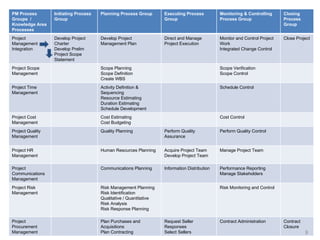
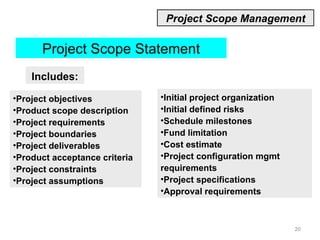
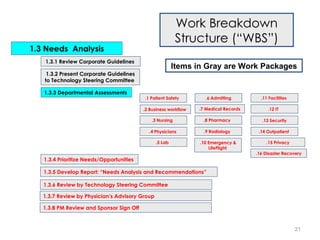
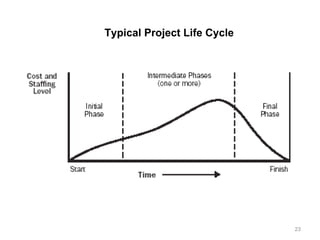
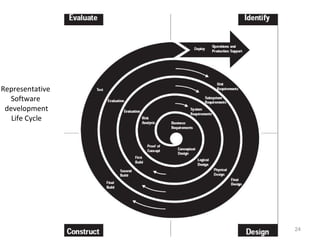
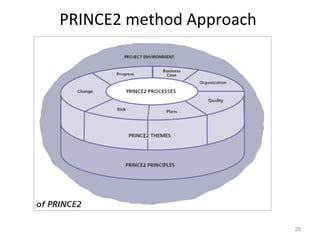
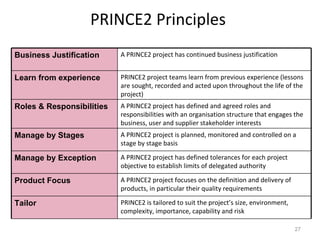
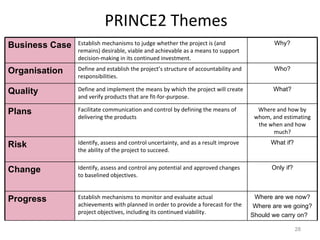
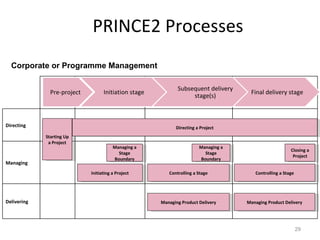
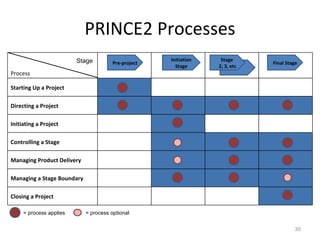
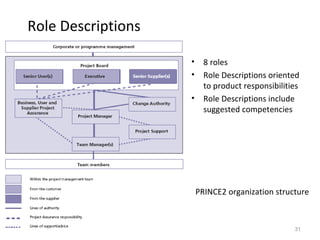
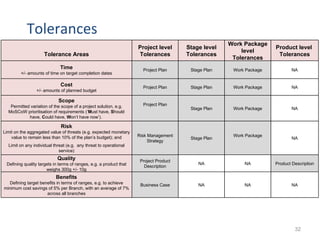
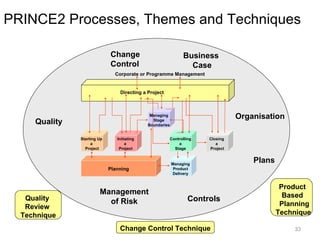
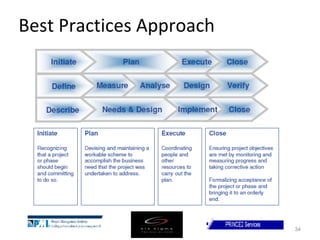
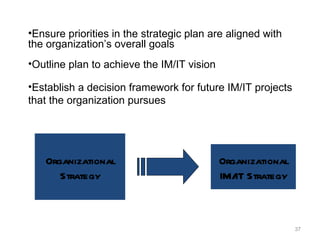
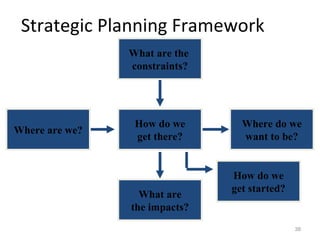
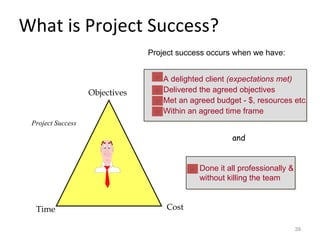
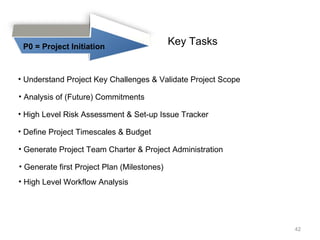
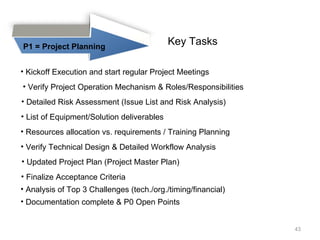
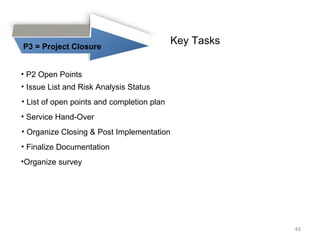
