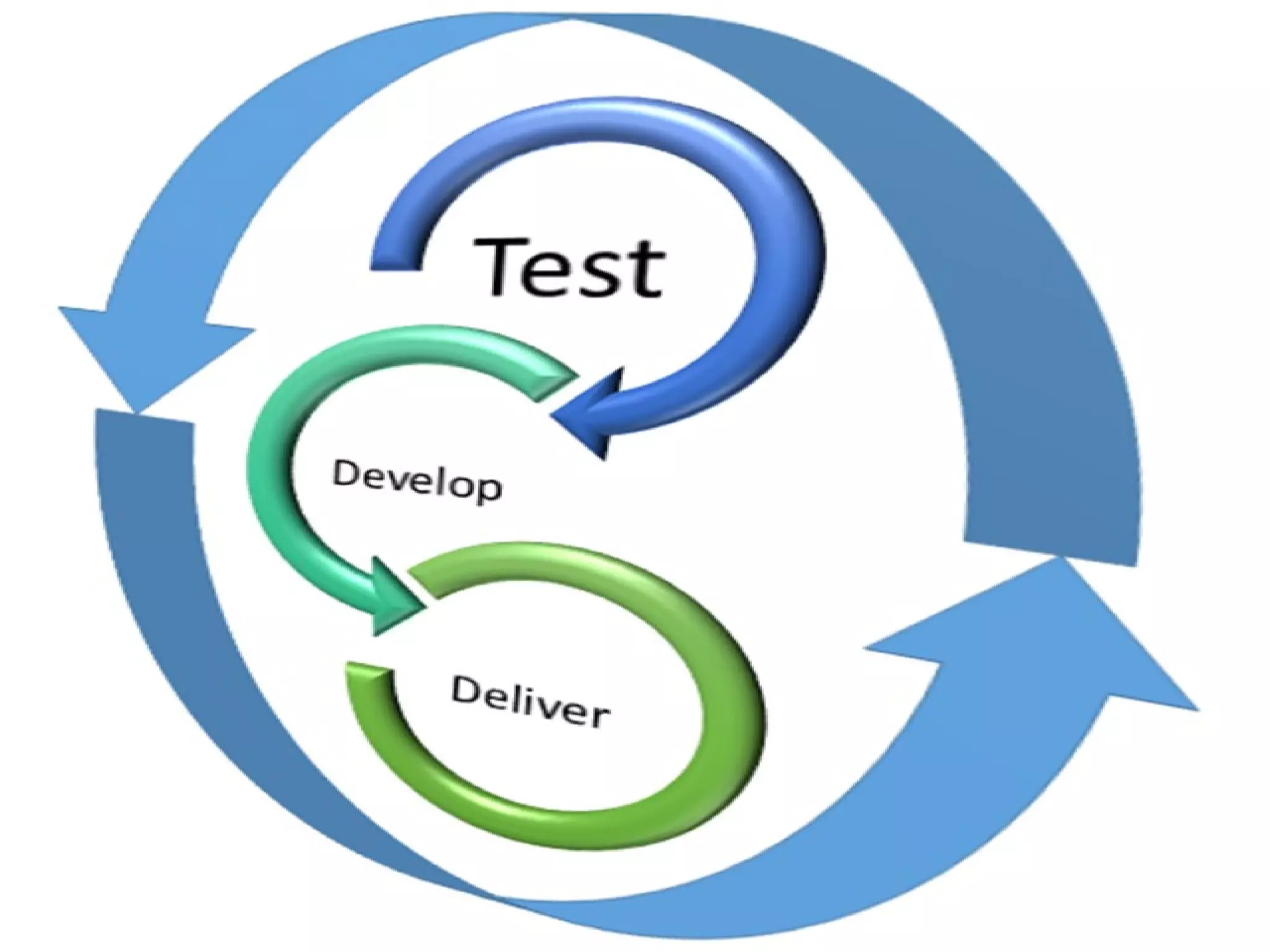
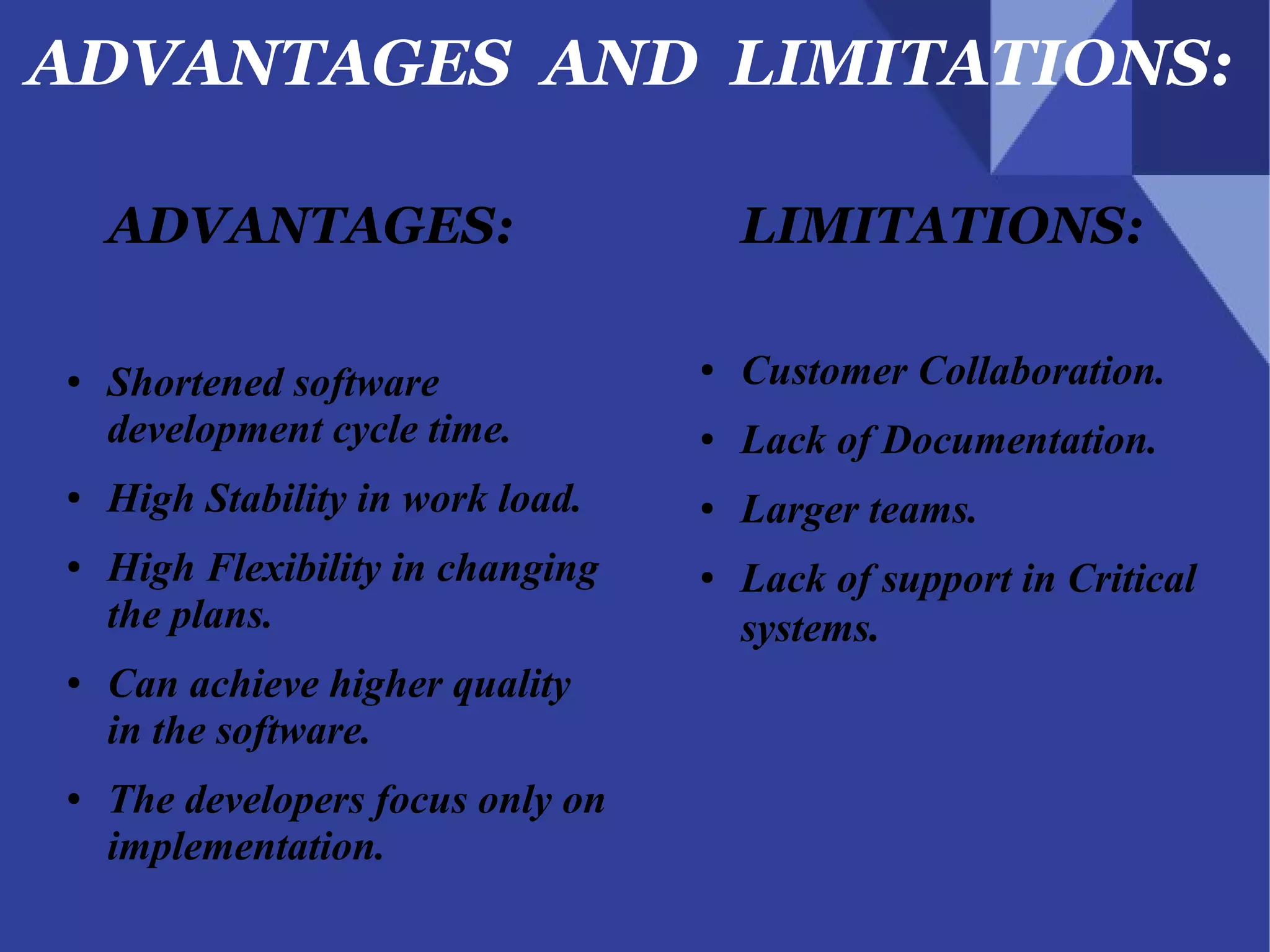
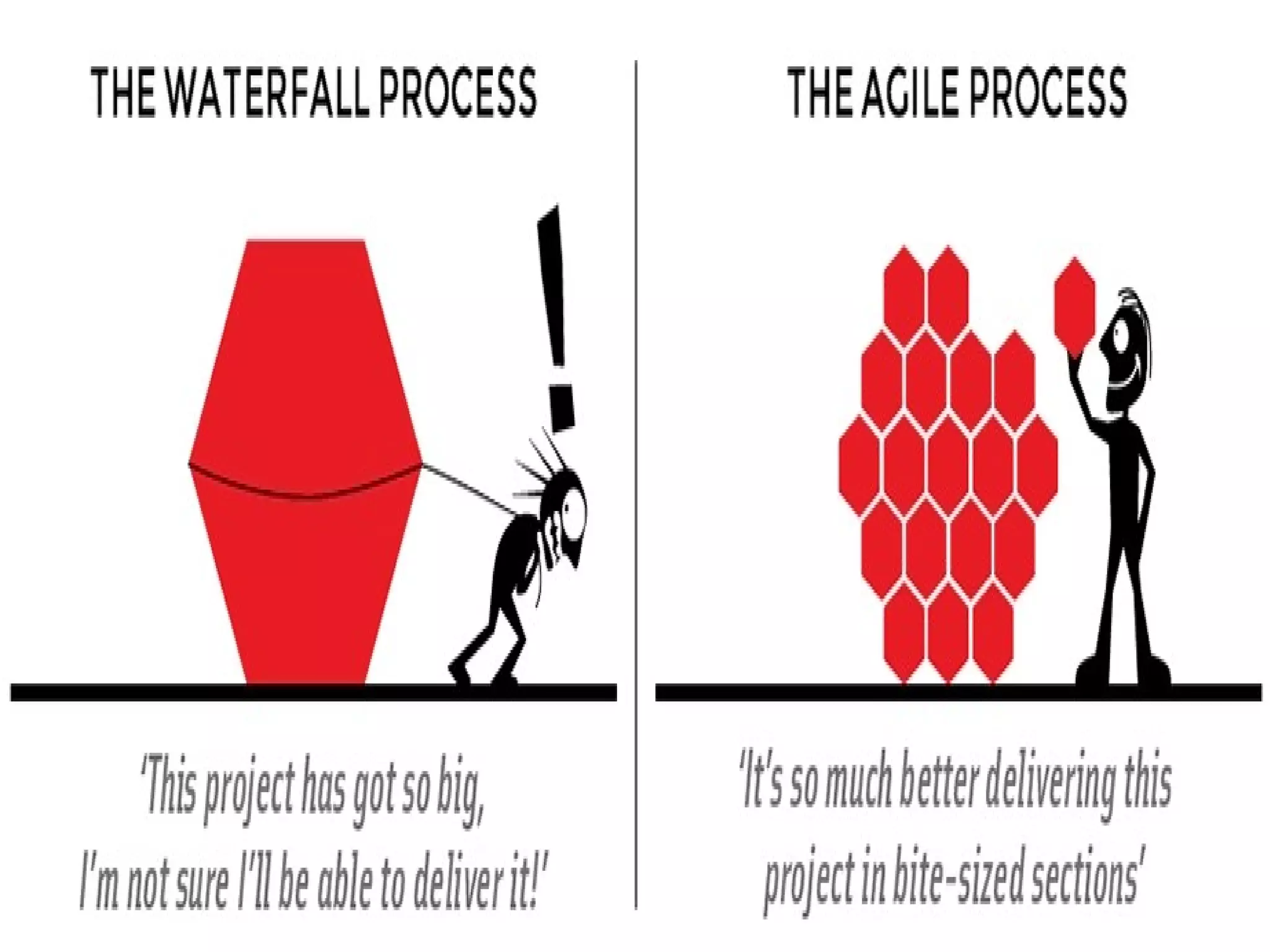
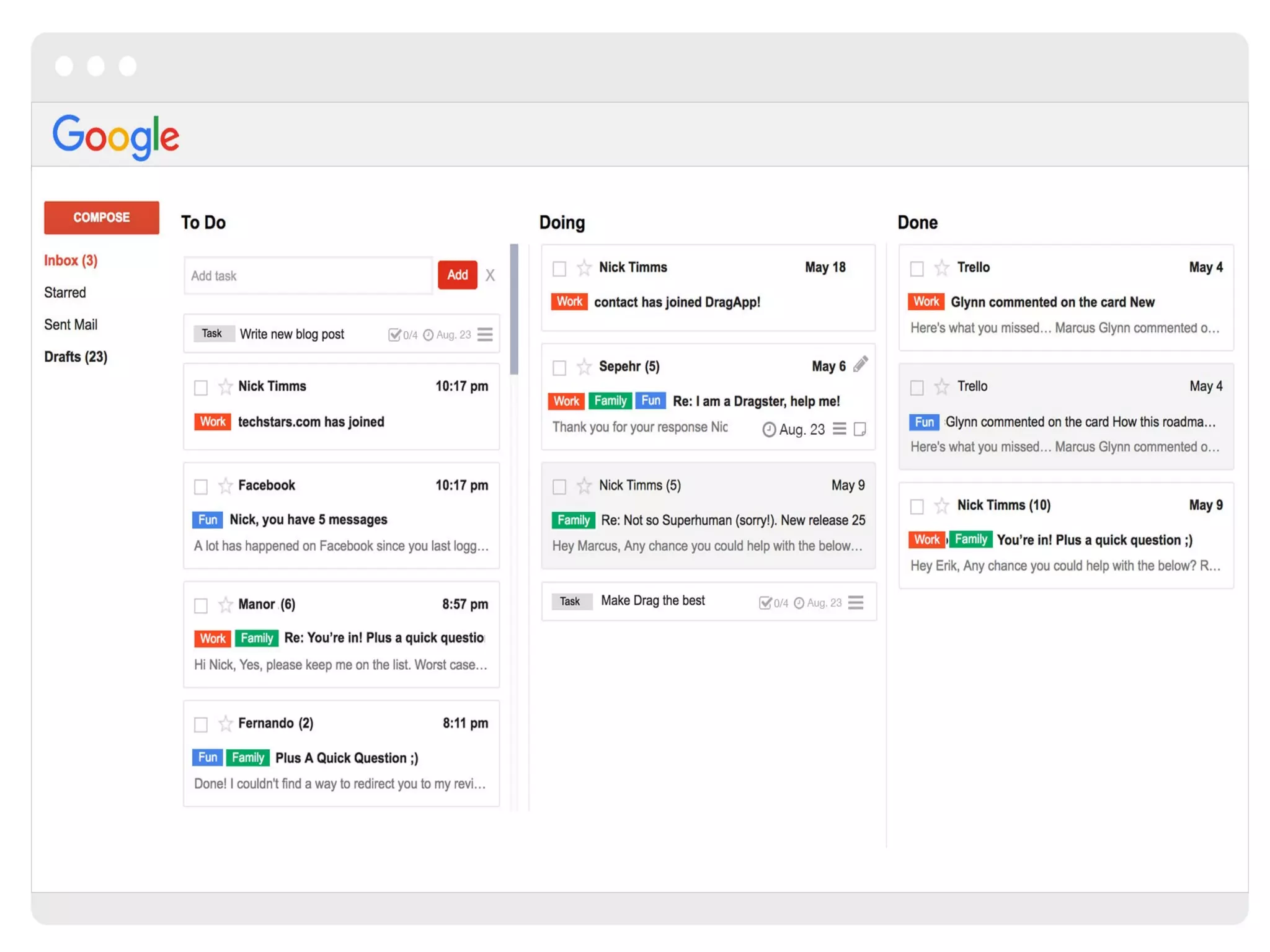
