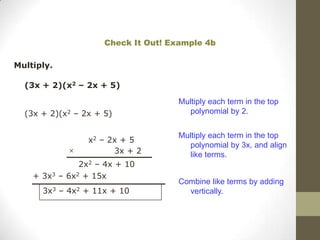
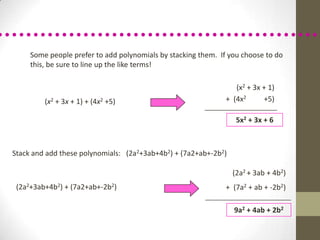
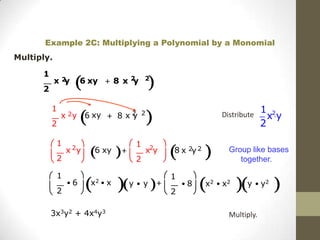
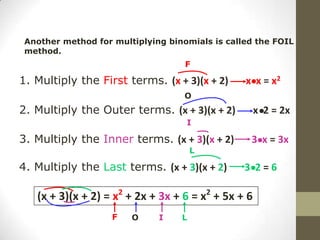
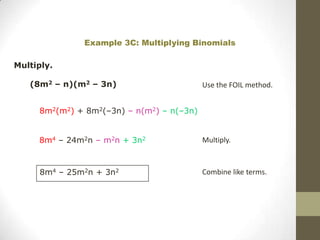
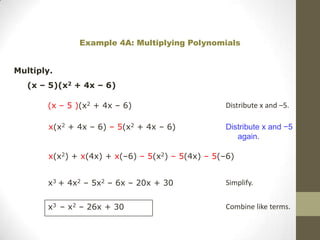
To multiply polynomials, you can use the distributive property and properties of exponents. When multiplying monomials, group terms with the same bases and add their exponents. When multiplying binomials, use FOIL or distribute one binomial over the other. For polynomials with more than two terms, you can distribute or use a rectangle model to systematically multiply each term.
































 Write as the product of three
binomials.
[x(x+3) + 3(x+3)](x + 3) Use the FOIL method on the
first two factors.
(x2 + 3x + 3x + 9)(x + 3) Multiply.
(x2 + 6x + 9)(x + 3) Combine like terms.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2operationsonpolynomials-121028022010-phpapp02/85/Operations-on-Polynomials-38-320.jpg)