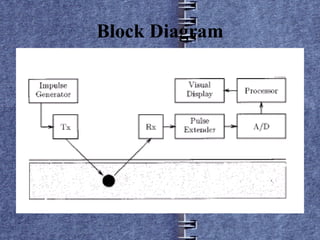
The document discusses landmine detection using ground penetrating radar (GPR). It provides background on the landmine problem, current detection methods, and how GPR works to detect landmines. GPR transmits electromagnetic pulses into the ground and receives reflected signals that can reveal the presence of landmines. While GPR shows promise for landmine detection, challenges remain around generating false alarms from background signals and the size and power needs of GPR systems.