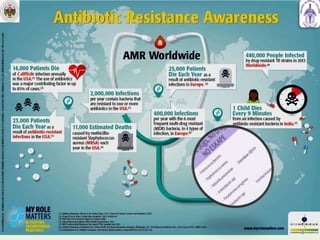
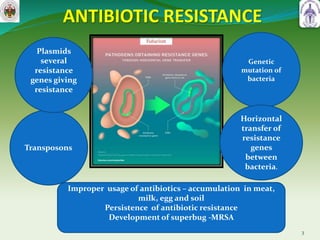
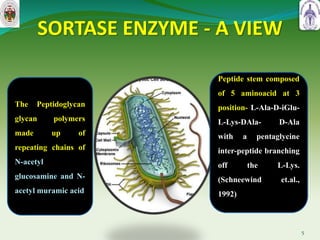
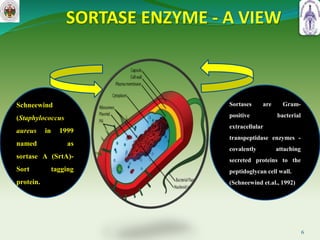
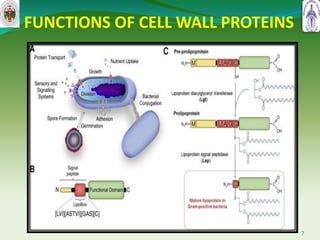
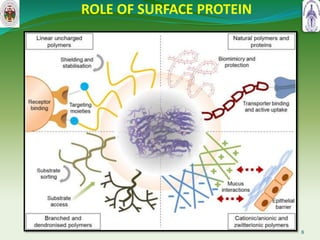
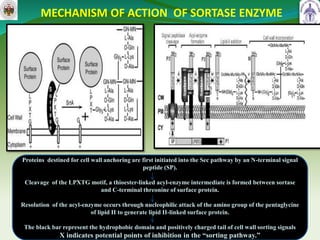
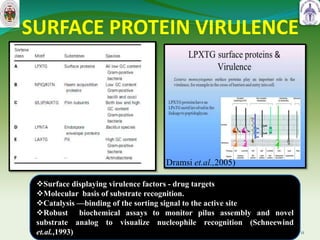
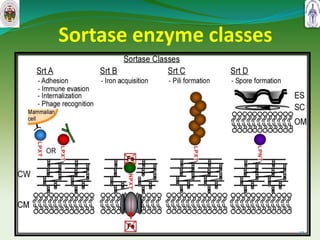
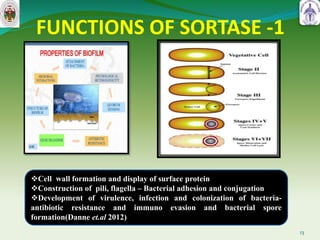
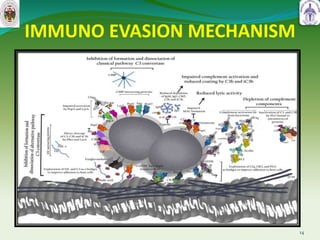
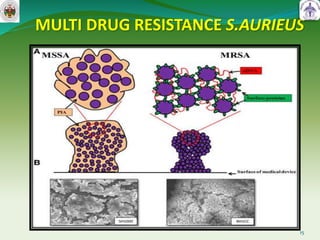
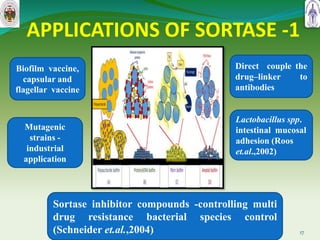
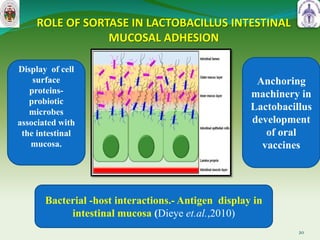
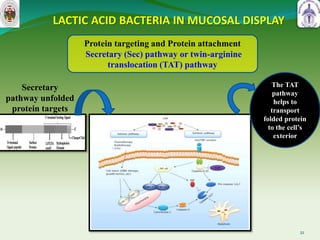
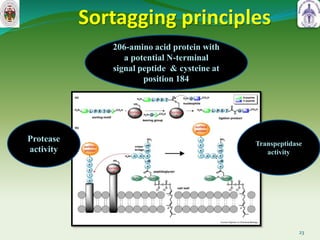
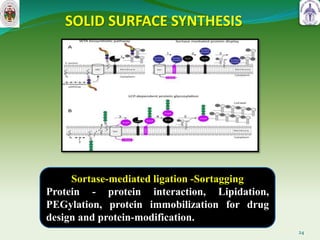
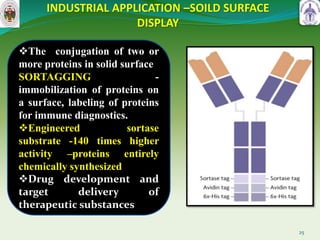
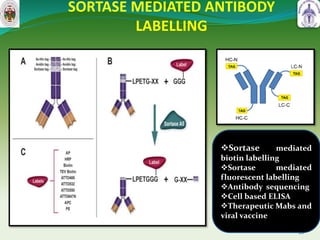
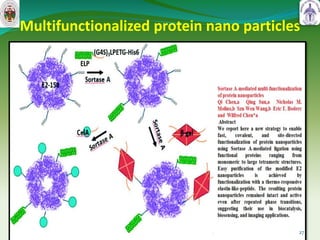
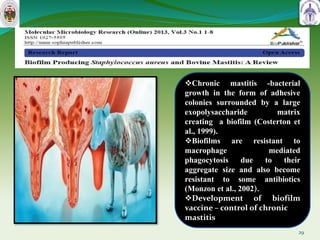
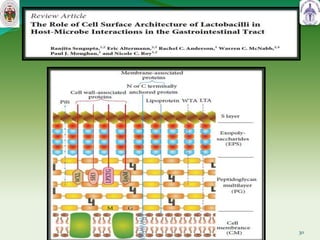
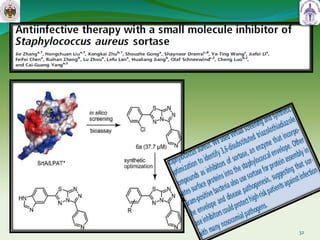
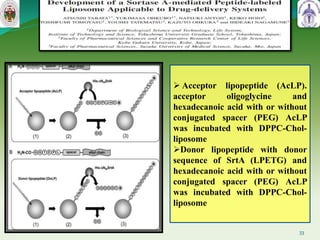
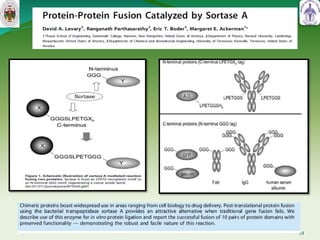
