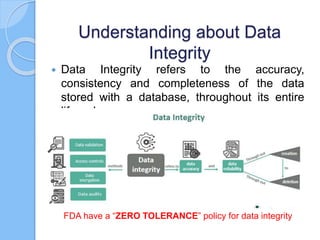
The document outlines essential concepts of data integrity, including definitions, principles, governance, and key steps for ensuring data quality and compliance in various domains. It highlights the importance of data integrity in maintaining quality, efficiency, compliance, and trust while detailing causes and consequences of data breaches, along with prevention strategies. Additionally, real-world examples of regulatory actions against companies for data integrity violations emphasize the critical nature of adherence to standards in pharmaceutical development.