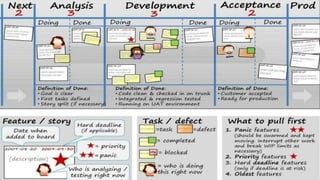
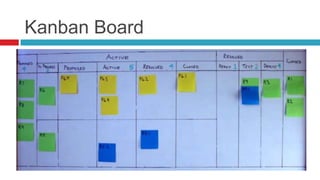
Kanban is a system for achieving just-in-time production through continuous parts supply. It uses visual signals like cards or boards to enable workers to obtain what they need, where and when they need it. Kanban systems can be implemented manually, through software, or as a hybrid. They aim to visualize and limit workflow to lower inventory costs and improve customer service through reduced waste and variability. Kanban involves starting with the current process and making small modifications like pulling work only when there is capacity.