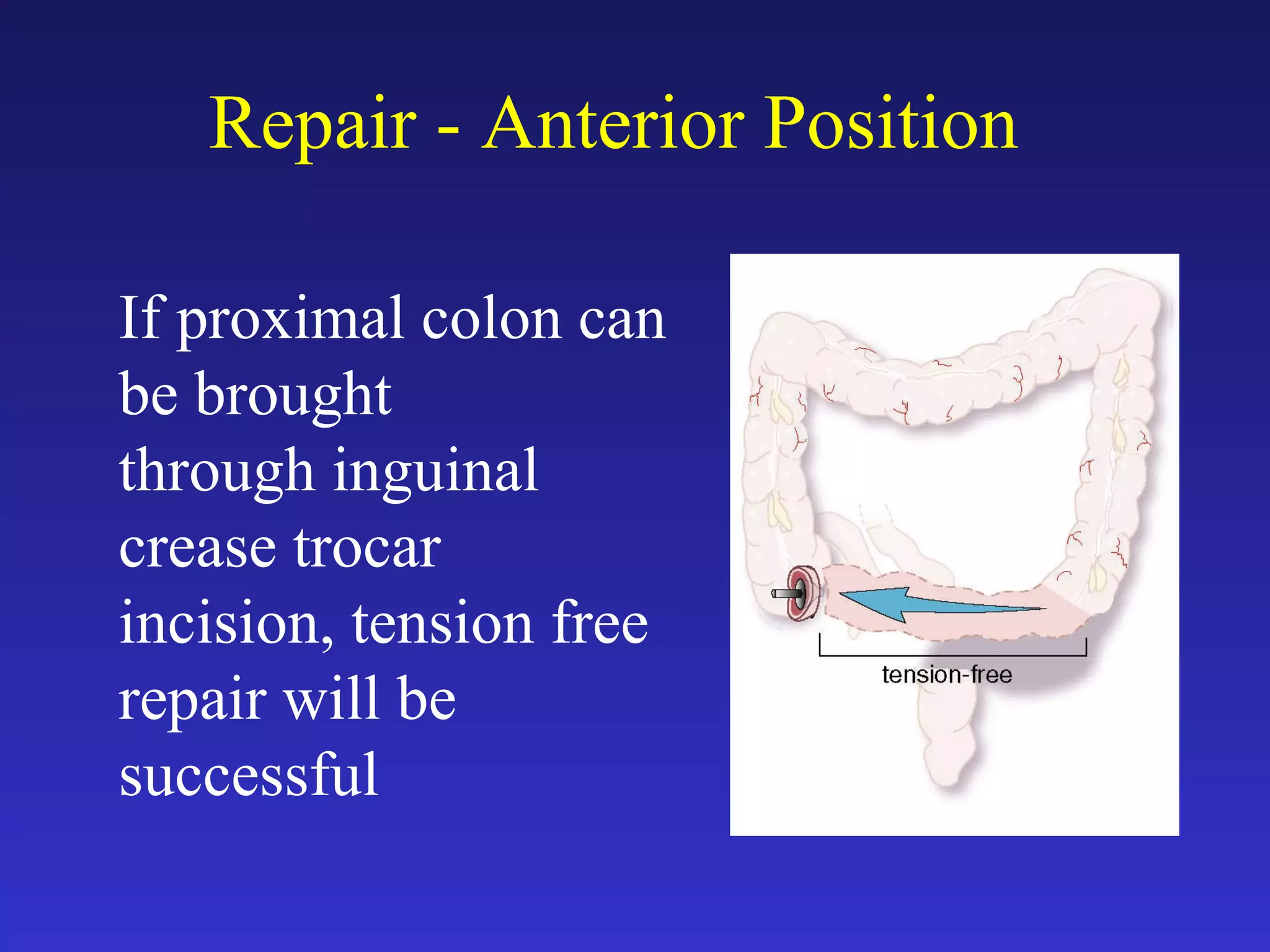
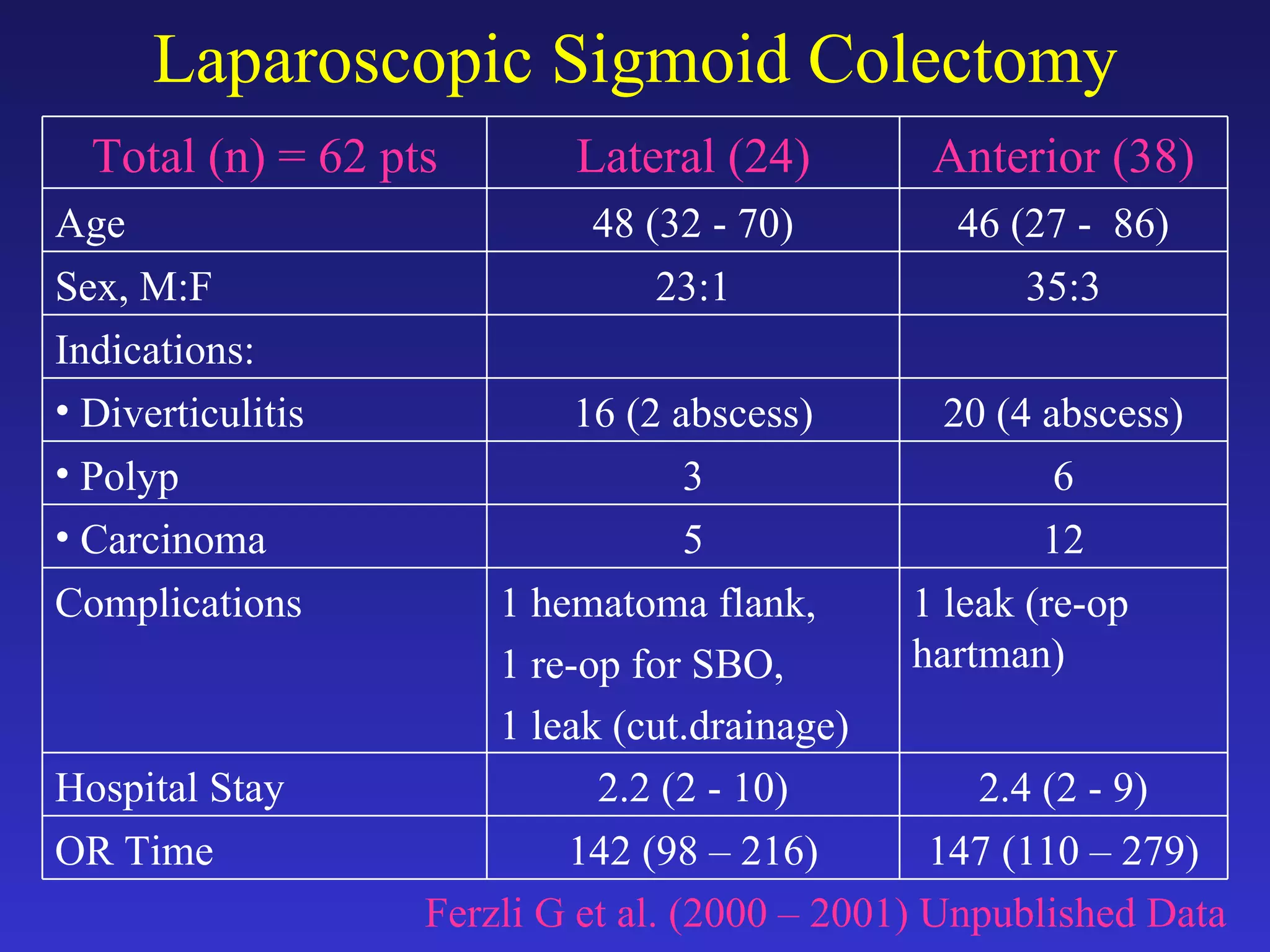
1) The document discusses laparoscopic colon resection techniques, including an anterior approach where trocars are placed in the inguinal crease and the sigmoid colon is cut.
