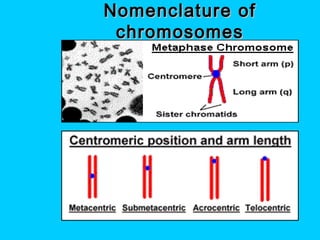
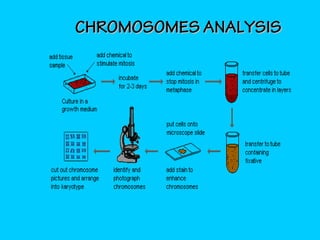
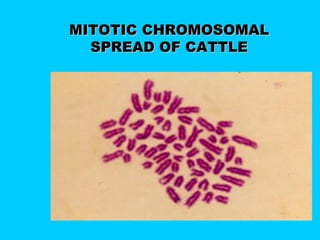
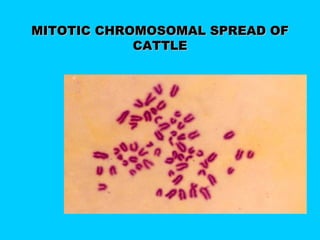
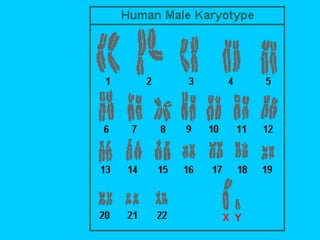
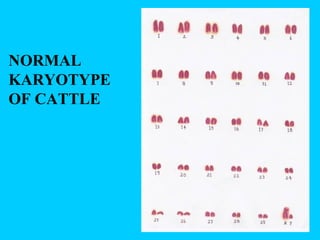
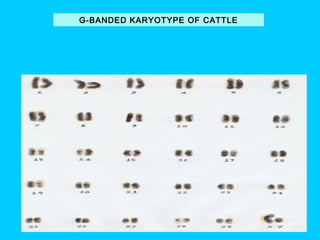
This document discusses chromosome banding techniques. It defines chromosomes and karyotypes, and describes various methods for staining and identifying bands on chromosomes, including G-banding, Q-banding, C-banding, R-banding, and T-banding. The importance of karyotyping is explained for identifying chromosomal abnormalities. Methods are provided for collecting samples from amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling and culturing cells for analysis. The document outlines the process for chromosome preparation and slide preparation prior to staining.