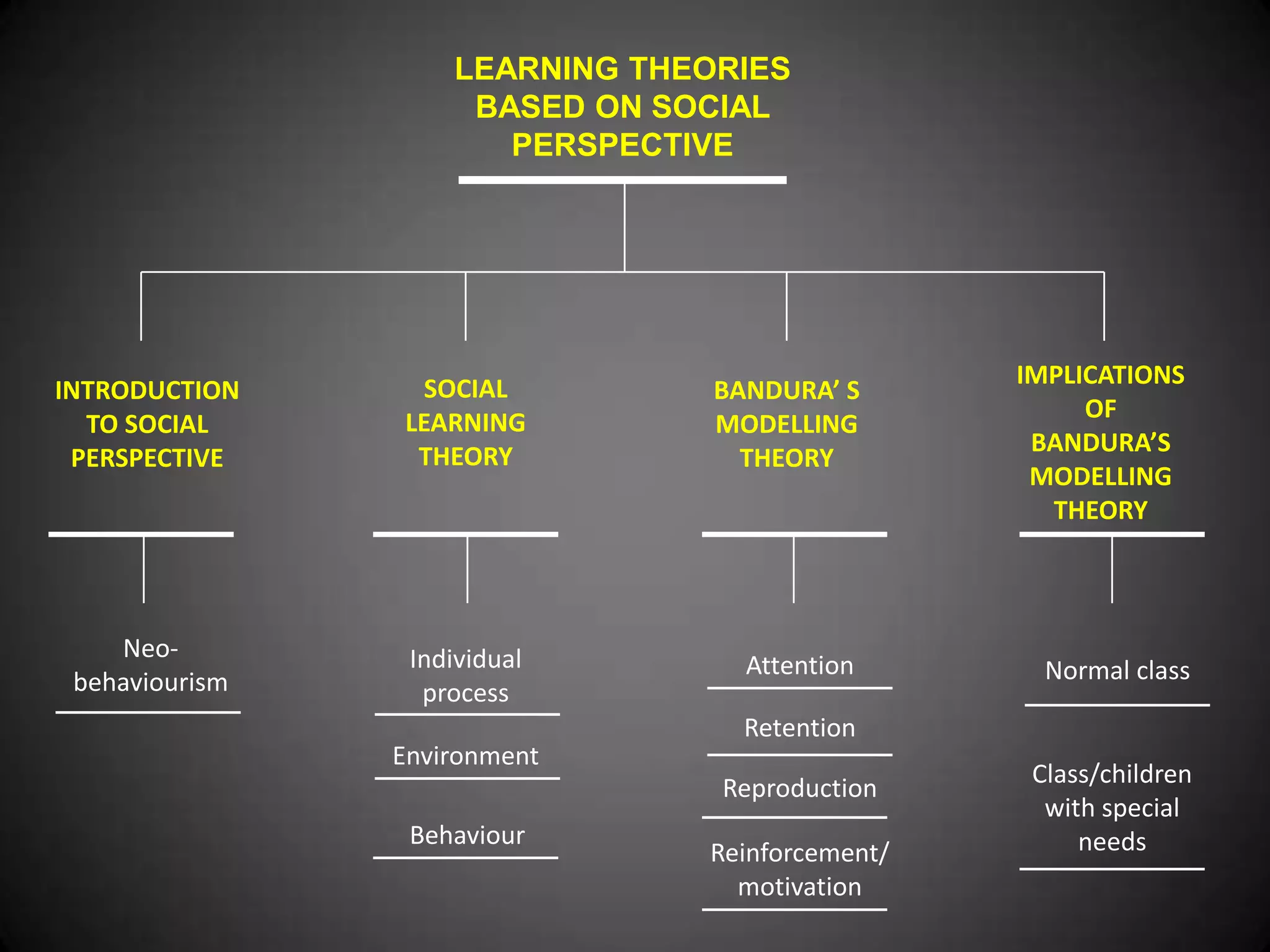
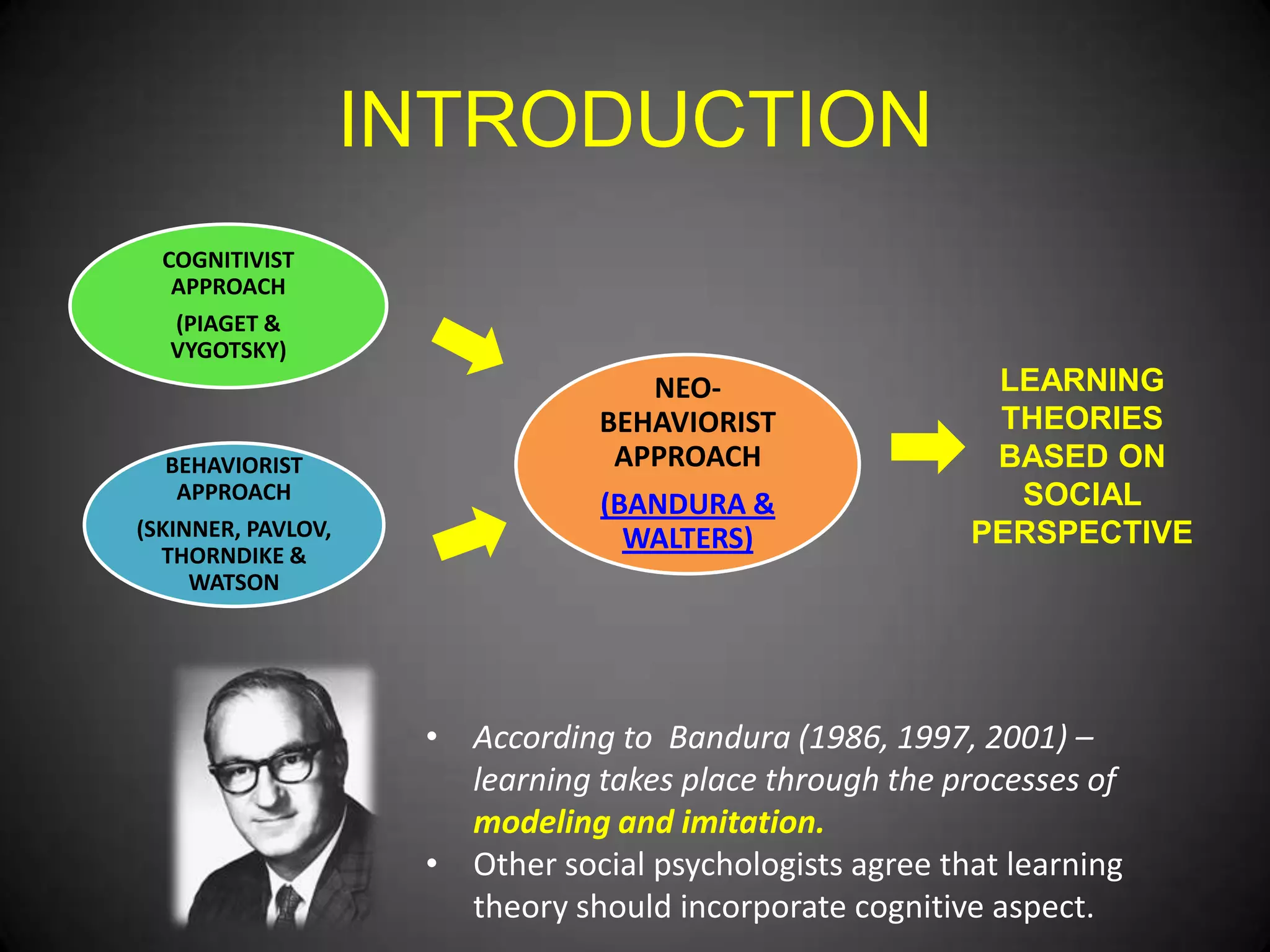
This document discusses learning