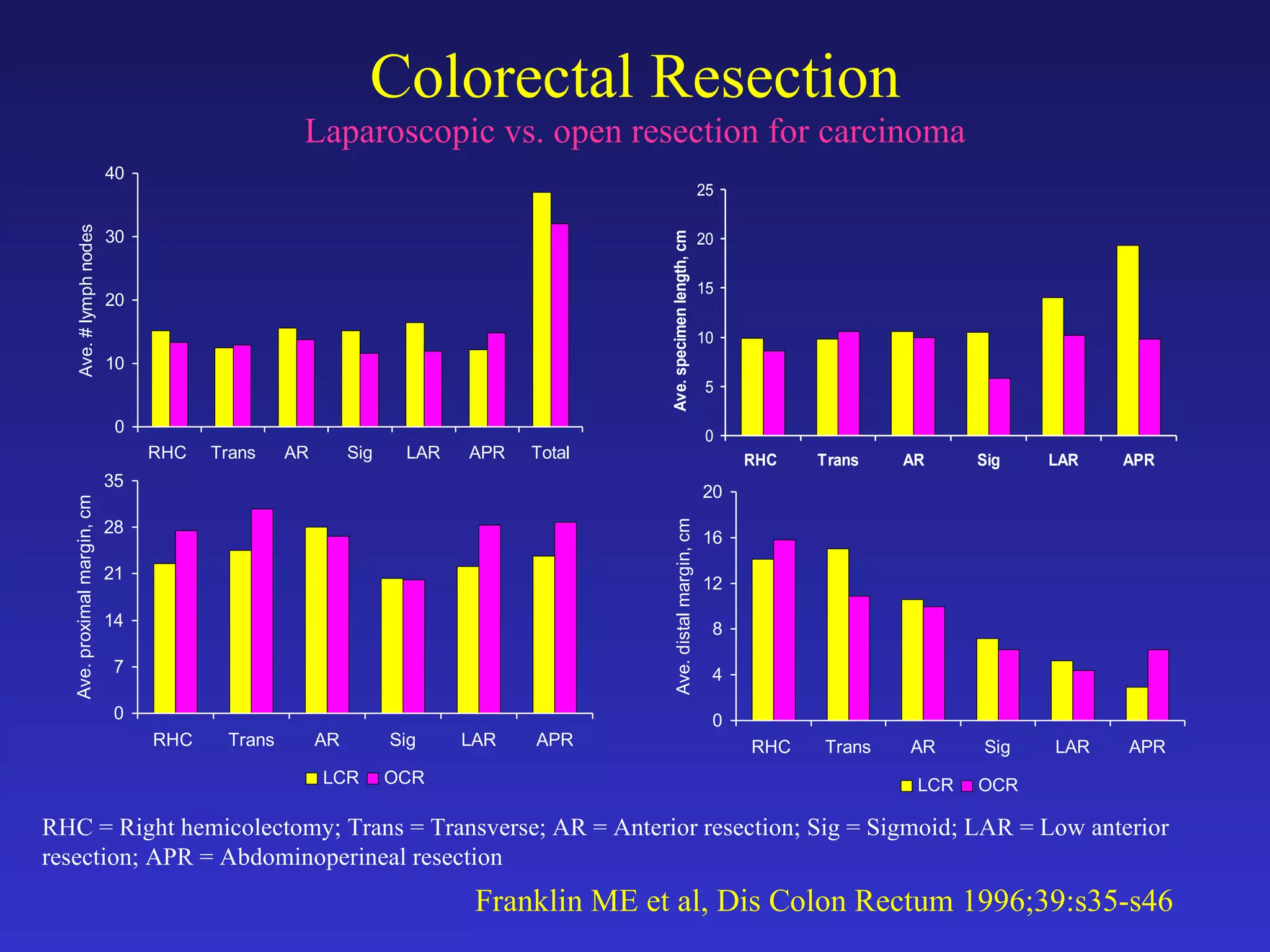
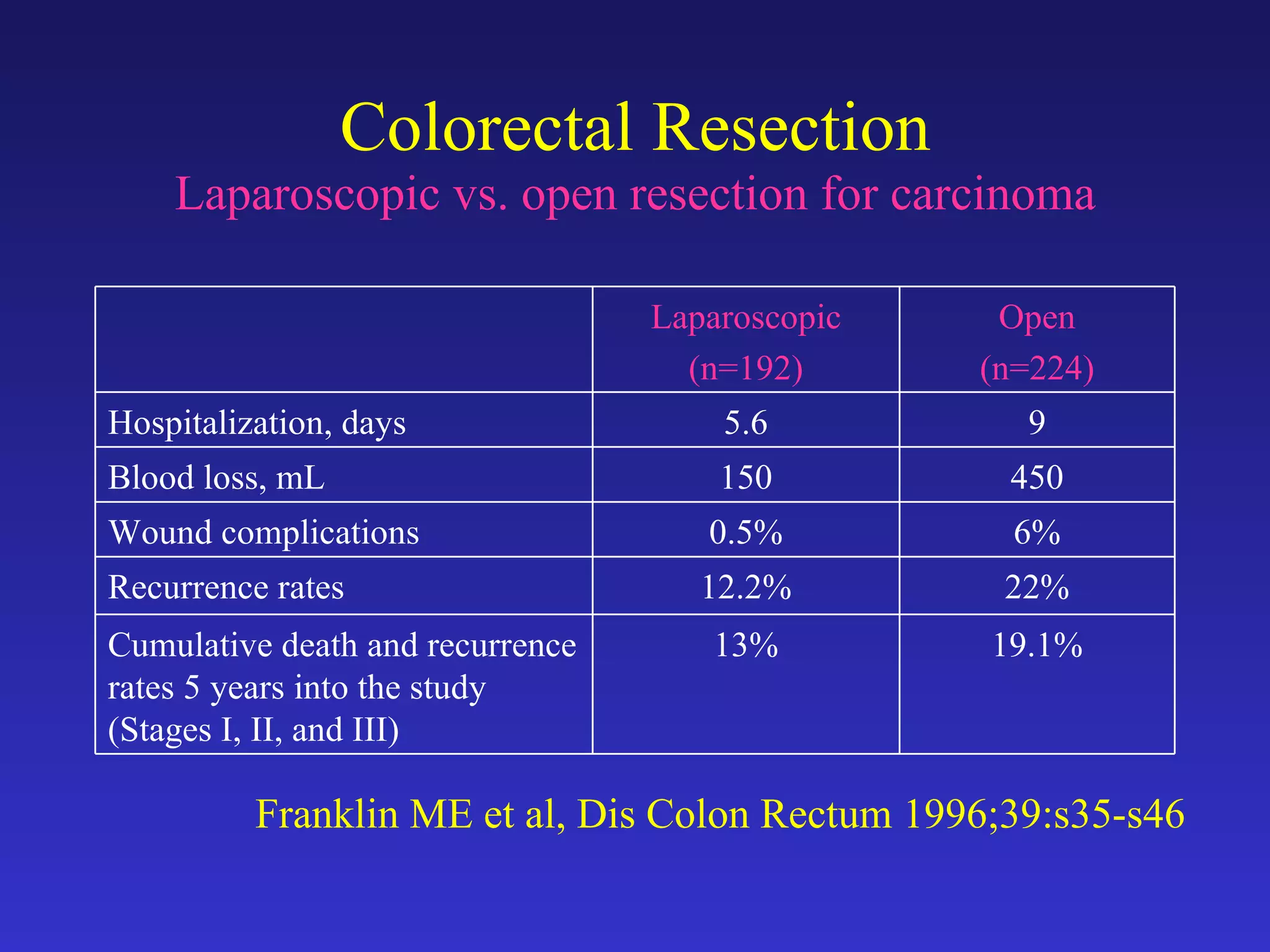
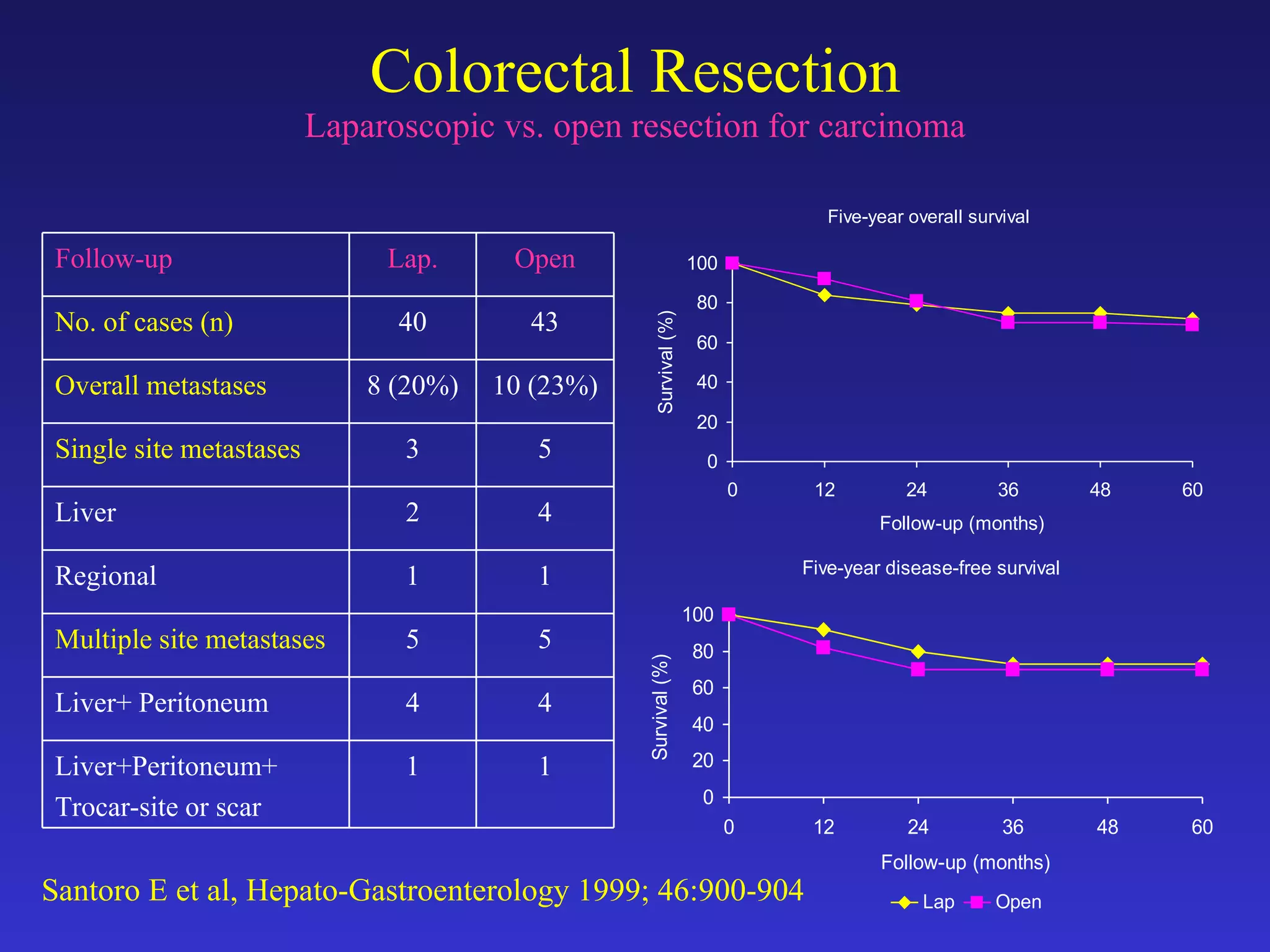
