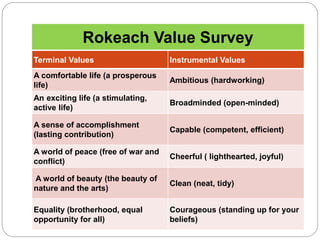
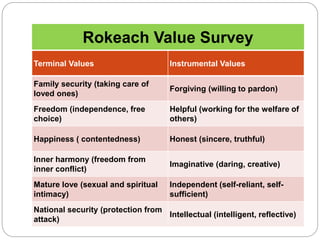
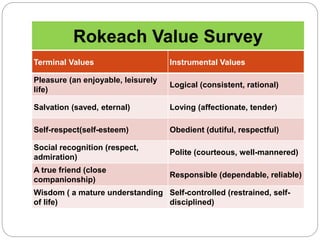
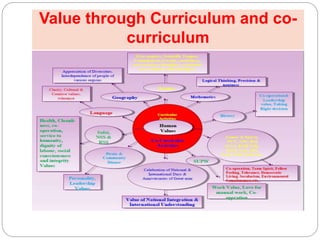
The document discusses the importance of inculcating values in students, defining values as principles that enhance the quality of life and guide behavior. It outlines the different types of values, their sources, and the crises surrounding declining values in society, emphasizing the need for educational institutions to foster a stronger sense of morality and social responsibility. Various strategies for value inculcation are suggested, including club activities, community service, and the role of teachers as role models.