theories based on social perspectives. It covers several topics:
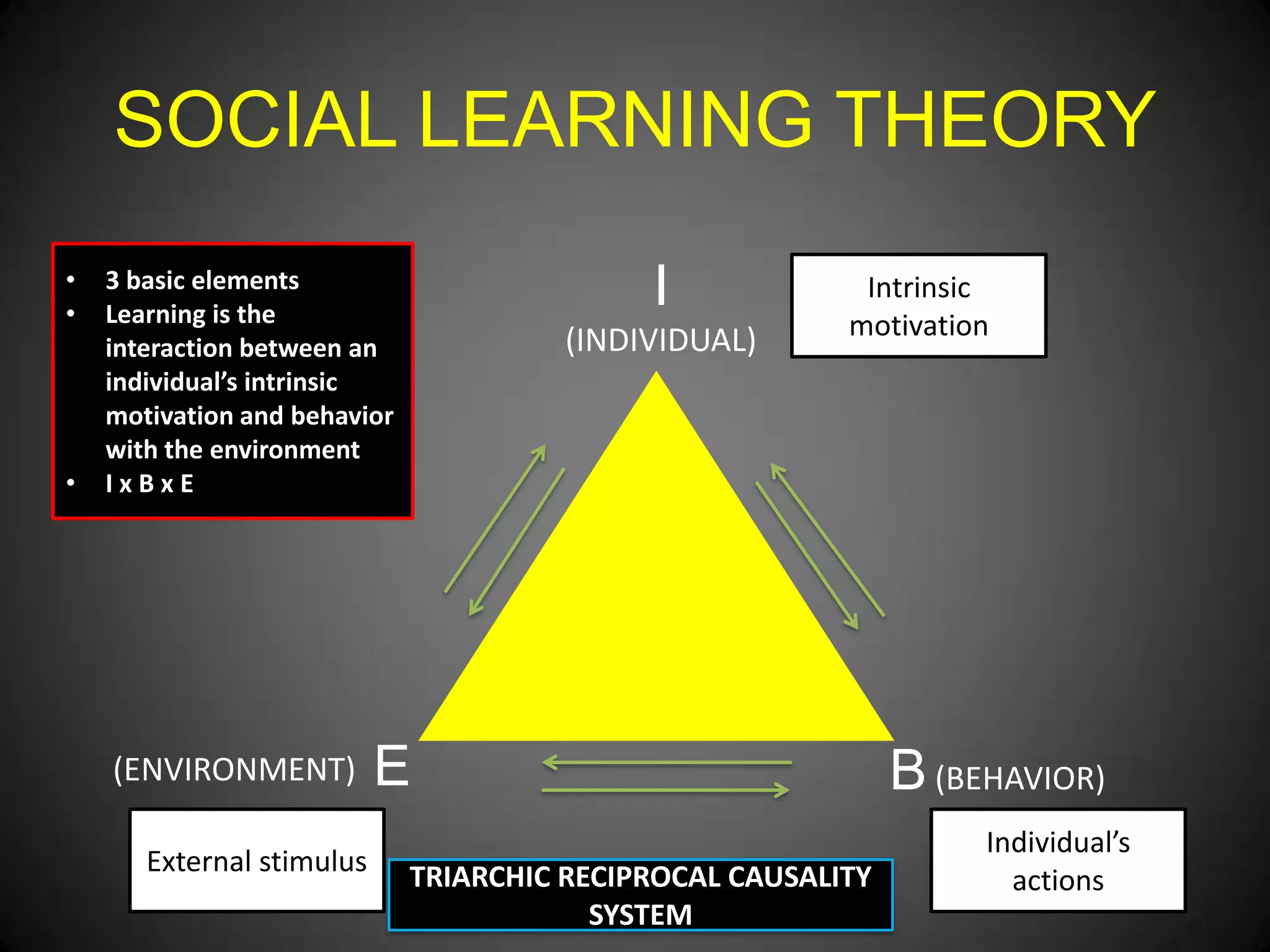
- Social learning theory which posits that learning occurs through interactions between individuals, behaviors, and the environment.
