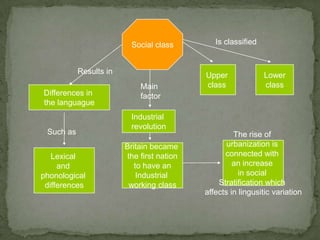
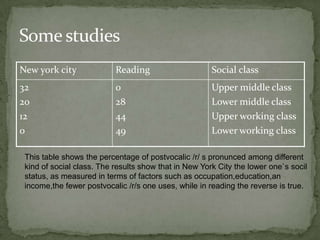
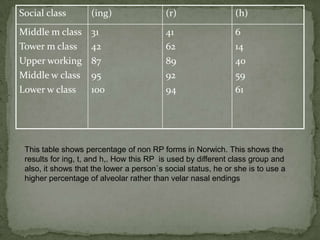
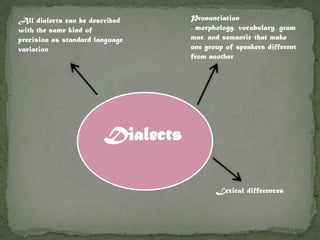
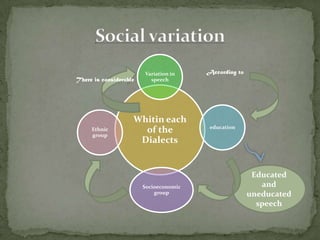
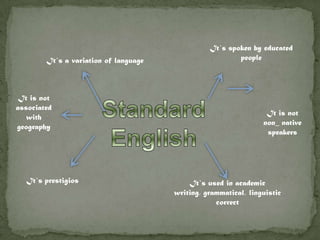
The document discusses how language is influenced by society and culture. It notes that language variation is influenced by both regional dialects and social factors like social class. The rise of the industrial revolution and urbanization in Britain increased social stratification and linguistic variation. Studies show differences in pronunciation patterns between social classes in cities like New York and Reading. Additional examples show variation according to age, gender, education level, and social network density. The process of standardizing a language converts a variety into a standard by fixing its spelling, grammar, etc. While standard languages are prestigious, all dialects can be systematically described.