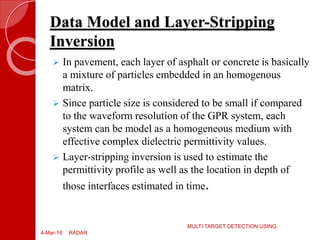
This document discusses high performance concrete and ground penetrating radar (GPR) technology. It provides an introduction to GPR, describing its components, working principle, data acquisition, and technology. It discusses GPR applications in pavement profiling, detecting multiple interfaces, and evaluating concrete. The advantages of GPR are its low cost, accuracy, speed, and ability to perform non-destructive testing. Limitations include similar dielectric properties complicating detection and thin layers being difficult to detect. In conclusion, GPR is a useful geophysical method for imaging the subsurface and detecting buried objects.



![Components of GPR
4-Mar-16
MULTI TARGET DETECTION USING
RADAR
1.Transmitting and receiving unit
2.Control unit
3.Display unit
4.Power supplies
Fig no.:-01, Process of GPR[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarppttemplate-160304122312/85/GROUND-PENETRATING-RADAR-GPR-ppt-4-320.jpg)
![GPR Working Principle
4-Mar-16
MULTI TARGET DETECTION USING
RADAR
Fig no.:-02,GPR working principle
[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarppttemplate-160304122312/85/GROUND-PENETRATING-RADAR-GPR-ppt-6-320.jpg)


![4-Mar-16
MULTI TARGET DETECTION USING
RADAR
Fig no.:-03,schematic diagram of a GPR
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarppttemplate-160304122312/85/GROUND-PENETRATING-RADAR-GPR-ppt-10-320.jpg)
![GPR Technology
4-Mar-16
MULTI TARGET DETECTION USING
RADAR
Fig no.:-04 ,GPR technology [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarppttemplate-160304122312/85/GROUND-PENETRATING-RADAR-GPR-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![GPR Technology(cont.)
4-Mar-16
MULTI TARGET DETECTION USING
RADAR
Air coupled antenna.
Ground coupled antenna.
Fig no.:-05,Air coupled antenna[5] Fig no.:-06,Ground coupled
antenna[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarppttemplate-160304122312/85/GROUND-PENETRATING-RADAR-GPR-ppt-12-320.jpg)