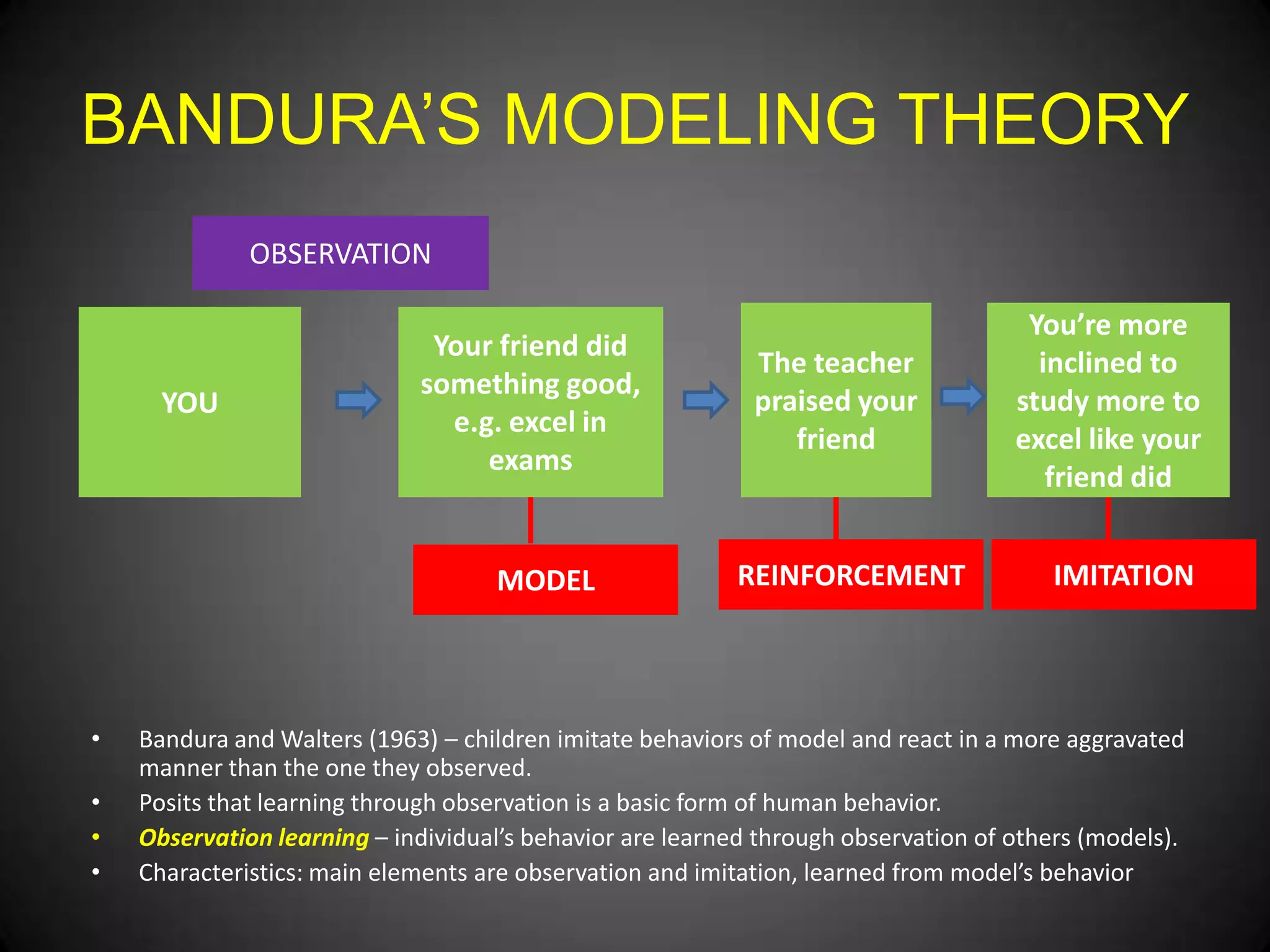
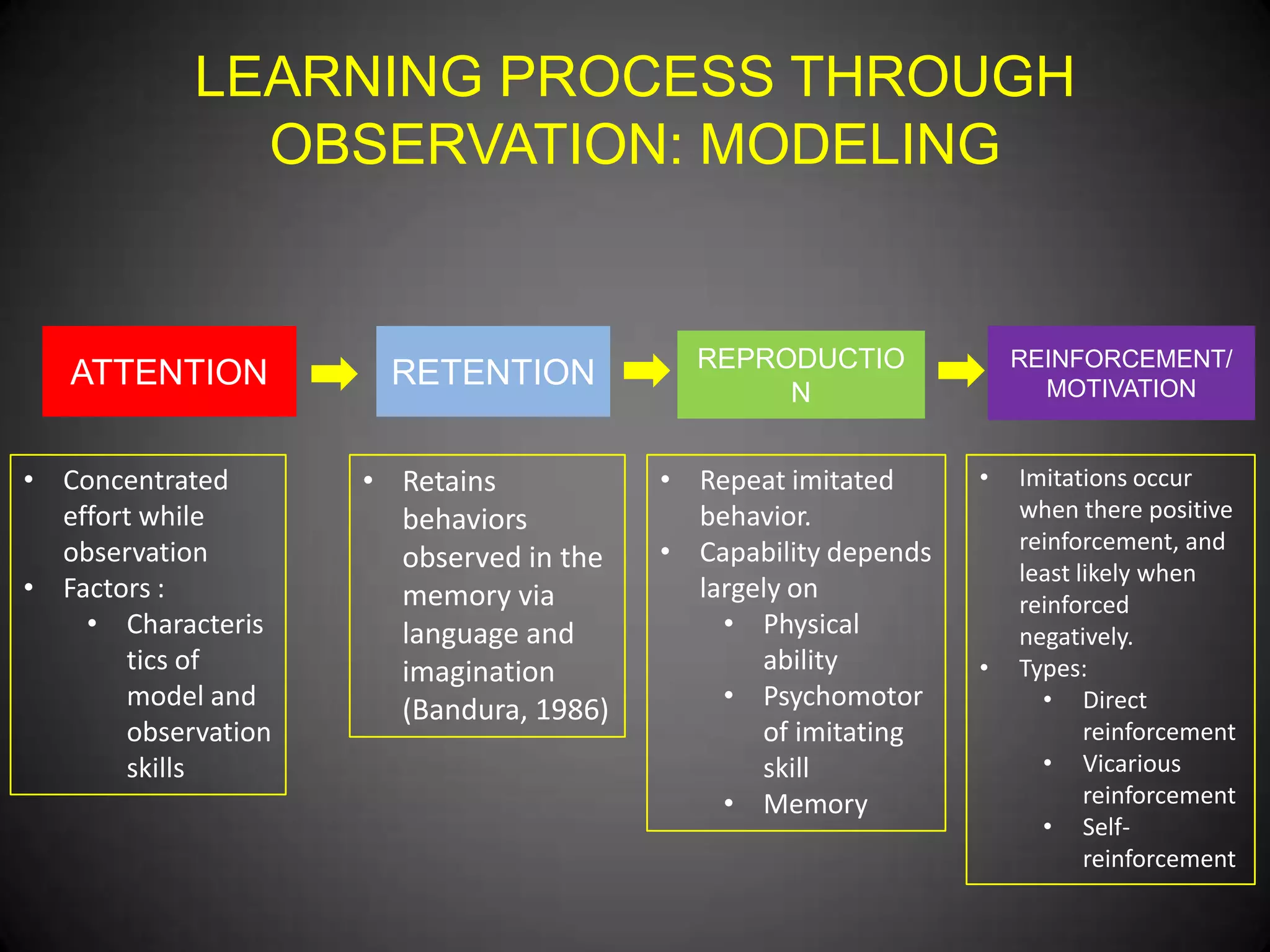
