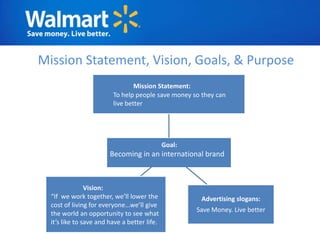
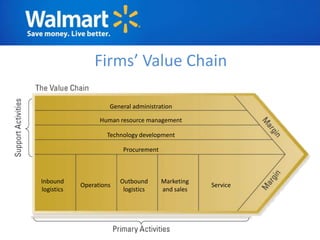
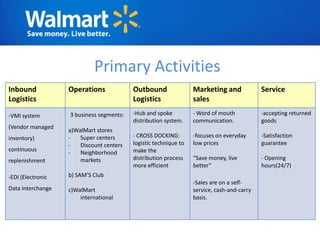
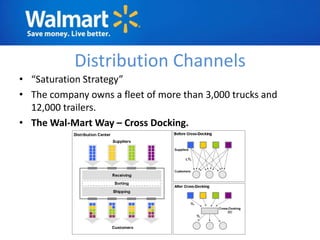
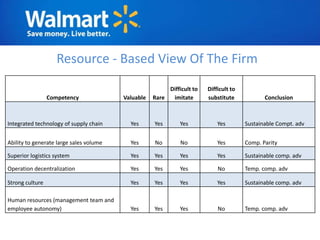
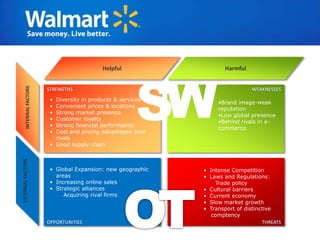
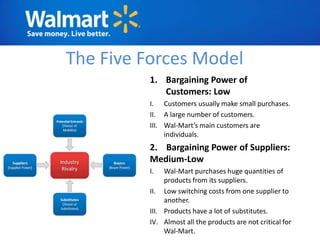
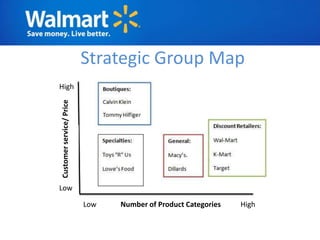
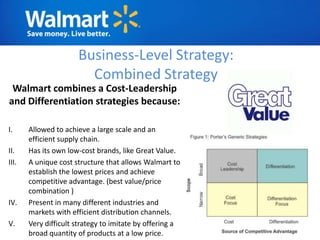
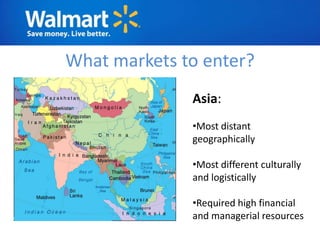
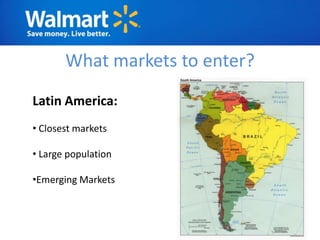
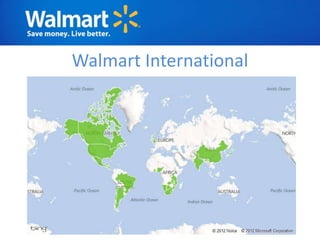
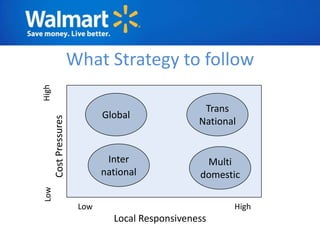
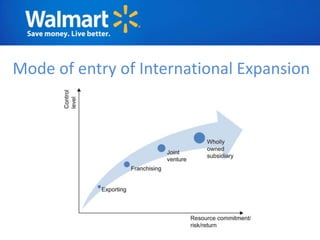
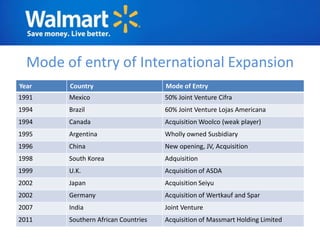
The document provides an overview of Walmart's history, operations, strategies for international expansion, and lessons learned. It discusses Walmart's vision, mission, and goals, as well as its business model, value chain, and key competitive advantages. Regarding internationalization, the document examines Walmart's reasons for expanding abroad, entry decisions, examples of success in Mexico and Canada, and failures in Germany and India. Overall, the document analyzes Walmart's path to becoming a global retailer and identifies factors for successful international transfer of core competencies.