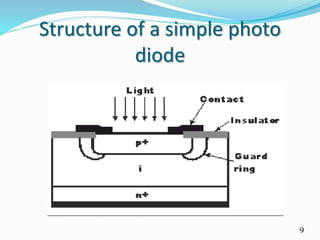
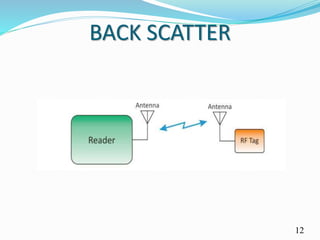
This document discusses a batteryless phone prototype that was developed by researchers. The phone is able to operate without a battery by harvesting energy from ambient light and radio frequency signals using a small photo diode. It converts the harvested light and RF energy into direct current power that allows the phone to perform basic calling functions. While this prototype demonstrates the potential of batteryless phones, their range is currently limited and they lack many features of traditional smartphones. Researchers hope to expand the technology to add capabilities like encryption, video streaming, and internet access in the future.