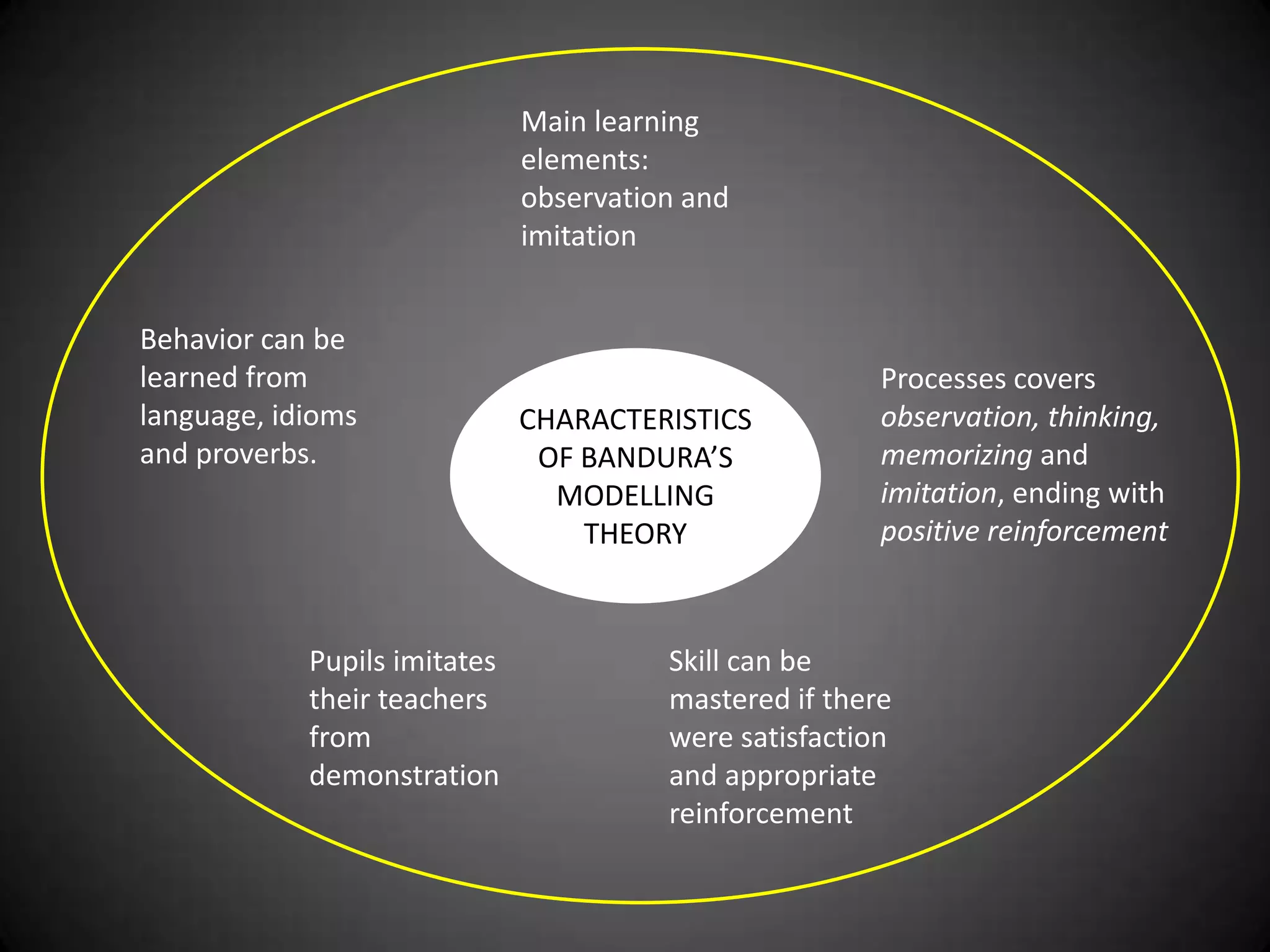
- Bandura's modeling theory which states that learning happens through observation and imitation of models. This includes attention, retention, reproduction, and reinforcement.