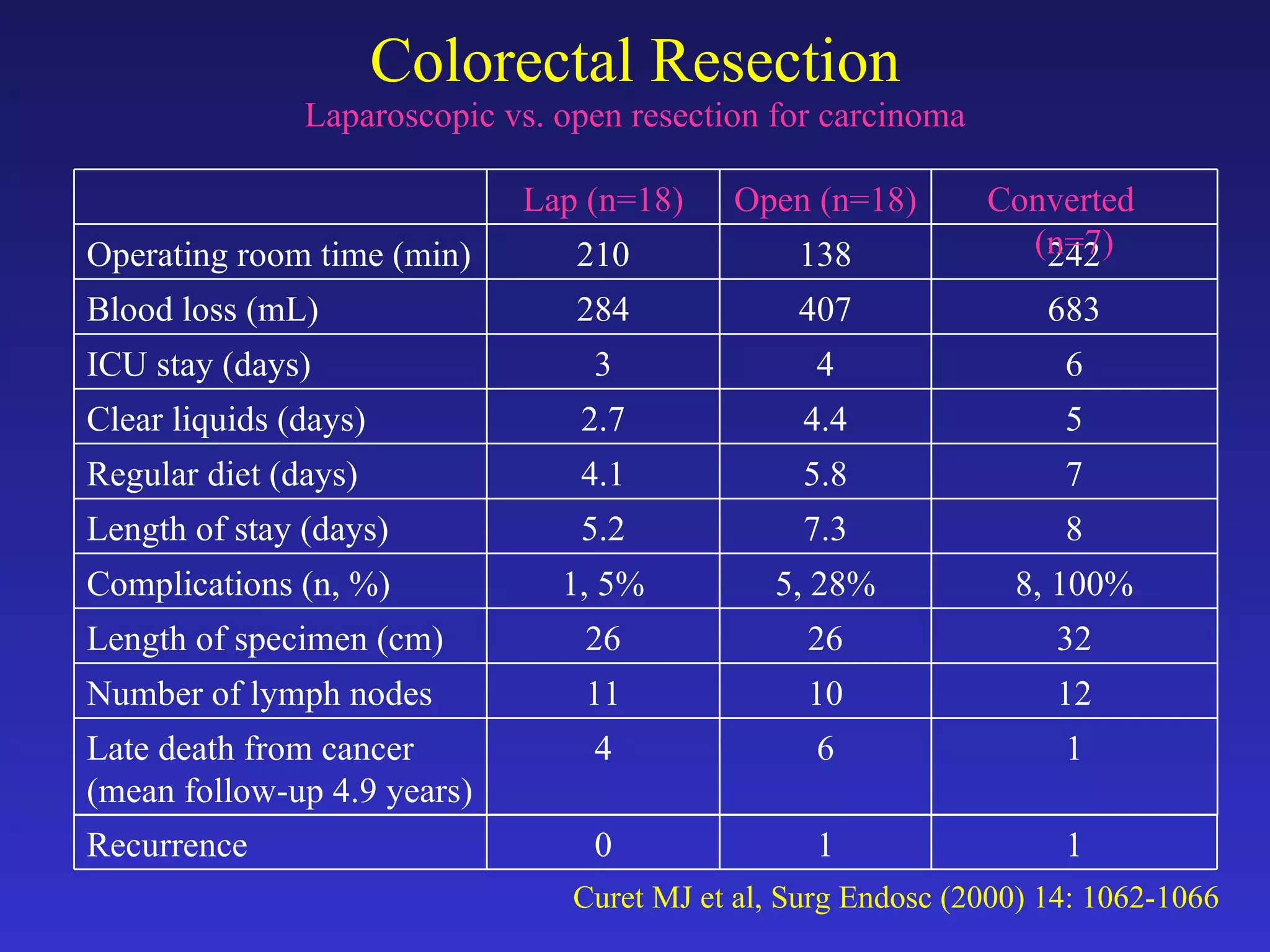
2) Studies comparing laparoscopic and open colon resection for cancer show that laparoscopic surgery results in less blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and fewer wound complications with similar long-term survival and recurrence rates.
