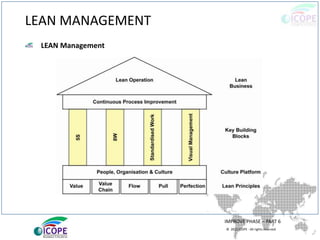
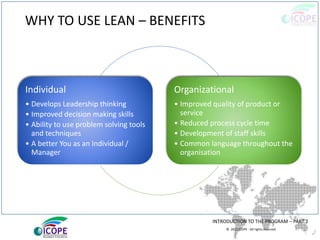
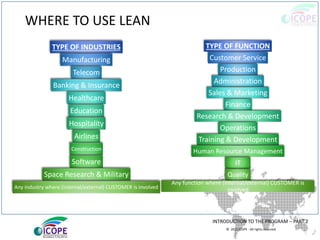
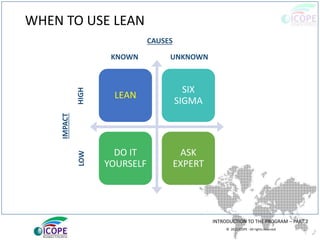
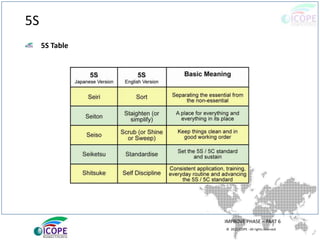
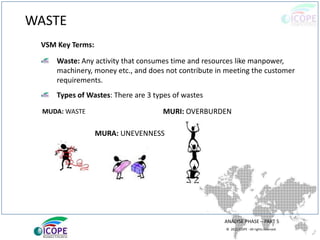
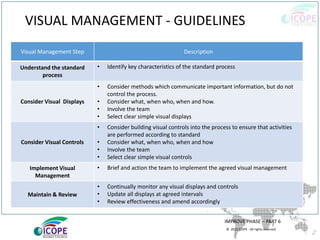
The document provides a comprehensive overview of lean management, emphasizing its customer-focused, waste-elimination methodology aimed at improving process efficiency across various industries. Key components include the 5S methodology for workplace organization, identification of 8 types of waste, visual management techniques, and the importance of standard work practices. The benefits highlighted range from individual skill development to enhanced organizational productivity and customer satisfaction.