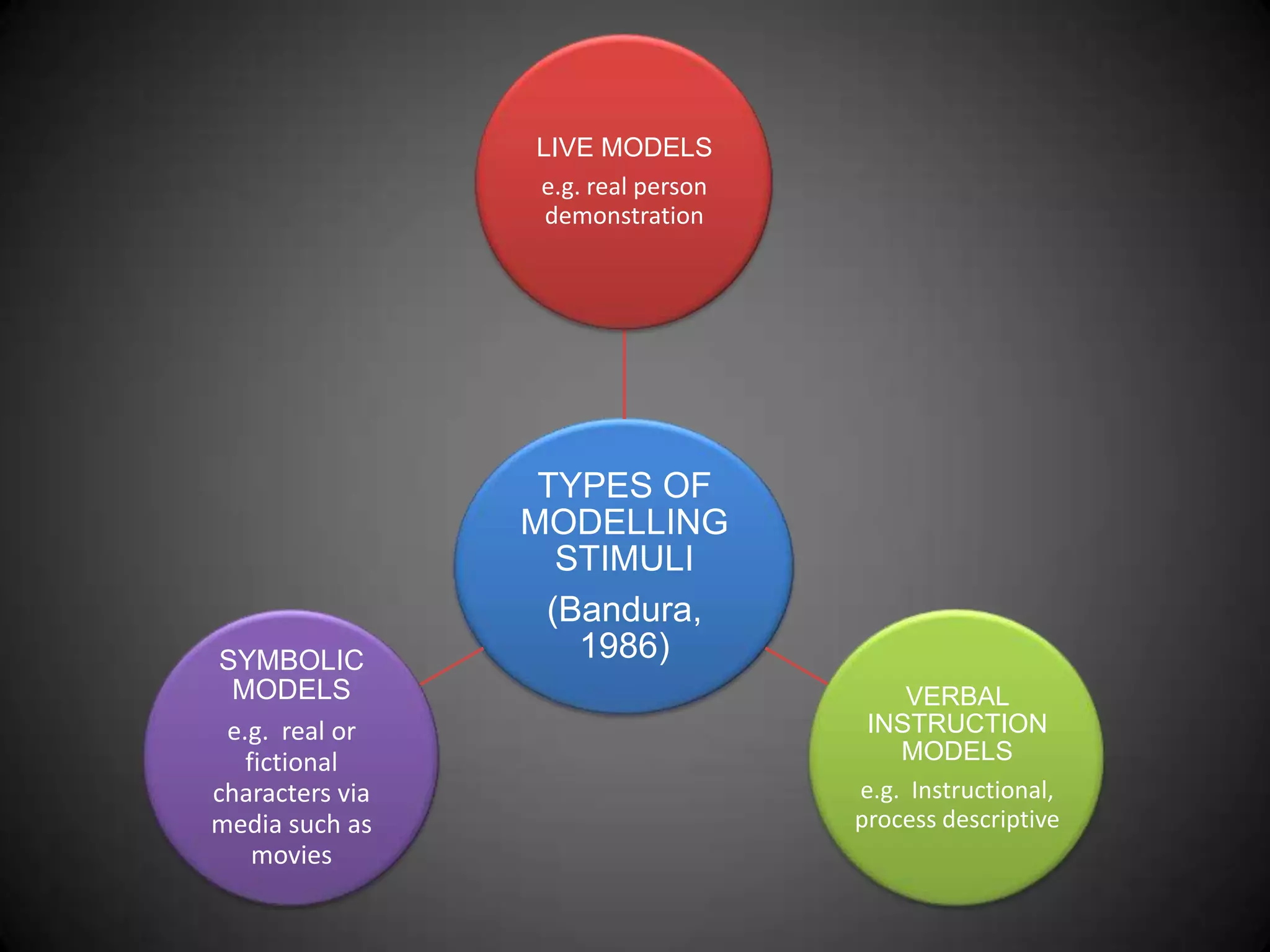
- Types of modeling stimuli like live models, symbolic models, and verbal instruction models.
