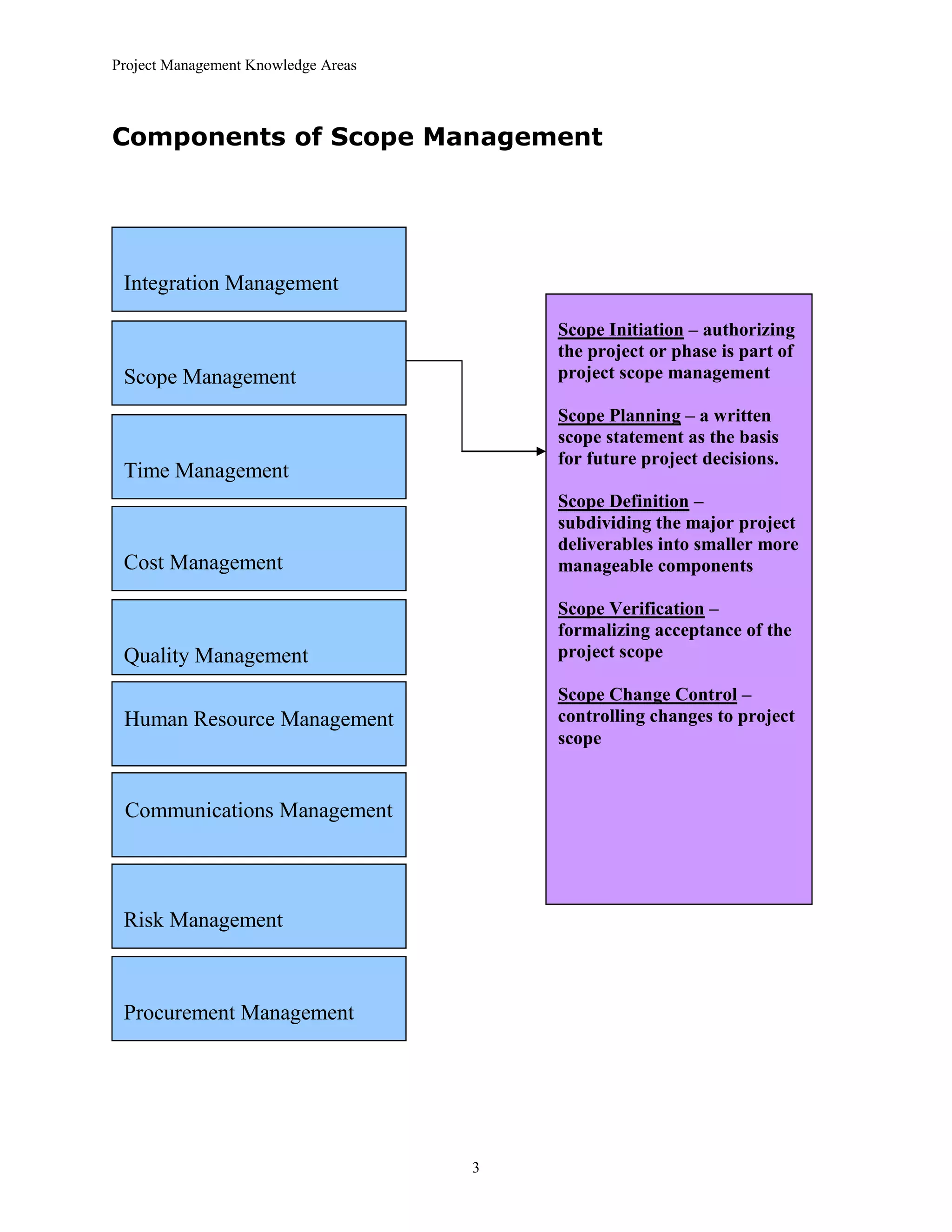
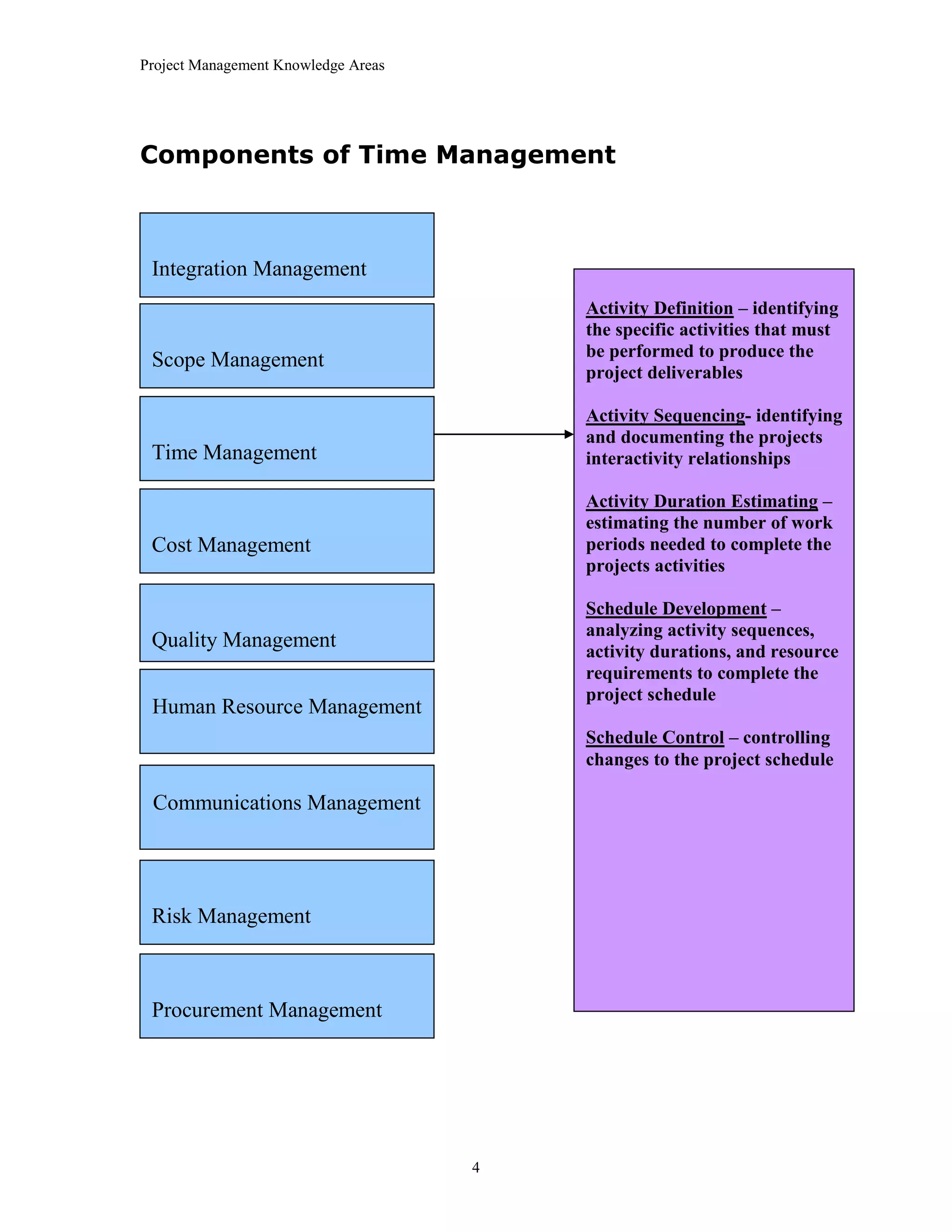
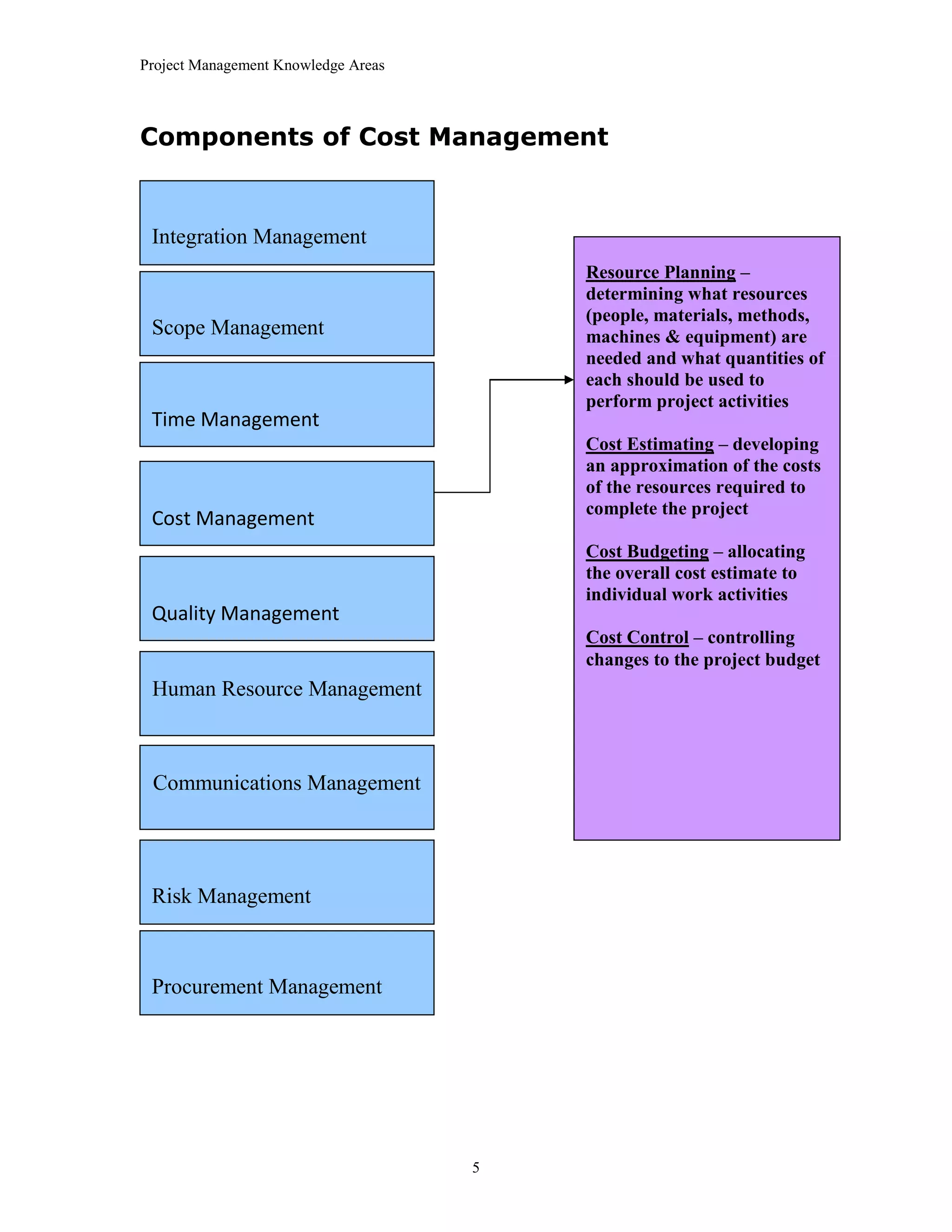
