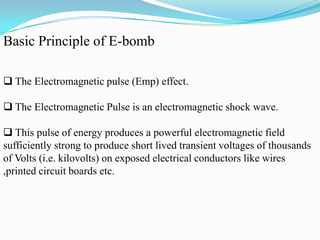
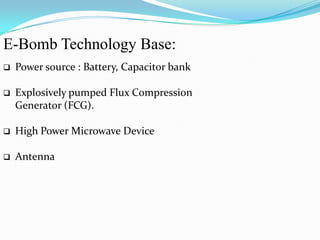
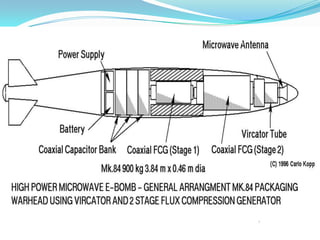
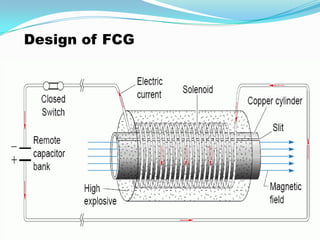
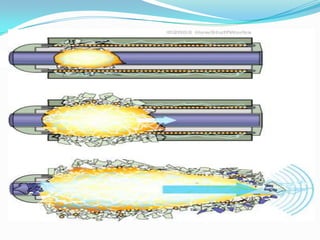
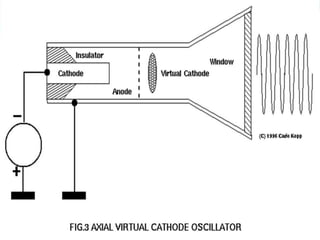
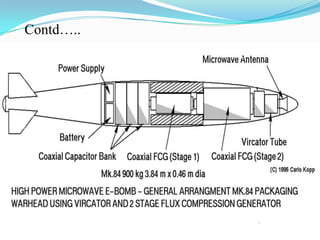
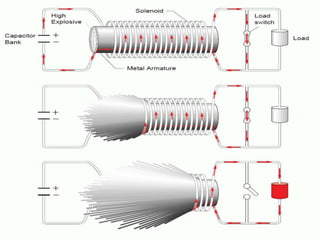
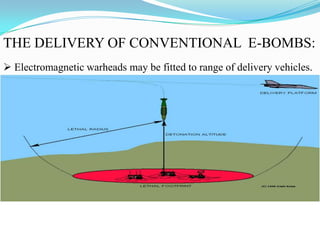
An electromagnetic bomb, or E-bomb, is a weapon that generates a powerful electromagnetic pulse capable of disabling electronics over a wide area without harming people. It works by using an explosively-pumped flux compression generator or high power microwave device to generate an intense electromagnetic burst. This electromagnetic pulse induces damaging voltages in exposed wiring and circuitry. While an E-bomb could knock out power grids and communication systems across an entire coast, it has limitations in accuracy and risks harming medical equipment. There is ongoing research focused on developing more advanced E-bomb technologies and defenses against electromagnetic weapons.



















![REFERENCES
[1]. Abrams, Michael, “ Dawn of The E-bomb”, IEEE
spectrum, November 2003.
[2]. Kopp, C., “A doctrine for the use of electromagnetic pulse
bombs”, Air Power Studies Centre, Paper No. 15, 1993.
[3]. Kopp, C., “ An introduction to the technical and operational
aspects of the electromagnetic bomb”, Air Power Studies
Centre, Paper No.-50,19
[5] E-Bomb – FAQ by Carlo Kopp (2012)
http://www.ausairpower.net/E-Bomb-FAQ.html
[6] How E-Bombs Work by Tom Harris
http://science.howstuffworks.com/e-bomb.htm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-bomb-140330005445-phpapp02/85/E-bomb-29-320.jpg)

