The document discusses landmine detection using ground penetrating radar (GPR). It begins with background on the landmine problem and existing detection technologies. It then provides a block diagram of the impulse GPR system, describing the impulse generator, antenna system, pulse extender, A/D converter, processor, and visual display. The document discusses implementation of the impulse GPR system and its applications in fields like engineering and military demining. It notes advantages like accurate measurements and ability to detect non-metallic mines, as well as limitations like false alarms. Future work aims to improve detection probabilities and scan rates.







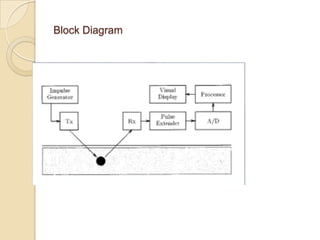







![Implementation:
> The impulse generator produces 0.8ns monocycle pulse.
> The generator spectrum covers a wide frequency band from 500MHZ on
3dB level.
> After striking the mine, pulses return and are received by the receiver
antenna.
[Cont..]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/landminedetectionusingimpulsegroundpenetratingradar-130402084311-phpapp02/85/Landmine-detection-using-impulse-ground-penetrating-radar-16-320.jpg)






