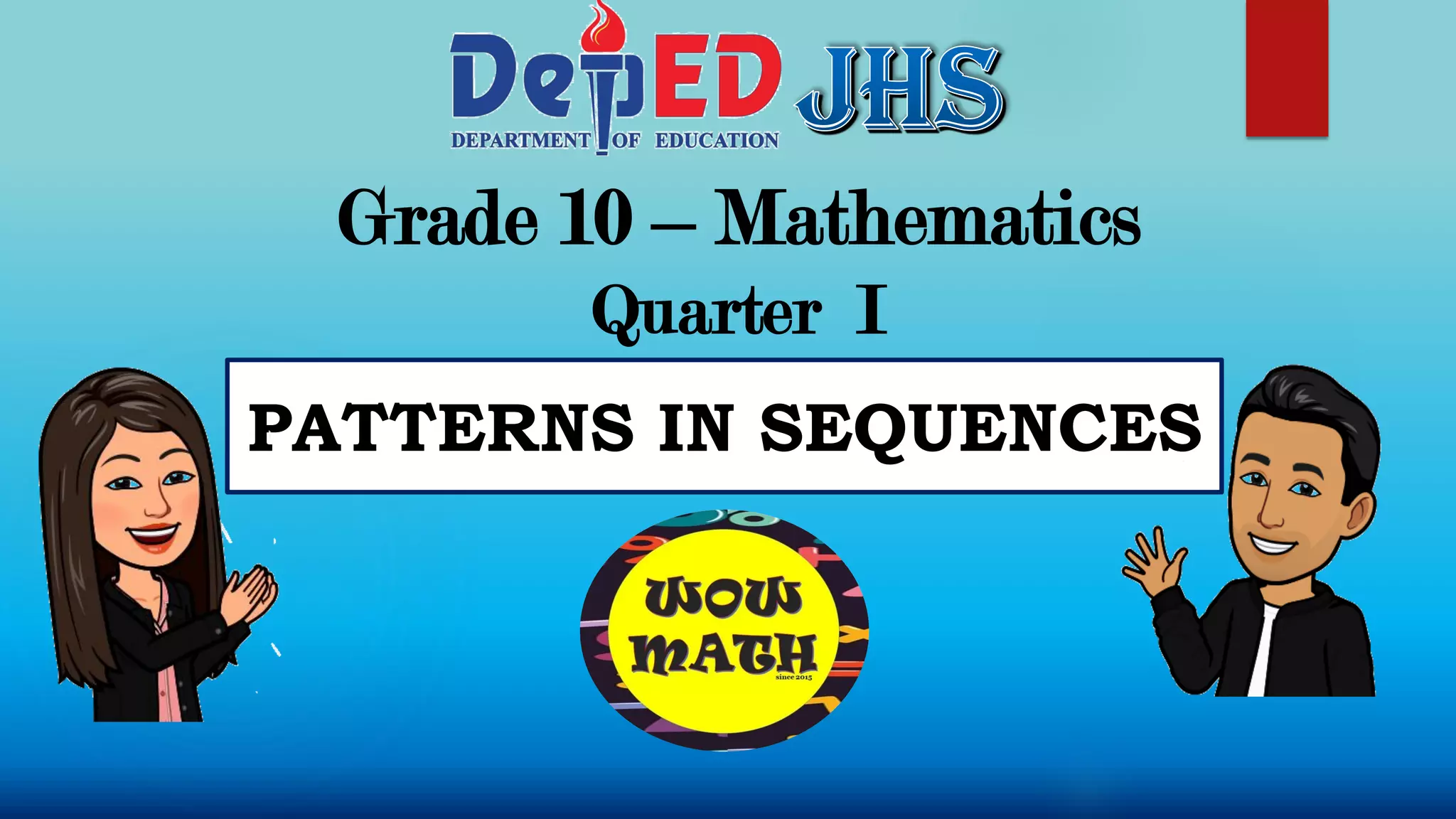
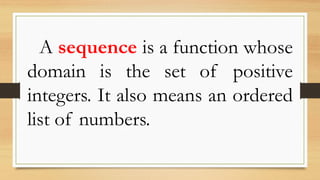
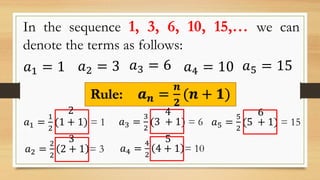
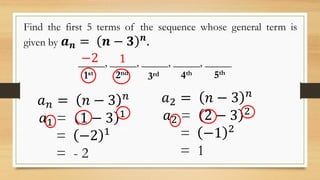
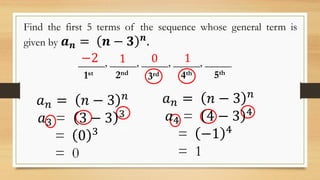
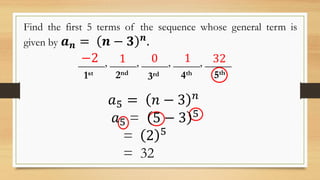
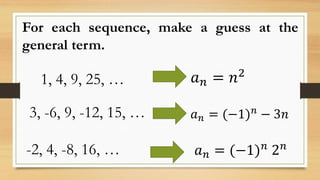
The document outlines objectives for a Grade 10 mathematics lesson on sequences, focusing on defining the terms and finding mathematical expressions. It provides activities to identify terms in various sequences and derives rules for generating them. The content includes examples of finite and infinite sequences, along with exercises for determining specific terms based on general formulas.