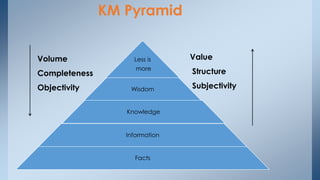
This document discusses knowledge management (KM). It defines KM as efforts to increase useful knowledge within an organization, such as by encouraging communication and knowledge sharing. The document outlines different types of knowledge, KM processes, tools and technologies used by Ford, advantages of KM, and barriers to effective KM like lack of top management commitment, technological infrastructure, and organizational culture that supports knowledge sharing. It presents an interpretive structural modeling analysis of the relationships between various KM barriers.