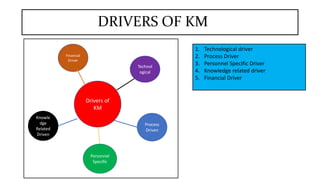
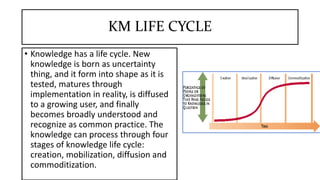
This document discusses drivers, challenges, tools, and lifecycle of knowledge management. It identifies the main drivers as technological, process-related, personnel-specific, knowledge-related, and financial. The key challenges are convincing organizations and employees of knowledge management's value, capturing and processing knowledge, addressing collaboration, ongoing research, and dealing with tacit knowledge. Common tools include internet/intranets, videoconferencing, knowledge sharing, knowledge centers, and cross-departmental teams. Finally, it describes knowledge lifecycle as moving from creation to mobilization, diffusion, and commoditization.