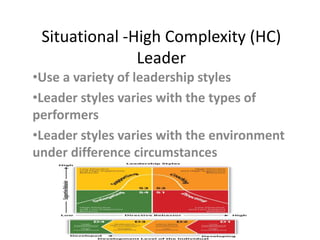
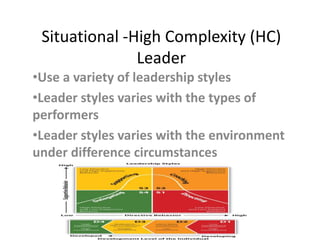
The document discusses different leadership styles including achievement-oriented, autocratic, bureaucratic, democratic, laissez-faire, servant, situational, transactional, and transformational. Each style has pros and cons depending on the situation and type of followers. An effective leader adapts their style to the specific people and circumstances rather than relying on only one rigid approach.