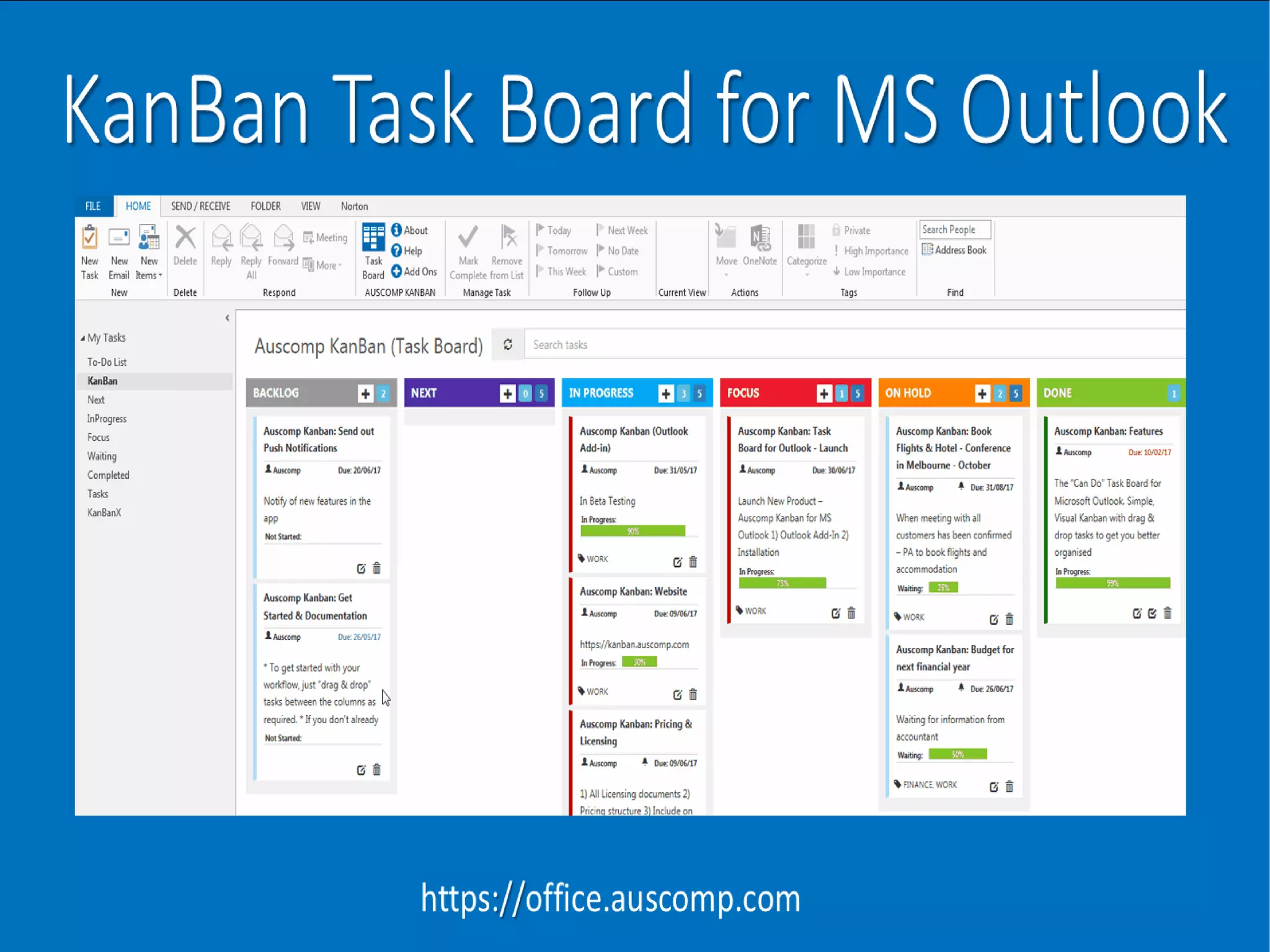
The document discusses the Kanban system, which originated at Toyota and is used for lean manufacturing. Kanban uses visual boards and limits on work-in-progress to optimize workflow and identify bottlenecks. It consists of three principles: visualize the workflow, limit work-in-progress, and continuously measure and improve the process. Tasks move through columns like to-do, doing, and done, and WIP limits prevent multi-tasking to encourage finishing work. The document provides examples of Kanban and discusses its advantages in reducing waste and improving flexibility, as well as potential areas for improvement like disrupted shared resources.