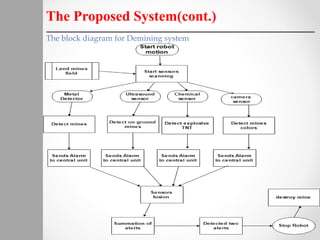
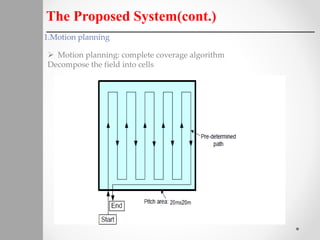
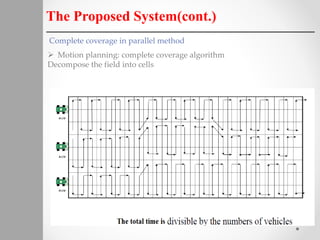
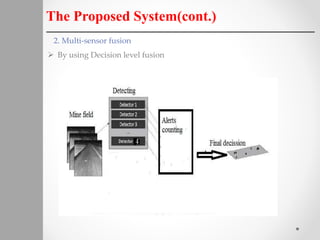
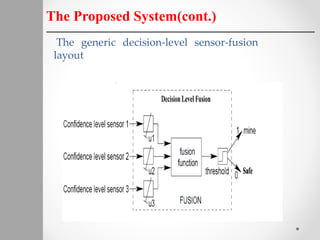
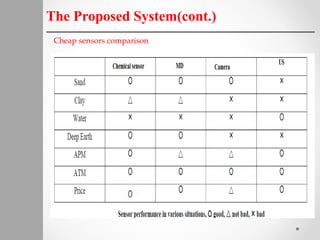
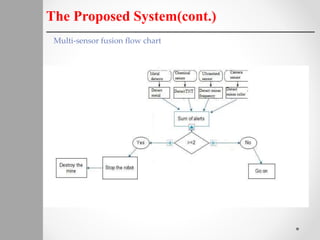
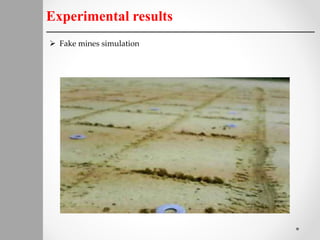
The document describes a proposed system for detecting landmines using mobile robots. The system involves designing an autonomous, low-cost mobile robot that uses effective motion planning and multi-sensor fusion to detect landmines. Experimental results show that the robot is able to autonomously detect fake mines in a simulated environment using multiple low-cost sensors, with decreased false alarms compared to using a single sensor. The system aims to provide a low-cost solution to landmine detection that ensures safety for human operators.












![Related Work
Akhtar [2012] Used GPR to captures an image in real-
time.
• Fed into a processing unit where smaller segments of
it, analyzed after being processed for noise reduction.
• Then recognized and classified landmines with
success rate 90%
• This scheme has some drawbacks:
• The sensor such as GPR is larger and heavier.
• GPR is more power hungry.
• GPR can suffer falls alarm rates as high as metal detectors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-160507105723/85/Landmines-Detection-by-Robots-presentation-14-320.jpg)
![Related Work (cont.)
Ghribi et al. [2013] developed a cheap
wheeled robot that could detect only metal
mines.
The robot mounted on a metal detector to
detect mines.
The system used to color paint to mark the
position of detected mines. This scheme has
some drawbacks:
high false alarms due to metal objects in the
soil.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-160507105723/85/Landmines-Detection-by-Robots-presentation-15-320.jpg)
![Related Work (cont.)
Garcia et al [2002] proposed awaking robot for
detecting and locating antipersonnel landmines,
consisted of: ahead with detector, locator with GPS.
• The robot was controlled remotely
• There is some drawback in their scheme, such as
High cost
The robot can be triggered
False alarms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-160507105723/85/Landmines-Detection-by-Robots-presentation-16-320.jpg)