CAPM is a credential for project team members and entry-level project managers that demonstrates skills in project performance. A project deliverable is a tangible work product like a feasibility study. Portfolio management involves grouping projects and programs together to facilitate effective strategic management of resources and work. The 10 knowledge areas of project management are project integration management, scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, human resource management, communication management, risk management, procurement management, and stakeholder management.
















![20. Develop project charter data flow diagram
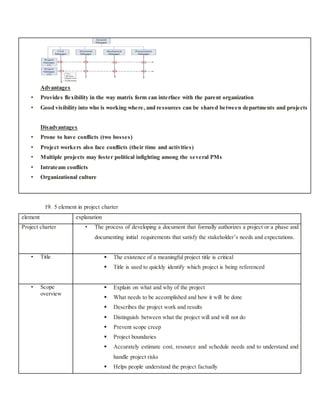
21. Purpose of project charter
Authorize the project manager to proceed [authorization]
Help the project team and sponsor develop common understanding [understanding]
Help the project team and sponsor commit [commitment]
Quickly screen out obviously poor project [screening
22. Identifying stakeholder
Individuals and organizations that are actively involved in the project or whose interests
may be positively or negatively affected as a result ofproject execution or project completion
Stakeholder:
1. Internal & External
2. Owners & Funders
3. Sellers & Contractors
4. Government agencies & Media Outlets
5. Individual citizens
6. Temporary or permanent lobbying organizations
7. Society](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/answersheetprojectmanagement-150928175332-lva1-app6891/85/Answer-sheet-project-management-20-320.jpg)



![32. WBS format
• Indented outline format [1]
• Organizational Chart Format [2]
• Free format [3]
• [2] + [3] [1] imported into Ms Project
33. Project failure characteristics
• When fixed price project has a cost overrun, the developer must absorb the excess cost, suffering
a lost or reduced profit [developer]
• The project end-items is not being accepted or utilized even though it was delivered on schedule,
under budget and according to specifications [users]
34. Why fail?
1. Inadequate Project Management Approach
2. Unsupportive Top Management
3. The Wrong Project Manager
4. Inappropriate or Misuse of Management Technique
5. Inadequate Communication in the Project
6. Inadequate Project Planning
7. Inadequate Project Definition
8. Bad Estimating of Time and Resources
9. Incorrect Scheduling and Handling Resources
10. Numerous Changes during the Execution Phase
11. Inadequate Control
12. Project Termination is poorly Planned
35. Characteristics of successful project:
– Project objectives achieved
– User involvement
– Executive management support](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/answersheetprojectmanagement-150928175332-lva1-app6891/85/Answer-sheet-project-management-24-320.jpg)


