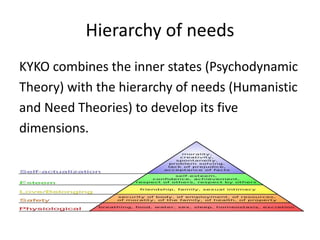
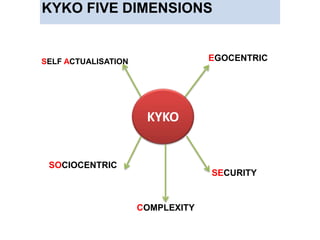
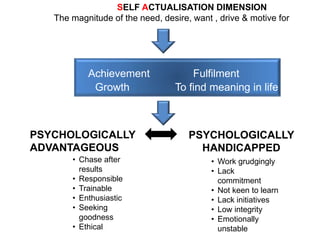
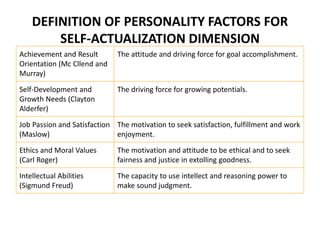
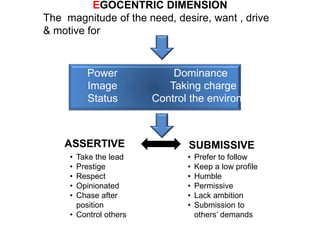
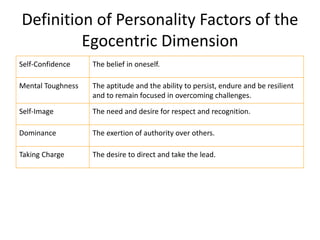
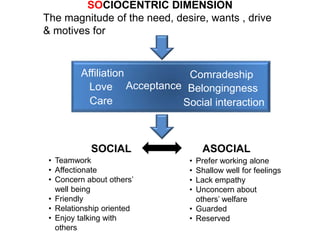
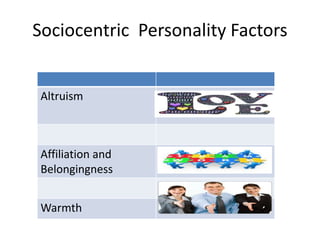
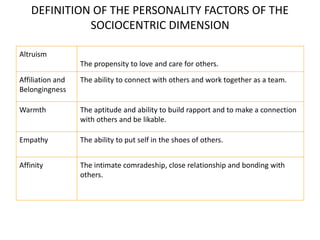
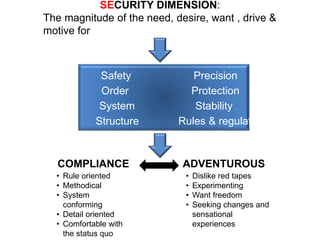
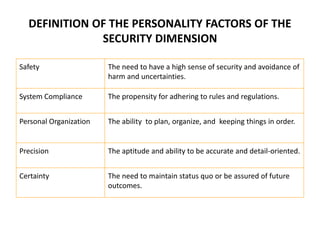
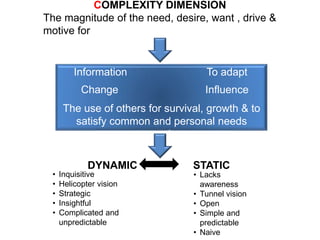
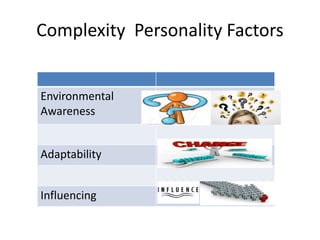
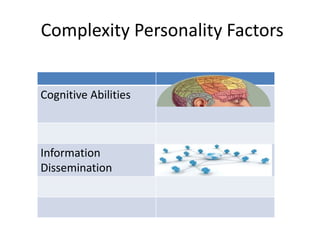
KYKO is an integrated personality profile model that combines six major schools of personality theory - psychodynamic, behaviorism, humanism, cognitive, biological, and trait theories. It uses premises and concepts from these theories to develop a comprehensive model with five dimensions: self-actualization, egocentric, sociocentric, security, and complexity. The goal is to predict human differences by taking a broader, more inclusive view than models based on only one or two theories.