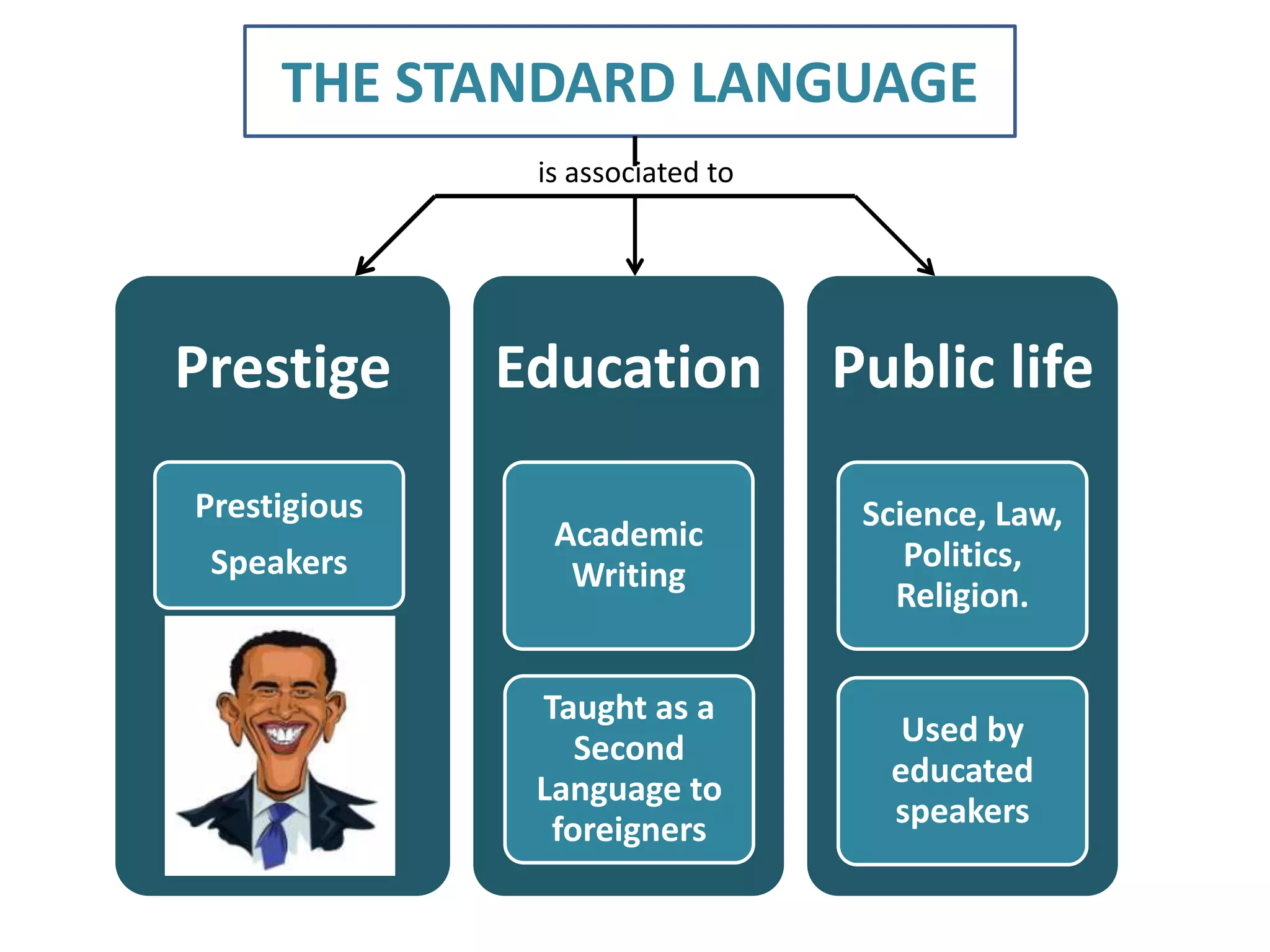
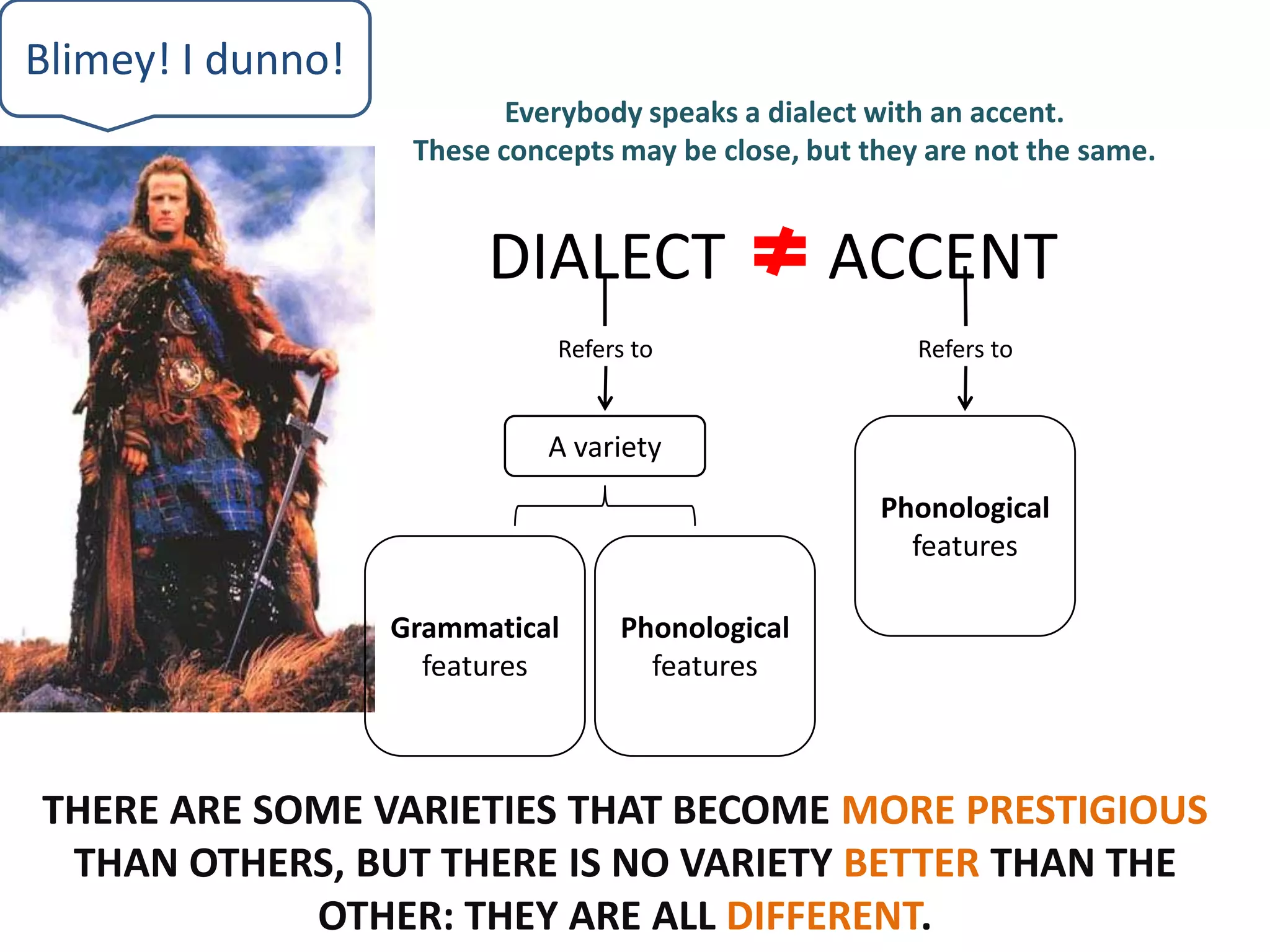
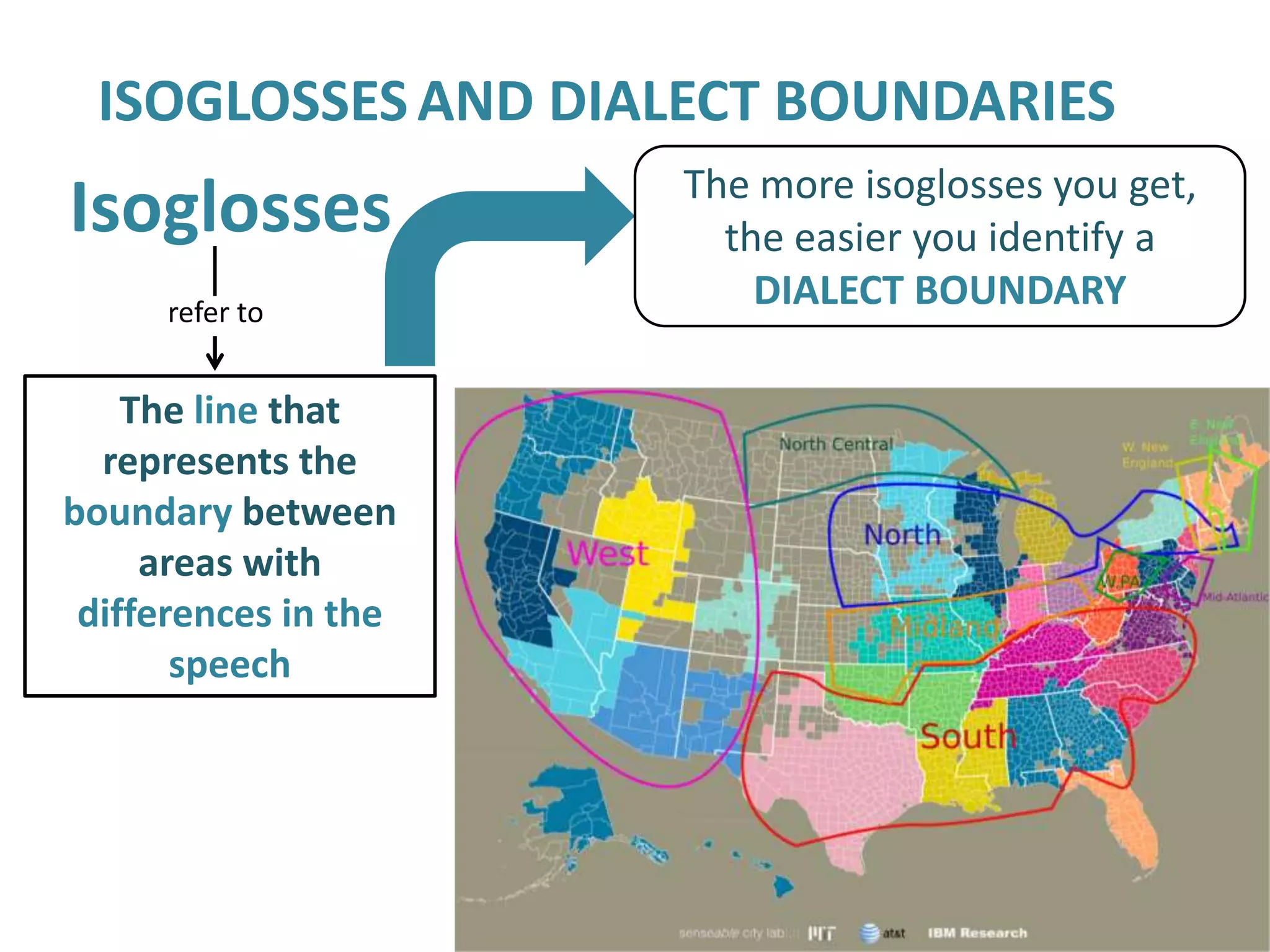
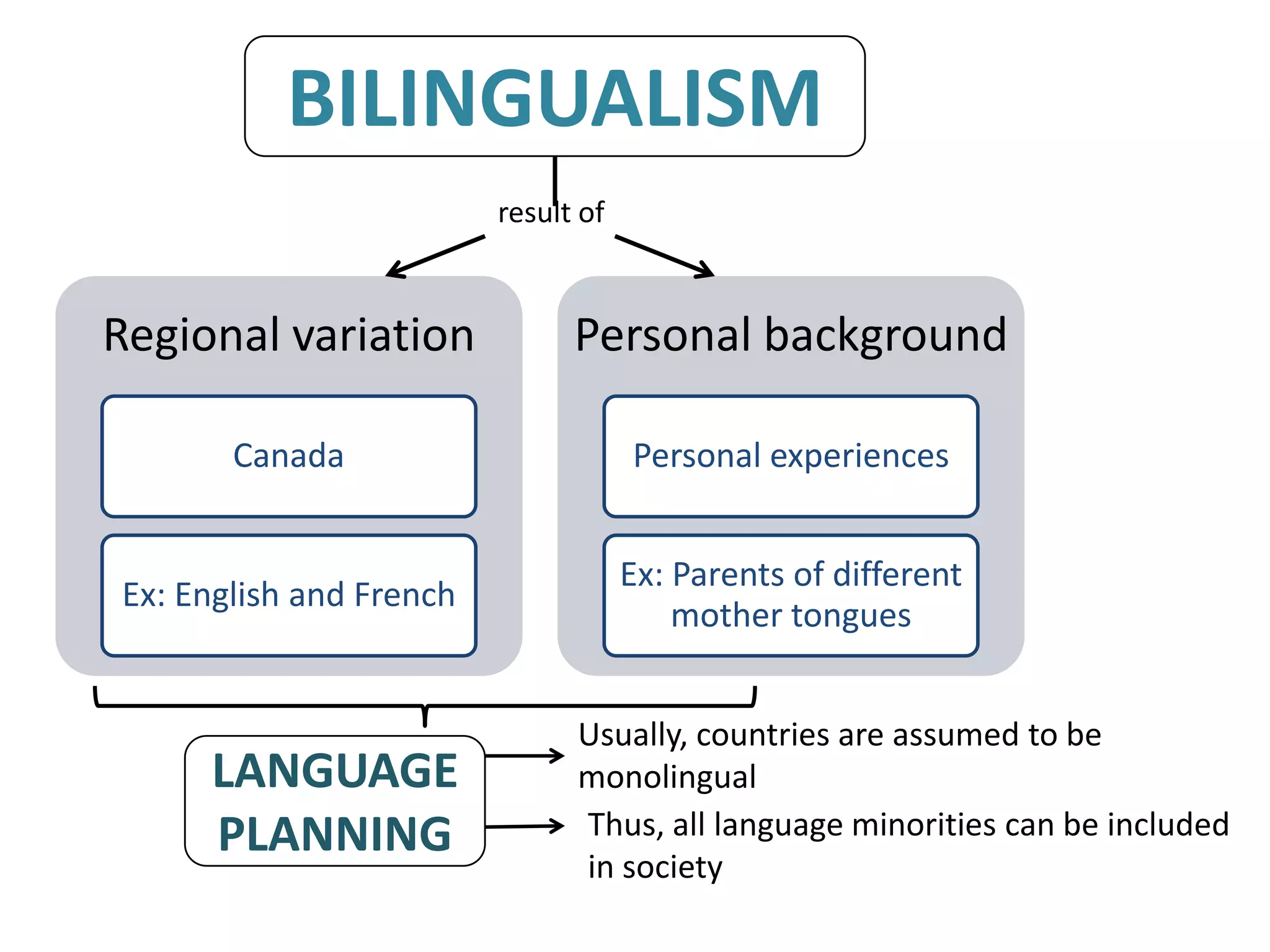
The standard language is associated with prestige, education, public life, science, law, politics, and religion. It is taught as a second language to foreigners and used by educated speakers. While there are some varieties that become more prestigious, no variety is inherently better than others - they are all different. Dialects refer to grammatical and phonological features that vary regionally and are known for stereotyped pronunciations. Isoglosses identify dialect boundaries by representing the line between areas with differing speech. A dialect continuum is a group of mutually intelligible dialects that differ more as geographic distance increases. Bilingualism can result from regional variation or personal background, while language planning often assumes countries are monolingual and includes all