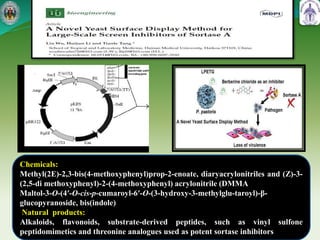
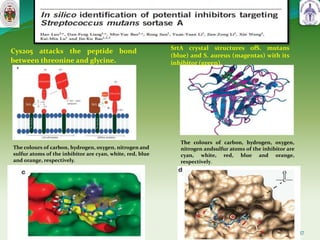
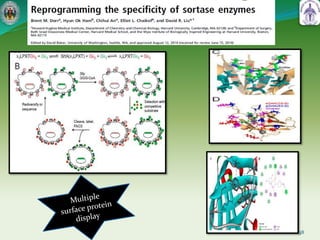
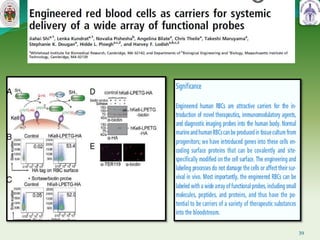
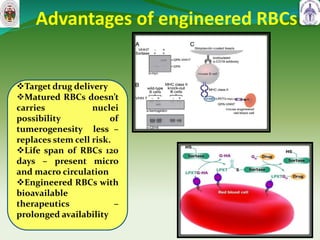
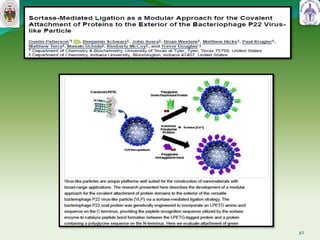
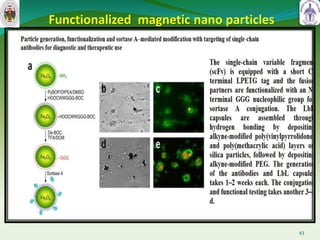
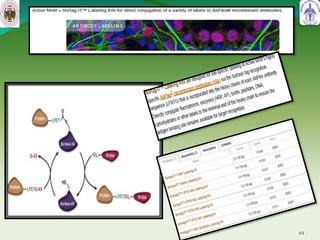
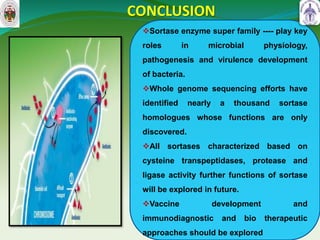
This document summarizes research on sortase enzymes. Sortases are bacterial transpeptidase enzymes that covalently attach secreted proteins to the bacterial cell wall. They play important roles in virulence and pathogenesis. The document discusses various classes of sortases, their mechanisms of action, roles in antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation. It also outlines applications of sortases in areas like vaccine development, drug targeting, and protein immobilization. Overall, the document provides an overview of the sortase enzyme family and their significance in microbial physiology and disease.