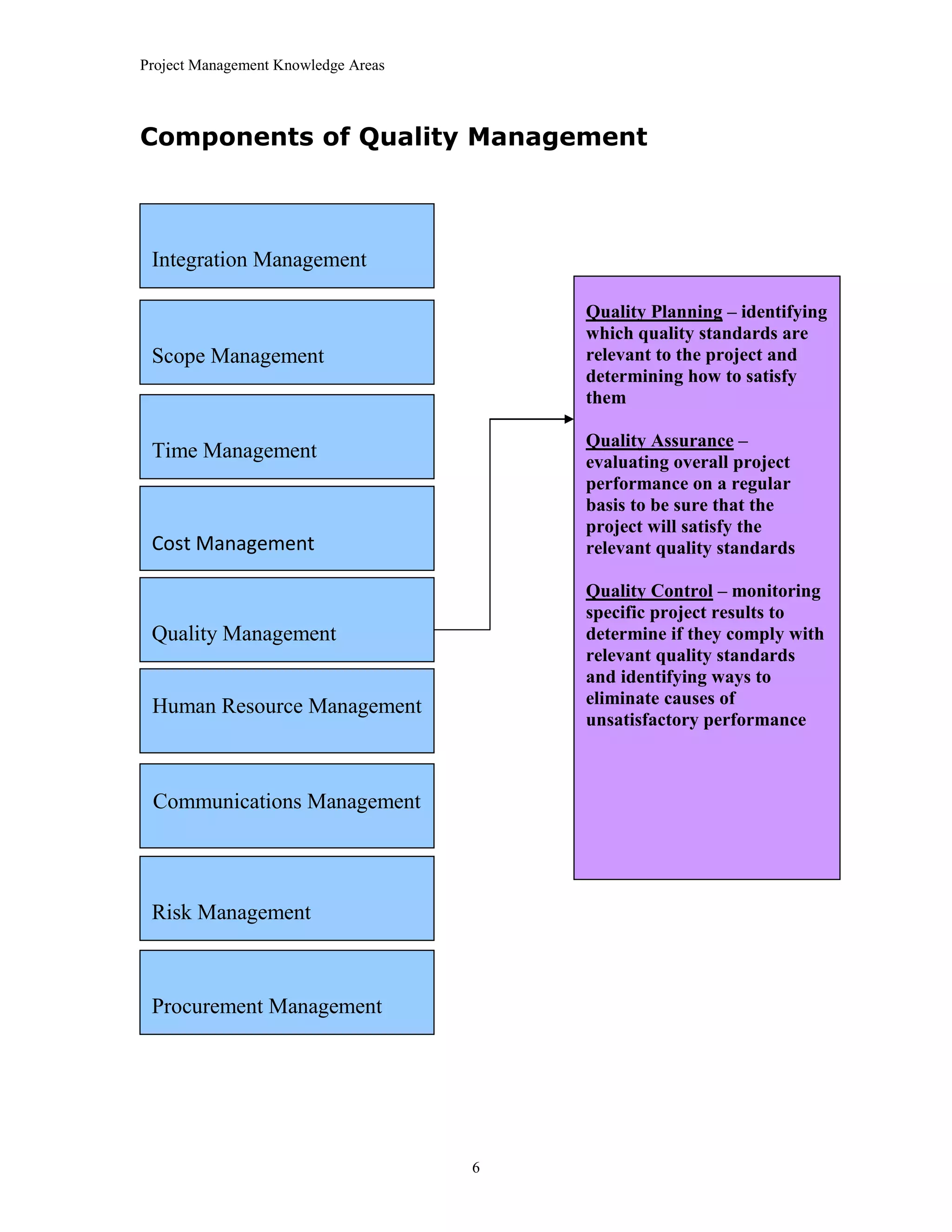
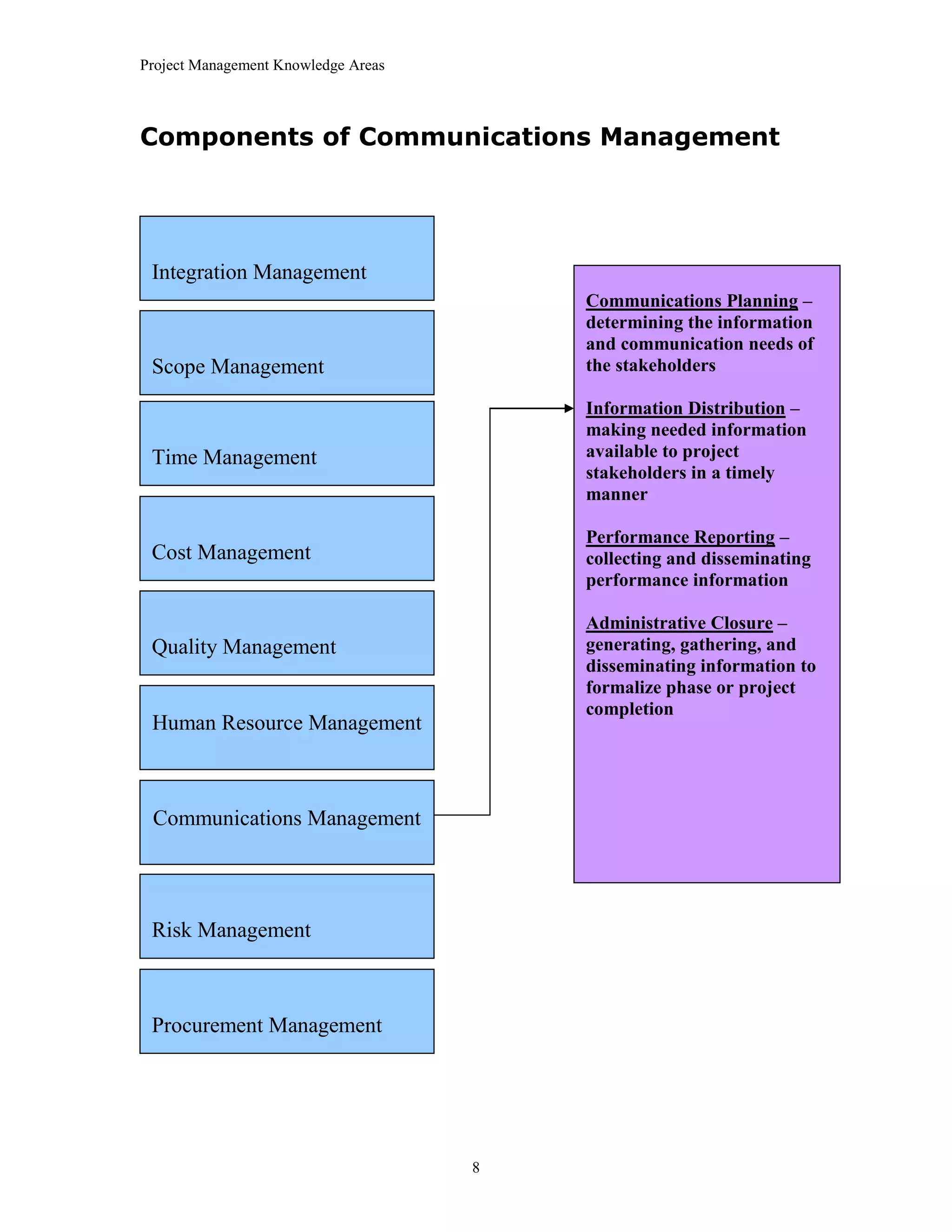