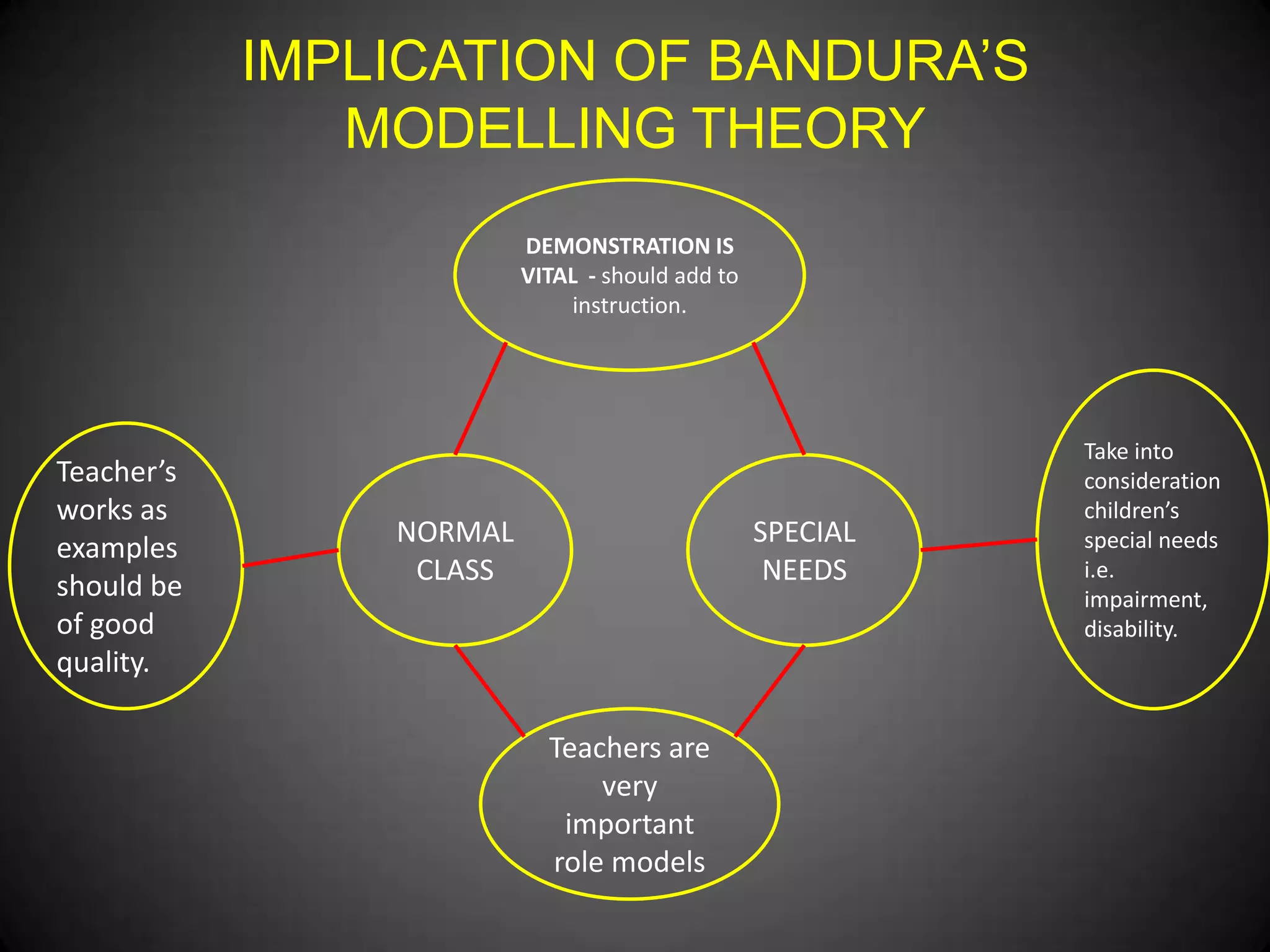
- The implications of Bandura's modeling theory for teaching practices, including the importance of teacher demonstration and considering students' individual needs.