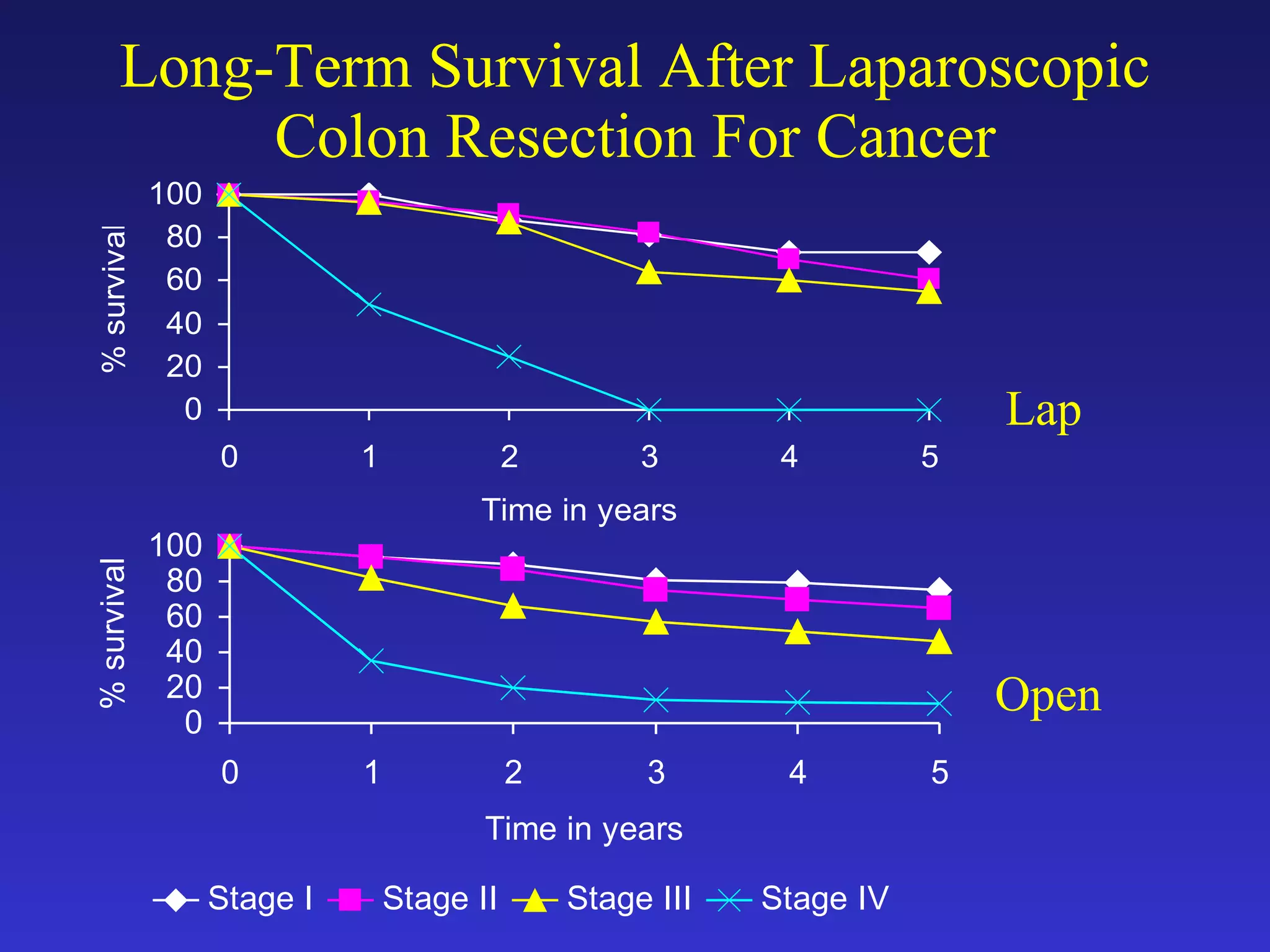
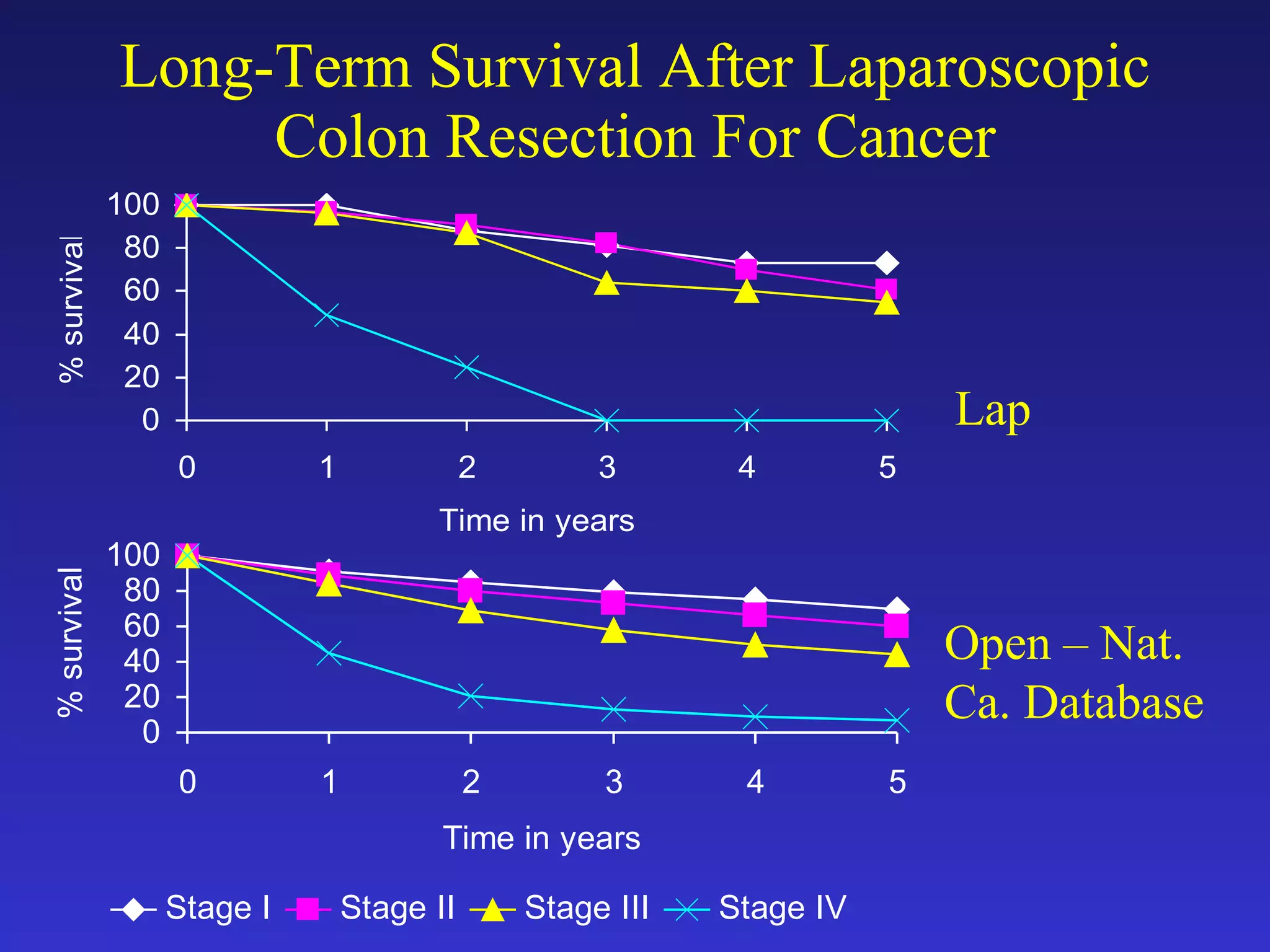
3) A retrospective study of over 100 patients undergoing laparoscopic colon resection for cancer found 5-year survival rates similar to open surgery and rates reported in the National Cancer Database, suggesting laparoscopic surgery is a safe and effective treatment for colon cancer.