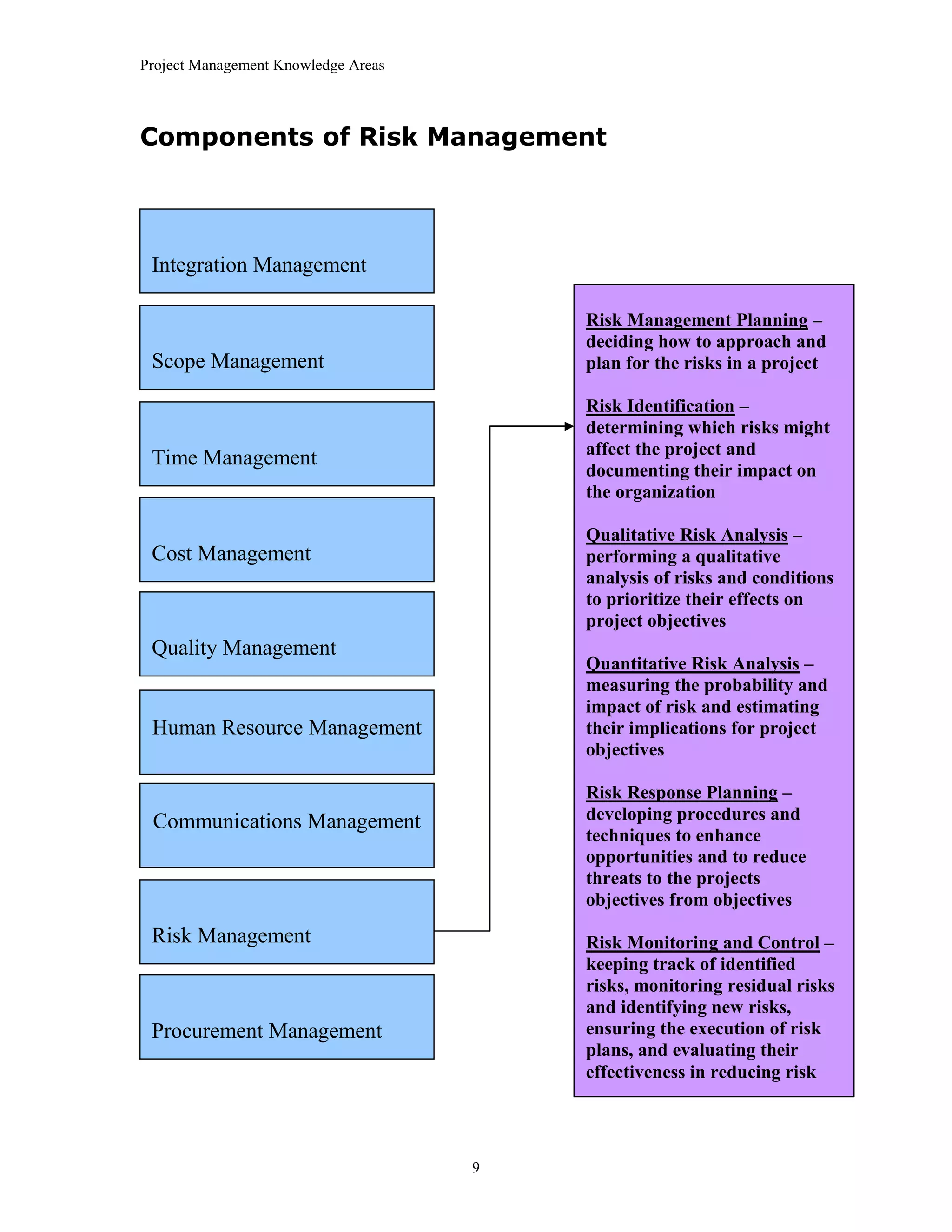
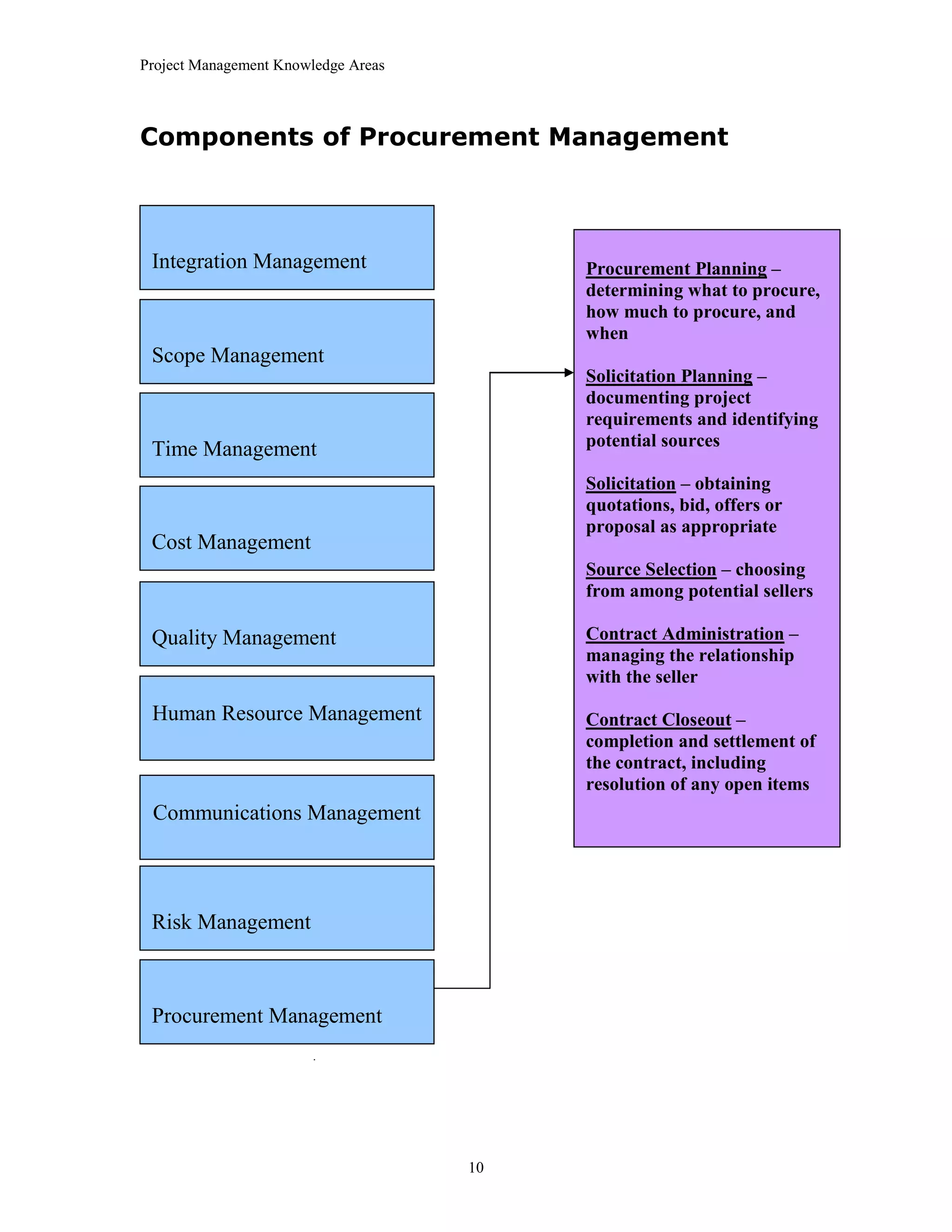
The document outlines the 10 project management knowledge areas as defined by PMI, including integration management, scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, human resource management, communications management, risk management, and procurement management. For each knowledge area, the key components and processes involved are summarized.