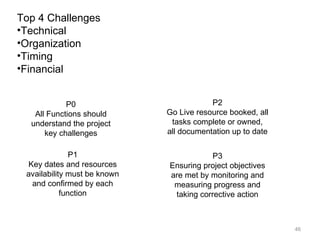
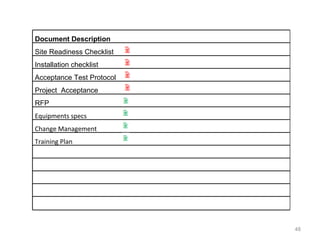
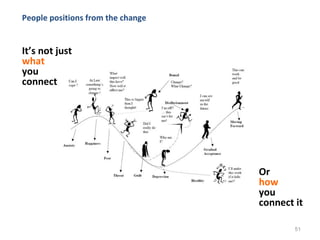
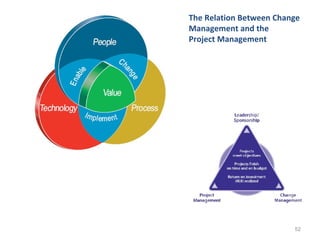
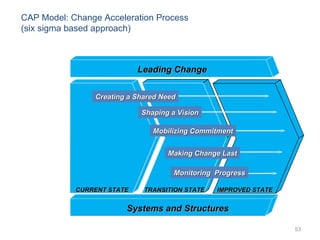
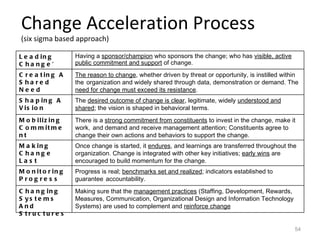
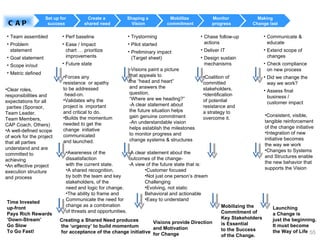
This document provides a summary of the candidate's experience and qualifications for project management roles. They have 15 years of experience in healthcare consulting utilizing their biochemistry degree and Six Sigma training. They are PRINCE2 certified and have extensive experience utilizing PMBOK methodologies for project management. Their experience includes developing RFPs, managing budgets and timelines, implementing change management processes, and leading teams of over 20 stakeholders on complex projects.